 полная версия
полная версияThe Illustrated London Reading Book
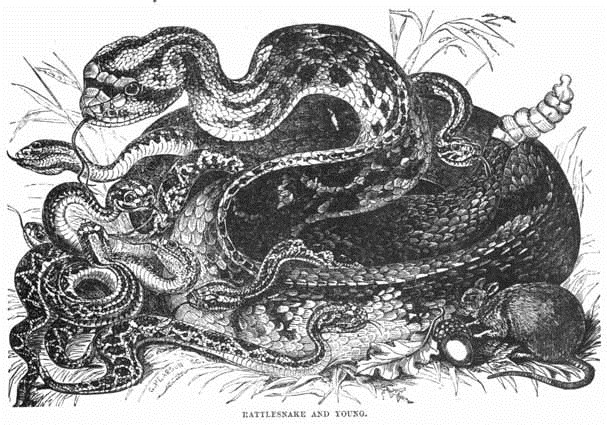
This terrible reptile is found in great abundance on the continent of America; and if its instinct induced it to make use of the dreadful means of destruction and self-defence which it possesses, it would become so great a scourge as to render the parts in which it is found almost uninhabitable: but, except when violently irritated, or for the purpose of self-preservation, it seldom employs the fatal power bestowed upon it. The rattlesnake inserts its poison in the body of its victim by means of two long sharp-pointed teeth or fangs, which grow one on each side of the forepart of the upper jaw. The construction of these teeth is very singular; they are hollow for a portion of their length, and in each tooth is found a narrow slit communicating with the central hollow; the root of the fang rests on a kind of bag, containing a certain quantity of a liquid poison, and when the animal buries his teeth in his prey, a portion of this fluid is forced through these openings and lodged at the bottom of the wound. Another peculiarity of these poison teeth is, that when not in use they turn back, as it were, upon a hinge, and lie flat in the roof of the animal's mouth.
The name of rattlesnake is given to it on account of the singular apparatus with which the extremity of its tail is furnished. This consists of a series of hollow horn-like substances, placed loosely one behind the other in such a manner as to produce a kind of rattling noise when the tail is shaken; and as the animal, whenever it is enraged, always carries its tail raised up, and produces at the same time a tremulous motion in it, this provision of nature gives timely notice of its dangerous approach. The number of pieces of which this rattle is formed points out the age of the snake, which acquires a fresh piece every year. Some specimens have been found with as many as from forty to fifty, thus indicating a great age.

The poison of the Viper consists of a yellowish liquid, secreted in a glandular structure (situated immediately below the skin on either side of the head), which is believed to represent the parotid gland of the higher animals. If a viper be made to bite something solid, so as to avoid its poison, the following are the appearances under the microscope:—At first nothing is seen but a parcel of salts nimbly floating in the liquor, but in a very short time these saline particles shoot out into crystals of incredible tenuity and sharpness, with something like knots here and there, from which these crystals seem to proceed, so that the whole texture in a manner represents a spider's web, though infinitely finer and more minute. These spiculae, or darts, will remain unaltered on the glass for some months. Five or six grains of this viperine poison, mixed with half an ounce of human blood, received in a warm glass, produce no visible effects, either in colour or consistence, nor do portions of this poisoned blood, mixed with acids or alkalies, exhibit any alterations. When placed on the tongue, the taste is sharp and acrid, as if the tongue had been struck with something scalding or burning; but this sensation goes off in two or three hours. There are only five cases on record of death following the bite of the viper; and it has been observed that the effects are most virulent when the poison has been received on the extremities, particularly the fingers and toes, at which parts the animal, when irritated (as it were, by an innate instinct), always takes its aim.
F. T. BUCKLANDORIGIN OF "JACK THE GIANT-KILLER."
After various adventures, Thor, accompanied by Thialfi and Loke, his servants, entered upon Giantland, and wandered over plains—wild uncultivated places—among stones and trees. At nightfall they noticed a house; and as the door, which indeed formed one whole side of the house, was open, they entered. It was a simple habitation—one large hall, altogether empty. They stayed there. Suddenly, in the dead of the night, loud voices alarmed them. Thor grasped his hammer, and stood in the doorway, prepared for fight. His companions within ran hither and thither, in their terror, seeking some outlet in that rude hall: they found a little closet at last, and took refuge there. Neither had Thor any battle; for lo! in the morning it turned out that the noise had been only the snoring of a certain enormous, but peaceable, giant—the giant Skrymir, who lay peaceably sleeping near by; and this, that they took for a house, was merely his glove thrown aside there: the door was the glove-wrist; the little closet they had fled into was the thumb! Such a glove! I remark, too, that it had not fingers, as ours have, but only a thumb, and the rest undivided—a most ancient rustic glove!
