 полная версия
полная версияNatural History of the Mammalia of India and Ceylon
McMaster says that these shrews will also eat bread, and adds: "insects, however, form their chief diet, so they thus do us more good than harm. I once disturbed one that evidently had been eating part of a large scorpion."
NO. 126. SOREX MURINUSThe Mouse-coloured Shrew (Jerdon's No. 70)HABITAT.—India generally, Burmah and Ceylon.
DESCRIPTION.—Brownish-grey above, paler beneath; fur coarser and longer than in the last species, and in the young ones the colour is more of a bluish-grey, browner on the back. The ears are larger than those of S. cærulescens; tail nearly equal to the body, thick at the base, and sparsely covered with long coarse hairs; feet and tail flesh-coloured in the living animal.
SIZE.—Head and body about 6 inches; tail, 3½ inches.
"This," as Jerdon says, "is the common musk-rat of China, Burmah, and the Malayan countries, extending into Lower Bengal and Southern India, especially the Malabar Coast, where it is said to be the common species, the bite of which is considered venomous by the natives." Kellaart mentions it in Ceylon as the "common musk shrew or rat of Europeans;" but he confuses it with the last species. He gives the Singhalese name as "koone meeyo." The musky odour of this species is less powerful, and is almost absent in the young. Blyth states that he was never able to obtain a specimen of it in Lower Bengal, yet the natives here discriminate between the light and dark-coloured shrews, and hold, with the people of Malabar, that the bite of the latter is venomous. Horsfield states that it has been found in Upper India, Nepal, and Assam, and he gives the vernacular name in the last-named country as "seeka."
NO. 127. SOREX NEMORIVAGUSThe Nepal Wood Shrew (Jerdon's No. 71)HABITAT.—Nepal.
DESCRIPTION.—Differs from the last "by a stouter make, by ears smaller and legs entirely nude, and by a longer and more tetragonal tail; colour sooty black, with a vague reddish smear; the nude parts fleshy grey; snout to rump, 3-5/8 inches; tail, 2 inches, planta, 11/16 inch. Found only in woods and coppices."—Hodgson.
NO. 128. SOREX SERPENTARIUSThe Rufescent Shrew (Jerdon's No. 72)HABITAT.—Southern India, Burmah and Ceylon.
DESCRIPTION.—Colour dusky greyish, with rufous brown tips to the hairs (Blyth). Above dusky slate colour with rufescent tips to the fur; beneath paler, with a faint rufous tinge about the breast (Jerdon). Fur short ashy-brown, with a ferruginous smear on the upper surface; beneath a little paler coloured (Kellaart). Teeth and limbs small; tail slender.
SIZE.—Head and body about 4½ inches; tail, 2 inches; skull, 1-2/10 inch.
The smell of this musk shrew is said by Kellaart, who names it S. Kandianus, to be quite as powerful as that of S. cærulescens. Blyth seems to think that this animal gets more rufescent with age, judging from two examples sent from Mergui. By some oversight, I suppose, he has not included this species in his 'Catalogue of the Mammals of Burmah.'
NO. 129. SOREX SATURATIORThe Dark Brown Shrew (Jerdon's No. 73)HABITAT.—Darjeeling.
DESCRIPTION.—"Colour uniform deep brown, inclining to blackish, with a very slight rufescent shade; fur short, with an admixture of a few lengthened piles, when adpressed to the body smooth, but reversed somewhat harsh and rough; tail cylindrical, long, gradually tapering; mouth elongated, regularly attenuated, ears moderate, rounded."
SIZE.—Head and body, 5½ inches; tail, 3 inches.
Jerdon seems to think this is the same as S. Griffithi or closely allied; I cannot say anything about this, as I have no personal knowledge of the species, but on comparison with the description of S. Griffithi (which see further on) I should say they were identical.
NO. 130. SOREX TYTLERIThe Dehra Shrew (Jerdon's No. 74)HABITAT.—Dehra Doon.
DESCRIPTION.—"Light rufescent sandy brown, paler beneath; unusually well clad even on the feet and tail, this last being covered with shortish fur having numerous long hairs intermixed; form very robust; basal portion of tail very thick."
