
Полная версия
The fourth industrial revolution glossarium: over 1500 of the hottest terms you will use to create the future
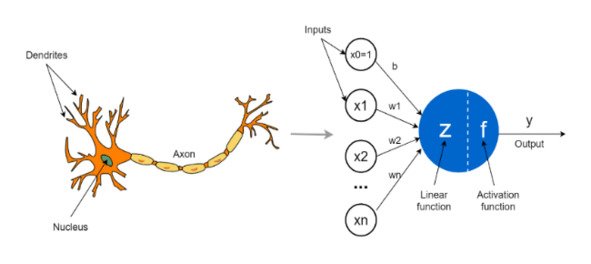
Artificial neuron is a mathematical function conceived as a model of biological neurons, a neural network. The difference between an artificial neuron and a biological neuron is shown in the figure.
Artificial neurons are the elementary units of an artificial neural network. An artificial neuron receives one or more inputs (representing excitatory postsynaptic potentials and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials on nerve dendrites) and sums them to produce an output signal (or activation, representing the action potential of the neuron that is transmitted down its axon). Typically, each input is weighted separately, and the sum is passed through a non-linear function known as an activation function or transfer function. Transfer functions are usually sigmoid, but they can also take the form of other non-linear functions, piecewise linear functions, or step functions. They are also often monotonically increasing, continuous, differentiable, and bounded77,78.
Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) is a term referring to the time when the capability of computers will surpass humans. «Artificial intelligence,» which has been much used since the 1970s, refers to the ability of computers to mimic human thought. Artificial superintelligence goes a step beyond and posits a world in which a computer’s cognitive ability is superior to a human.
ASCII is a character-encoding scheme used by many computers. The ASCII standard uses 7 of the 8 bits in a byte to define the codes for 128 characters. Example: In ASCII, the number «7» is treated as a character and is encoded as: 00010111. Because a byte can have a total of 256 possible values, there are an additional 128 possible characters that can be encoded into a byte, but there is no formal ASCII standard for those additional 128 characters. Most IBM-compatible personal computers do use an IBM «extended» character set that includes international characters, line and box drawing characters, Greek letters, and mathematical symbols. (ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange)79.
Asset are mission-critical systems, physical hardware, applications, support systems, high-impact programs, personnel, equipment, locations, and more80.
Asset framework is a hierarchy tree depicting the high level assets, sub assets, and individual sensors at the leaf level of the tree81.
Assist – assessment and evaluation tools for e-service deployment in health, care and ageing – is an assessment and evaluation framework and tool built by Empirica for assessing the economic sustainability of telemedicine and telehealth services. Originally developed and successfully applied for business case development in telemedicine on behalf of the European Space Agency, the ASSIST tool exists also in adaptations for use in integrated eCare and eHealth services82.
Assisted registration – the process that enables healthcare providers to assist their patients to register for a My Health Record83.
Assisted Registration Tool (ART) – purpose-built software to enable an HPI-O to assert a patient’s identity and then submit their details to the My Health Record system for registration84.
Assistive intelligence is AI-based systems that help make decisions or perform actions.
Assistive technology (AT) is any item, piece of equipment, software program, or product system that is used to increase, maintain, or improve the functional capabilities of persons with disabilities85.
Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) — an international, nonprofit, scientific society devoted to promote research in, and responsible use of, artificial intelligence. AAAI also aims to increase public understanding of artificial intelligence (AI), improve the teaching and training of AI practitioners, and provide guidance for research planners and funders concerning the importance and potential of current AI developments and future directions.
Assumed Consent – informational consent done in the absence of any formal recorded or verbal indication of agreement or any overt action (or inaction) on the part of the data subject86.
Assurance – activities designed to reach a measure of confidence. Assurance is different from audit, which is more concerned with compliance to formal standards or requirements87.
Asynchronous inter-chip protocols are protocols for data exchange in low-speed devices; instead of frames, individual characters are used to control the exchange of data.
Athenahealth Inc. is a developer of cloud-based practice management, point-of-care mobile applications and electronic health record (EHR) systems for small to medium-sized (SMB) physician practices and hospitals88.
Attack Surface refers to the system elements and interactions that are vulnerable to cyberattacks89.
Attack Vector is a pathway by which a cybercriminal can gain access to an entity90.
