 полная версия
полная версияConstantinople and the Scenery of the Seven Churches of Asia Minor
Next in succession is the “Guiumuch Hané,” or Silver Foundery, from whence the prepared metal is brought to the Tarap Hané in the outer court of the seraglio to be stamped. There is no copper coin in circulation in Turkey; but silver is debased so as to become a more worthless metal. The coins of this imitation formerly were the asper, parasi, beslik, and onlik, they have become extinct except the parasi, and another, formerly unknown, introduced the piaster and its several denominations. The parasi is a minute coin, so very small and light, that it can only be taken up by the tip of a wet finger. Every shopkeeper has a board secured by a ledge and running to a point, on which the paras are reckoned, and then spouted into a canvass bag. At the present rate of exchange, this apparently silver coin is less than one third of a farthing, and, as all money is reckoned by it, a stranger is startled to see his baccul’s or huckster’s bills amount to 10,000 paras. Turkish coins contain no representation of the head of the sovereign, but give his name and title, the place where they were struck, the date and year of the sovereign’s reign; the inscription on the present, coin is−“Sultan Mahmoud ibn Sultan Abdul Hamed el Sultan ibn el Sultan,” that is, Sultan Mahmoud, the son of Sultan Abdul Hamed Khan, himself a sultan, and son of a sultan;” the reverse is−“Sultan alberim vehaka nul bahrim sarb fi Constantami,” that is, “Sultan, conqueror of the world, sovereign of men, struck at Constantinople.” All this is generally expressed by a convoluted cipher, called nizam. Three cities in the empire are allowed to coin, beside the capital; Adrianople, Smyrna, and Cairo.
This part of the harbour opens into a deep valley, ascending up to the high grounds on which stands the elevated village, called by the Turks Tatavola, and by the Greeks, Aya Demetri. Small streams, running down the sides of the hills, carry with them all kinds of offal, and the deposit below is sometimes so enormous that the whole surface becomes a most foul and putrid mass, the fumes of contagion, from whence it periodically expands itself over the city. So tremendous was the miasma generated on one occasion, that 1000 persons were brought out to be buried every day through the Top-Kapousi gate. It is in such places that the plague is never extinguished, but remains always slumbering, till some circumstance calls it into activity. But a still more dreadful calamity issued from this valley. It is supposed to be the avenue through which the Turkish fleet was conveyed into the harbour. Ascending from the Bosphorus by a corresponding valley on the other side, and climbing on machines the eminence between, the Greeks, secure as they thought themselves by closing the mouth of the harbour, were astonished to see the enemy’s fleet issue from the side of the hill, and ride directly under their walls. This decided the fate of the city−paralyzed by terror and despair, they made from that moment a feeble resistance.
The next object that presents itself is the village of Hasskui, the favourite residence of the Jews. It is computed, that there are 50,000 of these people living here, and in other districts, in or near the capital. They have a cemetery in this place, of considerable extent; and though the dead are assigned a residence on a healthful, breezy eminence, decorated with sculptured tombs and monuments of marble, inscribed with epitaphs in high relief, the abodes of the living are even more wretched than in any other place. They inhabit a valley shut out from the winds of the north by a high ridge of hills, and open to the sultry heat of the south; while the pestilential effluvia arising from the vegetable decomposition of the marsh, the suffocating smoke of brick and tile kilns, and the metallic vapours of the silver foundery, form the atmosphere they breathe. Their own habits are singularly dirty, and the streets are filled with putrid water stagnating into offensive pools, without any current of air to disperse the foul accumulation of gases in the atmosphere. They are a prey, therefore, to all the diseases resulting from such a combination of evils. Their houses are small, low, damp, dark, and unventilated; yet they contain a crowded population. The women living in such abodes are generally a deteriorated race. They marry at an early age, and bring forth children, diminutive, pale, bloated, and rickety. On every Saturday, their day of rest, they are seen swarming about the open doors, to breathe, as it were, a pure air; and a passing stranger is astonished at so wretched a population. The adult males are distinguished by dirty ragged garments. Small mean hats, bound round with a coarse cross-bar cotton handkerchief; trousers which scarcely reach to the leg, exposing stockings full of holes. The people here, like the Ephraimites, seem doomed to a sibboleth−a pronunciation so imperfect, that they are scarcely understood in any language they attempt to speak. They snatch with avidity at things rejected by others as unfit to be used. Their soiled ragged clothes are the refuse of other men’s dress; and their food, whatever withered vegetables or stale meat are cast away as improper for human consumption. They exercise all callings by which money can be made, and make no exception to the vilest; but particularly delight in the sale of old clothes, a propensity which seems to mark them in every country where they are scattered. Such are the characteristics which distinguish this people in whatever district they are established, forming a striking contrast with all about them, and evincing the indelible impression of a peculiar nation. Above Hasskui is the village of Halish-oglon, inhabited by Armenians; and while these robust, comely, healthy, and well-dressed people breathe the pure air in fine spacious houses above, the miserable Jew is thrust down below, grovelling in dirt, disease, and misery.
