 полная версия
полная версияThe Battle of the Marne
On September 7, the encounter became closer and more severe, without any marked change of position, the 67th and 75th Divisions, on the right, carrying Ippecourt by assault (to lose it next day), the 6th Corps resisting obstinately on either side of Rembercourt, and, on the left, the 5th Corps meeting furious attacks around Vassincourt. In the evening, the 29th Division of Castelnau’s 15th Corps passed the Marne to Combles and Fains, two battalions of chasseurs reaching Couvonges and the neighbouring woods. On the morning of the 8th, Sarrail’s 5th Corps was supported and extended by the full strength of the 15th. One brigade of the latter was directed by Vassincourt toward Revigny, but could make no headway. Other brigades came into action near Louppy and Mognéville; nevertheless, Villotte and Louppy-le-Château were lost. News arriving that de Langle’s right had been driven back from Sermaize to Cheminon, and that Duke Albrecht’s forces were at the foot of the Trois-Fontaines plateau, d’Urbal was ordered to take his cavalry corps round, and to harry the east flank of Tchenk’s movement. No sooner had it reached the upper Saulx valley for this purpose than Sarrail hurried it back and away north-eastward to meet a yet extremer danger beyond the Meuse.
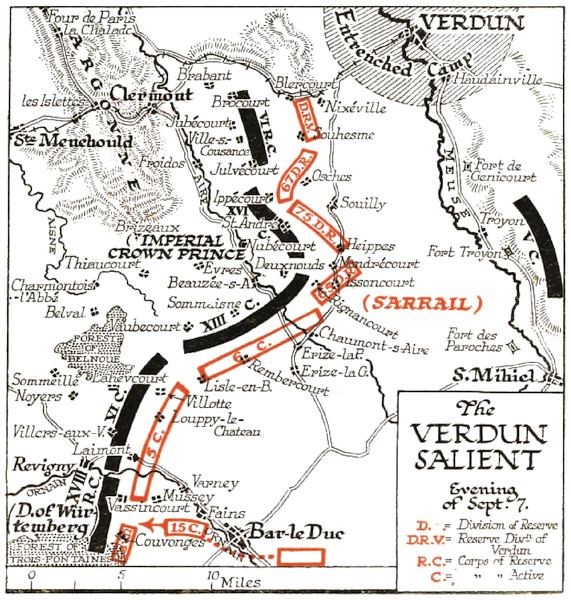
The VERDUN SALIENT
Evening of Sept. 7.
Below St. Mihiel, the river meanders beside a wall of steep hills, on the crests of which were situated a number of forts, dependencies of the Toul and Verdun systems, designed as observatories and points of arrest against an enemy march toward the principal crossings. The most important of these forts were Genicourt, Troyon, and the Roman Camp along the east, and Paroches on the west, banks. Troyon was an extensive square structure, sunk in a deep, wide moat, and garrisoned by about 450 men. Commanding the gap of Spada, it enjoyed, in its remote solitude, magnificent views over the plain of the Woevre as far as Metz, and the hills and valleys between St. Mihiel and Verdun. It has not been explained why the troops of Metz did not reach the Meuse earlier; probably their heavy artillery delayed them. On the morning of September 7, there was no sign of trouble on the Heights, and the commander of Troyon, Captain Xavier Heym, went out partridge shooting. At noon, forces of infantry and cavalry, with thirty cannon, were reported on the roads from Hattonchatel and Heudicourt. The bombardment began at 2 p.m.; and before another day had passed, 400 heavy shells, some of them from 12-inch mortars, had been thrown upon the fort, putting seven guns out of action, and demolishing large parts of the casemates and galleries. This news was a crown to Sarrail’s anxieties. He had no reserves left; the 3rd Army was wholly engaged. Its right might at any time be crushed, its left enveloped: now it was menaced in the rear. The dispatch thither of some tired cavalry was, of course, the merest bluff. Whatever might have been the fate of Verdun, the crossing of the Meuse at a higher point would have meant the withdrawal of Sarrail’s right, and the opening for the Crown Prince of the shorter route for reinforcements and supplies which he so much needed.