Attention mechanism is one of the key innovations in the field of neural machine translation. Attention allowed neural machine translation models to outperform classical machine translation systems based on phrase translation. The main bottleneck in sequence-to-sequence learning is that the entire content of the original sequence needs to be compressed into a vector of a fixed size. The attention mechanism facilitates this task by allowing the decoder to look back at the hidden states of the original sequence, which are then provided as a weighted average as additional input to the decoder.
Attributes (XML) (Атрибуты (XML)) XML elements can have attributes that further describe them, such as the following:
Audit – an independent examination of an effort to determine its compliance with a set of requirements. An audit may be carried out by internal or external groups92.
Audit Trail is a record that can be interpreted by auditors to establish that an activity has taken place. Often, a chronological record of system activities to enable the reconstruction and examination of the sequence of events and/or changes in an event. An audit trail of system resource usage may include user login, file access, and triggers that indicate whether any actual or attempted security violations occurred93.
Auditability – property that ensures that any action of any security subject on any security object may be examined in order to establish the real operational responsibilities94.
Augmented and virtual reality enable the creation of immersive and interactive experiences using digital simulations. In a post-pandemic world, where buying takes place at a distance, serving up products virtually has never been so crucial95.
Augmented Intelligence is the intersection of machine learning and advanced applications, where clinical knowledge and medical data converge on a single platform. The potential benefits of Augmented Intelligence are realized when it is used in the context of workflows and systems that healthcare practitioners operate and interact with. Unlike Artificial Intelligence, which tries to replicate human intelligence, Augmented Intelligence works with and amplifies human intelligence96.
Augmented Reality (AR) is an enhanced version of the real physical world that is achieved through the use of digital visual elements, sound, or other sensory stimuli delivered via technology. It is a growing trend among companies involved in mobile computing and business applications in particular. Also, Augmented Reality (AR) refers to an interactive experience that blends together the virtual world and the real world. For example, visuals of a product or component can be overlaid onto the real world via a mobile phone or tablet, enabling users to visualize a virtual object in a real-world space97,98.
Augmented reality technologies are visualization technologies based on adding information or visual effects to the physical world by overlaying graphic and/or sound content to improve user experience and interactive features.
Authentication – process of reliably identifying security subjects by securely associating an identifier and authenticator99.
Authoring organisation – the healthcare provider organisation that created the content of a document100.
Authorization – permission to perform certain operations or use certain methods or services101.
Authorization link is a link that connects a healthcare provider to a healthcare provider organisation so the healthcare provider can access the My Health Record system via the National Provider Portal on behalf of their organisation102.
Authorized employee – an employee of a registered healthcare provider organisation who has been authorized by the organisation to use the My Health Record system and access an individual’s My Health Record on behalf of the organisation103.
Authorized representative – someone who can apply for and manage a My Health Record on behalf of another person. For the purposes of the My Health Record system someone can be an authorized representative if they: Have parental responsibility for a person under 14; or Have legal authority to act on behalf of a person who is at least 14 and who is not capable of making his or her own decisions. If there is no one with parental responsibility or legal authority, a person who is otherwise appropriate to act on behalf of the individual can be an authorized representative. An individual can have more than one authorized representative104.
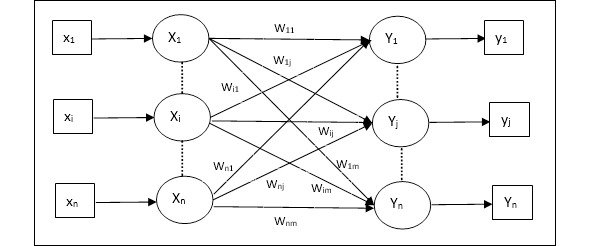
Auto Associative Memory is a single layer neural network in which the input training vector and the output target vectors are the same. The weights are determined so that the network stores a set of patterns. As shown in the following figure, the architecture of Auto Associative memory network has «n’ number of input training vectors and similar «n’ number of output target vectors105.
Autoclave is a strong heated container used for chemical reactions and other processes using high pressures and temperatures, e.g., steam cleaning and sterilization106.
Automata theory is the study of abstract machines and automata, as well as the computational problems that can be solved using them. It is a theory in theoretical computer science and discrete mathematics (a subject of study in both mathematics and computer science). Automata theory (part of the theory of computation) is a theoretical branch of Computer Science and Mathematics, which mainly deals with the logic of computation with respect to simple machines, referred to as automata107,108.