SIZE.—Head and body, 4½ inches; tail, 2¾ inches; hind foot, 7/8 inch.
NO. 131. SOREX NIGERThe Neilgherry Wood Shrew (Jerdon's No. 75)HABITAT.—Ootacamund, Neilgherry hills.
DESCRIPTION.—"Blackish-brown, with a rufescent shade on the upper parts; abdomen greyish; tail equal in length to the entire animal, exclusive of the head, gradually tapering to a point; snout greatly attenuated. Length of head and body, 3½ inches; of the tail, 2½ inches."—Horsfield.
NO. 132. SOREX LEUCOPSThe Long-tailed Shrew (Jerdon's No. 76)HABITAT.—Nepal.
DESCRIPTION.—Uniform blackish-brown colour; tail very long and slender, exceeding in length the head and body, terminating in a whitish tip of half an inch long.
SIZE.—Head and body, 3 inches; tail, 2½ inches. Jerdon supposes that it is found at great altitudes, from Hodgson having in another place described it (MSS.) under the name nivicola.
NO. 133. SOREX SOCCATUSThe Hairy-footed Shrew (Jerdon's No. 77)HABITAT.—Nepal, Sikim, Mussoorie.
DESCRIPTION.—According to Hodgson, nearly the size of S. nemorivagus, "but distinguished by its feet being clad with fur down to the nails, and by its depressed head and tumid bulging cheeks (mystaceal region); ears large and exposed; colour a uniform sordid or brownish-slaty blue, extending to the clad extremities; snout to rump, 3½ inches; tail, 2½ inches; planta, 13/16 inch. This animal was caught in a wood plentifully watered, but not near the water. It had no musky smell when brought to me dead."
NO. 134. SOREX MONTANUSThe Ceylon Black ShrewHABITAT.—Ceylon, mountainous parts.
DESCRIPTION.—"Fur above sooty black without any ferruginous smear, beneath lighter coloured; whiskers long, silvery grey; some parts of legs and feet greyish, clothed with adpressed hairs; claws short, whitish; ears large, round, naked; outer margin lying on a level with the fur of the head and neck, the ears being thus concealed posteriorly; tail tetragonal, tapering, shorter than head and body."—Kellaart.
SIZE.—Head and body, 3¾ inches; tail, 2¼ inches; hind feet, 1/3 inch.
NO. 135. SOREX FERRUGINEUSThe Ceylon Rufescent ShrewHABITAT.—Ceylon, Dimboola, below Newara Elia.
DESCRIPTION.—"Colour uniform dusky or dusky slate, with the tips of the fur rufescent; fur long; large sebaceous anal glands; smell very powerful."—Kellaart.
SIZE.—Head and body, 3¾ inches; tail, 2¼ inches.
NO. 136. SOREX GRIFFITHIThe Large Black ShrewHABITAT.—Khasia hills and Arracan.
DESCRIPTION.—"Deep blackish-brown, with a slight rufous reflection in a certain light; fur short, close, soft, and adpressed; tail thick at the base, with a few long very slender straggling hairs along its entire length; ears small and rounded; snout elongated."—Horsfield.
SIZE.—Head and body, 5¾ inches; tail, 2½ inches.
Horsfield puts this down as having been found in Afghanistan by Griffiths, but this is an error owing to Griffiths' Afghanistan and Khasia collections having got mixed up.
NO. 137. SOREX HETERODONHABITAT.—Khasia hills.
DESCRIPTION.—"Very similar to S. soccatus in general appearance, but less dark coloured, with shorter fur, and pale instead of blackish feet and tail underneath; the feet too are broader, especially the hind feet, and they have a hairy patch below the heel" (Blyth). The skull is narrower, and the upper incisors less strongly hooked.
GENUS FEROCULUSTeeth small; upper incisors shorter and less strongly hooked than in restricted Sorex; posterior spur large; lower incisors serrated with three coronal points. Feet very large.
NO. 138. FEROCULUS MACROPUSThe Large-footed ShrewHABITAT.—Ceylon.
DESCRIPTION.—Fur, long, soft uniform blackish—faint rufescent tinge.