On the evening of September 8, Joffre authorised the commander of the 3rd Army to draw back from Verdun along the west bank of the Meuse. Sarrail, who by this time knew of Kluck’s retreat and the magnificent efforts of the French centre, was determined to hold on, at least till Troyon should fall; but the river bridges were cut and the forts left to their own resources. At 9 a.m. on the 9th, Verdun signalled that Fort Genicourt was being bombarded by heavy guns. At 11 o’clock, Troyon no longer had a piece in action. There were then in the neighbouring hills enemy columns amounting to the greater part of an army corps, with artillery, aviation parks, and convoys. Two infantry assaults were repelled by rifle and machine-gun fire. Meantime, General Durand’s Reserve Divisions maintained their ground near Verdun, the 75th suffering severely in repeated attacks on the Crown Prince’s line of communications; and, on the left, part of the 15th Corps having pushed across the Saulx into the Trois-Fontaines Forest, and then struck north, Mognéville was captured by assault from two sides.
The turning-point of the battle had been reached. During the night of September 9, while his 6th Corps was repelling a furious attempt of the XIII and XVI Corps to break through, Sarrail learned that the British were well over the Marne, with d’Espérey nearly abreast of them, that Bülow had succumbed to Foch’s will, and that the Saxons had begun to yield before Langle. Many an exhausted trooper, in lonely thickets, ditches, and broken farm buildings, only received the glad tidings two days later; yet the magic spark of a definite hope was lit. The 4th Army could now look after itself. The 3rd had failed to make good its first threat against the German flank. Even at this distance, however, the western “effect of suction” was at last faintly felt. The XVIII Reserve Corps was perceptibly weakening. During the 10th, the 15th Corps pushed through to the edge of the Trois-Fontaines Forest, approached Sermaize and Andernay, and sent some hundreds of prisoners to the rear. If the right could only hold! In the afternoon the XIII and XVI were reinforced by the VI Reserve Corps (replaced by the V Reserve). Rembercourt, Courcelles, Seraucourt, and Souilly, were lost in succession. The struggle continued unrelaxed along a line but slightly withdrawn, from Condé-en-Barrois, through Erize-la-Petite and Neuville, to Rambluzin; and on the extreme right, about Vaudelaincourt, the 72nd Division performed prodigies. In the evening, the 67th and 75th Reserve Divisions were actually removed from the line, preparatory to an abandonment of Verdun. The enemy did not perceive the movement till too late.
And the gallant four hundred of Troyon continued to bar the way to the Meuse. Under cover of a flag, two German officers and a trumpeter rode up to the fort, and demanded its surrender. “Never!” replied Heym; “I shall blow it up sooner.” And finally: “Get out, I’ve seen enough of you. A bientôt, à Metz.”71 Who could imagine that “bientôt” was four years away?
CHAPTER IX
VICTORY
It is now apparent that a record of the battle covering the whole front day by day would give no clear view of its development. The climax came not everywhere at the same hour, or even on the same day, but in a remarkable succession—beginning on the Ourcq about noon on September 9, and immediately afterward on Foch’s front (the two areas most directly menaced by the advance of French and d’Espérey), reaching de Langle de Cary the next morning, and Sarrail only on the night of the 10th. It remains to trace the completion of the victory.