Automated control system is a set of software and hardware designed to control technological and (or) production equipment (executive devices) and the processes they produce, as well as to control such equipment and processes.
Automated is a machine that has been preprogrammed for a task, such as automated work order creation. While automated processes do not require outside control to complete the tasks for which they are programmed, automated processes do not have the ability to respond independently109.
Automated processing of personal data – processing of personal data using computer technology.
Automated system is an organizational and technical system that guarantees the development of solutions based on the automation of information processes in various fields of activity.
Automation is a technology by which a process or procedure is performed with minimal human intervention.
Autonomic computing is the ability of a system to adaptively self-manage its own resources for high-level computing functions without user input.
Autonomous artificial intelligence is a biologically inspired system that tries to reproduce the structure of the brain, the principles of its operation with all the properties that follow from this.
Autonomous refers to a machine that 1) has the ability to self-govern or undertake actions without external control and 2) can respond independently to new information. One example is autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), which navigate without an operator, intelligently choosing the best path and avoiding obstacles110.
Autonomous vehicle is a mode of transport based on an autonomous driving system. The control of an autonomous vehicle is fully automated and carried out without a driver using optical sensors, radar and computer algorithms.
Autonomy is an intelligent system’s ability to independently create and select different courses of action to achieve goals based on the system’s understanding and knowledge of the world and other factors111.
Auxiliary intelligence – systems based on artificial intelligence that complement human decisions and are able to learn in the process of interacting with people and the environment.
Ayasdi is an enterprise scale machine intelligence platform that delivers the automation that is needed to gain competitive advantage from the company’s big and complex data. Ayasdi supports large numbers of business analysts, data scientists, end users, developers and operational systems across the organization, simultaneously creating, validating, using and deploying sophisticated analyses and mathematical models at scale.
«B»
B2B E-commerce refers to an online store for businesses. Normally, B2B (business-to-business) e-commerce is understood as an ordering system. The difference to a B2C online store targeting consumers is, for example, the requirement to identify the buyer through registering and the need to provide different billing options (such as invoicing)112.
B2C (business-to-consumer) E-commerce is a form of online commerce colloquially known as online shopping. B2C e-commerce refers to an online service that provides consumers with goods to purchase113.
B2D (business-to-developer) marketing is an operational model that aims to engage software developers directly and by doing so affect customer acquisition. B2D marketing is a method of the platform economy which typically provides APIs in as developer-friendly form as possible to enable their proactive deployment114.
B2D marketing is an operational model that aims to engage software developers directly and by doing so affect customer acquisition. B2D marketing is a method of the platform economy which typically provides APIs in as developer-friendly form as possible to enable their proactive deployment115.
Backhaul refers to the process of reporting event information from tagged assets related to things like movement, temperature, distress and so forth116.
Baldwin effect is the skills acquired by organisms during their life as a result of learning, after a certain number of generations, are recorded in the genome.
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower frequencies in a continuous band of frequencies. It is typically measured in hertz, and depending on context, may specifically refer to passband bandwidth or baseband bandwidth. Passband bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. Baseband bandwidth applies to a low-pass filter or baseband signal; the bandwidth is equal to its upper cutoff frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the frequency spectrum. Also, Bandwidth refers to the data throughput capacity of any communication channel. As bandwidth increases, more information per unit of time can pass through the channel117,118,119.
Bar coded medication administration (BCMA) is a hospital inventory control system that uses barcodes in the distribution of prescription medications with the goal of ensuring the patient is receiving the correct medication120.
Bayesian classifier in machine learning is a family of simple probabilistic classifiers based on the use of the Bayes theorem and the «naive» assumption of the independence of the features of the objects being classified121.
Belief-desire-intention software model (BDI) is a software model developed for programming intelligent agents. Superficially characterized by the implementation of an agent’s beliefs, desires and intentions, it actually uses these concepts to solve a particular problem in agent programming. In essence, it provides a mechanism for separating the activity of selecting a plan (from a plan library or an external planner application) from the execution of currently active plans. Consequently, BDI agents are able to balance the time spent on deliberating about plans (choosing what to do) and executing those plans (doing it). A third activity, creating the plans in the first place (planning), is not within the scope of the model, and is left to the system designer and programmer122.
