 полная версия
полная версияThe Arena. Volume 4, No. 24, November, 1891
In the first place, the question of free trade or protection is in no sense a moral one. Free traders are prone to forget that their great prophet, Adam Smith, drew this distinction very plainly at the outset. He wrote two important works. One of them all the world has read. It is called “The Wealth of Nations,” deals with the selfish interests of mankind, and embodies the author’s political economy. The other is an equally elaborate work entitled “The Moral Sentiments.” It is the complement of “The Wealth of Nations,” which is devoted to the selfish side of human nature and the world at large has found no trouble in forgetting it. Adam Smith himself was under no confusion of mind as to his subject when he wrote about political economy. He knew that he was dealing with questions of a selfish character, of an enlightened selfishness, no doubt, but none the less questions of self-interest. He never for a moment thought of putting his political economy on a plane of pure morality.
When the great political movement toward free trade began in England, it was largely a movement of the middle classes and of the industrial interests of Great Britain. The great middle class of England, which furnishes the backbone and sinew of the nation, is essentially a moral class, and in appealing to it the political leader is always tempted to put forward the moral aspect of his theme, even if he has to twist his argument and his facts to find one. The manufacturers of England believed that free trade would be profitable, but it soothed them to be assured that the system was also highly moral. It is to the Manchester School, therefore, that we owe the attempt to give to the entire free trade system a moral coloring for which the narrower question of the repeal of the corn laws afforded an opportunity. Our own free traders for the most part are devout followers of the Manchester School, and take all their teachings and practices with little discrimination. They are essentially imitative. The anti-corn law agitators pointed their arguments by exhibiting loaves of bread of different sizes, and so our free traders, during a campaign, have gone about in carts and held up pairs of trousers, a more humorous if less intelligent form of object lesson. They attempt, too, in like fashion, to give the weight of morality to their doctrines. Unfortunately for them, inasmuch as everyone likes to be moral at some one’s else expense, their position is untenable. Adam Smith’s distinction was a broad and sound one; and deeply important as political economy and questions of tariff are, they are in no sense matters of morals. They are purely questions of self-interest, of profit and loss, and can be decided properly on these grounds alone.
In the second place, the assumption made tacitly, at least, if not avowedly, that political economy is an exact science is wholly misleading. Political economy covers a wide range of subjects of which the tariff is only one; but in none of its branches is it an exact science. Modern investigation has, no doubt, revealed certain economic laws which we may fairly say operate with reasonable certainty, but this is a very different proposition from that which would make the conclusions of economists in all directions as absolute as those of mathematicians. Political economy, in fact, does not differ greatly in this respect from history, because both deal with subjects where the conditions and sympathies of men and women play a large part, and where human passions are deeply engaged. In fields like these, where the personal equation of humanity plays a controlling part, it is absurd to attempt to argue as if we were dealing with a mathematical formula. There may be a philosophy of political economy as there is of history; there may be scientific methods of dealing with it and certain economic laws, subject to many exceptions, which we may consider to be established, but nevertheless it is as far from being an exact science as one can conceive. The exact science notion is the misconception of cloistered learning which can build impregnable systems where there are none to attack them, but which has no idea of the practical difficulties of an unsympathetic world where the precious system must meet every possible objection and not merely those devised by its framers. In discussing a question of political economy, therefore, it is well to bear in mind that we are handling a subject where new facts are always entering in to modify old conclusions, and where there are many conditions, the effect of which it is impossible to calculate.
In the third place, the ardent tariff reformer at the present moment always discourses upon his subject as if he had some perfectly new truth to lay before the world from which it would be as impossible to differ, unless one was illiterate or corrupt, as from the conclusion of Galileo in regard to the movement of the earth. In one of our recent political campaigns I quoted an argument of Hamilton’s in favor of protection from his famous Report of Manufactures. Thereupon one of my opponents in a public speech, referring to this quotation, said it would be as sensible to adopt Hamilton’s views on the tariff as to go back to stage coaches simply because those vehicles were the means of conveyance in Hamilton’s time. I could not help wondering what my learned opponent would have thought if I had retorted that, by parity of reasoning, we ought to reject the “Wealth of Nations” because Adam Smith flourished a little earlier than Hamilton, and stage coaches were used in his day also. The simple truth is that there is nothing very new to-day in the question of free trade or protection. The subject is one which has been under consideration for some time. It has received great developments in the last hundred years, and is still so far from the last word that it is safest not to be too dogmatic about it.