Maunoury had failed of his objective: after four days of grinding combat, he had advanced his centre some 10 miles eastward, but was, at noon on September 9, still an average of 6 miles short of the Ourcq, before Vareddes, Etrepilly, and Acy-en-Multien; while his left was painfully bent back from the last-named point westward to Silly-le-Long. Every effort to obtain an effective superiority of strength, and to break through or around the enemy’s right, had been thwarted by Kluck’s speed in supporting that flank. Looking at this part of the field only, it might be supposed that a substantial reinforcement of either side at this moment would have precipitated a disaster on the other. A wider view shows a very different balance. If Maunoury could have found one or two fresh divisions, the German I Army might have been shattered; a further French withdrawal to and beyond the Marne would not have entailed any such grave consequences. In fact, both armies were exhausted; neither had any remaining reserve to call in. The decision came from the next sector of the front.
Since Le Cateau, the little British Army had played only a secondary part; it was now to have the honour of saving the left wing of the Allies for the third time. From the moment it began to recross the Marne, solidly extended by d’Espérey, its intervention became a conclusive factor. It must have been during the morning of the 9th that the German Grand Staff reconciled itself to the necessity of a general retreat, at least from Senlis as far east as Fère Champènoise. In after years, when the simple art of entrenchment had been elaborated and the men had become incredibly hardened to shell-fire, these same wooded hillsides would be contested foot by foot. At this time, freer and larger movements were required, especially when no considerable aid could be expected, when supplies were short, and the danger appeared on two sides. Kluck’s very persistence, not having attained any positive result, told against him. His men might be persuaded that this was “not a retreat, but only a regrouping of forces for strategic reasons”;72 all officers but the youngest knew that the “smashing blow” had been broken, the famous enveloping movement had failed, a new plan of campaign must be thought out. For that, rest must be found upon a naturally strong defensive position such as the line of the Aisne and the Laon mountains.
By noon on September 9—a gloomy, showery day—the call was urgent. The I Army could do no more. Its ammunition was nearly exhausted. Its best units were physically and morally broken. It had no longer the strength to bury its dead—they were unclothed and cast upon great pyres of straw and wood; and the odour of burning flesh added a new horror to the eastern part of the battlefield. Kluck’s advance from Nanteuil and Betz, during the morning, was only a diversion, a last blow to secure liberty of movement. At 11 a.m., the French found Betz evacuated; Nanteuil and Etavigny were still held. Whipped on by Headquarters, General Boëlle’s two divisions of the 4th Corps crept forward again. During the afternoon, aviators observed long enemy convoys, followed by troop columns of all arms, crowding all the roads from the Ourcq to the Aisne. For several critical hours they were screened by a vigorous defence of the centre lines east of Etrepilly and Puisieux. This and a slight reaction near Nanteuil were the final spasms of the battle of the Ourcq. We have seen that Marwitz, beaten by the 1st British Corps at Montreuil-aux-Lions, 13 miles due east of Etrepilly, in the early afternoon, had gone back to the Clignon, and that the whole angle of the Marne and Ourcq had been evacuated. Kluck could flatter himself to have held out to the last possible moment. Gradually the remainder of his artillery was removed from the Trocy plateau; and, under cover of night, all but rearguards made off to the north-east. The 6th Army seems to have been too weary to discover the flight of its redoubtable foe until daybreak on the following morning. The pursuit began at once, following both sides of the Ourcq. It was checked on the left by small detachments under cover of the Forest of Villers-Cotterets, an obstacle the importance of which was to be more fully proved in the last year of the war; while Kluck established new lines along the hills beyond the Aisne, from the Forest of Laigle to Soissons.
