 полная версия
полная версияBlackwood's Edinburgh Magazine. Volume 55, No. 343, May 1844
My alarm dispelled all my reminiscences of Lord Cochrane, and my visions of the Olympic games. I sprang into the droschky of a Greek sailor, who drove over the rocks as if he only expected his new profession to endure for a single day. We were soon on the Piræus road, which I well knew runs along the foundations of one of the long walls; but I was too glad to escape, like Lord Palmerston and M. Thiers, unscathed from the imbroglio I had created, to honour even Themistocles with a single thought. My charioteer was a far better specimen of the present, than foundations of long walls, ruined temples, and statues without noses, can possibly be of the past. He informed me he was a sailor: by so doing, he did not prove to me that he estimated my discernment very highly, for that fact required no announcement. He added, however, what was more instructive; to wit, that he had received the droschky with the horses, that morning, from a Russian captain, in payment of a bad debt. He had resolved to improviso the coachman, though he had never driven a horse before in his life—εὔκολον εἶναι—“it is an easy matter;” and he drove like Jehu, shouted like Stentor, and laughed like the Afrite of Caliph Vathek. He ran over nobody, in spite of his vehemence. Perhaps his horses were wiser than himself: indeed I have remarked, that the populace of Greece is universally more sagacious than its rulers. In taking leave of this worthy tar at the Hotel de Londres, I asked him gravely if he thought that, in case Russia, England, or France should one day take Greece in payment of a bad debt, they would act wisely to drive her as hard as he drove his horses? He opened his eyes at me as if he was about to unskin his head, and began to reflect in silence; so, perceiving that he entertained a very high opinion of my wisdom, I availed myself of the opportunity to advise him to moderate his pace a little in future, if he wished his horses to survive the week.
During my stay at Athens, King Otho was absent from his capital; so that, though I lost the pleasure of beholding the beautiful and graceful queen, I escaped the misfortune of being dishonoured by receiving the cross of an officer of the order of the Redeemer. His Hellenic majesty takes a peculiar satisfaction in hanging this decoration at the buttonholes of those who served Greece during the revolutionary war; while he suspends the cross of Commander round the necks, or ornaments with the star of the order the breasts, of all the Bavarians who have assisted him in relieving Greece of the Palmerstonian plethora of cash gleaned from the three powers. For my own part, I am not sure but that I should have made up my mind to return the cross, with a letter full of polite expressions of contempt for the supposed honour, and a few hints of pity for the donor; as a very able and distinguished friend of Greece, whose services authorized him so to act, did a few days before my arrival.
On attempting to find my way through Bavarian Athens, I was as much at a loss as Lady Francis Egerton, and could not help exclaiming, “Voila des rues qui ont bien peu de logique!” After returning two or three times to the church Kamkarea, against whose walls half the leading streets of the new city appear to run bolt up, I was compelled to seek the assistance of a guide. At length I found out the dwelling once inhabited by my friend Michael Kalliphournas. A neat white villa, with green Venetian blinds, smiling in a court full of ruins and rubbish, had replaced the picturesque but rickety old Turkish kouak of my former recollections. I enquired for the owner in vain; the property, it was said, belonged to his sister; of the brother nobody had heard, and I was referred for information to the patriotic and enterprising Demarch, or mayor, who bears the same name.
In the end my enquiries were successful, and their result seemed miraculous. To my utter astonishment I learned that Michael had become a monk, and dwelt in the monastery of Pentelicus; but I could obtain no explanation of the mystery. His relations referred me to the monk himself—strangers had never heard of his existence. How often does a revolution like that of Greece, when the very organization of society is shaken, compress the progress of a century within a few years! There remained nothing for me but to visit the monastery, and seek a solution of the singular enigma from my friend’s own mouth; so, joining a party of travellers who were about to visit the marble quarries of Pentelicus, and continue their excursion to the plain of Marathon, I set out on such a morning as can only be witnessed under the pure sky of Attica.
The scenery of our ride is now familiar to tourists. Parnes or Parnethus with its double top,27 Brilessus or Pentelicus with its numerous rills and fountains, and Hymettus with its balmy odours, have been “hymned by loftier harps than mine.” My companions proved gay and agreeable young men. They knew every body at Athens, and every thing, and willingly communicated their stores of knowledge. I cannot resist recounting some of the anecdotes I heard, as they do no discredit to the noble princes to whom they relate.
