 полная версия
полная версияBlackwood's Edinburgh Magazine — Volume 53, No. 331, May, 1843
Other and unmistakeable signs of the spirit of commercial combination, or confederation, abroad, and more or less explicitly avowed and directed against this country, are, and have been for some time past, only too patent, day by day, in most of those continental journals, the journals of confederated Germany, of France, with some of those of Spain and of Portugal, which exercise the largest measure of influence upon, and represent with most authority the voice of, public opinion. Nor are such demonstrations confined to journalism. Collaborateurs, in serial or monthly publications, are found as earnest auxiliaries in the same cause—as redacteurs and redactores; pamphleteers, like light irregulars, lead the skirmish in front, whilst the main battle is brought up with the heavy artillery of tome and works voluminous. Of these, as of brochures, filletas, and journals, we have various specimens now on our library table. All manner of customs, or commercial unions, between states are projected, proposed, and discussed, but from each and all of these proposed unions Great Britain is studiously isolated and excluded. We have the "Austrian union" planned out and advocated, comprising, with the hereditary states of that empire, Moldavia, Wallachia, Bulgaria, Servia, Bosnia, as well as those provinces of ancient Greece, which, like Macedonia, remain subject to Turkey, with, perhaps, the modern kingdom of Greece. We have the "Italian union," to be composed of Sardinia, Lombardy, Lucca, Parma, and Modena, Tuscany, the two Sicilies, and the Papal States. There is the "Peninsular union" of Spain and Portugal. Then we have one "French union" sketched out, modestly projected for France, Belgium, Switzerland, and Savoy only. And we have another of more ambitious aspirations, which should unite Belgium, Switzerland, and Spain under the commercial standard of France. One of the works treating of projects of this kind was, we believe, crowned with a prize by some learned institution in France.
From this slight sketch of what is passing abroad—and we cannot afford the space at present for more ample development—the right honourable Vice President of the Board of Trade will perhaps see cause to revise the opinion too positively enounced, that "foreign countries neither have combined, nor ought to combine, nor can combine, against the commerce of Great Britain;" and that it is a "calumny" to conceive that they are "disposed to enter into such a combination."
With these preliminary remarks, we now proceed to the consideration of the commercial relations between Spain and Great Britain, and of the policy in the interest of both countries, but transcendently in that of Spain, by which those relations, now reposing on the narrowest basis, at least on the one side, on that of Spain herself, may be beneficially improved and enlarged. It may be safely asserted, that there are no two nations in the old world—nay more, no two nations in either, or both, the old world and the new—more desirably situated and circumstanced for an intimate union of industrial interests, for so direct and perfect an interchange of their respective products. The interchange would, indeed, under a wise combination of reciprocal dealing, resolve itself purely almost into the primitive system of barter; for the wants of Spain are such as can be best, sometimes only, supplied from England, whilst Spain is rich in products which ensure a large, sometimes an exclusive, command of British consumption. Spain is eminently agricultural, pastoral, and mining; Great Britain more eminently ascendant still in the arts and science of manufacture and commerce. With a diversity of soil and climate, in which almost spontaneously flourish the chief productions of the tropical as of the temperate zone; with mineral riches which may compete with, nay, which greatly surpass in their variety, and might, if well cultivated, in their value, those of the Americas which she has lost; with a territory vast and virgin in proportion to the population; with a sea-board extensively ranging along two of the great high-ways of nations—the Atlantic and the Mediterranean—and abundantly endowed with noble and capacious harbours; there is no conceivable limit to the boundless production and creation of exchangeable wealth, of which, with her immense natural resources, still so inadequately explored, Spain is susceptible, that can be imagined, save from that deficient supply of labour as compared with the territorial expanse which would gradually come to be redressed as industry was promoted, the field of employment extended, and labour remunerated. With an estimated area of 182,758 square miles, the population of Spain does not exceed, probably, thirteen millions and a half of souls, whilst Great Britain and Ireland, with an area of 115,702 square miles, support a population of double the number. Production, however, squares still less with territorial extent than does population; for the stimulus to capital and industry is wanting when the facilities of exchanges are checked by fiscal prohibitions and restrictions. Agricultural produce, the growth of the vine and the olive, is not unfrequently known to run to waste, to be abandoned, as not worth the toil of gathering and preparation, because markets are closed and consumption checked in countries from which exchangeable commodities are prohibited. The extent of these prohibitions and restrictions, almost unparalleled even by the arbitrary tariff of Russia, may be estimated in part by the following extract from a pamphlet, published last year by Mr James Henderson, formerly consul-general to the Republic of New Granada, entitled "A Review of the Commercial Code and Tariffs of Spain;" a writer, by the way, guilty of much exaggeration of fact and opinion when not quoting from, or supported by, official documents.