SIZE.—Head and body 4¼ inches; tail 2¼.
The following species are of a more diminutive type, and are commonly called "pigmy-shrews;" in other respects they are true shrews.
NO. 139. SOREX HODGSONIThe Nepal Pigmy-Shrew (Jerdon's No. 78)HABITAT.—Nepal and Sikim.
DESCRIPTION.—Brown, with a slight tinge of chestnut; feet and tail furred; claws white.
SIZE.—Head and body 1½ inch; tail, 1 inch.
Found in coppices and fields; rarely entering houses.
NO. 140. SOREX PERROTETIThe Neilgherry Pigmy-Shrew (Jerdon's No. 79)HABITAT.—Neilgherry hills, probably also other parts of Southern India.
DESCRIPTION.—"Back deep blackish-brown; belly pale; limbs and feet brown; palms and plantæ clad with hairs; ears large, conspicuous."
SIZE.—Head and body, 1-4/12 inch; tail, 11/12 inch.
NO. 141. SOREX MICRONYXThe Small-clawed Pigmy-Shrew (Jerdon's No. 80)HABITAT.—West Himalayas, Kumaon, Mussoorie.
DESCRIPTION.—Claws very minute, with fine hairs impending them, only to be detected by a lens; fur paler and more chestnut-brown than any other of these minute shrews, and more silvery below.
SIZE.—Head and body, 1-5/8 inch; tail 1-1/8 inch.
NO. 142. SOREX MELANODONThe Black-toothed Pigmy-Shrew (Jerdon's No. 81)HABITAT.—Calcutta.
DESCRIPTION.—Called melanodon from the remarkable colouring of its teeth, which are piceous and white-tipped; colour uniform fuscous, scarcely paler beneath.
SIZE.—Head and body, 1-7/8 inch; tail, 1-1/16 inch.
NO. 143. SOREX NUDIPESThe Naked-footed ShrewHABITAT.—Tenasserim.
DESCRIPTION.—"Remarkable for its naked feet and very large ears; also for the odoriferous glands on the sides being strongly developed, whereas we can detect them in no other of these minute species" (Blyth). Colour brown above, a little grizzled and glistening, more silvery below.
SIZE.—Head and body, 1¾ inch; tail, 1-1/16 inch.
NO. 144. SOREX ATRATUSThe Black Pigmy-ShrewHABITAT.—Khasia hills.
DESCRIPTION.—"Very dark colour, extending over the feet and tail which is even blackish underneath; fur blackish-brown above, a little tinged rufescent, and with dark greyish underneath; the feet and tail conspicuously furred, beside the scattered long hairs upon the latter."—Blyth.
This species was determined by Blyth on a single specimen, which was found without its head, impaled by some shrike upon a thorn at Cherrapunji. The same thing occasionally occurs in England, when the common shrew may be found impaled by the rufous-backed shrike (Lanius collurio).
SUB-GENUS SORICULUS (Blyth)The foregoing species being of the white-toothed variety (with the exception of S. melanodon, which, however, exhibits coloration decidedly the reverse of the following type), we now come to the shrews with teeth tipped with a darker colour; the dentition is as in the restricted shrews, with the peculiarity of colour above mentioned. The hind feet of ordinary proportions, unadapted for aquatic habits, and the tail slender and tapering, like that of a mouse, instead of being cylindrical with a stiff brush at the end.
NO. 145. SORICULUS NIGRESCENSThe Mouse-tailed Shrew (Jerdon's No. 82)HABITAT.—Sikim and Nepal.
DESCRIPTION.—"Above dark-blackish or blackish-brown, slightly tinged rufescent, and with a silvery cast in certain lights; beneath greyish-black" (Jerdon). Feet and claws pale; tail slender, straight and naked.
SIZE.—Head and body, 3¼ inches; tail, 1½ inch; hind foot, 5/8 inch.
Jerdon says that Kellaart named an allied species from Ceylon Corsira newera ellia, but I have not been able to find it in his 'Prodromus Faunæ Zeylanicæ,' nor elsewhere.