Near this is a mosque, distinguished by an extraordinary circumstance. The minarets attached to every other, are always seen of a pure white, and carefully kept so, particularly those of Imperial edifices: but the minaret here is red, and displays the only one so coloured, perhaps, in the Turkish empire. The reason assigned for it is characteristic of a Turk. When Constantinople was besieged by Bajazet, a desperate conflict took place in this valley, and the effusion of blood was so great from the slaughter of the Greeks, that it rose to the height of the minaret; and when it subsided, it left its own colour upon the tower, which it has ever since retained in memory of the event.
The palace of the “Tersana emini,” or master of the arsenal, next comes in view and the extensive and noble establishment over which he presides. The stores, docks, and other edifices connected with it, extend for nearly a mile and a half along the shores of the harbour. They are constructed of solid masonry, and contain rope-yards, and an hospital: 500 labourers, and the same number of slaves in chains, condemned for various offences, are daily at work there. The forests near the Black Sea furnish an inexhaustible supply of timber; hemp for cordage, and metal for ordinance, are ready in abundance in the neighbouring shores of Russia. Should any cause interrupt the communication, and render these resources unavailable, supplies of all kinds are found within the limits of the Ottoman empire. Negroponte sends pitch, tar, and rosin; Samsoun, hemp; Gallipoli and Salonichi, gunpowder. With these materials the Turks launch the largest ships in the world; but, manned by inferior crews, they are weak and worthless. They are seen riding before the arsenal, and among them the Mahmoud, supposed to be the largest vessel of war ever built. She is 223 feet long, is pierced for 140 guns, some of her carronades carry sixty-pound balls, and her burden is 3,934 tons. During the Greek war, these vast machines suffered severely from the small-craft of their more skilful and active enemies; and such was the terror their brulots inspired, that the Turks did not consider their ships safe, even within the protection of their harbours. Each of them, therefore, was insulated by a pile of stakes, to which were moored rafts, where sentinels kept watch night and day, warning off even the smallest caïque that approached. They were supplied with heaps of stones, piled on the rafts like cannon-balls, and pelted without mercy every incautious straggler that came within the reach of their missiles.
On the water’s edge, raised on piles, is seen the elegant edifice of the “Divan Hané,” or Council Chamber of the Admiralty. It is a light and airy specimen of Oriental architecture, of which the Turks are vain. It was built by two ingenious Greek architects, who soon after disappeared. It was said they were put to death by their employers, lest they should build another to rival it. Besides, it is the “Caïque Hané,” or Arsenal of the Sultan’s Barges: and near this, the quarters of “Galiongees,” or Marines. These soldiers of the fleet are distinguished by the richness and gaiety of their dress, and by the assumption and insolence of their demeanour.
In the rear of the arsenal appears the tower of Galata, shooting up its tall spire above the hills, that its vigilant sentinel should command a view of whatever fire may burst out, and its beacon-drum may be heard far and near, whenever it announces one to the Bektchi, who, with his iron-shod pole stamping on the pavement below, alarms the sleepy inhabitants. From hence the sweep of the shore gives to the water the appearance of a lake, and the peninsula of Constantinople seems joined to that of Pera. Along the horizon are seen the Imperial mosques, crowning the seven hills; Santa Sophia impending over the gardens and kiosks of the seraglio; the mosque of Achmet distinguished by its six minarets; Bajazet; the vast Sulimanie apparently as large as the hill on which it stands; Osmanie, Mahomet II., and Selim.