"The 'Aranceles,' or Tariffs, are four in number; 1st, of foreign importations; 2d, of importations from America; 3d, from Asia; and, 4th, of exportations from Spain.
"The Tariff of foreign importations contains 1326 articles alphabetically arranged:—
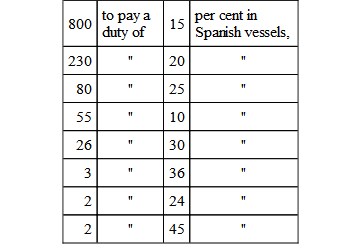
about 50 from 1 to 8 per cent, and the rest free of duty.
"The preceding articles imported in foreign vessels are subject to an increased duty, at the following rates:—
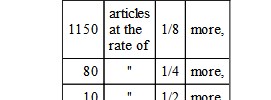
"There is, besides, a duty of 'consumo,' principally at the rate of 1/8 of the respective duties, and in some very few cases at the rate of 1/4 and 1/2.
"Thus the duty of 15 per cent levied, if the importation is by a Spanish vessel, will be increased by the 'consumo' to 20 per cent. And the duty of 20 per cent on the same articles, in foreign vessels, will be augmented to 27 per cent.
"The duty of 20 per cent will be about 27 in Spanish vessels, and in foreign vessels, on the same articles, 36 per cent. The duty of 25 per cent, will in the whole be 33 per cent by Spanish, and by foreign vessels 44 per cent.
"The duty on articles, amounting to seventy-three, imported from America, vary from 1 to 15 per cent, with double the duty if in foreign vessels.
"The articles of importation from Asia are—sixty-nine from the Phillipines at 1 to 5 per cent duty, and thirty-six from China at 5 to 25 per cent duty, and can only be imported in Spanish ships.
"The articles of export are fourteen, with duties at 1 to 80 per cent, with one-third increase if by foreign vessels.
"There are eighty-six articles of importation prohibited, amongst which are wrought iron, tobacco, spirits, quicksilver, ready-made clothing, corn, salt, hats, soap, wax, wools, leather, vessels under 400 tons, &c. &c. &c.
"There are eleven articles of exportation prohibited, amongst which are hides, skins, and timber for naval purposes."
Such a tariff contrasts strangely with that of this country, in which 10 per cent is the basis of duty adopted for importations of foreign manufactures, and 5 per cent for foreign raw products.
