 полная версия
полная версияFirst virtual Bilateral Conference on Functional Materials (BiC-FM)
We offer a simple synthesis of porous nanostructured MoS2 materials by decomposition of ammonium tetrathiomolybdate (NH4)2MoS4 aerogel in thermal shock conditions in an inert atmosphere at different temperatures. The obtained MoS2 materials possess a three-level architecture: thin carbon skin/expanded MoS2 layers/internal intertwined MoS2 nanosheets. The presence of pores was confirmed by the nitrogen adsorption-desorption method and their size was 2-35 nm. Increasing the temperature leads to the creation of the extended MoS2 layers at the plate surfaces. The lateral size and the number of adjacent layers on the surface and inside were also grown. The resulting materials were tested in lithium-ion half-cells. The porous MoS2 synthesized at 700 °C showed superior rate capability 817 mAh g-1 at a current density of 2 A g-1 and 1139 mAh g-1 during cycling at 0.1 A g-1.
Acknowledgment.This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, grant 19-73-10068.
References:
[1] T.Stephenson, Z. Li and D. Mitlin, D. Energy Environmental Science, 7, 209 (2014).
Polarons In Two-dimensional Pnictogens: DFT Study
Vasilchenko V.1, Gonze X.1,2, Levchenko S.1, Perebeinos V.3, Zhugayevych A.1
1 – Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology, Moscow, Russia
2 – Université Catholique de Louvain, Louvain-la-Neuve, Belgium
3 – University at Buffalo, NY, United States
vasilii.vasilchenko@skoltech.ru
Present work is dedicated to the study of small polarons in emerging semiconductors: two-dimensional pnictogens. They are great candidates for application in electronics and the work done will allow for better understanding of the nature of charge carriers in these materials. Up to this point, no information on their polaronic character has been provided and generally they were considered as free electrons and holes. First-principles cluster calculations and finite-size scaling show stability of a small hole polaron in blue phosphorene and arsenene. It is localized on a phosphorus atom, leading to the contraction of the bonds around it. Commonly used hybrids including PBE0, HSE06, B3LYP show consistent results with the adiabatic polaron relaxation energy slightly below 0.1 eV for phosphorene and 0.15 eV for arsenene. The adiabatic barriers for motion of the polaron are small compared to the frequency of strongly coupled phonons implying barrierless motion of the polaron.
Multifunctional Brownmillerites for Efficient Energy Harvesting and Storage Applications
Durga Sankar Vavilapalli1, M. S. Ramachandra Rao2, Shubra Singh1
1-Crystal Growth Centre, Anna University, Chennai – 600025, Tamil Nadu, India.
2-Nano Functional Materials Technology Centre, Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai 600036, India
v.durgasankar@yahoo.com
In search of new and advanced materials for energy harvesting and storage applications, we come across certain brownmillerite (A2B2O5) multiferroic compounds, which are also called oxygen deficient perovskites (ABO3). Oxygen vacancies and magnetic ordering in these compounds lead to possess smaller bandgap (less than 2eV) compared to regular perovskites. These materials are promising candidates for Ferroelectric photovoltaic (PV) applications, as it enhances the optical and electrical properties. A well-known multiferroic material, BiFeO3, featuring relatively low solar cell efficiency (~ 7 %) due to the relatively large band gap (2.6 eV), has attracted much attention. In the present case we have developed several multifunctional brownmillerite compounds and these are promising materials for PV, photocatalytic and energy storage application. The optical and catalytic properties of these compounds make them potential photocatalysts for waste water treatment2. Co-existence of transition metal-oxide active sites and oxygen vacancies in these brownmillerites is useful for efficient energy storage application. These studies point towards the role of multifunctional brownmillerites in the field of energy and environmental applications. The results will be presented in detail.
References:
1. Durga Sankar Vavilapalli et al. "Nitrogen Incorporated Photoactive Brownmillerite Ca2Fe2O5 for Energy and Environmental Applications" Scientific Reports 10 (1), 2713 (2020).