Returning by the harbour along the water’s edge, the various objects of the city come in view. The Yeni Djami, close on the shore, erected by the piety of the Sultana Valadi, mother of the reigning sovereign, from the dower settled on her, not to purchase pins as in Europe, but paponches or sandals, and hence the edifice is called the “Mosque of the Slipper.” Next the district called “Istambol dichare,” or exterior quarter, comes in view. This is the alluvial portion, lying between the walls and the water, and formed by the deposits of charcoal, ashes, and various heaps of dirt brought from the higher grounds by the many little rills which trickle down. It is a black, muddy stratum, seldom exceeding forty or fifty yards in breadth, but extending the length of a quarter of a mile. The streets formed on it are narrow, wet, and dirty, but far more populous than any other part of the city. Various iskelli, or slips, project into the water, whence passengers pass from side to side. It is the inlet for all foreign merchandise brought by Frank ships to the harbour. Tobacco, oil, wood, flour, green and dried fruits, are stored in various warehouses. Here, too, is the great depôt for gunpowder, which lies among wooden houses, with oil, charcoal, and other inflammable substances, where the crowded population are all smoking, and casting about the red embers of their chiboques, originating some of those tremendous conflagrations, which have at different times devastated the city.
It is here the Emirs reside, who are supposed to be the descendants of Fatimah, the daughter of Mahomet. They are endued by the Prophet with the faculty of healing all diseases by praying, breathing, and touching, but particularly erysipelas and eruptive distempers. They are allowed by the Porte a tahim, or a certain quantity of provisions for their maintenance, on the condition of dispensing their gift of the healing art to the people; and the patient is enjoined to give them for every cure a fee of five paras, something less than a farthing. They are distinguished by green turbans and a tebsib, or “chaplet of beads,” on which they count their prayers for the recovery of their patients. Their mode of cure is simple. They are found standing in the streets; and when a diseased man distinguishes the green turban among the crowd, he approaches with reverence. The emir lays his thumb on the side of his nose, breathes upon his forehead, utters a short prayer, and the cure is effected in five minutes. A belief in the efficacy of touch and prayer, in healing disease, is universal among the Christian and Jewish, as well as the Islam population of Constantinople, and constantly resorted to.
The Fanal, or celebrated Greek quarter, now succeeds. It is so called from a “phanar,” or light-house, which illumined the gate, and was assigned exclusively to the Christians, on the capture of Constantinople. Here is the residence of the patriarch, and here the venerable head of the Oriental church was hanged over his own gate-way, when the Greek insurrection commenced in the province, and hence his lifeless body was dragged through filth and mud with gratuitous insult by the Jews, and cast into the water. Here also is the metropolitan church, conferred by Mahomet II. on the Christians, when the Moslem took possession of Santa Sophia. Among the reliques which confer interest and
value to this edifice, is the actual pillar to which our Saviour was bound when he was scourged, and the chair inlaid with mother-of-pearl, from which Chrysostom, with “the golden mouth,” delivered those eloquent homilies, which have been handed down to us in fourteen folio volumes. Here reside the seven princes of the Greek nation, which formerly filled the office of hospodars of Wallachia and Moldavia, once the proud and the powerful, but now steeped in misery and humiliation. The streets of this celebrated district are dark and dirty; the houses, mean and neglected. During the tempest of the revolution they were entirely sacked by the Turkish mob, the property of their inhabitants confiscated by the government, the princely population strangled or exiled; and the Fanariots, once composing a noble and opulent community of 40,000 persons, are now confined to half the number, and that half reduced to the most abject poverty.