When an English prince visited Athens, King Otho, who it seems is his own minister, and conducts business quite in a royal way, learned that he was no Whig, and instantly conceived the sublime idea of making use of his royal highness’s services to obtain Lord Palmerston’s dismissal from office. The monarch himself arranged the plan of his campaign. The prince was invited to a fête champêtre at Phyle, and when the party was distributed in the various carriages, he found himself planted in a large barouche opposite the king and queen. King Otho then opened his intrigue; he told the prince of the notes in favour of constitutional government and economical administration which Lord Palmerston had written, and Sir Edmund Lyons had presented; and he exclaimed, “I assure you, my dear prince, all this is done merely to vex me, because I would not keep that speculating charlatan Armansperg! Lord Palmerston cares no more about a constitution, nor about economy, than Queen Victoria, or you and I. When the Duc de Broglie, who has really more conscience than our friend the Viscount, proposed that Greece should be pestered with a constitution and such stuff, Palmerston answered very judiciously, ‘Greece—bah!—Greece is not fit for a constitution, nor indeed for any other government but that of my nabob!’ Now, my dear prince, Queen Victoria can never mean to offend me, the sovereign of Greece, when the Ottoman empire is so evidently on the eve of dismemberment; and,” quoth Otho the gleaner, “I am deeply offended, at which her British majesty must feel grievously distressed.” The prince doubtless thought her majesty’s distress was not inconsolable; but he only assured his Hellenic majesty that he could be of no possible use to him in his delicate intrigue at the court of St James’s. He tried to get a view of the scenery, and to turn the conversation on the state of the country; but Otho was not so easily repulsed. He insisted that the prince should communicate his sentiments to Queen Victoria; and, in spite of all the assurances he received of the impossibility of meddling with diplomatic business in such a way, his Hellenic majesty, to this very day, feels satisfied that Lord Palmerston was sent to the right-about for offending him; and he is firmly persuaded that, unless Lord Aberdeen furnish him with as many millions as he demands to secure his opposition to Russia, the noble earl will not have a long tenor of office.
A young Austrian of our party shouted, “Ah, it requires to be truly bon garçon, like the English prince, to submit to be so bored, even by a king! But,” added he, “our gallant Fritz managed matters much better. The Archduke Frederick, who behaved so bravely at Acre, and so amiably lately in London, heard, it seems, of the treatment the prince had met with, and resolved to cure his majesty of using his guests in such style. Being invited to a party at Pentelicus, he was aware that he would be placed alone on the seat, with his back to the horses, and deprived of every chance of seeing the country, if it were only that the diplomatic intrigue at the court of Queen Victoria might remain concealed from the lynx-eyed suspicion of the corps diplomatique of Athens; for King Otho fancies his intrigues always remain the profoundest secrets. When the archduke handed the lovely queen into the carriage, politeness compelled King Otho to make a cold offer to the young sailor to follow; the archduke bowed profoundly, sprang into the carriage, and seated himself beside her majesty. The successor of Agamemnon followed, looking more grim than Hercules Furens: he stood for a moment bolt upright in the carriage, hoping his guest would rise and vacate his seat; but the young man was already actively engaged in conversation. The Emperor of the East—in expectancy—was compelled to sit down with his back to the horses, and study the landscape in that engaging manner of viewing scenery. Never was a fête given by a sulkier host than King Otho that day proved to be. In returning, the archduke had a carriage to himself. When questioned on the subject of his ride, he only remarked that he always suffered dreadfully from sickness when he rode with his back to the horses. He was sure, therefore, that King Otho had placed him beside the queen to avoid that horrible inconvenience.”