1. Durga Sankar Vavilapalli et al. "Multifunctional brownmillerite KBiFe2O5: Structural, magneto-dielectric, optical, photoelectrochemical studies and enhanced photocatalytic activity over perovskite BiFeO3" Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells 200, 109940 (2019).
1. Durga Sankar Vavilapalli et al. "Photoactive Brownmillerite Multiferroic KBiFe2O5 and Its Potential Application in Sunlight-Driven Photocatalysis" ACS Omega 3 (12), 16643-16650 (2018).
The influence of chlorine and chloroauric acid treatment on electromechanical properties of SWCNT fibers
Vershinina A.I., Gordaya O.R., Lomakin M.V., Shandakov S.D.
Kemerovo State University, Kemerovo, Russia
annaver89@mail.ru
The effects of mechanical deformation on the electrical properties of carbon nanotubes are of interest in electromechanical devices. Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) doping with chloroauric acid (HAuCl4) and treatment in gaseous chlorine (Cl2) are effective methods for improving their electrical properties [1,2]. In this work, we study the electromechanical behavior of SWCNT fibers functionalized in chloroauric acid and chlorine.
The fibers have been fabricated from SWCNT films which were synthesized by floating catalyst (aerosol) CVD [3,4]. A part of the SWCNT films was treated in gaseous chlorine and then we prepared fibers using a recently developed wet pulling technique (WP) [5] with ethanol (C2H5OH), acetone (C3H6O), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) (C2H6OS), and tetrahydrofuran (THF) (C4H8O) as solvents. We also obtained fibers from the pristine SWCNT films by WP technique using ethanol as solvent. These fibers were treated with a 0.1 M aqueous solution of HAuCl4 diluted with ethanol to form 10 mM solution. The fibers' length were 10 mm. The electromechanical properties of the fibers were investigated using a tensile stage on the base of a microscrew and a stepper motor.
The study by a two-contact method employing the NI ELVIS II workstation showed the change of the SWCNT fibers' electrical resistance after the treatment in HAuCl4 and Cl2. The gauge factor (GF) of the fibers exhibited monotonic increase with deformation after the treatment by chloroauric acid, and the maximum GF value was found to be about 2. The GF of the samples treated in chlorine using ethanol, acetone, and THF as solvent had maximum value of about 3, while for the fibers prepared with DMSO, the value of GF reached ~4.
Acknowledgement.This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 18-29-19169) and by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation (project no. FZSR-2020-0007 in the framework of the state assignment no. 075-03-2020-097).
References:
[1] A.P. Tsapenko, A.E. Goldt, E. Shulga, et al. Carbon, 130, 448–457 (2018)
[2] A.I. Vershinina, M.V. Lomakin, D.M. Russakov, et al. Russian Physics Journal, 61, 1185–1186 (2018)
[3] A. Moisala, A.G. Nasibulin, D.P. Brown, et al. Chemical Engineering Science, 61, 4393–4402 (2006)
[4] A. Moisala, A.G. Nasibulin, S.D. Shandakov, H. Jiang, E.I. Kauppinen, Carbon, 43, 2066–2074 (2005)
[5] M.A. Zhilyaeva, E.V. Shulga, S.D. Shandakov, et al. Carbon, 150, 69–75 (2019)
Preparation of functional carbon coatings on the surface of hollandite-like ceramics with composition of K1.53(Сu0.76Ti7.24)O16
Vikulova M.A.1, Tsiganov A.R.1, Artyukhov D.I.1, Gorshkov N.V.1,2
1 – Yuri Gagarin State Technical University of Saratov, Saratov, Russia
2 – N.N. Semenov Federal Research Center for Chemical Physics RAS, Moscow, Russia
vikulovama@yandex.ru
Carbon-ceramic composite materials based on potassium titanate with hollandite structure are of great research interest due to the possibility of their application in potassium ion energy storage devices and as fillers in polymer matrices for elements of modern electronics producing. The advantages of using carbon are that it can be easily adapted to suit your needs. Carbon materials provide high surface area as well as good electronic and ionic conductivity. The use of carbon coatings makes it possible to compensate for the low electrical conductivity of potassium titanate with hollandite structure, which will increase the specific energy of electrode materials based on them.