After the Fanal succeeds the district of Blachernæ, where the wall, which runs from sea to sea, meets the harbour, and impends over it with its lofty battlements. From hence it reaches to Eyoub, and that singular factory is seen on the water’s edge, so peculiar to the present state of Turkey. A distinguishing characteristic of the turban was a small red cap, called a fez, which covered the crown, and round which the turban was wound. When this ponderous head-dress was laid aside by the sultan, the fez was retained, as a remnant of Orientalism, but as its circumference was less than that of a saucer, its border was enlarged till it reached the ears, and it became the adopted and distinguishing covering of the head under the new regime. It was originally manufactured at Tunis, and cost the government such immense sums, that the sultan resolved to establish a manufactory of it at home, and extensive edifices were erected for the purpose. A number of African workmen were invited, and they succeeded in every thing except the vivid colour, the preparation of which was kept a profound secret at Tunis. At length the process was discovered by an intelligent and enterprising Armenian; and the establishment, now complete in all its parts, exceeds, perhaps, that of any in Europe. Nearly one thousand females, of all persuasions, Raya as well as Turk, assemble here, and receive the wool weighed out to them. This they knit into caps of the prescribed form, and then return them. They are next subject to a process of fulling, and teazel heads, to raise the knap, then to clipping with shears, and finally pressed under a screw, till at length the texture becomes so dense as to obliterate all trace of knitting, and appears like the finest broad cloth. When it has attained this state, it is dyed by the newly-discovered process, and assumes a hue of rich dark scarlet or crimson. The altered shape of the cap is now a cylinder with a flat top, from the centre of which a thrum of purple silk-thread depends, encircled by a piece of crumpled white paper, which is always suffered to remain as part of the ornament. This, which resembles the undignified red night-cap of Europe, drawn down about the ears, is the regulation cap, which the sultan presented to all his subjects as the first reformation in Oriental dress, and which he wore himself as an example to others: but it is a miserable substitute for his splendid turban. The demand for it, however, is so great, that 180,000 are here annually manufactured, and sent to all parts of the empire. They impress it with the sultan’s cipher, and thus designate it as of imperial manufacture.
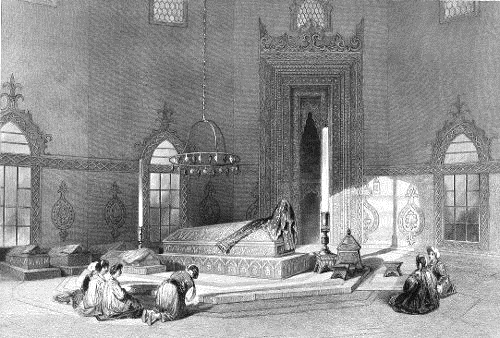
MAUSOLEUM OF SULTAN MAHOMED AND HIS FAMILY, BRUSA.
ASIA MINOR
W. H. Leitch. G. Presbury.
A tomb attached to an Imperial mosque is called a Turbé. It is usual for every Sultan to erect one for himself, in which the mortal remains of himself and his family are deposited, and it forms a detached portion of the Djami which he has built. Whenever any cause prevents him from performing this sad but pious duty before his death, the tomb of one of his ancestors is assigned for the purpose. This permission for intrusion into the precincts of another’s resting-place, is subject to the assent of the reigning Sultan that succeeds him, who from any cause may exclude his body, and send it to be interred in a strange sepulchre. The Valadé Sultana, or Queen-mother, has also a right to erect a Turbé for herself, and for such members of the Imperial family, male or female, as she chooses to admit. These are the only inmates of the Seraglio who are legally allowed to enter these sacred precincts; but when a Sultan wishes to pay particular respect to the memory of a departed Vizir, he suffers him to be buried in a corner below the grating: but this distinguished honour, and strong mark of personal affection, has been conferred on few, and the ashes of the Imperial descendants of the Prophet are seldom polluted by such profane mixture. No kadinos, or odalique, whatever attachment the Sultan may feel for her during life, is allowed to approach him when life becomes extinct. There is, however, a separate public cemetery in the centre of the city, reserved exclusively for the deceased female population of the Seraglio.
The body of the person permitted to be here interred, is simply buried in a grave dug for the purpose, and covered with earth in the usual manner of Turkish sepulture. This grave, generally surrounded with masonry, is the sarcophagus where the body is left to decay. It is approached by a passage protected by an iron grating; through which, on occasions of more than usual importance, the body may be approached, and its state examined; but no human being save the existing Sultan is allowed to enter, and profane by a glance of his eye the mouldering remains of one who had sat on the throne of the Osmanli. Over the grave thus formed is raised a Catafalque of wood, called a Sanndoucha. This is covered with plain stuffs and shawls, of different qualities and manufacture. Through this is embroidered in gold, various passages of the Koran. Frequently a deputation is sent to Mecca for a strip of the veil of the Keabé, or to Medina for a portion of that which covers the tomb of the Prophet. This forms a decoration to that part of the covering which is over the head of the deceased. There is also laid beside the head of a Sultan, or prince of the blood, a turban of muslin, to distinguish them from others. At each end of the Sanndoucha are enormous wax tapers, and suspended from the roof are circular lamps. The first are seldom used, but the last are kept constantly burning. The apartment is lighted from without by casements of gilded lattice-work, through which even a Giaour is allowed to view the interior.