GENUS CROSSOPUS (Wagner)The hind feet large; the lower surface, as also of the tail, fringed with stiff hairs; tail somewhat compressed towards the tip; habits aquatic.
NO. 146. CROSSOPUS HIMALAICUSThe Himalayan Water-Shrew (Jerdon's No. 83)NATIVE NAMES.—Oong lagniyu, Lepcha; Choopitsi, Bhot.
HABITAT.—Darjeeling.
DESCRIPTION.—Fur dark brown above, paler beneath; rusty brown on the lower part of throat and middle of belly, according to Jerdon; slate coloured back with scattered long hairs, which are longer and white-tipped on the sides and rump, according to Blyth's memoir; ears very small, hairy, concealed; tail long, slender, fringed with stiff whitish hair beneath; whiskers long and brown.
SIZE.—Head and body, 5 to 6 inches; tail about 3½ inches; hind foot, ¾ to 11/12 inch.
Jerdon procured this water-shrew at Darjeeling in the Little Rungeet river; it is said to live on small fish, tadpoles, water insects, &c. The movements of the English water-shrew, when swimming, are very agile. It propels itself by alternate strokes of its hind feet, but with an undulating motion, its sides being in a manner extended, and body flattened, showing a narrow white border on each side; then the fur collects a mass of tiny air bubbles which make the submerged portion glow like silver. It prefers clear still water, but at the same time will make its way up running streams and ditches, and occasionally wanders away into fields, and has been found in houses and barns.
Its food is principally aquatic insects, worms, mollusca, and freshwater crustacea. In Bell's 'British Quadrupeds' its mode of poking about amongst stones in search of fresh-water shrimps (Gammarus pulex) is well described. Mr. F. Buckland states that he once dissected a water-shrew and found the intestines to contain a dark fluid pulpy matter, which, on being examined by a microscope, proved to consist entirely of the horny cases and legs of minute water insects. Continental writers declare that it will attack any small animal that comes in its way, giving it quite a ferocious character, and it is said to destroy fish spawn. I can hardly believe in its destroying large fish by eating out their brain and eyes. Brehm, who gives it credit for this, must have been mistaken. I have also read of its attacking a rat in a trap which was dead, and was discovered devouring it, having succeeded in making a small hole through the skin.
In England this animal breeds in May. The young are from five to seven in number, and are brought forth in a small chamber in the bank, which is constructed with several openings, one of which is usually under the level of the water.
Dr. Anderson has very fully described the Himalayan species under the name of Chimarrogale Himalaica. He caught a specimen in a mountain stream at Ponsee in the Kakhyen hills, 3500 feet above the sea level, and observed it running over the stones in the bed of the stream and plunging freely into the water hunting for insects.
GENUS NYCTOGALEHead and skull as in Soricidæ, but with palmated feet and compressed tail, as in Myogalidæ. Special characteristic, large pads on the soles of the feet, which form sucking discs.
NO. 147. NYCTOGALE ELEGANSThe Thibet Water-ShrewHABITAT.—Moupin in Thibet.
DESCRIPTION.—Fur of two kinds, a soft under down of slaty grey colour through which pass longer hairs, grey at the base with white tips, "causing the animal to vary considerably in appearance according as these hairs are raised or laid flat;" ears quite concealed, and without a conch; tail stout, longer than the body, quadrangular at the base, then triangular, and finally flattened; feet large and palmated, with large pads on the soles, depressed in the middle, forming sucking discs, which are a peculiar characteristic of this animal.
SIZE.—Head and body about 3½ inches; tail about 4 inches.
Though this is not properly an Indian animal, I have thought fit to include it as belonging to a border country in which much interest is taken, and which has as yet been imperfectly explored.
GENUS CORSIRAOf Gray, Amphisorex of Duvernoy; differs in dentition from the last in having the lower quasi-incisors serrated with three or four coronal points, and the anterior point of the upper incisors not prolonged beyond the posterior spur, tipped with ferruginous; the lateral small teeth in the upper jaw are five in number, diminishing in size from the first backwards. Tail cylindrical, not tapering, and furnished with a stiffish brush at the extremity. The common British land-shrew is of this type.