So the red tide of battle sank from the stubble-fields and coppices above Meaux; but burning farmsteads and hayricks, broken bridges, shattered churches and houses, many unburied dead, and piles of abandoned ammunition and stores spoke of the frightful frenzy that had passed over a scene marked a week before by quiet charm and happy labour. In the orchards and folds of the open land, the bodies of invader and defender lay over against each other, sometimes still grappling. Every here and there horses rotted on the roads and fields, presently to be burned on pyres of wood, for fear of pestilence arising. Most of the human victims had been buried where they fell; little wooden crosses sometimes marked their great common graves. On September 10, General Maunoury addressed to his troops the following message of congratulation and thanks:
“The 6th Army has supported for five full days, without interruption or slackening, the combat against a numerous enemy whose moral was heightened by previous success. The struggle has been hard; the losses under fire, from fatigue due to lack of sleep and sometimes of food, have surpassed what was to be anticipated. You have borne it all with a valour, firmness, and endurance that words are powerless to glorify as they deserve. Comrades! the Commander-in-Chief asked you in the name of the Fatherland to do more than your duty; you have responded to his appeal even beyond what seemed possible. Thanks to you, victory crowns our flags. Now that you know the glorious satisfaction of it, you will not let it slip away. As for me, if I have done some good, I have been repaid by the greatest honour that has been granted me in a long career, that of commanding such men as you.”
Fifteen miles of high, open farmlands, cut by deep valleys, divide the Upper Ourcq from the Aisle. The British Army covered rather more than this distance on September 11 and 12, meeting serious opposition only at Braisne and on the high ground between the Vesle and the Aisne. The cavalry on the left, indeed, reached the latter river at Soissons on the evening of the 11th. Here the German retreat came to an abrupt end. Sir John French speaks loosely of the German losses as “enormous”; in fact, his 1st and 2nd Corps and cavalry took in one day 13 guns, 7 machine-guns, about 2000 prisoners, and many broken-down wagons. The spectacle of booty, always fallacious, was in this case peculiarly so. The main body of the enemy was defeated, but not routed; driven back, but not dispersed. From Courchamp to Soissons, the fullest measure of the retreat, is, by road, about 60 miles. Many stragglers gave themselves up along this route in a starving condition; many others hid for days in the woods of the Brie tableland and the Tardenois, where I witnessed several man-hunts conducted by French and British rearguards. In the final pursuit, Kluck may have lost 5000 or 6000 men—a small number compared with the costs to either side of the previous fighting.
The best of battle-plans is the most adaptable. Perhaps Joffre had not looked to the British Expeditionary Force for such a contribution to the general end. Maunoury, by his original orders, was to cross the Ourcq toward Château-Thierry, driving Kluck up against Bülow; d’Espérey was to sweep up northward and meet him at right angles. The shifting of the greater part of the German I Army to the west of the Ourcq, and the consequent thinning of its connection with the II Army, displaced the action without changing its essential character. In the event, it was the British Army that led the northward movement73; d’Espérey, who, at the outset, had four active corps and three divisions of reserve for a front of only 25 miles (from Jouy-le-Chatel to Sezanne), while quickly compelling the withdrawal of Bülow’s right, was able to give his neighbour, Foch, aid without which the whole victory would have been compromised.
On the evening of September 9, General Franchet d’Espérey issued from his headquarters at Montmirail the following stirring message to his army:
“Soldiers! On the memorable fields of Montmirail, Vauchamps, and Champaubert, which a century ago witnessed our ancestors’ victories over the Prussians of Blücher, our vigorous offensive has triumphed over the German resistance. Held on his flanks, his centre broken, the enemy is now retreating toward the east and north by forced marches. The most redoubtable Corps of old Prussia, the Westphalian, Hanoverian, and Brandenburg contingents, are falling back hurriedly before you.
“This first success is only a prelude. The enemy is shaken, but not definitely beaten. You will still have to undergo severe hardships, to make long marches, to fight hard battles. May the image of your country soiled by barbarians be ever before your eyes! Never has a complete sacrifice for it been more necessary.
“While saluting the heroes who have fallen in the last few days, my thoughts turn toward you, the victors in the next battle. Forward, soldiers, for France!”