In this matter of the tariff, then, we have before us a question which is not new, which is not moral, but which deals simply with matters of self-interest according to the dictates of an enlightened selfishness. What is the condition of the question of free trade to-day in its practical aspect? Fifty years ago, roughly speaking, the movement for it in England became successful, and the English people abandoned a protective tariff which they had maintained for some centuries and adopted the free trade tariff which they have to-day. The latter system has had a thorough trial in England under the most favorable circumstances. If there is any country in the world which, by its situation, its history and its condition, is adapted for free trade, England is that country. If free trade, therefore, is the certain and enormous benefit which its advocates assert, and if it is the only true system for nations to adopt, its history in England ought to prove the truth of these propositions. How near has free trade come to performing all that its original promoters claimed in its behalf? How brilliant has been its success in practise? One thing at least is certain: it has not been such an overwhelming and glittering success as to convince any other civilized nation of its merits. England stands alone to-day, as she has stood for the last fifty years, the one free trade nation in the world. Possibly England of all the nations may be right and everybody else may be wrong, but there is, at least, a division of opinion so respectable that we may assume, with all due reverence for our free trade friends, that there are two sides to this question as to many others.
Let us look for a moment at some of the early promises. Free trade, according to its originators, was to usher in an era of peace and good-will. It was, in its extension, to put an end to wars. It has certainly not brought peace to England, which has had a petty war of some sort on her hands almost every year since the free trade gospel was preached. I do not mean to say that this is in the least due to free trade, but it is quite obvious that free trade did not stop fighting. The prosperity of England has, of course, been undeniably great, and it has been especially great among the vast industrial and manufacturing interests which supported the free trade policy. Possibly they have thriven better under this system than they would have done under the old one, but this must remain mere speculation, and as we know that some protected countries have prospered as much if not more than England, the prosperity argument has little weight. There are, however, other fields where we need not rely on conjecture. Has free trade been an unquestionable benefit not merely to the industrial but to all classes in England? It certainly has not put an end to strikes, for strikes have never been more frequent anywhere than they have been in Great Britain of late years. It does not seem to have perceptibly diminished poverty, if we may judge from such recent books as “The Bitter Cry of Outcast London,” and “Through Darkest England.” The state of Ireland has not been indicative of a healing and life-giving prosperity. In a word the great problems of labor, of poverty, and of over-population seem as severe in free trade England as in protective countries. Free trade again does not seem to have prevented the rise of trusts and syndicates, nor to have stopped the accumulation of vast wealth in a few hands. In other words, there is no evidence that free trade has had any effect on the most serious questions of the day, which touch the welfare of the great masses of the people. All that can be said is that the manufacturing and industrial interests of Great Britain seem to have thriven under it. For a system which arrogates to itself absolute truth, this is a meagre showing.