Can we wonder that, with such a tariff, legitimate imports are of so small account, and that the smuggler intervenes to redress the enormously disproportionate balance, and administer to the wants of the community? Can we wonder that the powers of native production should be so bound down, and territorial revenue so comparatively diminutive, when exchanges are so hampered by fiscal and protective rapacity? Canga Arguelles, the first Spanish financier and statistician of his day, calculated the territorial revenue of Spain at 8,572,220,592 reals, say, in sterling, L.85,722,200; whilst he asserts, with better cultivation, population the same, the soil is capable of returning ten times the value. As a considerable proportion of the revenue of Spain is derived from the taxation of land, the prejudice resulting to the treasury is alone a subject of most important consideration. For the proprietary, and, in the national point of view, as affecting the well-being of the masses, it is of far deeper import still. And what is the financial condition of Spain, that her vast resources should be apparently so idle, sported with, or cramped? Take the estimates, the budget, presented by the minister De ca Hacienda, for the past year of 1842:—

Thus, with a revenue of L.8,791,934, an expenditure of L.15,416,398, and a deficit of L.6,624,460, the debt of Spain, foreign and domestic, is almost an unfathomable mystery as to its real amount. Even at this present moment, it cannot be said to be determined; for that amount varies with every successive minister who ventures to approach the question. Multifarious have been the attempts to arrive at a clear liquidation—that is, classification and ascertainment of claims; but hitherto with no better success than to find the sum swelling under the labour, notwithstanding national and church properties confiscated, appropriated, and exchanged away against titulos of debt by millions. It is variously estimated at from 120 to 200 millions sterling, but say 150 millions, under the different heads of debt active, passive, and deferred; debt bearing interest, debt without interest, and debt exchangeable in part—that is, payable in certain fixed proportions, for the purchase of national and church properties. For a partial approximation to relative quantities, we must refer the reader, for want of better authority, to Fenn's "Compendium of the English and Foreign Funds"—a work containing much valuable information, although not altogether drawn from the best sources.
In the revenues of Spain, the customs enter for about 70,000,000 of reals, say L.700,000 only, including duties on exports as well as imports. Now, assuming the contraband imports to amount only to the value of L.6,000,000, a moderate estimate, seeing that some writers, Mr Henderson among the number, rashly calculate the contraband imports alone at eight, and even as high as ten, millions sterling, it should follow that, at an average rate of duty of twenty per cent, the customs should yield additionally L.1,200,000, or nearly double the amount now received under that head. As, through the cessation of the civil war, a considerable portion of the war expenditure will be, and is being reduced, the additional L.1,200,000 gained, by an equitable adjustment of the tariff, on imports alone, perhaps we should be justified in saying one million and a half, or not far short of two millions sterling, import and export duties combined, would go far to remedy the desperation of Spanish financial embarrassments—the perfect solution and clearance of which, however, must be, under the most favourable circumstances, an affair of many years. It is not readily or speedily that the prodigalities of Toreno, or the unscrupulous, but more patriotic financial impostures of Mendizabal, can be retrieved, and the national faith redeemed. The case is, to appearance, one past relief; but, with honest and incorruptible ministers of finance like Ramon Calatrava, hope still lingers in the long perspective. With an enlightened commercial policy on the one hand, with the retrenchment of a war expenditure on the other, the balance between receipts and expenditure may come to be struck, an excess of revenue perhaps created; whilst the sales of national domains against titulos of debt, if managed with integrity, should make way towards its gradual diminution.
As there is much misapprehension, and many exaggerations, afloat respecting the special participation of Great Britain in the contraband trade of Spain, its extraordinary amount, and the interest assumed therefrom which would result exclusively from, and therefore induces the urgency for, an equitable reform of the tariff of Spain, we shall briefly take occasion to show the real extent of the British share in that illicit trade, so far as under the principal heads charged; and having exhibited that part of the case in its true, or approximately true, light, we shall also prove that it is, as it should be, the primary interest of this country to regain its due proportion in the regular trade with Spain, and which can only be regained by legitimate intercourse, founded on a reciprocal, and therefore identical, combination of interests. In this strife of facts we shall have to contend against Señor Marliani, and others of the best and most steadfast advocates of a more enlightened policy, of sympathies entirely and patriotically favourable