Other anecdotes were recounted during our ride, and our opinion of his Hellenic majesty’s tact and taste did not become more favourable, when it was discovered that his proceedings had utterly ruined the immense quarries of Pentelicus—
“Still in its beam Pentele’s marbles glow,”can now only be said of the ruins, not of the quarries. In order to obtain the few thousand blocks required for the royal palace at Athens, millions of square feet of the purest statuary marble have been shivered to atoms by the random process of springing mines with gunpowder. If King Otho had done nothing worse in Greece than converting the marble quarries of Pentelicus into a chaos of rubbish, when he found them capable of supplying all Europe for ages with the most beautiful material for the sculptor, he would have merited the reputation he so justly bears, of caring as little about the real welfare of Greece as Lord Palmerston himself. My companions quitted me at the quarries, making pasquinades on the royal palace and its royal master; while I put up my horse and walked slowly on to the ancient monastery of Pentele, not Mendele, as Lord Byron has it.
I was soon sitting alone in the cell of Michael, and shall now recount his history as I had it from his own mouth. Michael Kalliphournas was left an orphan the year the Greek revolution broke out. He was hardly fourteen years old, and yet he had to act as the guardian and protector of a sister four years younger than himself. The storm of war soon compelled him to fly to Ægina with the little Euphrosyne. The trinkets and gold which his relations had taught him to conceal, enabled him to place his sister in a Catholic monastery at Naxos, where she received the education of a European lady. Michael himself served under Colonel Gordon and General Fabvier with great distinction. In 1831, when the Turks were about to cede Attica to Greece, Michael and Euphrosyne returned to Athens, to take possession of their family property, which promised to become of very great value. At that time I had very often seen Phróssa, as she was generally called; indeed, from my intimacy with her brother, I was a constant visitor in the house. Her appearance is deeply impressed on my memory. I have rarely beheld greater beauty, never a more elegant figure, nor a more graceful and dignified manner. She was regarded as a fortune, and began to be sought in marriage by all the young aristocracy of Greece. It was at last conjectured that a young Athenian, named Nerio, the last descendant of the Frank dukes of Athens, had made some impression on her heart. He was a gay and spirited young man, who had behaved very bravely when shut up with the troops in the Acropolis during the last siege of Athens, and he was an intimate friend of her brother. I had left Athens about this time, and my travels in the East had prevented my hearing any thing of my friends in Greece for years.
There is a good deal of society among the Greek families at Athens for a few weeks before the Carnival. They meet together in the evenings, and amuse themselves in a very agreeable way. At one of these parties the discourse fell on the existence of ghosts and spirits; Michael, who was present, declared that he had no faith in their existence. With what groans did he assure me his opinion was changed, and conjured me never to express a doubt on the subject. All the party present exclaimed against what they called his free-masonry; and even his sister, who was not given to superstition, begged him to be silent lest he should offend the neraiïdhes, who might punish him when he least expected it. He laughed and ridiculed Phróssa, offering to do any thing to dare those redoubted spirits which the company could suggest. Nerio, a far greater sceptic than Michael, suddenly affected great respect for the invisible world, and by exciting Michael, gradually engaged him, amidst the laughing of his companions, to undertake to fry a dozen of eggs on the tomb of a Turkish santon, a short distance beyond the Patissia gate—to leave a pot of charcoal, to be seen next morning, as a proof of his valour, and return to the party with the dish of eggs.
The expedition was arranged, in spite of the opposition of the ladies; four or five of the young men promised to follow at a little distance, unknown to Michael, to be ready lest any thing should happen. Michael himself, with a zembil containing a pot of charcoal, a few eggs and a flask of oil in one hand, and a frying-pan and small lantern in the other, closely enveloped in his dusky capote, proceeded smiling to his task. The tomb of the Turk consisted of a marble cover taken from some ancient sarcophagus, and sustained at the corners by four small pillars of masonry—the top was not higher than an ordinary table, and below the marble slab there was an empty space between the columns. It has long since disappeared; but that is not wonderful, since King Otho and his subjects have contrived to destroy almost every picturesque monument of the past in the new kingdom. The thousands of Turkish tombs which not many years ago gave a historic character to the desert environs of Negrepont, and the splendid sérail of Zeitouni, with its magnificent marble fountains and baths, have almost disappeared—the storks have bid adieu to Greece—nightly bonfires, caused by absurd laws, destroy the few trees that remain; and in short, unless travellers make haste and visit Greece quickly, they will see nothing but the ruins which King Otho cannot destroy nor Pittaki deface, and the curiosities which Ross cannot give to Prince Pückler, added to the pleasure they will derive from beholding King Otho’s own face and the façade of his new palace.