Free trade has not demonstrated its infallibility in the single country where it has been tried. The question, therefore, for the people of the United States is, whether under their conditions it is well to make the change which England made nearly fifty years ago, and to adopt a system of which the success has been doubtful in its chosen field. In order to decide the question intelligently we must put aside all vague confusions about an exact science which will work the same results everywhere because it operates under an immutable law. Even if free trade had been a brilliant and conclusive success in England, of which there is no proof, does it follow that it would be a better system for us? We have, to begin with, in our possession, instead of a small island a continent capable of almost every variety of natural production and mechanical industry. This is also a new country and a young country. We have been developing our resources rapidly for the last hundred years, but they are still not fully developed. The policy of the United States, although with many fluctuations, has been in the main to develop all our natural and mechanical opportunities to their fullest extent. The free trader is always ready with the terse statement that, “You cannot make yourself rich by taxing yourself,” followed by a freshly humorous allusion to lifting one’s self by one’s boot-straps. He then feels that he has met the case. If political economy and the financial policy of nations were as simple as this argument seems to imply, life would be an easier thing both for nations and individuals. Unluckily the problems of mankind which engage their interests and passions cannot be solved by cheap aphorisms. The statement of the free trader about taxing yourself in order to grow rich has a final and conclusive sound, but it is simply sound. There are, for example, plenty of towns in New England which have built factories and relieved certain persons from taxation in order to secure their capital and industry, and the additional population and the increased taxes which have thus come to the town have made it rich or at least richer than it was before. It is quite possible to adjust taxes or to offer bounties or premiums in such a way as to add to the aggregate wealth of the community.
The free trader’s question is not really pertinent. The point is not whether you will tax yourself in order to grow rich, but whether you will so frame your tax laws and so raise your revenues as to discriminate in favor of your own production and your own wages against the production and wages of other countries, or whether, on the other hand, you will let everything strictly alone and leave the country to come out the best way it can. The general policy of the United States has been to give encouragement to the domestic producer and manufacturer, and maintenance to high rates of wages, by laying duties in such a way as to discriminate in their favor against those outside. The result, speaking broadly, has been to put the United States as a competitor into countless lines of new industries. The effect of the competition of the United States, added to that already existing in the rest of the world, has been to reduce the world’s prices in the products of those industries according to the well-known laws of competition. Hence comes the lowering of prices to the consumer in protected articles, a fact which is the cause of much satiric laughter to the free trader because he can neither deny nor explain it.
The practical question now before the people of the United States is twofold: shall we protect new and nascent industries, and shall we continue to guard existing industries and existing rates of wages against an undue competition? John Stuart Mill admits the soundness of the former policy, and with that admission protectionists may be content. In fact, it may be doubted whether any intelligent man would argue to-day that it would have been wiser for the United States never to have built up any industries, but to have remained a purely agricultural community, dependent on Europe for everything in the way of manufacture. I think we may assume that the wisdom of protecting nascent industries in a country with such capacities and resources as the United States can hardly be questioned.
Nevertheless, the most hotly contested feature of the McKinley bill was that which continued the policy of protecting nascent industries in certain products, and notably that of the manufacture of tin plate. If the protection of nascent industries at the beginning of this century was a sound policy, then it is a sound policy to industries of that description to-day. Whether we have tin mines or not (and it now appears that we have) there is no reason on the surface why we should not buy our Straits tin and manufacture tin plate as well as England. Some Democratic newspapers appear to have an idea that the tin mines of Cornwall and Wales make a monopoly in this direction for England. They forget that to-day the tin used by England comes chiefly from the Straits, and she can buy it there on no better terms than the United States. If the policy of protection to nascent industries is sound, then the tariff of 1890 is sound in this direction, and we should seek its results in the new industries which have been started since it became a law.
In the second branch, the question of whether we should continue protection to industries already established is one largely of degree and of discretion. Where a removal of the duty would mean either a heavy reduction of wages or a stopping of existing industries with the rise of prices consequent upon the withdrawal of the United States from the world’s competition, then the removal of the duty would be a misfortune. It would be a misfortune not only to the industry which was ruined and to the wage earners who were reduced to idleness or poverty, but it would be an injury to the consumer because it would in a short time raise the price of the world’s production diminished by our withdrawal. In industries where no such results could possibly be feared, or where the production of the article is not possible in the United States, it would certainly be wise to remove duties, and this has been the purpose of the protectionists and of the Republican party.