Skrymir now carried their portmanteau all day; Thor, however, who had his suspicions, did not like the ways of Skrymir, and determined at night to put an end to him as he slept. Raising his hammer, he struck down into the giant's face a right thunderbolt blow, of force to rend rocks. The giant merely awoke, rubbed his cheek, and said, "Did a leaf fall?" Again Thor struck, as soon as Skrymir again slept, a better blow than before; but the giant only murmured, "Was that a grain of sand!" Thor's third stroke was with both his hands (the "knuckles white," I suppose), and it seemed to cut deep into Skrymir's visage; but he merely checked his snore, and remarked, "There must be sparrows roosting in this tree, I think."
At the gate of Utgard—a place so high, that you had to strain your neck bending back to see the top of it—Skrymir went his way. Thor and his companions were admitted, and invited to take a share in the games going on. To Thor, for his part, they handed a drinking-horn; it was a common feat, they told him, to drink this dry at one draught. Long and fiercely, three times over, Thor drank, but made hardly any impression. He was a weak child, they told him; could he lift that cat he saw there? Small as the feat seemed, Thor, with his whole godlike strength, could not: he bent up the creature's back, could not raise its feet off the ground—could at the utmost raise one foot. "Why, you are no man," said the Utgard people; "there is an old woman that will wrestle you." Thor, heartily ashamed, seized this haggard old woman, but could not throw her.

And now, on their quitting Utgard—the chief Jotun, escorting them politely a little way, said to Thor—"You are beaten, then; yet, be not so much ashamed: there was deception of appearance in it. That horn you tried to drink was the sea; you did make it ebb: but who could drink that, the bottomless? The cat you would have lifted—why, that is the Midgard Snake, the Great World Serpent—which, tail in mouth, girds and keeps up the whole created world. Had you torn that up, the world must have rushed to ruin. As for the old woman, she was Time, Old Age, Duration: with her what can wrestle? No man, nor no god, with her. Gods or men, she prevails over all! And then, those three strokes you struck—look at these valleys—your three strokes made these." Thor looked at his attendant Jotun—it was Skrymir. It was, say old critics, the old chaotic rocky earth in person, and that glove house was some earth cavern! But Skrymir had vanished. Utgard, with its sky-high gates, when Thor raised his hammer to smite them, had gone to air—only the giant's voice was heard mocking; "Better come no more to Jotunheim!"
Carlyle.VALUE OF THE BIBLE
What an invaluable blessing it is to have the Bible in our own tongue. It is not only the oldest, but the best book in the world. Our forefathers rejoiced when they were first favoured with the opportunity of reading it for themselves. Infidels may reject, and the licentious may sneer; but no one who ever wished to take away this foundation-stone, could produce any other equal to it, on which the structure of a pious mind, a solid hope, a comfortable state, or wise conduct, could be raised. We are told, that when Archbishop Crammer's edition of the Bible was printed in 1538, and fixed to a desk in all parochial churches, the ardour with which men flocked to read it was incredible. They who could, procured it; and they who could not, crowded to read it, or to hear it read in churches. It was common to see little assemblies of mechanics meeting together for that purpose after the labour of the day. Many even learned to read in their old age, that they might have the pleasure of instructing themselves from the Scriptures.
It is recorded of Edward VI., that upon a certain occasion, a paper which was called for in the council-chamber happened to be out of reach; the person concerned to produce it took a Bible that lay near, and, standing upon it, reached down the paper. The King, observing what was done, ran to the place, and taking the Bible in his hands kissed it, and laid it up again. This circumstance, though trifling in itself, showed his Majesty's great reverence for that best of all books; and his example is a striking reproof to those who suffer their Bibles to lie covered with dust for months together, or who throw them about as if they were only a piece of useless lumber.
