 полная версия
полная версияThe Battle of the Marne

George Herbert Perris
The Battle of the Marne
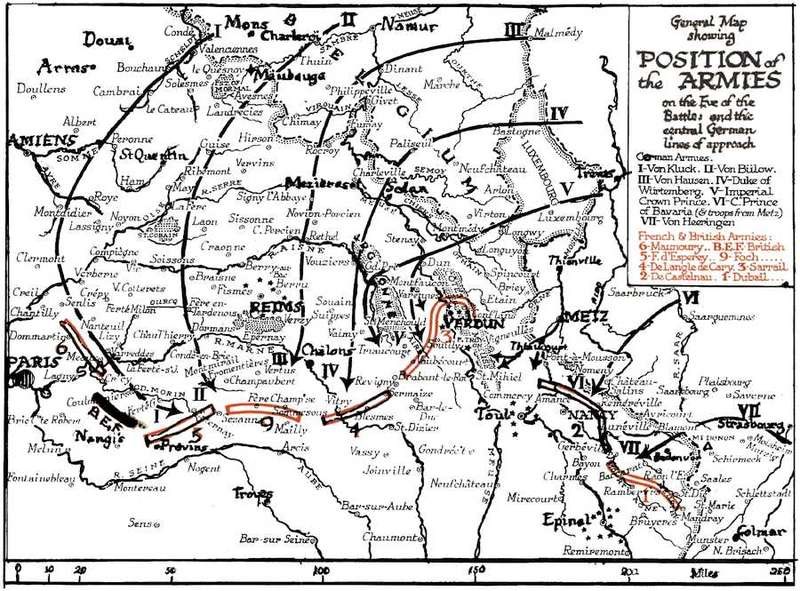
General Map showing
POSITION of the ARMIES on the Eve of the Battle, and the central German lines of approach.
German Armies.
I–Von Kluck. II–Von Bülow. III–Von Hausen. IV–Duke of Würtemberg. V–Imperial Crown Prince. VI–C. Prince of Bavaria (& troops from Metz). VII–Von Heeringen.
French & British Armies:
6–Marmoury. B.E.F. British.
5–F. d’Espérey. 9–Foch.
4–DeLangle de Cary. 3–Sarrail.
2–DeCastelnau. 1–Dubail.
PREFACE
The great war has entered into history. The restraints, direct and indirect, which it imposed being gone with it, we return to sounder tests of what should be public knowledge—uncomfortable truths may be told, secret places explored. At the same time, the first squall of controversy in France over the opening of the land campaign in the West has subsided; this lull is the student’s opportunity. No complete history of the events culminating in the victory of the Marne is yet possible, or soon to be expected. On the German side, evidence is scanty and of low value; on that of the Allies, there is yet a preliminary work of sifting and measuring to undertake ere definitive judgments can be set down. Any narrative conceived in a scientific, not an apologetic or romantic, spirit may claim to further this end.
The difficulty lies less in following the actual movements of that great encounter—the most important of which, and their part in the result, can now be traced pretty accurately—than in estimating the factors that produced and moulded it. Yet, if we are right in holding the battle of the Marne to be essentially the completion of a chapter, the resultant of certain designs and certain misadventures, a vast strategical reversal and correction, such an estimate is necessary to the subject. How did the two chief antagonists envisage the process of modern warfare? Why was the action which was to close the first phase of the war, and largely to shape its after-course, fought not near the northern or eastern frontiers, but between Paris and Verdun? Why and how were the original plans of campaign modified to reach this result? What conditions of victory existed on the Marne that had been lacking on the Sambre? In a word, the key to the meaning of the battle must be sought in the character of the forces in play, their comparative numbers, organisation, and training, armament and equipment, leadership and inspiration.
No sooner is such an inquiry opened than a number of derivative problems appear. Where exactly lay the German superiority of force at the outset, and why was it not maintained? Was the first French concentration justifiable? If not, was it promptly and soundly changed? Could the northern frontier have been defended? Was Lanrezac responsible for Charleroi, and, if so, why not Castelnau for Morhange? Was the German plan of envelopment exaggerated? Could the British have done more at Mons, and were they slow and timorous when the hour arrived to turn about? Was Paris ever in danger? And, coming to the battle itself, how was it decided? What parts did Gallieni, Von Kluck, Sir John French, and Foch play? Was Joffre really master of the field? It may be too soon to answer fully such questions as these; it is too late to evade them.