The policy of protection has received its most recent expression in this country in the tariff of 1890. It is a truism that no tariff bill, whether passed by free traders or protectionists, can hope to be perfect. It is sure to have defects in detail and some inequalities. The McKinley bill was not exempt from error, but the question for the people to decide now is whether it is well to abandon the protective policy and substitute that of free trade. In 1888 the cry was that we must get rid of the surplus revenue and that that necessity made a revision of the tariff imperative. The Republican party since it has been in power has taken two hundred and forty-six millions of the accumulated surplus and paid off the bonded indebtedness of the country to that amount. It has also, by the removal of the duty on sugar and other articles, reduced the annual surplus revenue some fifty or sixty millions. The danger from the surplus, therefore (and it was a very real danger), is at an end. No party need be called upon now to dispose of the annual surplus which was taking so many millions out of the channels of trade. The question between the parties and before the country on this issue is very much simpler than it was. It is whether we shall repeal the tariff of 1890, abandon the protective system and take up free trade, or whether we shall maintain the protective system, making such amendments to the law as may from time to time seem necessary.
I have tried to state the general argument upon the question of free trade or protection in its broadest way. It only remains to bring forward so far as possible the facts which show, in part at least, the results of the tariff of 1890, for upon those results as a whole its justification or condemnation must rest. It is important to know first whether the new industries which the McKinley bill was designed to encourage have begun to start, and second, whether the bill has had the disastrous effect in raising prices which was so loudly asserted and prophesied by its opponents at the last election.
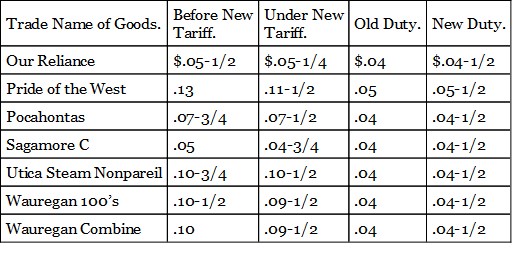
I will give first a table showing comparative prices before and after the tariff of 1890 of some of the cotton fabrics most commonly used. They are all protected industries and ought to have been advanced in price if any part of the assertions made by the advocates of free trade during the last campaign were true.
PRICES OF PRINT GOODS SIX MONTHS BEFORE THE MCKINLEY TARIFF PASSED COMPARED WITH THEIR PRESENT PRICES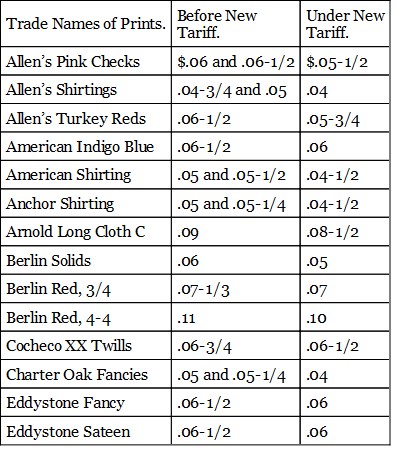
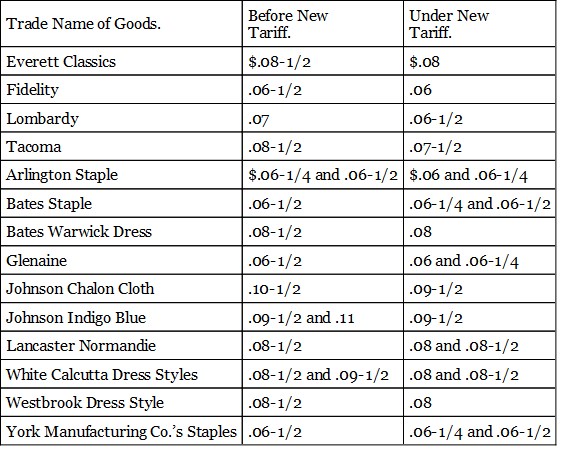