At the time when the commander of the 5th Army penned these words, the situation was a singular one. The issue of the battle as a whole was, in fact, decided: the retreat of the three western, if not also of the next two, German armies had been ordered. Yet the only part of the Allied line that had been materially advanced was that before French and d’Espérey; and Foch, Langle, and Sarrail were still in a situation apparently desperate. Instead of being on the Marne between Epernay and Châlons, Foch’s centre was lying in fragments 30 miles to the south, at Faux and Salon, after the debacle of Fère Champènoise. Why, then, did Bülow beat a hasty retreat at about 5 p.m. on that critical day? We have done justice to the manœuvre of Grossetti’s Division; even if this had been executed six hours earlier, it could not have sufficed to produce a transformation so sudden and complete. To understand the German collapse, a wider stretch of the front at the hour named must be scrutinised. Its chief feature will be found in the length of Bülow’s right flank, extended no less than 40 miles from Château-Thierry to Corroy. Over against this flank were gathered three corps of the 5th and five divisions of the 9th Armies; while the German thrust was being made by only four Prussian corps with a few Saxon detachments. The disparity was greater in quality than in numbers. D’Espérey’s Corps were relatively fresh, and in high spirits; Bülow’s were fagged and to some extent disorganised. In these circumstances, the detachment of the 10th Corps to Foch, and the attack of the 1st Corps at Corfelix and Le Thoult, would probably have an effect upon the German Command which the transfer of the 42nd Division to Linthes would emphasise. Grossetti’s movement might be risked; the possibility of a larger blow from the west against a flank of 40 miles could not be faced. On a smaller scale, the Saxons were in like danger from the east, where the 21st Corps, just detrained from the Vosges, had made a disturbing appearance during the day. The German centre had had too much and too little success—too little to give an immediate decision, too much, and at too heavy a price, for the security of its own formation.
That evening it blew a half-gale, and poured cats-and-dogs, along the Marne valley and the Sezanne hills. The clay pocket of St. Gond became a quagmire; the few roads crossing the west part of the marshes were covered by the French “75’s,” and the slaughter they wrought gave rise to legends recalling what happened a century before. The 10th Corps, extended by the 51st Reserve Division, struck out eastward during the night from Champaubert, Baye, and Soizy, and on September 10 cleared the plain between the marshes and the Châlons highroad. At 5 a.m. on the 10th, the Moroccan Division and the 9th Corps reached the east end of the marshes, but were stopped before Pierre-Morains and Ecury, where a sharp engagement took place. The 42nd Division was also checked on the Somme before Normée and Lenharrée, as was the 11th Corps, which had come up on its right, before Vassimont and Haussimont. On Friday, September 11, the French entered Epernay, the champagne capital; and on the following day the enemy evacuated the city of Rheims, continuing to hold the neighbouring hill forts. Thousands of men and large quantities of ammunition and material were abandoned; but it soon became evident that the retreat was not an aimless flight. On September 11, 12, and 13, the German gunners on Mt. Berru and Nogent l’Abbesse bombarded the ancient and beautiful city. The façade of the cathedral, with its precious sculptures and windows, received irreparable damage; the choir-stalls and other fine woodwork within were destroyed, the Archiepiscopal Palace, the City Hall, and neighbouring buildings burned down.
The establishment of a solid German rampart extending from the Oise across the Laon hills, dipping to the outlying forts of the old Rheims defences, and then reaching across Champagne, through the Argonne, and around Verdun, to Metz, was to prove one of the great achievements of the war, a defiance through nearly four years of sacrifice. For a moment, at the end of the battle of the Marne, it seemed that such a possibility might be averted. Conneau’s 2nd Cavalry Corps, the 18th Corps, and the 53rd and 69th Reserve Divisions had all passed the Aisne, between Bourg and Berry-au-Bac, on September 14. Conneau now found himself supporting a frontal attack of d’Espérey’s 18th Corps and reserves upon the abrupt cliffs by which the Aisne hills fall to the flats of Champagne, the Craonne plateau. A force from Lorraine under General von Heeringen was to be brought into this vital sector, between Kluck and Bülow; meanwhile, the connection was uncertain. While, a little farther west, Sir Douglas Haig was boldly reaching up to the Chemin des Dames, d’Espérey sent Conneau north-eastward as far as Sissonne; and thence one of his divisions was ordered to take in reverse the German troops posted above Craonne. Success seemed assured, when the 18th Corps and the reserve divisions were beaten back; and Conneau, fearing to be isolated on the north of the river, recrossed it. All the energy of General Maud’huy was needed to preserve a foothold on the right bank. Within a fortnight, the long deadlock of trench warfare had begun, and a new phase of the war had opened in the north-west.