The greatest simplicity is observed in the interior of these Turbés. There are no gilded ornaments, no display of pomp or splendour which distinguished the tenant of the tomb while alive. The walls within are generally covered with square slabs of porcelain marked with poetical inscriptions. These are said to be the composition of a blind Arabian poet, named Boordé, who, like Homer, wandered about reciting his rhapsodies, and who has obtained as much celebrity in the East, as his Greek predecessor in the West. The Achilles of his poem is Mahomet.
Each Turbé has six guardians, called Turbedar, and twelve aged men called Djuzê Khenana, or “reciters of the sacred page.” Their duty is to repeat the whole Koran every morning, for the repose of the souls of the departed. Each undertakes a certain number of pages, or Djuzy, till the whole is gone through. Among the acts of piety which a Sultan sometimes imposed upon himself, was transcribing the Koran with his own hands. These pious MSS. are always deposited in the Turbé of the transcriber. They are all marked with the name of the person, and form a singular and interesting series of Imperial autographs. When a stranger is admitted to see the interior of a Turbé, the Turbedar never fails to show their manuscripts, to which they attach a solemn interest, particularly to that of Mahomet II., who, in the midst of excited passions, turbulent events, and ferocious cruelties, calmly sat down to write out the precepts of his religion; and it appears did so with a tranquil mind and steady hand, as his autograph at this day testifies. Besides these Imperial Korans, a number of copies are kept, which the Turbedars present to every person who enters, that he may join with the reciters in their pious labours.
These Imperial sepulchres are much frequented by the Turks for various reasons. Some resort thither from affection to their ancient masters, particularly officers of the Seraglio. Others are drawn by feelings of general devotion to the sacred dead, whom they consider as Kalifs, or lineal descendants of the Prophet, and as such invested with an hereditary sanctity. But the tombs most frequented are those of Bajazet II., Mahomet II. and Selim I. Every day these visits are paid by some, but it is during the season of the fast of the Ramazan, and the seven holy nights, that they are crowded. The officers of the Seraglio, either from inclination or command, perform this duty of respect to the deceased Sultan for forty successive days after his death. The example is set by the reigning Sultan, who thinks this a task of indispensable obligation to his predecessor, whom perhaps he had ordered to be strangled or poisoned; and, as if to atone for his offence, gives liberally to the guardian, and distributes alms in every direction. Alms is the indispensable duty of every Moslem; the Koran says that “prayer conducts halfway to heaven−fasting brings to the gate−but alms alone procure entrance.” When no such occasion calls for this bounty, it is demanded by other causes. If any unfortunate event has occurred to himself−if any public calamity assails or threatens the state−or if any important enterprise is to be undertaken, destiny is propitiated in this manner.
In the city of Constantinople there are eighteen Imperial Turbés, where the monarchs repose who died after this city had been made the capital of the Turkish Empire; and in Brusa there are six, in which are deposited the remains of those who sat on the throne in this Asiatic city, before the empire was transferred to Europe: Gummusch Kubbe, where the bodies of Osman I. and Orchan are deposited; Dic Kirke, where the corpses of Murad I., Bajazet I., and Murad II. are laid; and Yeshil Jami in which moulder the remains of Mehmet, or Mahomet I. This last is that given in our illustration, which presents the general features in all Turbés. The head of the Sanndoucha, principal Catafalque, is covered with cashmere shawls, &c., part of the veil said to be taken from the covering of the Prophet’s tomb at Medina; the rest, is green with gilded mouldings. At each end are the enormous unlighted tapers which stand at the head and feet of the deceased, and above the circle of suspended lamps by which the mausoleum is always illuminated. The sides are covered with porcelain tiles. Around, on the matted floor, are the “Reciters” going through their daily task, and at one end is the case where their copies of the Koran are deposited. Behind are the smaller tombs of the various members of his family admitted into the sacred enclosure.