However, obtaining carbon coatings on the surface of titanate ceramics is a difficult task. This may be partly due to the incompatibility of C with the TiO2 lattice, along with the high temperature and pressure requirements for such materials production. Commonly used methods for preparing TiO2-C composites include flame pyrolysis, high-temperature sintering, hydrothermal or sol-gel technology. In addition, it is usually required an external carbon source with little or no control over the degree or arrangement of the С atoms. Hence, another popular approach is to modify the TiO2 surface with C nanostructures such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, reduced graphene oxide, and carbon nitride.
In this regard, the aim of this work is to study the possibility of obtaining hollandite-like ceramics K1.53(Cu0.76Ti7.24)O16 with a carbon-modified surface by various methods.
Acknowledgement.This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation, grant 19-73-10133.
Phosphorus-filled single-walled carbon nanotubes: synthesis, characterization and electrochemical properties
Vorfolomeeva A.A.1, Stolyarova S.G.1, Bulusheva L.G.1, Okotrub A.V.1
1 – Nikolaev Institute of Inorganic Chemistry, SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia
vorfolomeeva@niic.nsc.ru
Single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) can fill with various inorganic compounds changing the electronic structure and chemical activity of the material [1]. Phosphorus can penetrate the cavity of a nanotube, forming various chain structures and nanoclusters, or be embedded in the graphene lattice with the formation of a phosphorus-carbon bond. SWCNTs have good conductivity and provide mechanical and chemical stability during electrochemical cycling. However, their theoretical capacity in the lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) does not exceed 600 mAh g-1, which is not enough for use in new high-capacity devices. Phosphorus has a high theoretical specific capacity 2595 mAh g-1 [2]. Combination of SWCNTs as a conductive base and phosphorus in the internal cavity can allow the creating an effective electrode material for LIB LIBs.
One of the most effective and simple methods of synthesis of filled SWNTs is the ampoule method of synthesis. The filling was carried out in an H-shaped ampoule, in one part of which phosphorus was placed, and in another – SWCNTs. By varying such parameters as the ratio of reagents, synthesis time, and synthesis temperature, we achieve 8 at.% of phosphorus content according to XPS. To increase the degree of filling of nanotubes, the synthesis conditions were modified and ultrasonic treatment was introduced. Ultrasonic treatment was carried out at different stages of obtaining materials, due to which it was possible to increase the phosphorus content to 15 at.% according to XPS.
The resulting series of samples were studied as an anode material in LIBs. The best characteristics were demonstrated by a sample with a phosphorus content of 15 at.% and showed a specific capacity of 760 mAh g-1 at a current density of 0.1 A g-1, which is three times higher than the capacity of the initial SWCNTs (245 mAh g-1 at a current density of 0.1 A g-1). This effect is associated with the reversible reaction of the interaction of lithium with phosphorus with the formation of intermediates of various compositions LixP and with the reaction of lithium intercalation between bundles of nanotubes.
References:
[1] J.C.Zheng, M.C.Payne, Y.P.Feng, and A.T.L.Lim, Physical Review B, 67, 15 (2003)
[2] W.Liu, H.Zhi and X.Yu, Energy Storage Materials, 16 (2019)
Deagglomeration of carbon nanotubes via rapid expansion of supercritical suspensions
Zuev Ya. I.1, Vorobei A. M.1, Novikov I. V. 2, Fedorov F. S. 2, Goldt A. E. 2, Krasnikov D. V. 2, Parenago O.O. 1, Nasibulin A.G. 2
1 – Kurnakov Institute of General and Inorganic Chemistry of Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow, Russia
2 – Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology, Moscow, Russia
vorobei@supercritical.ru
The main difficulty in the preparation of carbon nanotubes (CNTs) composites is the agglomeration of CNTs due to huge intermolecular attraction forces between them. The commonly used method for CNT de-aggregation is ultrasonication which sometimes can be harmful to CNT structure. In this work, we use a RESS (the Rapid Expansion of Supercritical Suspensions) method as an additional tool for CNTs de-bundling. In the RESS process, CNTs are suspended in a supercritical fluid (SCF) in a high-pressure vessel. After storing the suspension for the required amount of time at high pressure, it is rapidly sprayed into the precipitation chamber at atmospheric pressure. Following the spraying, the fluid rapidly expands behind the nozzle and undergoes a transition from supercritical to a gas phase. The microstructure of the dispersed material changes, mainly due to the rapid and non-uniform pressure drop.