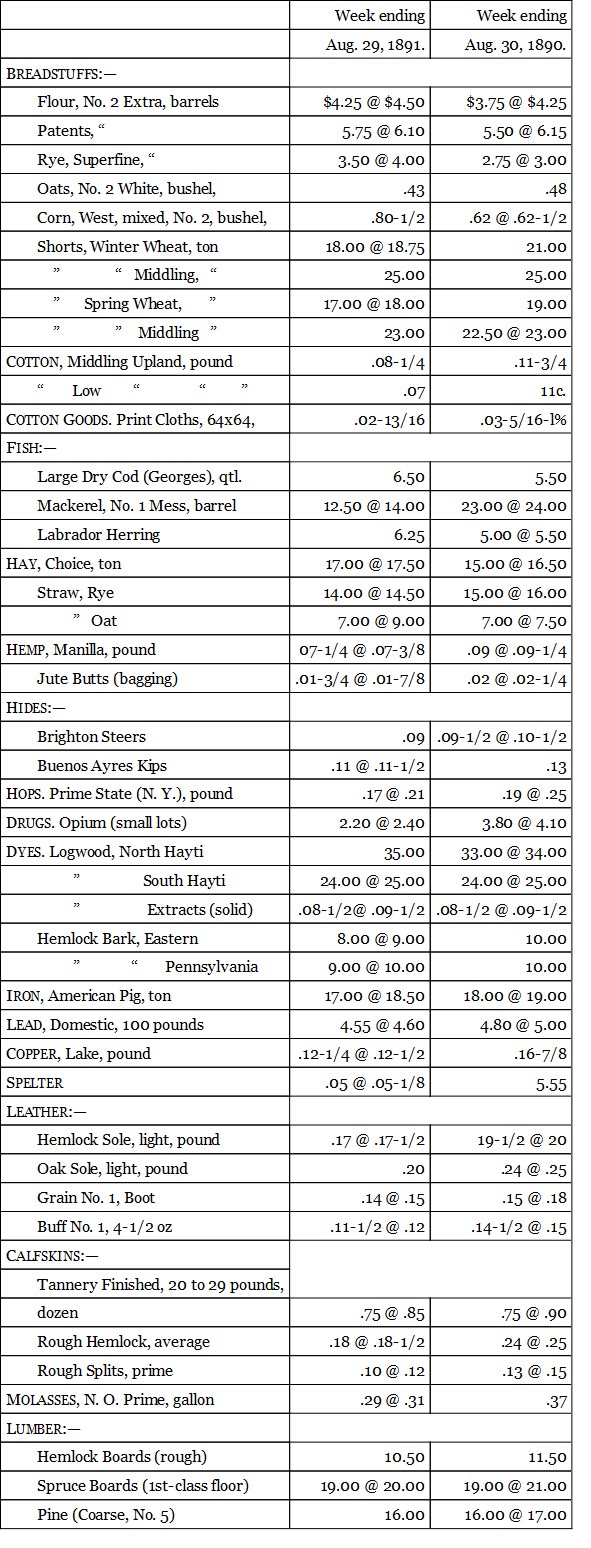
I give now a table comparing the market quotations for 1890 of the articles which enter most largely into the cost of living, with those for the same period in 1891:—
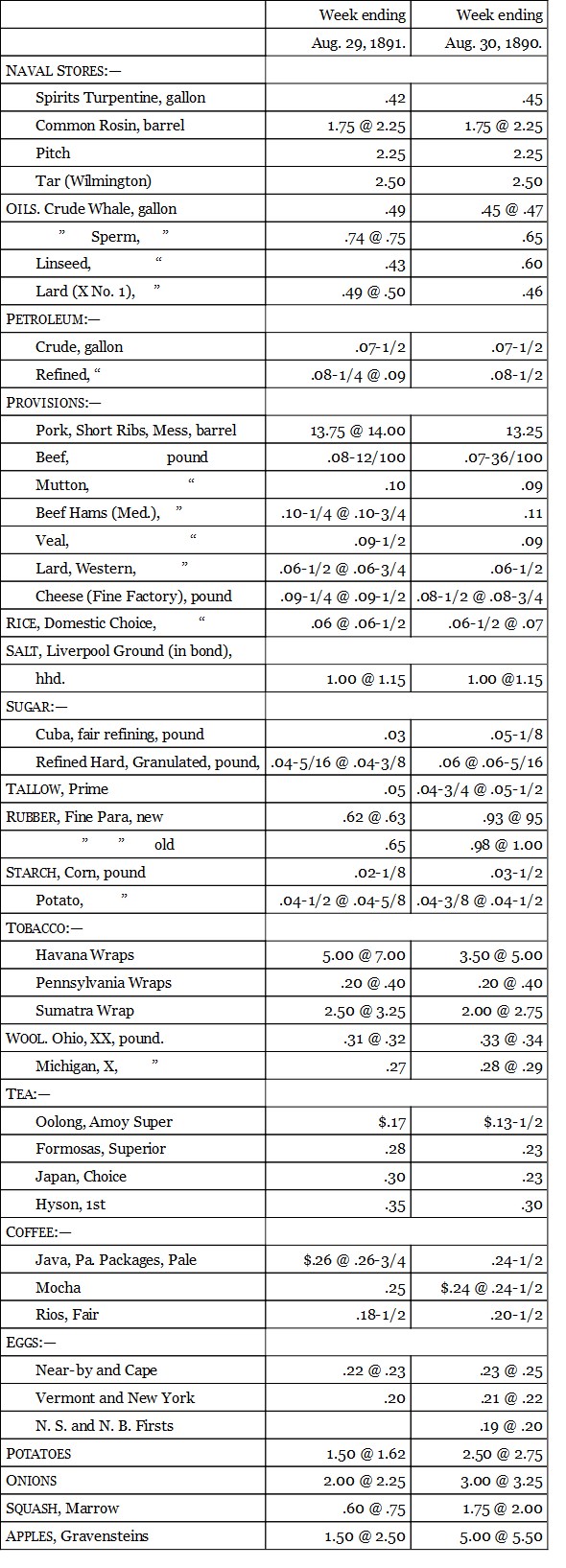
If the articles given in the foregoing table be classified we find the following results as to the rise and fall of prices before and after the tariff of 1890.
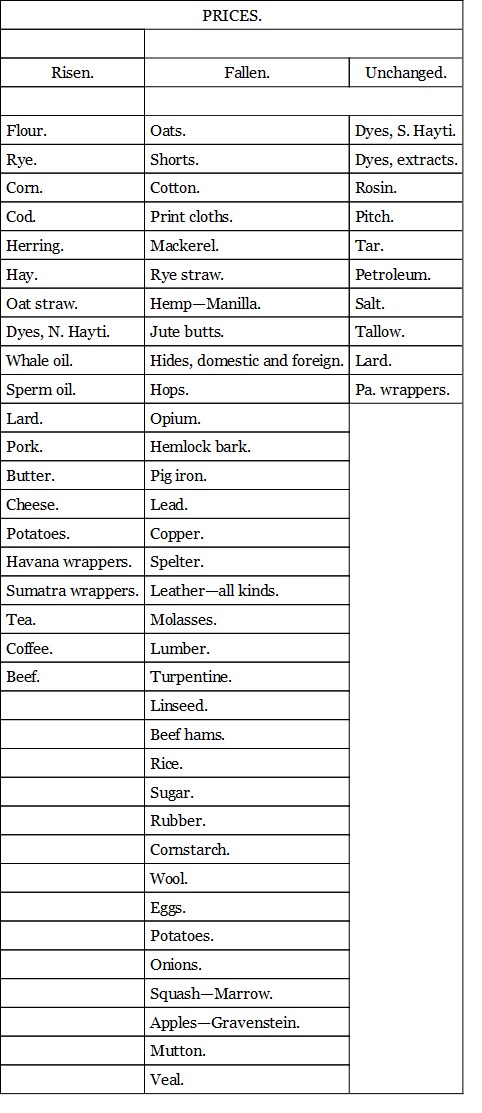
From these tables it is obvious that there has been, in the first place, no general rise of prices such as was confidently predicted by the panic-mongers of last year. On the contrary, the large majority of prices show a downward tendency. But more important than this is the fact made obvious by these tables that the price of the protected product has not risen. The foreign goods have advanced in some instances and been shut out in consequence, but domestic goods have taken their places, the price being kept down by domestic competition. In a word these tables prove that except for the enormous reduction in the cost of sugar, the new tariff has had but slight effect if any on the course of prices of the necessaries of life, and that the statements of the free traders as to a general rise of prices was entirely false.