Buck's Anecdotes.NATURE AND ITS LORD
There's not a leaf within the bower,There's not a bird upon the tree,There's not a dew-drop on the flower,But bears the impress, Lord, of Thee!Thy hand the varied leaf design'd,And gave the bird its thrilling tone;Thy power the dew-drops' tints combined,Till like a diamond's blaze they shone!Yes, dew-drops, leaves, and buds, and all—The smallest, like the greatest things—The sea's vast space, the earth's wide ball,Alike proclaim thee King of Kings.But man alone to bounteous heavenThanksgiving's conscious strains can raise;To favour'd man alone 'tis given,To join the angelic choir in praise!THE STEPPING-STONES
The struggling rill insensibly is grownInto a brook of loud and stately march,Cross'd ever and anon by plank or arch;And for like use, lo! what might seem a zoneChosen for ornament—stone match'd with stoneIn studied symmetry, with interspaceFor the clear waters to pursue their raceWithout restraint. How swiftly have they flown—Succeeding, still succeeding! Here the childPuts, when the high-swoll'n flood runs fierce and wild,His budding courage to the proof; and hereDeclining manhood learns to note the slyAnd sure encroachments of infirmity—Thinking how fast time runs—life's end how near.Wordsworth.
HUMANITY
During the retreat of the famous King Alfred at Athelney, in Somersetshire, after the defeat of his forces by the Danes, the following circumstance happened, which shows the extremities to which that great man was reduced, and gives a striking proof of his pious and benevolent disposition:—A beggar came to his little castle, and requested alms. His Queen informed him that they had only one small loaf remaining, which was insufficient for themselves and their friends, who were gone abroad in quest of food, though with little hopes of success. But the King replied, "Give the poor Christian the one half of the loaf. He that could feed live thousand with five loaves and two fishes, can certainly make that half of the loaf suffice for more than our necessities." Accordingly the poor man was relieved; and this noble act of charity was soon recompensed by a providential store of fresh provisions, with which his people returned.
Sir Philip Sydney, at the battle near Zutphen, displayed the most undaunted courage. He had two horses killed under him; and, whilst mounting a third, was wounded by a musket-shot out of the trenches, which broke the bone of his thigh. He returned about mile and a half on horseback to the camp; and being faint with the loss of blood, and parched with thirst from the heat of the weather, he called for drink. It was presently brought him; but, as he was putting the vessel to his mouth, a poor wounded soldier, who happened to be carried along at that instant, looked up to it with wistful eyes. The gallant and generous Sydney took the flagon from his lips, just when he was going to drink, and delivered it to the soldier, saying, "Thy necessity is greater than mine."
Frederick, King of Prussia, one day rang his bell and nobody answered; on which he opened the door and found his page fast asleep in an elbow-chair. He advanced toward him, and was going to awaken, him, when he perceived a letter hanging out of his pocket. His curiosity prompting him to know what it was, he took it out and read it. It was a letter from the young man's mother, in which she thanked him for having sent her part of his wages to relieve her in her misery, and finished with telling; him that God would reward him for his dutiful affection. The King, after having read it, went back softly into his chamber, took a bag full of ducats, and slipped it with the letter into the page's pocket. Returning to his chamber, he rang the bell so violently that he awakened the page, who instantly made his appearance. "You have had a sound sleep," said the King. The page was at a loss how to excuse himself and, putting his hand into his pocket by chance, to his utter astonishment he there found a purse of ducats. He took it out, turned pale, and looking at the bag, burst into tears without being able to utter a single word. "What is that?" said the King; "what is the matter?" "Ah, sire!" said the young man, throwing himself on his knees, "somebody seeks my ruin! I know nothing of this money which I have just found in my pocket!" "My young friend," replied Frederick, "God often does great things for us even in our sleep. Send that to your mother, salute her on my part, and assure her that I will take care of both her and you."
Beauties of History.THE SPANIELS OF THE MONKS OF ST. BERNARD
The convent of the Great St. Bernard is situated near the top of the mountain known by that name, near one of the most dangerous passes of the Alps, between Switzerland and Savoy. In these regions the traveller is often overtaken by the most severe weather, even after days of cloudless beauty, when the glaciers glitter in the sunshine, and the pink flowers of the rhododendron appear as if they were never to be sullied by the tempest. But a storm suddenly comes on; the roads are rendered impassable by drifts of snow; the avalanches, which are huge loosened masses of snow or ice, are swept into the valleys, carrying trees and crags of rock before them.