Benchmarking is a set of techniques that allow you to study the experience of competitors and implement best practices in your company.
Beta release is a term that refers to a phase in online service development in which the service is coming together functionality-wise but genuine user experiences are required before the service can be finished in a user-centered way. In online service development, the aim of the beta phase is to recognize both programming issues and usability-enhancing procedures. The beta phase is particularly often used in connection with online services and it can be either freely available (open beta) or restricted to a specific target group (closed beta)123.
Bias is a systematic trend that causes differences between results and facts. Error exists in the numbers of the data analysis process, including the source of the data, the estimate chosen, and how the data is analyzed. Error can seriously affect the results, for example, when studying people’s shopping habits. If the sample size is not large enough, the results may not reflect the buying habits of all people. That is, there may be discrepancies between survey results and actual results.
Biased algorithm is systematic and repetitive errors in a computer system that lead to unfair results, such as one privilege persecuting groups of users over others. Also, sexist and racist algorithms.
Big Data analytics. As our world becomes digitized, vast quantities of data are generated and stored. This data holds hidden secrets that promise to revolutionize our understanding of the human condition. We need Big Data analytics to extract these insights124.
Big Data is a term for sets of digital data whose large size, rate of increase or complexity requires significant computing power for processing and special software tools for analysis and presentation in the form of human-perceptible results. Also, Big Data refers to the collection, storage, sharing, searching, analyzing and presenting of enormous, unorganized and continuously growing masses of data with the help of statistics and information technology. As the Internet of Things and the Industrial Internet continue to spread, there is believed to be a growing demand for Big Data -related expertise. Big Data is a large amount of information about an organization (both structured and unstructured) that cannot be analyzed using traditional computing methods. Big Data in health refers to large routinely or automatically collected datasets which are electronically captured and stored. The data is reusable in the sense that it is multipurpose data. It involves the fusion and connection of existing databases for the purpose of improving health and health system performance. It does not refer to data collected for a specific study. Also, Big Data is data sets that are too large to be handled manually. Big Data must be analyzed by a computer, revealing patterns, associations between groups, or overall trends. Big Data also comes into systems in increasingly greater complexity, variety, volume, and velocity – and exponential increase over time125,126,127,128.
Binance Coin (BNB) is a utility cryptocurrency that operates as a payment method for the fees associated with trading on the Binance Exchange. It is the third-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization.10 Those who use the token as a means of payment for the exchange can trade at a discount. Binance Coin’s blockchain is also the platform on which Binance’s decentralized exchange operates. The Binance Exchange was founded by Changpeng Zhao and is one of the most widely used exchanges in the world based on trading volumes129.
Binance USD (BUSD) was created by the cryptocurrency exchange Binance as a stablecoin pegged to the U.S. dollar. The stablecoin was approved by the New York State Department of Financial Services; thus, it is also regulated130.
Binary choice regression model is a regression model in which the dependent variable is dichotomous or binary. Dependent variable can take only two values and mean, for example, belonging to a particular group.
Binary format is any file format in which information is encoded in some format other than a standard character-encoding scheme. A file written in binary format contains information that is not displayable as characters. Software capable of understanding the particular binary format method of encoding information must be used to interpret the information in a binary-formatted file. Binary formats are often used to store more information in less space than possible in a character format file. They can also be searched and analyzed more quickly by appropriate software. A file written in binary format could store the number «7» as a binary number (instead of as a character) in as little as 3 bits (i.e., 111), but would more typically use 4 bits (i.e., 0111). Binary formats are not normally portable, however. Software program files are written in binary format. Examples of numeric data files distributed in binary format include the IBM-binary versions of the Center for Research in Security Prices files and the U.S. Department of Commerce’s National Trade Data Bank on CD-ROM. The International Monetary Fund distributes International Financial Statistics in a mixed-character format and binary (packed-decimal) format. SAS and SPSS store their system files in binary format131.
Binary number is a number written using binary notation which only uses zeros and ones. Example: Decimal number 7 in binary notation is: 111132.
Binary tree – a tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, which are referred to as the left child and the right child. A recursive definition using just set theory notions is that a (non-empty) binary tree is a tuple (L, S, R), where L and Rare binary trees or the empty set and S is a singleton set. Some authors allow the binary tree to be the empty set as well133.