The night was extremely dark and cold, so that the friends of Michael, familiar as they were with their native city, found some difficulty in following him without a lantern through the mass of ruins Athens then presented. As they approached the tomb, they perceived that he had already lighted his charcoal, and was engaged in blowing it vigorously, as much to warm his hands as to prepare for his cooking operations. Creeping as near to him as possible without risking a discovery, they heard, to their amazement, a deep voice apparently proceeding from the tomb, which exclaimed, “Bou gedje kek sohuk der adamlera.—It must be a cold night for mankind.” “To pisevo effendi,” said Michael in a careless tone, but nervously proceeded to pour a whole bottle of oil into the frying-pan. As soon as the oil was boiling and bubbling, the voice from the tomb again exclaimed, “Gaiour ne apayorsun, mangama pisheriorsun—yuckle buradam—aiyer yiklemassun ben seni kibab ederem, tahamun yerine seni yerim,” signifying pretty nearly, “Infidel, what are you doing here? You appear to be cooking; fly hence, or I will eat my supper of thy carrion.” And at the instant a head covered by an enormous white turban protruded itself from under the tombstone with open mouth. Michael, either alarmed at the words and the apparition, or angry at the suspicion of a premeditated trick on the part of his companions, seized the panful of boiling oil, and poured the whole contents into the gaping mouth of the spectre, exclaiming, “An echeis toson orexin, na to ladhi, Scheitan oglou!—If you are so hungry, take the oil, son of Satan!” A shriek which might have awakened the dead proceeded from the figure, followed by a succession of hideous groans. The friends of Michael rushed forward, but the lamp had fallen to the ground and was extinguished in the confusion. Some time elapsed ere it was found and lighted. The unfortunate figure was dragged from the tomb, suffocated by the oil, and evidently in a dying state, if indeed life was not already extinct. Slowly the horrible truth became apparent. Nerio had separated himself from the rest of the party unperceived, disguised himself, and gained the tomb before the arrival of Michael, who thus became the murderer of his sister’s lover. I shall not attempt to describe the feelings of Michael in recounting this dreadful scene.
The affair never made much noise. The Turks did not consider themselves authorized to meddle in the affairs of the Greeks. Indeed, the infamous murder of the Greek bakalbashi, a short time before by Jussuf-bey, with his own hand, had so compromised their authority, that they were in fear of a revolution. The truth was slowly communicated to Euphrosyne by Michael himself—she bore it better than he had anticipated. She consoled her brother and herself by devoting her life to religious and charitable exercises; but she never entered a monastery nor publicly took the veil. She still lives at Athens, where her charity is experienced by many, though few ever see her. When I left Greece on a visit to Mount Athos, my friend Michael insisted on accompanying me; and, after our arrival on the holy mountain, he exacted from me a promise that I would never discover to any one the monastery into which he had retired, nor even should we by chance meet again, address him as an acquaintance, unless he should speak to me. His sister alone is entrusted with his secret.
AFRICA—SLAVE TRADE—TROPICAL COLONIES
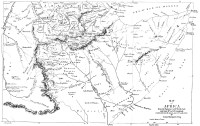
The readers of this magazine will readily remember the part which it took, at an early period, in discussing and in delineating the geographical features of Africa. In the number for June 1826 there is an article, accompanied by a map, showing from undoubted authorities the course and termination of the great river Niger in the sea in the Bight of Benin, where, from similar authorities, it was placed by me in 1820 and 1821, and where actual observation by Englishmen has lately clearly established the fact that it does terminate. In the upper and middle parts of its course the longitudes were erroneous, having adopted Major Rennell’s delineation of Western Africa as a guide; but in 1839 the whole of that quarter of Africa was narrowly examined, and the courses of the western rivers reduced to their proper positions, as delineated in my large map of Africa constructed in that year, to which, with the “Geographical Survey of Africa,” for which it was made, the reader is referred for further and particular information on all these subjects.