The hospitable monks, though their revenue is scanty, open their doors to every stranger that presents himself. To be cold, to be weary, to be benighted, constitutes the title to their comfortable shelter, their cheering meal, and their agreeable converse. But their attention to the dis tressed does not end here. They devote themselves to the dangerous task of searching for those unhappy persons who may have been overtaken by the sudden storm, and would perish but for their charitable succour. Most remarkably are they assisted in these truly Christian offices. They have a breed of noble dogs in their establishment, whose extraordinary sagacity often enables them to rescue the traveller from destruction. Benumbed with cold, weary in the search of a lost track, his senses yielding to the stupefying influence of frost, the unhappy man sinks upon the ground, and the snow-drift covers him from human sight. It is then that the keen scent and the exquisite docility of these admirable dogs are called into action. Though the perishing man lie ten or even twenty feet beneath the snow, the delicacy of smell with which they can trace him offers a chance of escape. They scratch away the snow with their feet; they set up a continued hoarse and solemn bark, which brings the monks and labourers of the convent to their assistance.
To provide for the chance that the dogs, without human help, may succeed in discovering the unfortunate traveller, one of them has a flask of spirits round his neck, to which the fainting man may apply for support; and another has a cloak to cover him. Their wonderful exertions are often successful; and even where they fail of restoring him who has perished, the dogs discover the body, so that it may be secured for the recognition of friends; and such is the effect of the cold, that the dead features generally preserve their firmness for the space of two years. One of these noble creatures was decorated with a medal, in commemoration of his having saved the lives of twenty-two persons, who, but for his sagacity, must have perished. Many travellers, who have crossed the pass of St. Bernard, have seen this dog, and have heard, around the blazing fire of the monks, the story of his extraordinary career. He perished about the year 1816, in an attempt to convey a poor traveller to his anxious family.
The Menageries.
JOPPA
Joppa is the principal sea-port town of Palestine and it is very often mentioned in Scripture.
Hiram, King of Tyre, is said to have sent cedars of Lebanon by sea to Joppa, for the building of Solomon's Temple; and from Joppa the disobedient Jonah embarked, when ordered by God to go and preach to the people of Nineveh.
It was at Joppa that the apostle Peter lived, for some time, with one Simon, a tanner, whose house was by the sea-shore; and it was on the flat roof of this dwelling that he saw the wonderful vision, which taught him not to call any man common or unclean.

Tabitha or Dorcas, the pious woman who spent all her life in working for the poor, and in giving alms to those who needed relief, lived in Joppa; and here it pleased God that she should be taken ill and die, and her body was laid out in the usual manner before burial, in an upper chamber of the house where she lived. The apostle Peter, to whom this pious woman had been well known, was then at Lydda, not far from Joppa, and the disciples sent to tell him of the heavy loss the Church had met with in the death of Dorcas, and begged that he would come and comfort them. The apostle directly left Lydda and went over to Joppa. He was, by his own desire, taken to the room where the corpse lay, and was much moved when he saw the tears of the poor women who had been fed and clothed by the charity of Dorcas, and who were telling each other how much good she had been the means of doing them.
Peter desired to be left alone with the body, and then he knelt down and prayed, and, receiving strength from God, he turned to the body and cried, "Tabitha, arise!" She then, like one awaking from sleep, opened her eyes, and when she saw Peter she sat up. He then took her by the hand, and she arose and was presented alive to those who, thinking she was dead, had so lately been mourning for her loss. This was the first miracle performed by the apostles, and it greatly surprised the people of Joppa, who began one and all to believe that Peter was really a preacher sent by God.
The name of Joppa signified beautiful. It was built upon the side of a rocky mountain, which rises from the sea-shore, and all around it were lovely gardens, full of vines, figs, and other fruits.