It was shown that RESS treatment leads to a significant increase in CNT bulk volume (up to 11 times). Usage of supercritical nitrogen instead of carbon dioxide is more promising since due to a very low nitrogen critical temperature value there is no risk of the formation of a two-phase liquid-vapour system during fluid rapid expansion, which could bring up capillary effects detrimental to highly disperse materials. It is demonstrated that the dispersion of CNTs strongly depends on nanotubes type. For CNTs obtained from different manufacturers, the value of the increase in specific volume may differ in 10 times.
Moreover, RESS-processed CNTs were used preparation of polyurethane composites. The conductivity of such composites was several orders of magnitude higher than those synthesized without additional treatment. The use of RESS technology also gives a possibility to obtain composites with a percolation threshold of ca. 0.01 %-wt. which is 50 times lower when compared with unprocessed CNTs composites.
Acknowledgement.This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, grant 18-29-06071
Electrocatalytic Activities of Nitrogen Doped Carbon Nanostructures
Ram Manohar Yadav#*
#Department of Materials Science and Nano Engineering, Rice University, Houston -77005, USA *Department of Physics, VSSD College Kanpur, INDIA-208002
rmanohar28@gmail.com
The conversion of CO2 into fuels or commodity chemicals, incorporated with intermittent renewable energy sources like solar and wind, is an attractive venture that could offer an alternative solution to both the contemporary energy crisis and environmental issues. Elaborating highly active electrocatalysts for carbon dioxide reduction, oxygen reduction and oxygen evolution reactions are among the most promising areas of materials research. In this regards, chemically modified carbon nanostructures have emerged as a new metal-free electrocatalysts for these reactions due to their low cost, high activity and excellent durability. We have studied nitrogen doped carbon nanostructures (NCNTs, N Graphene etc) as electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction, carbon dioxide reduction and oxygen evolution reactions. The details about the work will be presented in the conference.
Biogenic synthesis of titanium dioxide: its composite with iron oxide and their potential biomedical application
Muhammad Azri Muhamad Yusop 1,2, Che Azurahanim Che Abdullah 1, Roshasnolyza Hazan 2
1-Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, University Putra Malaysia, 43400 UPM Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia
2-Malaysian Nuclear Agency, Bangi, 43000 Kajang, Selangor, Malaysia
muhammadazri0909@gmail.com
In recent years, biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles has received substantial attention owing to the ability in develop clean and safe chemicals, low-cost methods, eco – friendly and renewable materials. In the current study, the biogenic synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles (TiO2NPs) is attained by a chemical and biosynthesized method by using the aqueous plant extract of Malaysian based agricultural. Iron oxide been produced via co-precipitation and alkaline fusion. The product (iron oxide) been doped with biogenic synthesized of titanium dioxide. TiO2 NPs pure and doped with iron oxide (composite) are characterized by FTIR, UV, and XRD. The antimicrobial activities of biosynthesized nanoparticles are examined using disc diffusion method. The TiONPs expected to show significant antimicrobial activity against all the tested microorganisms.
References:
[1] Muniandy, S. S., Kaus, N. H. M., Jiang, Z. T., Altarawneh, M., & Lee, H. L. (2017). Green synthesis of mesoporous anatase TiO 2 nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activities. RSC advances, 7(76), 48083-48094.
Topochemical transformations in MWCNTs-Si composites at high temperatures
Kuznetsov V.L.1,2, Moseenkov S.I.1, Zavorin A.V.1,2, Tsendsuren Tsog-Ochir2, Schmakov A.N.1,2, Volodin V.A.2,3.