towards a policy which shall cement and interweave indissolubly the material interests and prosperity of Spain and Great Britain—of two realms which possess each those products and peculiar advantages in which the other is wanting, and therefore stand seized of the special elements required for the successful progress of each other. Our contest will, however, be one of friendly character, our differences will be of facts, but not of principles. But we hold it to be of importance to re-establish facts, as far as possible, in all their correctness; or rather, to reclaim them from the domain of vague conjecture and speculation in which they have been involved and lost sight of. The task will not be without its difficulties; for the position and precise data are wanting on which to found, with even a reasonable approximation to mathematical accuracy, a comprehensive estimate, to resolve into shape the various and complex elements of Spanish industry and commerce, legitimate and contraband. Statistical science—for which Spain achieved an honourable renown in the last century, and may cite with pride her Varela, Musquiz, Gabarrus, Ulloa, Jovellanos, &c., was little cultivated or encouraged in that decay of the Spanish monarchy which commenced with the reign of the idiotic Carlos IV., and his venal minister Godoy, and in the wars and revolutions which followed the accession, and ended not with the death of Fernando his son, the late monarch—was almost lost sight of; though Canga Arguelles, lately deceased only, might compete with the most erudite economist, here or elsewhere, of his day. Therefore it is, that few are the statistical documents or returns existing in Spain which throw any clear light upon the progress of industry, or the extent and details of her foreign commerce. Latterly, indeed, the Government has manifested a commendable solicitude to repair this unfortunate defect of administrative detail, and has commenced with the periodical collection and verification of returns and information from the various ports, which may serve as the basis—and indispensable for that end they must be—on which to reform the errors of the present, or raise the superstructure of a new, fiscal and commercial system. Notwithstanding, however, the difficulties we are thus exposed to from the lack or incompleteness of official data on the side of Spain, we hope to present a body of useful information illustrative of her commerce, industry, and policy; in especial, we hope to dispel certain grave misconceptions, to redress signal exaggeration about the extent of the contraband trade, rankly as it flourishes, carried on along the coasts, and more largely still, perhaps, by the land frontiers of that country, at least so far as British participation. Various have been the attempts to establish correct conclusions, to arrive at some fixed notions of the precise quantities of that illicit traffic; but hitherto the results generally have been far from successful, except in one instance. In a series of articles on the commerce of Spain, published under the head of "Money Market and City Intelligence," in the months of December and January last, the Morning Herald was the first to observe and to apply the data in existence by which such an enquiry could be carried out, and which we purpose here to follow out on a larger scale, and with materials probably more abundant and of more recent date.
The whole subject of Spanish commerce is one of peculiar interest, and, through the more rigorous regulations recently adopted against smuggling, is at this moment exciting marked attention in France, which, it will be found with some surprise, is far the largest smuggler of prohibited commodities into Spain, although the smallest consumer of Spanish products in return. It is in no trifling degree owing to the jealous and exclusive views which unhappily prevail with our nearest neighbour across the Channel, that the prohibitory tariff, scarcely more adverse to commercial intercourse than that of France after all, which robs the revenue of Spain, whilst it covers the country with hosts of smugglers, has not sooner been revised and reformed. France is not willing to enter into a confederacy of interests with Spain herself, nor to permit other nations, on any fair equality of conditions, and with the abandonment of those unjust pretensions to special privileges in her own behalf, which, still tenaciously clinging to Bourbonic traditions of by-gone times, would affect to annihilate the Pyrenees, and regard Spain as a dependent possession, reserved for the exclusive profit and the commercial and political aggrandisement of France. That these exaggerated pretensions are still entertained as an article of national faith, from the sovereign on his throne to the meanest of his subjects, we have before us, at this moment of writing, conclusive evidence in the report of M. Chégaray, read in the Chamber of Deputies on the 11th of April last, (vide Moniteur of the 12th,) drawn up by a commission, to whom was referred the consideration of the actual commercial relations of France with Spain—provoked by various petitions of the merchants of Bayonne, and other places, complaining of the prejudice resulting to their commerce and shipping from certain alterations in the Spanish customs' laws, decreed by the Regent in 1841. We may have occasion hereafter to make further reference to this report.