Outside the mass of official and semi-official bulletins, dispatches, and explanations, much of it now best left to oblivion, a considerable literature has accumulated in France, including personal narratives by combatants of all arms, and critical essays from points of view the most diverse. With the rather cruel sincerity of the French intelligence, the whole military preparation of the Republic has been challenged; and, in the consequent discussion, many important facts have come to light. Thus, we have the texts of the most decisive orders, and many details of the dispositions of troops. We have Marshal Von Bülow’s valuable diary of field movements, and the critical reflections of distinguished officers like Lt.-Col. de Thomasson, Generals Malleterre, Berthaut, Verraux, Percin, Canonge, Bonnal, Palat, Cherfils, and Col. Feyler. Fragmentary statements by General Joffre himself, by Generals Foch, Lanrezac, and Maunoury, the Ministers of War, MM. Messimy and Millerand, by Generals von Freytag-Loringhoven, Von Kluck, and other German officers and men, give useful indications. We are also indebted to the more systematic works of MM. Hanotaux, Reinach, Engerand, and Babin; and, with regard to the British Force, the volumes of Marshal French and Major-General Maurice are important. These and other sources are cited in the pages of “Notes and References” at the end of the volume, in which some questions of detail, especially relating to the preparation of the battle, are discussed.
Having been privileged to watch the war in France from beginning to end, and to live with the French armies (as Correspondent attached to General Headquarters) for more than two years, the writer has also had exceptional opportunities of studying the terrain, and of discussing the drama as a whole and in detail with officers and men from the highest to the most humble. To name all those from whom he has received aid would be impossible; to name any might seem to associate them with conclusions for which he is solely responsible; but he may record his deep gratitude to the French Government, the Headquarters Staff, and the various Army Staffs, for the rare experience of which this volume is unworthy fruit.
February 1920.
CHAPTER I
THE DELUGE
August 25, 1914: three weeks after Von Emmich opened the war before Liège; five days after the French Army of Lorraine was trapped at Sarrebourg and Morhange; two days after Namur fell, and Charleroi and Mons were abandoned.
On this black day, the 25th, while Louvain was burning, the 80,000 men of the old British regular Army made an average of 20 miles under a brazen sun, pursued by the enormous mass of Von Kluck’s marching wing. The 1st Corps under Haig came into Landrecies at 10 p.m., and, after a stiff fight and two or three hours’ sleep, trudged on to Guise; while the 2nd, Smith-Dorrien’s, at Le Cateau and towards Cambrai, spent most of a showery night in preparing for the battle of the morrow, which was to save the western flank of the Allies. On the British right, the French 5th Army, Lanrezac’s, surprised in the Charleroi–Namur–Dinant triangle by the onset of Von Bülow and the cleverly secreted approach of Von Hausen, had struck a wild blow, and then reeled back; the two German commanders were now driving it over the Belgian frontier from Avesnes to Rocroi. The 4th Army, under de Langle de Cary, no less heavily punished between Paliseul and Neufchateau in the Belgian Ardennes, was just reaching the French Meuse between Sedan and Stenay, there to dispute the passages against the Duke of Würtemberg. Eastward again, Ruffey, beaten back on a wide crescent from Virton to Briey in the Woevre by the Imperial Crown Prince, was standing better against a relaxed pressure, from toward Montmédy, through Spincourt, to Etain. Thus, Sarrail, in taking over the command of the 3rd Army, was able to make ready, though with inadequate means, for the three-sided defence of Verdun. On the eastern border, Castelnau and Dubail, withdrawing hardly from ill-starred adventures in Lorraine and Alsace, were rallying the 2nd and 1st Armies around the Nancy hills and on both sides of the Gap of Charmes. Mulhouse, twice captured, was finally abandoned by General Pau, with all save a corner of Alsace and the southern passes of the Vosges. “It is a cruel necessity,” said the official communiqué of August 26, “which the Army of Alsace and its chief have submitted to with pain, and only at the last extremity.” They had discovered that “the decisive attack” had to be met “in the north.” At that moment, in fact, a hardly less “decisive” attack was being met in the heart of Lorraine.
It was everywhere the same bitter story of defeat—defeat by surprise, by locally superior numbers, by superior armament, sometimes by superior generalship; and everywhere the retreat was accompanied and hampered by the flight of masses of peasantry and townsfolk whose flaming homes lit upon the horizon behind a warning to hasten their feeble steps.