NO. 148. CORSIRA ALPINAThe Alpine Shrew (Jerdon's No. 84)HABITAT.—Darjeeling.
DESCRIPTION.—Deep blackish brown, very slightly rufescent in certain lights; tail slender, nearly naked, very slightly attenuated, compressed at the tip.
SIZE.—Head and body, 2½ inches; tail 2½ inches.
This is identical with the European Alpine shrew; the Sorex caudatus of Horsfield's Catalogue (No. 148), which was a specimen named by Hodgson, is also the same animal.
GENUS ANUROSOREXRemarkably for its large head, nude, scaly extremities, and extremely short, nude, scaly tail. "The structure of the ear, limbs and tail has special reference to a burrowing animal—the ear being valvular, so that it may be effectually closed against the entrance of foreign substances, and the feet devoid of hair, but scaly, and the tail reduced to very small dimensions. The eye is also excessively small, and buried deep in the dense silky fur. The hind feet, contrary to what is almost invariably the case in burrowing mammals, are larger than the fore feet."—Anderson.
NO. 149. ANUROSOREX ASSAMENSISThe Assam Burrowing ShrewHABITAT.—Assam, Thibet.
DESCRIPTION.—General colour dark slaty, faintly washed with brownish rusty on the long hairs of the rump; fur long and silky, longest over the rump; occasional long brown hairs with pale tips are scattered over the body; long whiskers, yellow claws; naked parts of snout, limbs and tail flesh-coloured.
SIZE.—Head and body nearly 3 inches; tail, ½ inch; forefoot, ½ inch; hind foot, ¾ inch.
The skull and dentition of this animal are essentially soricine. The Thibetan species (A. squamipes) is described as being over four inches in length, of a greyish colour, with a greenish-brown tinge; feet and nails whitish. It lives in burrows which it digs in the earth. I think it should properly come after the moles, which it resembles in some particulars.
FAMILY ERINACEIDÆ—THE HEDGEHOGS
The molar teeth broad; the hinder ones nearly square, the tubercles on their upper surface rounded; the other teeth are three incisors on each side, of which the inner one is considerably larger than the rest; behind these, separated by a little gap, come three premolars gradually increasing in size, then one having much the appearance of a true molar, but furnished with a cutting edge; then three molar teeth, two of which are nearly square with strong tubercles. The last molar is small. In the lower jaw the lowermost incisor is very large, and projects almost horizontally forwards, and it is followed by three small teeth now acknowledged to be premolars, with another large premolar, which is of the nature of a carnassial or cutting tooth acting on the one in the upper jaw. Then three molars as above, two large and one small, but with sharp tubercles. The skull has a more carnivorous form; it has "a complete zygomatic arch, and the tympanic bone forms a bundle-like swelling on each side of the back of the skull." Feet pentadactylous or five-toed; legs very short. The tibia and fibula (two bones of the shank) are joined together. The back is clothed with hair intermixed with sharp spines or bristles. Tail short or wanting entirely.
GENUS ERINACEUSThe European hedgehog is well known to most of us. Few boys who have lived a country life have been without one at some time or other as a pet. I used to keep mine in a hole at the root of an old apple-tree, which was my special property, and they were occasionally brought into the house at the cook's request to demolish the black-beetles in the kitchen. These they devour with avidity and pursue them with the greatest ardour. They also eat slugs, worms, and snails; worms they seize and eat from end to end, like a Neapolitan boy with a string of maccaroni, slowly masticating, the unconsumed portion being constantly transferred from one side of the mouth to the other, so that both sides of the jaws may come into play. Dr. Dallas quaintly remarks on the process: "This must be an unpleasant operation for the worm, much as its captor may enjoy it." Toads, frogs, mice, and even snakes are eaten by the European hedgehog. It would be interesting to find out whether the Indian hedgehog also attacks snakes; even the viper in Europe is devoured by this animal, who apparently takes little heed of its bite. The European species also eats eggs when it can get them, and I have no doubt does much damage to those birds who make their nests on the ground.