The population of Spain may be rated in round numbers at thirteen millions and a half, whilst that of the United Kingdom may be taken at about double the number. With a wise policy, therefore, the interchange should be of an active and most extensive nature betwixt two countries, reckoning together more than forty millions of inhabitants, one of which, with a superficial breadth of territory out of all proportion with a comparatively thinly-scattered community, abounding with raw products and natural riches of almost spontaneous growth; whilst the other, as densely peopled, on the contrary, in comparison with its territorial limits, is stored with all the elements, and surpasses in all the arts and productions of manufacturing industry. Unlike France, Great Britain does not rival Spain in wines, oils, fruits, and other indigenous products of southern skies, and therefore is the more free to act upon the equitable principle of fair exchange in values for values. Great Britain has a market among twenty-seven millions of an active and intelligent people, abounding in wealth and advanced in the tastes of luxurious living, to offer against one presenting little more than half the range of possible customers. She has more; she has the markets of the millions of her West Indies and Americas—of the tens of millions of British India, amongst whom a desire for the various fruits and delicious wines of Spain might gradually become diffused for a thousand of varieties of wines which, through the pressure of restrictive duties, are little if at all known to European consumption beyond the boundaries of Spain herself. With such vast fields of commercial intercourse open on the one side and the other, with the bands of mutual material interests combining so happily to bind two nations together which can have no political causes of distrust and estrangement, it is really marvellous that the direct relations should be of so small account, and so hampered by jealous adherence to the strict letter of an absurd legislation, as in consequence to be diverted from their natural course into other and objectionable channels—as the waters of the river artificially dammed up will overflow its banks, and, regaining their level, speed on by other pathways to the ocean. We shall briefly exemplify the force of these truths by the citation of official figures representing the actual state of the trade between Spain and the United Kingdom antecedent to and concluding with the year 1840, which is the last year for which in detail the returns have yet issued from the Board of Trade. That term, however, would otherwise be preferentially selected, because affording facilities for comparison with similar but partial returns only of foreign commerce made up in Spain to the same period, little known in this country, and with the French customhouse returns of the trade of France with Spain. It must be premised that the tables of the Board of Trade in respect of import trade, as well as of foreign and colonial re-exports, state quantities only, but not values; nor do they present any criteria by which values approximately might be determined. Where, therefore, such values are attempted to be arrived at, it will be understood that the calculations are our own, and pretend no more—for no more could be achieved—than a rough estimate of probable approximation.
Total declared value of British and Irish produce and manufactures exported to Spain and the Balearic Isles in—
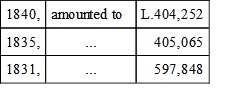
From the first to the last year of the decennial term, the regular trade, therefore, had declined to the extent of above L.193,000, or at the rate of about 33 per cent. But as for three of the intermediate years 1837, 1838, and 1839, the exports are returned at L.286,636, L.243,839, and L.262,231, exclusive of fluctuations downwards in previous years, it will be more satisfactory to take the averages for five years each, of the term. Thus from—

The average decline in the latter term, was therefore above 27½ per cent.
Of the Foreign and Colonial merchandise re-exported within the same period it is difficult to say what proportion was for British account, and, as such, should therefore be classed under the head of trade with Spain. It may be assumed, however, that the following were the products of British colonial possessions, whose exports to Spain are thus stated in quantities:—
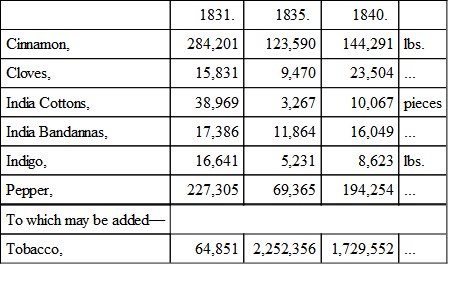
The tobacco, being of United States' growth, may, to a considerable extent, be bonded here for re-exportation on foreign account merely. The foregoing, though the heaviest, are not the whole of the foreign and colonial products re-exported for Spain, but they constitute the great bulk of value. Taking those of the last year, their value may be approximatively estimated in round numbers, as calculated upon what may be assumed a fair average of the rates of the prices current in the market, as they appear quoted in the London Mercantile Journal of the 4th of April. It is only necessary to take the more weighty articles.