1 – Boreskov Institute of Catalysis, Novosibirsk, Russia
2 – Novosibirsk State University, Novosibirsk, Russia
3 – Rzhanov Institute of Semiconductor Physics, Novosibirsk, Russia
zavorin@catalysis.ru
Multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) have unique physicochemical properties, allowing their use in a wide range of applications (composites, functional materials, electronics and others). One of the practical applications of carbon nanotubes is their use as part of an anode material in electrochemical power sources, where the addition of MWCNTs makes it possible to improve operational properties: maximum allowable charge-discharge currents, capacity and service life of lithium-ion power sources [1]. Another possible practical application of MWCNTs is their use as a reinforcing component of ceramic materials [2]. The introduction of MWCNTs in the composition of ceramics makes it possible to increase crack resistance, strength, improve tribological properties and achieve the appearance of electrical conductivity of such modified materials [3–4].
In this paper we study the high temperature initiated (700-1400 °C) topological transformation of MWCNTs-Si [5] composites produced by gas-phase deposition of silicon on the surface of nanotubes (at 500 °C). Si nanoparticles crystallization on MWCNTs surface and further topochemical reaction leading to SiC were studied using in-situ and ex-situ XRD and TEM, SEM, Raman spectroscopy. The data obtained were compared with results available after the study of macro Si-C systems. Industrial production of SiC regularly occurs at temperatures above 1500 °C. In the case of using the processes of decomposition of silicon organic compounds, the formation of SiC proceeds above 1100–1200 °C. In the case of MWCNTs-Si systems the formation of SiC began at temperatures of 700–800 °C. It was found that the topology of SiC particles is influenced by the sizes of the initial silicon particles. The kinetic parameters of the formation of silicon carbide in the MWCNTs-Si systems were also estimated.
Acknowledgement.Serkova A.N. for the study of MWCNTs-Si composites by the SEM method and Ishchenko A.V. and Chuvilin A.L. for the study of MWCNTs-Si composites by TEM.
References:
[1] N.Coppey et al., Chem. Eng. Res. Des., 12, P. 2491–2496, (2013).
[2] N.Song, H.Liu, J.Fang, Ceram. Int., 42, P. 351–356, (2016).
[3] А.Peigney, C.H.Laurent, Cambridge England, P. 309–333, (2006).
[4] S.Samal, S.Bal, Journal of Minerals & Materials Characterization & Engineering, 4, P. 355–370, (2008).
[5] A.Zavorin et al., J. Struct. Chem., 4, P. 617–627, (2020).
Enhanced imaging of single Si nanoparticles using non-reflective SWCNT membranes
Zhigunov D.M.1, Shilkin D.A.2, Kokareva N.G.2, Bessonov V.O.2,3, Dyakov S.A.1, Chermoshentsev D.A.1,4, Mkrtchyan A.A.1, Gladush Yu.G.1, Fedyanin A.A.2, Nasibulin A.G.1,5
1 – Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology, Moscow, Russia
2 – Faculty of Physics, M. V. Lomonosov Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia
3 – Frumkin Institute of Physical Chemistry and Electrochemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences, Russia
4 – Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Russia
5 – Department of Chemistry and Materials Science,Aalto University, Finland
d.zhigunov@skoltech.ru
We demonstrate that single-walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) membranes can be successfully utilized as nanometer-thick substrates for enhanced visualization and facilitated study of individual nanoparticles. As the model objects, optically resonant 200 nm silicon nanoparticles are transferred onto pristine and ethanol-densified SWCNT membranes by the femtosecond laser printing method. The nanoparticles are imaged by scanning electron and bright-field optical microscopy, and characterized by linear and Raman scattering spectroscopy. Using a pristine SWCNT membrane, an order-of-magnitude enhancement of the optical contrast of the nanoparticle bright-field image is achieved, as compared to the case of a glass substrate (Fig. 1). The observed optical contrast enhancement is in agreement with the spectrophotometric measurements showing an extremely low total reflectance of the pristine membrane (<1 %). Owing to the high transparency, negligibly small reflectance and thickness, SWCNT membranes offer a variety of perspective applications in nanophotonics, bioimaging and synchrotron radiation studies.