Few dogs will tackle a hedgehog, for the little creature at once rolls itself into a spiny ball, all sharp prickles, by means of the contraction of a set of cutaneous muscles, the most important of which, the orbicularis panniculi, form a broad band encircling the body which draws together the edges of the spiny part of the skin. There is a most interesting account of the mechanism of the spines in Mr. F. Buckland's notes to White's 'Natural History of Selborne,' vol. ii., page 76. A jet of water poured on to the part within which the head is concealed will make the creature unroll, and it is said that foxes and some dogs have discovered a way of applying this plan, and also that foxes will roll a hedgehog into a ditch or pond, and thus make him either expose himself to attack or drown. Gipsies eat hedgehogs, and consider them a delicacy—the meat being white and as tender as a chicken (not quite equal to porcupine, I should say); they cook them by rolling them in clay, and baking them till the clay is dry; when the ball is broken open the prickles come off with the crust.
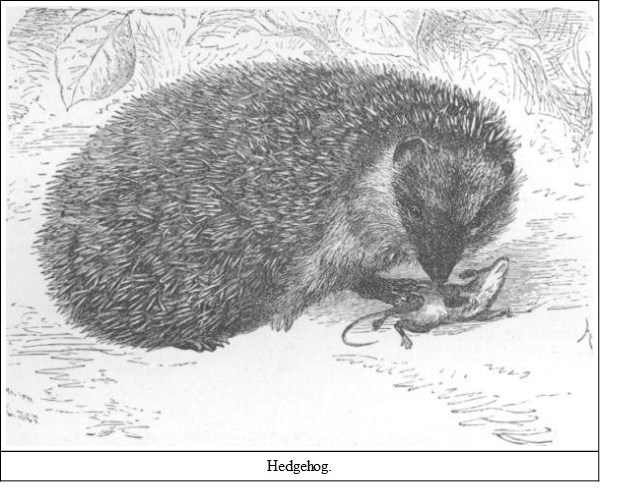

Hedgehogs have had several popular fallacies concerning them. They were supposed to suck cows dry during the night and to be proof against poisons. Mr. Frank Buckland tried prussic acid on one with fatal results, but he says the bite of a viper seemed to have no effect. Pallas, I know, has remarked that hedgehogs will eat hundreds of cantharides beetles with impunity, whereas one or two will cause extreme agony to a cat or dog. The female goes with young about seven weeks, and she has from three to eight in number. The little ones when born have soft spines—which, however, soon harden—are blind, and, with the exception of the rudimentary prickles, quite naked. They are white at birth, but in about a month acquire the colour of the mother.
NO. 150. ERINACEUS COLLARISThe Collared Hedgehog (Jerdon's No. 85)HABITAT.—Northern India and Afghanistan. Dallas says from Madras to Candahar; but Jerdon calls it the North Indian hedgehog, and assigns to it the North-west, Punjab, and Sind, giving Southern India to the next species.
DESCRIPTION.—Spines irregularly interwoven, ringed with white and black, with yellowish tips, or simply white and black, or black with a white ring in the middle; ears large; chin white; belly and legs pale brown.
SIZE.—Head and body, 8 to 9 inches; tail, 7/12 inch.
I have found this species in the Punjab near Lahore. One evening, whilst walking in the dusk, a small animal, which I took to be a rat, ran suddenly between my legs. Now I confess to an antipathy to rats, and, though I would not willingly hurt any animal, I could not resist an impulsive kick, which sent my supposed rat high in the air. I felt a qualm of conscience immediately afterwards, and ran to pick up my victim, and was sorry to find I had perpetrated such an assault on an unoffending little hedgehog, which was however only stunned, and was carried off by me to the Zoological Gardens. Captain Hutton writes of them that they feed on beetles, lizards, and snails; "when touched they have the habit of suddenly jerking up the back with some force so as to prick the fingers or mouth of the assailant, and at the same time emitting a blowing sound, not unlike the noise produced when blowing upon a flame with a pair of bellows." He also says they are very tenacious of life, bearing long abstinence with apparent ease; when alarmed they roll themselves up into a ball like the European species.
Hutton also remarks that E. collaris, on hearing a noise, jerks the skin and quills of its neck completely over its head, leaving only the tip of the nose free.