Before we seek the Staffs in their shifting quarters, to explain this extraordinary situation, let us see what it meant for the commonalty of the armies, without whose strength and confidence the best plans must be as chaff in the wind. Over a million strong, they had left their homes, and gathered at their depots during these three weeks, to be whirled off to the frontiers and the first scarcely imaginable trial of modern conscript systems. It was a new thing in the world’s history, this sudden tremendous clash of the whole manhood of highly developed nations, armed with the most murderous machinery science could devise, and supported by vast reserves of wealth. It had fallen swiftly upon them, the doom that many learned men had declared to be impossible in the twentieth century; yet its essential nature was crude enough to be immediately understood, and the intelligence of France, though shocked, was not stunned. This million of peasants and workmen, merchants, manufacturers, priests, artists, idlers, and the nation behind them, were unanimous as never before. They knew the issue was not of their making; they knew equally that it could not be refused, but must be fought out, and that it would be a hard fight. The Napoleonic wars were to be eclipsed; and there was now no Little Corporal to flash his genius like a searchlight across Europe. The enemy had no less advantage in prestige than in effectives, preparation, initiative.
Few of the million guessed, as yet, that most of them were marked down for sacrifice. The general opinion was that it would be all over by Christmas, at latest. A four months’ war seemed tragic enough in those first days. With the unwonted agreement, an unwonted gravity spread across the sunny lands from the Channel to the Alps where the crops were ripening. If international idealism lay shattered, national democracy rose well to the trial—never better. No recrimination (even the murderer of Jaurès was set aside), no conspiracy, no guillotine, marked the great revival of the republican spirit. England would at least guard the coasts, and keep the seaways open. France went into the struggle without wavering or doubt.
And so, “Aux armes, Citoyens!”—for these, mark you, are, in very fact, citizen armies, independent, free-thinking, high-spirited fellows, no Emperor’s “cannon-food.” From the smallest hamlet to the boulevards of the great city, every pulse of life is feverishly concentrated upon their gathering and departure. At the barracks the reservists, clad, armed, equipped, are ready to entrain. Crowds of women, whose red eyes belie their brave words, children at their skirts, surround the gates, and run forward with bunches of flowers and tricolor rosettes. The officers carry bouquets at their saddle-bows, the men cap their rifles with roses and ribbons. At the railway station, long lines of goods-vans, with a few passenger carriages; more flowers and little flags; allied colours in front of the engine; a wag chalks up the direction: “Berlin, aller et retour.” The horses and guns are aboard; the men jostle in the open doorways, and exchange cries with the crowd. A stanza of the “Marseillaise” is broken by last adieux, shouts of “Vive la France!” and the curtain falls upon the first memorable act.
Interminable journeys follow, by road and rail, toward the frontiers, then from town to village, and from farm to farm of countrysides more and more deserted and desolate. In the passes of the Vosges, the hills and flats of Lorraine, the woods of the French Ardennes, the men accustom themselves uneasily to the oppressive heat of day and the chill and damp of night; to sore feet and chafed shoulders; to spells of hunger due to late or lost convoys; to the deprivation of accustomed comfort, and the thousand minor ills which in all times have been the ground-stuff of the showy tapestries of war. Superfluous graces of civilised life vanish before the irreconcilable need of economy in every effort. Officers begin to be honoured not for rank or show, but for the solid talents of leadership; pals are chosen, not from effusion of heart, but for assurance of help in emergency.
The mantles of the chasseurs are still blue, the breeches of the infantry red, the uniforms of the artillery and engineers nearly black; but already bright colours tend to disappear, and every other tone to assimilate with the dust of the high roads. By day and night there is but one traffic throughout these northern and eastern departments—files of cavalry, batteries of field-guns, columns of heavy-laden men, convoys of Parisian autobuses and hooded carts, pass incessantly through the silent forests out into the open plains. The civilian population steadily diminishes, even in the larger towns; the gendarmerie keep those who remain under suspicion of espionage. The frontier villagers welcome the marching troops hospitably, until local food supplies are exhausted, and until news comes in from the front of reverses and of foul cruelty to the peasants on the part of the enemy. Only a fortnight has gone by when the national confidence in a speedy victory receives this heavy blow. Bad news gathers and reverberates. It is a little difficult, after years of bloodshed, to recover the fresh sense of these first calamities. Men were then not yet broken to the pains, the abominable spectacles, of war. That their self-offering to the fatherland should win them an honoured grave might well be. But defeat at the outset, the shame of retreat almost before a blow could be struck, this was an incredible, monstrous, intolerable thing.