At 7 a.m. on September 12, a patrol of chasseurs of the 9th Army entered Châlons, the Saxons hurrying off before them to the Suippes valley; a few hours later, General Foch established his headquarters in the old garrison town. The Saxon Army was now in a condition worse than that of the British after Le Cateau; and it disappeared as an independent command with the fixing of the lines in Champagne. Foch’s rapid march to the north-east made the German positions south of the Argonne impossible. From September 11, Langle was able to devote himself wholly to the IV Army. By noon that day, they had evacuated their defences in and around Vitry-le-François; and in the evening, the left of the 4th Army (21st, 17th, and 12th Corps) reached the Marne between Sogny and Couvrot, while the Colonial Corps passed the Saulx near Heiltz-l’Evêque, and the 2nd held the Ornain from Etrepy to Sermaize, in touch with the 15th Corps of Sarrail’s Army, which was approaching Revigny. When, on September 12, General Espinasse’s troops entered that town, it had been systematically destroyed. The central streets presented an extraordinary scene of devastation. Nothing remained except parts of the lower walls and, within, masses of stone, brick, and mortar broken small, with scraps of iron and charred wood. The town hall, a graceful building in French classic style, had about a half of its outer fabric standing. The church, which was of historic interest, was roofless and much damaged within. Houses and shops had been first pillaged, and then fired. Most of the neighbouring villages had been similarly treated. One scene stands out in my memory. Sermaize-les-Bains was a pleasant town of 4000 inhabitants, on the Saulx, with a mineral spring, a large sugar refinery, and a handsome old church. It had been demolished from end to end by skilled incendiarism. Of 500 houses, only half a dozen remained standing. Except a few chimneys and pieces of wall, the rest was a rubbish heap, recalling Pompeii before the antiquaries cleared it up. There had been an ironmonger’s shop—you could trace it by the masses of molten iron and clotted nails. There had been a glass and china shop—you could trace it by the lumps of milky coagulate that stuck out among the litter of brick. When I arrived, a few of the inhabitants were returning, women, children, and old men, carrying with them large, rough loaves of bread, or wheeling barrows of firewood. The church was roofless and gutted, the nave piled with fragments of stone. The curé’s house was also burned out. In the middle of a grass-plot behind it stood a white statue of the Virgin, turning clasped hands toward the ruins.
How much these and other indulgences impeded the military effort of the Crown Prince’s men, how much they strengthened the spirit of the French soldiers, may be supposed, but not measured. They mark with an odious emphasis for history the hour not only of a signal defeat, but of a profound disillusionment, which was to deepen slowly to the utter discredit of a system and an idea hitherto not seriously challenged. The game was played; with rage, the Prince Imperial submitted. Having held his left impassive for a day, while the right pivoted slowly backward toward the Argonne, on the night of September 12 the order was given for a general and rapid withdrawal; and on the following days, the French 4th and 3rd Armies found themselves in face of new enemy lines drawn iron the Moronvilliers hills near Rheims, by Souain, Ville-sur-Tourbe, and Varennes, to the Meuse at Forges, 8 miles north of Verdun. The Châlons–Verdun road and railway were disengaged, a result of great importance, and the old fortress, with its outposts on the Meuse Heights, was definitively relieved. The Crown Prince pitched his tent on the feudal eyrie of Montfaucon. General Sarrail picked up his direct communications with Paris, faced round to Metz and the north, and prepared for the future.