The following extract is from a letter from one of the largest wholesale clothing firms in Boston. It tells its own story:—
“In reply to yours of the 10th inst., would say that we sold clothing in every grade in August, 1891, at fully 10 per cent. less in prices than in August, 1886; for instance, a cassimere suit sold then for $12.00 which we sell now for $10.50, and one sold for $13.50 and we sell the same now for $12.00. An overcoat sold then for $11.50 which we sell now for $10.00. Another grade sold then for $16.50 and sells for $15.00 now. This difference will run through all grades in proportion to prices. The difference in prices between August, 1890, and ‘91, is very little, if any; less rather than more in ‘91.”
As to the development of manufacturing under the McKinley bill I will quote first the opinion of a disinterested witness. The British Consular General at New York, in his report of May 8, 1891, speaks as follows:—
“Influenced by the new and higher duties afforded for the benefit of American manufacturing interests, new life has been imparted to the cotton, worsted, woollen, and knit underwear industry. Everywhere, especially in the Southern States, new textile mills have been going up with surprising activity, and all the old corporations have been operated on full time….
“As a rule, all the cotton mills have had a year of unusual activity. The production has been of larger volume than in any previous year, and the goods have found a ready sale generally but at comparatively low prices, considering the high prices which prevailed during the first six months of the year for cotton. Market prices, except in a few cases, did not vary with the price of cotton. Opening generally at low rates, cotton goods have been steady, the home and export demand being sufficient to absorb the supply of all standard and staple makers of brown, bleached, and colored goods, if we except printing cloths and calicoes….
“The worsted goods industry has been marked by fresh life since the new tariff has, to a great extent, cut off the importation of the lowest grades of such goods. All the old factories have started up, and are making goods on safe orders; and new mills are being erected by European and British capitalists with a view to manufacturing a finer class of dress goods, etc., than ever before has been produced in this country. The woollen goods industry, apart from ladies’ cloths, does not show any perceptible signs of improvement, but keeps on a slow, steady gait, apart from carpetings and woollen underwear. Both of the latter industries have been unusually busy during the last six months at fairly profitable prices.”
To give a complete list of the new industries started since the passage of the McKinley bill would be impossible, and would occupy more space than The Arena could spare. I give, therefore, a partial list compiled from the Boston Commercial Bulletin, and covering only the first three months after the passage of the law, that is, from Oct. 1, 1890. These are the months most unfavorable to the bill, but the statistics show what the growth of new and old industries has been under the tariff of 1890 in three months, and indicate what the future increase is likely to be.
SHOES AND LEATHERShoe factory at Portsmouth, Va.
Tannery and horse collar manufactory at Demorest, Ga.
Shoe factory building by the town of Ayer to cost $15,000.
White Bros, new tannery at Lowell for finishing fine upper leather.
Towle’s new shoe factory at Northwood, N. H.
New shoe factory at Natick, Mass.
New shoe factory at Beverly, Mass.
New shoe factory at Salisbury, N. C.
Voltaire Electric Shoe Co., of Manchester, N. H. (Capital, $50,000.)
New factory at Ellsworth, Me.
New factory at Sherman, Me.
New factory at Whitman, Mass., for Commonwealth Shoe Co.
New factory at East Pepperell, Mass. (Employs over 700 hands.)
Manhattan Rubber Shoe Co., at New York. (Capital, $50,000.)
Crocker Harness Co., of Tisbury, Mass. (Capital, $77,000.)
COTTONMutual Land & Mfg. Co., at Durham, N. C. (Capital, $280,000.)
Stock company (capital, $250,000) to erect cotton mill, at Fort Worth, Texas.
Cabot Cotton Mfg. Co., at Brunswick, Me. (70,000 spindles.)
Shirt factory at Milford, Del. (To employ 30 women.)