The incredible, however, generalised itself over all the highways of Lorraine and Belgium. Take any typical scene on the march-routes of August 22 or the following days.1 The roads are black with columns of troops retreating west- and south-ward, more or less broken, linesmen, chasseurs, artillerymen, supply and special services, with their guns, munition wagons, Red Cross detachments, convoys of heavy-laden carts with wounded men sitting on top or clinging behind; and, in the breaks, crowds of panic-stricken peasants, in farm wagons or on foot, old men, women, and children, with bedding, boxes, bird-cages, and other strange belongings. Dismay broods like a palpable cloud over these pitiful processions. There is an incessant jostling. Drivers flog their horses cruelly. Wounded men drop by the wayside and lie there untended, their haggard faces stained with mire and powder, blood oozing through their coats, trickling out into the litter of torn knapsacks and broken arms. The sun blazes inexorably, the air is poisoned with clouds of dust, or drenching showers of rain produce another sort of misery; and ever the long stream of failure and fear flows on, eddying here and there into acute confusion as some half-mad woman sets up a cry: “The Prussians!”
Night follows day: soldiers and country-folk, hungry and exhausted, fall into the corners of any sheltered place they can find—an empty barn, the nave of a village church—for an unsatisfying sleep, or, too sick to sleep, watch the fantastic shadows and fugitive lights dancing upon the walls, mocking their anguished thoughts of the morrow. The batteries and convoys have gone on through the darkness, men rolling from side to side with fatigue on their horses or gun-carriages, as though drunk. With daybreak the greater trek recommences. The enemy has not been idle: in the distance behind rolls the thunder of heavy guns; pillars of smoke and flame rise from burning villages. And as, day after day, a new stage of retirement—increasingly controlled, it is true—is ordered, the question pierces deeper: What is to become of France?
Those who have lived at the centre as well as on the skirts of armed hosts become habituated to one enveloping condition: the rank and file, and even most of the officers, know little or nothing of what is passing outside their own particular spheres. It is in the nature and necessity of military operations, especially at the beginning and in a phase of rapid movement, that it should be so. Perhaps it is also a necessity of the psychology of endurance. Of these republican armies, only a small minority of the men were old soldiers; most of them had all they could do to adapt themselves, day by day and hour by hour, to the new world of violence, squalor, and general unreason in which they were now prisoned. They had to learn to bear fatigue and pain such as they had never known; to overcome the spasm of fear that grips the stoutest heart in unaccustomed emergencies; to thrust the bayonet not into a sandbag, but into soft, quivering flesh, and draw it forth again; to obey men who were incompetent and stupid, as well as born leaders. The German heavy shells, aeroplanes, motor transport, the formidable entrenchments and fields of wire—gradually they recognised these and other elements of the invader’s superiority. Weaklings cried: “We are betrayed. It is 1870 over again.” What could the bravest reply? Letters were few and far between. Newspapers were never so barren. What was Paris doing? What were Russia and England doing? The retreating columns marched with downcast eyes, wrapped in a moody silence.
By what revolt of the spirit did these apparently broken men become, a fortnight later, the heroes of the Marne? The answer must be that they were not broken, but were passing through the sort of experience which, in a virile race, wakens the dull-minded to their utmost effort, blows away the last traces of laxity and false idealism, and, by setting above every other fear the fear of a ruined Fatherland, rallies the whole mass on the elementary ground of defence to the death. Voices, lying voices, had whispered that France was diseased, body and soul, that the Republic would surely die of its corruptions. We have since discovered the immeasurable strength of democratic communities. Then it was questioned by the few, unsuspected by the many. England and America, even more than France, had outgrown any sort of liking for war. To be driven back to that gross test was a profound surprise. For the quick, proud French mind to find itself suddenly in face of defeat and the threat of conquest was a second and severer shock. The long retreat gave it time to perceive that this calamity arose largely from its own errors, and to re-group its forces in a truer conception of the character of modern warfare. Even Joffre may not have clearly realised this need; great instincts count in the crisis of leadership equally with powerful reasoning. Amid the tramp-tramp of the weary, dust-blinded columns, by the night bivouacs, under the rain of shrapnel and the crash of high explosive, men of the most diverse condition and character, shedding old vanities and new alarms, came down step by cruel step to the fundamental honesty, unity, and resolution of our nature. The mirage of an easy victory vanished; in its place a finer idea rose and rose till the armies saw nothing else: France must live! I may die, or be doomed to a travesty of life; at any price, France must be saved.