With these observations, I proceed to bring before the reader geographical information concerning eastern and central Africa of the highest and most gratifying importance, and obtained by the researches of different voyagers and travellers within the last four years. Foremost amongst these ranks, the expedition sent by the present Viceroy of Egypt to explore the Bahr-el-Abiad, or White River, above its junction with the Blue River, from Khartoum upwards and southwards; after it, the interesting travels of Messrs Krapf and Isenberg, two missionaries from the Church Missionary Society, from Tajura to Ankobar, from Ankobar south-west to the neighbourhood of the sources of the Hawash; and after that, Mr Krapf’s journey from Ankobar north by Lake Haik, through Lasta to Antalow, and thence to Massouah on the Red Sea. Next, the interesting accounts collected by M. Lefebvre and M. D’Abbadie, concerning the countries in some parts of the more eastern horn of Africa; and last, and the most specific and important of the whole, the accounts received of the country of Adel, and the countries and rivers in and south of Shoa, and those from the Blue Nile in Gojam and Damot to the sea at the mouth of the Jub, under the equator, by Major Harris, late British ambassador to the King of Shoa.
As the present article is accompanied by a map, constructed after great labour, and engraved most carefully by Mr Arrowsmith, the general outline of the whole may here be deemed sufficient, without lengthened discussion and observation.
The Egyptian expedition alluded to started from Khartoum (now become a fine town) at the close of the wet season in 1839. It consisted of four or five small sailing vessels, some passage boats, and four hundred men from the garrison of Senaar, the whole commanded by an able officer, Captain Selim. They completed their undertaking, and returned to Khartoum at the end of 135 days, during which time, in obedience to the commands of their master, they explored the Bahr-el-Abiad to the distance southwards of 1300 miles, (turnings and windings included,) to three degrees thirty minutes north latitude, and thirty-one east longitude, from Greenwich, where it divided into two streams; the smaller, and it is very small, coming from the south-west, and the larger, still even at the close of the dry season a very considerable river, which came from the south-east, upwards from the east, and still more upwards from the north-east. A subsequent voyage in 1841 gained the information that the stream descended past Barry, and there can be no doubt that another, if not the chief branch, comes from the south-east, in the bearing which Ptolemy gave it, and, as he states, from amongst mountains covered with perpetual snow, of which Bruce also heard, and which we now learn from Major Harris really stand in that quarter of Africa.
The longitude of the river at the bifurcation is exactly the same as Ptolemy has given it, which is very remarkable. The sources of the White River will therefore be found where Ptolemy and Bruce have placed them. The latter, in his notes, states expressly that the Bahr-el-Abiad rose to the south of Enarea, not far from the equator, and that it had no great western branch, nor was any necessary to give the river its magnitude. (Vol. vii. App. p. 92.)
The expedition in question found no very large affluents from the west side; but they found two of very considerable magnitude on the east side—one the Blue River, and the other the Red River, or Bahr-Seboth, which latter they navigated upwards of 150 miles in a direct line, and left it a considerable stream, nearly as large as the eastern branch of the White River, where they had left it. The banks of the Bahr-Seboth were precipitous and high, whereas those of the Bahr-el-Abiad were low, and on both sides covered with lakes, the remains probably of the preceding inundation. Scarcely a hill or mountain was in sight from the river till approaching the bifurcation, when the country became mountainous, the climate more cool, and the vegetation and trees around those of the temperate zone. The country on both sides is a high table-land, the scenery every where very beautiful, well peopled by different tribes, copper-coloured, and some of them even fair. Every where the banks are covered and ornamented with beautiful trees, and cattle, sheep, goats, elephants, &c., are numerous and abundant. Amongst the Bhours, they found Indian goods brought from the shores of the Indian ocean. Day by day, the breadth, depth, and current of the river were observed and marked. For a considerable distance above Khartoum, the breadth was from one and a half to one and a quarter mile, the depth three or four fathoms, and the current about one and a half mile per hour. Above the parallel of nine degrees, the river takes a remarkable bend due west for about 90 miles, when it passes through a large lake, the waters of which emitted an offensive smell, which might proceed from marshy shores.28 Above the lake, the breadth decreases to one-third or one-fourth of a mile, the depth to twelve or thirteen feet, with a current of one and a half mile per hour, the bottom every where sand, with numerous islands interspersed in the stream. The mountainous country around the upper part abounds with iron mines.