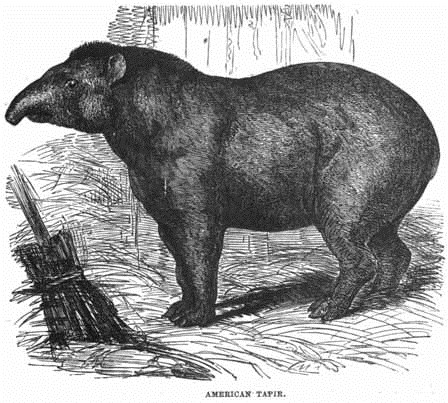
THE AMERICAN TAPIR
There are but three known species of the Tapir, two of which—the Peccary and the Tapir—are natives of South America, the other of Sumatra and Malacca. Its anatomy is much like that of the rhinoceros, while in general form the tapir reminds us of the hog. It is a massive and powerful animal, and its fondness for the water is almost as strong as that displayed by the hippopotamus. It swims and dives admirably, and will remain submerged for many minutes, rising to the surface for breath, and then again plunging in. When hunted or wounded, it always, if possible, makes for the water; and in its nightly wanderings will traverse rivers and lakes in search of food, or for pleasure. The female is very attentive to her young one, leading it about on the land, and accustoming it at an early period to enter the water, where it plunges and plays before its parent, who seems to act as its instructress, the male taking no share in the work.
The tapir is very common in the warm regions of South America, where it inhabits the forests, leading a solitary life, and seldom stirring from its retreat during the day, which it passes in a state of tranquil slumber. During the night, its season of activity, it wanders forth in search of food, which consists of water-melons, gourds, young shoots of brushwood, &c.; but, like the hog, it is not very particular in its diet. Its senses of smell and hearing are extremely acute, and serve to give timely notice of the approach of enemies. Defended by its tough thick hide, it is capable of forcing its way through the thick underwood in any direction it pleases: when thus driving onwards, it carries its head low, and, as it were, ploughs its course.
The most formidable enemy of this animal, if we except man, is the jaguar; and it is asserted that when that tiger of the American forest throws itself upon the tapir, the latter rushes through the most dense and tangled underwood, bruising its enemy, and generally succeeds in dislodging him.
The snout of the tapir greatly reminds one of the trunk of the elephant; for although it is not so long, it is very flexible, and the animal makes excellent use of it as a crook to draw down twigs to the mouth, or grasp fruit or bunches of herbage: it has nostrils at the extremity, but there is no finger-like appendage.
In its disposition the tapir is peaceful and quiet, and, unless hard pressed, never attempts to attack either man or beast; when, however, the hunter's dogs surround it, it defends itself very vigorously with its teeth, inflicting terrible wounds, and uttering a cry like a shrill kind of whistle, which is in strange contrast with the massive bulk of the animal.
The Indian tapir greatly resembles its American relative; it feeds on vegetables, and is very partial to the sugar-cane. It is larger than the American, and the snout is longer and more like the trunk of the elephant. The most striking difference, however, between the eastern and western animal is in colour. Instead of being the uniform dusky-bay tint of the American, the Indian is strangely particoloured. The head, neck, fore-limbs, and fore-quarters are quite black; the body then becomes suddenly white or greyish-white, and so continues to about half-way over the hind-quarters, when the black again commences abruptly, spreading over the legs. The animal, in fact, looks just as if it were covered round the body with a white horse-cloth.
Though the flesh of both the Indian and American tapir is dry and disagreeable as an article of food, still the animal might be domesticated with advantage, and employed as a beast of burthen, its docility and great strength being strong recommendations.
THE FIELD OF WATERLOO
Waterloo is a considerable village of Belgium, containing about 1600 inhabitants; and the Field of Waterloo, so celebrated as the scene of the battle between two of the greatest generals who ever lived, is about two miles from it. It was very far from a strong position to be chosen for this purpose, but, no doubt, was the best the country afforded. A gently rising ground, not steep enough in any part to prevent a rush of infantry at double-quick time, except in the dell on the left of the road, near the farm of La Haye Sainte; and along the crest of the hill a scrubby hedge and low bank fencing a narrow country road. This was all, except La Haye Sainte and Hougoumont. This chateau, or country-seat, one of those continental residences which unite in them something of the nature of a castle and a farm-house, was the residence of a Belgic gentleman. It stands on a little eminence near the main road leading from Brussels to Nivelles. The buildings consisted of an old tower and a chapel, and a number of offices, partly surrounded by a farm-yard. The garden was enclosed by a high and strong wall; round the garden was a wood or orchard, which was enclosed by a thick hedge, concealing the wall. The position of the place was deemed so important by the Duke of Wellington, that he took possession of the Château of Goumont, as it was called, on the 17th of June, and the troops were soon busily preparing for the approaching contest, by perforating the walls, making loop-holes for the fire of the musketry, and erecting scaffolding for the purpose of firing from the top.