So the steel was tempered for the supreme trial.
CHAPTER II
A TRAGEDY OF ERRORS
I. The German Plan of Campaign“Errors,” “vanities”? These words must be justified, however gently, however briefly. To regard the battle of the Marne without reference to the grievous beginnings that led to and shaped it would be to belittle and falsify a subject peculiarly demanding care for true perspective. The battle may be classed as negatively decisive in that it arrested the invasion long enough to enable the Allies to gain an equality of forces, and so to prevent a final German victory; it was only positively decisive in the larger sense that it re-created on a sounder base the military spirit and power of France, which alone among the Western Allies seriously counted in that emergency, and, by giving the army a new direction, the nation a new inspiration, made it possible for them to sustain the long struggle that was to follow. Perilous illusions, military as well as pacifist, were buried beside the Marne. A fashion of thought, a whole school of teaching was quietly sunk in its waters. The French mind rose to its full stature as the nature of the surprise into which it had fallen broke upon it.
This surprise was threefold. In the first place, the German plan of campaign was misconceived. That plan was grandiose in its simplicity. It rested upon a sound sense of the separation of the Allies: their geographical dispersion, which gave the aggressor the advantages famous in the career of Frederick the Great, as in that of Napoleon; the diversity of character, power, and interest within the Entente, which was, indeed, hardly more than an improvisation, without any sort of common organ, so far; its lack of unity not only in command but in military theory and practice generally. The first of these data indicated to the German Command the Frederician succession of swift offensives; the second narrowed the choice for the first effort, and suggested an after-work of political intrigue; the third had fortified Prussian pride and discipline with a daring strategy and an armament superior, in most respects, to anything the rest of the world had conceived to be possible. Which of the three great States, then, should be first struck down? The wildest Pan-Germanist could not reply “England,” in face of her overwhelming sea-power. So the British Empire, with the North Sea and Channel coasts, were, for the moment, ignored. Its internal problems, its peaceful, almost neutral, temper, its slow-mindedness in European affairs, were more regarded than the trivial military force which alone England could at once offer its friends. For speed was to be of the essence of the plan. Remained France and Russia; and here political as well as military calculations entered. The inchoate Empire of the East would, it was thought, be the slower in getting to its feet. Would a new Moscow expedition break its will for self-defence? The author of the “Willy-Nicky” letters imagined a better way. France would stand by her ally. The “Republic of the Rochettes and Steinheils,” however, was not naturally impregnable; when it was finished, would not “dear Nicky” be glad to return to the Drei-Kaiserbund, the old Bismarckian order, and to join in a friendly rearrangement of the world? So the conclusion, with all the neatness of a professorial thesis: Russia was to be held up—actively, on the south, by the Austro-Hungarian armies, passively on the north, by a screen of German troops—while France, as the principal enemy, was swiftly crushed. Thus far, there should have been no surprise.
It was otherwise with the plan of campaign itself, and there are details that will remain in question till all the archives are opened. Yet this now appears the only plan on which Germany could hope to bring an aggressive war to a successful issue. A repetition of the triumph of 1870 would not be enough, for, if France resisted as long this time, everything would be put in doubt. The blow must be still more swift and overwhelming. To be overwhelming, it must at once reach not portions, but the chief mass, of the French armies. But nowhere in the world had military art, working upon a favourable terrain, set up so formidable a series of obstacles to grand-scale manœuvre as along the line of the Meuse and Moselle Heights and the Vosges. A piercing of this line at the centre, between the fortified systems of Verdun–Toul on the north and Epinal–Belfort on the south, might be an important contributory operation; in itself it could not give a speedy decision. A mere diversion by Belgium, in aid of a main attack in Lorraine, would not materially alter this calculation. The full effects of surprise, most important of all factors in a short struggle, could only be expected where the adversary was least prepared, which was certainly across the north. These offensive considerations would be confirmed by a defensive consideration: German Lorraine, also, was so fortified and garrisoned as to be beyond serious fear of invasion. In neither direction could Alsace provide favourable conditions for a great offensive.