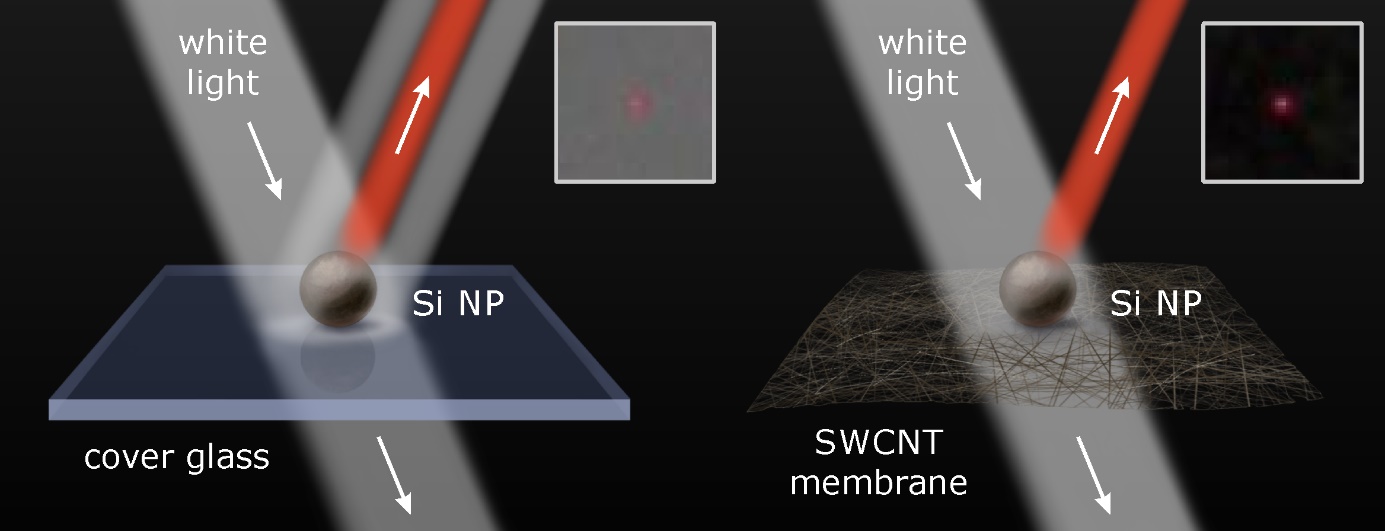
Fig. 1. Proof-of-concept demonstration of bright-field optical microscope image contrast enhancement using 200 nm Si nanoparticles (Si NP) transferred on a cover glass (left) and SWCNT membrane (right).
SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION AND TOXICITY STUDIES OF GOLD NANOPARTICLES FOR BIOMEDICAL APPLICATIONS
Siti Nadiah Zulkifli1, Manali Haniti Zahid2, Iskandar Zulkarnain Alias2, Che Azurahanim Che Abdullah1
1Institute of Advanced Technology (ITMA), Universiti Putra Malaysia, 43400 Serdang, Selangor
2 Department of Chemical Pathology, School of Medical Sciences, Health Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 16150 Kubang Kerian, Kelantan
sitinadiahzulkifli@gmail.com
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) is chosen for this project due to the fact that it is widely used in a variety of applications as well as straightforward synthesis methods that allow the fast and cheap production of AuNPs. Comparative analysis on characterization between two methods have been studied. One step synthesis method can reduce metal ions to nanoparticles. Both approaches chemical and green synthesis were successfully synthesized by using modified Turkevich method. The prepared samples were analyzed using ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometry (UV–Vis), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS). X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy have been used to study their structural phase composition and their functional group. The toxicity of AuNPs was then tested on brine shrimp. The nanoparticles produced will offer a potential materials for biomedical application.









