
Полная версия
Digital Transformation for Chiefs and Owners. Volume 1. Immersion
Plus is the speed of deployment and how fast the changes are coming.
Minus – duplication of costs. Often such teams begin to push elbows, in terms of the cost of the whole organization they are not very effective, constantly «invent bicycles», and they always have something to optimize.
– Hybrid model
It’s that all small digital offices need a focal point. His task is to build uniform rules of work, development, to form processes and tools, to develop a common strategy, so that local offices already use his knowledge. It becomes a methodological centre and coordinates all the centres so that they work towards a common goal and are synchronized with the strategy.
As an analogy you can take the company Google, which develops its «market place». Developers do not create apps from scratch, and use many proprietary ready-made applications from Google. For example, if you want to use maps in your app, you take ready-made maps from Google.
If you want to do local digitization, you need to understand the level of organizational development of your company. If you have a centralized organizational environment with a large digital block, you can assume that there will be problems with speed. If you have a distributed environment, there will be a problem with duplication and unnecessary costs to develop your products.
Always keep your structure in mind – this will protect you from irrelevant actions.
Risks
The introduction of any changes is risky, and digitalization and digital transformation projects are no exception. With dozens of projects of different sizes behind me, I can confidently say that risk management is a key element.
What risks do we have?
– Information security
New information systems, huge volumes of data require protection from losses and «hacking», as well as from incorrect operations. New levels of security are needed. New requirements for personal data protection are emerging. However, it should be remembered that if you start to ban everything that is not allowed, your people will look for workarounds, thus increasing the risks. Then it looks like you’re protecting everything, and the data is still compromised. And the key here – the ability to evaluate what is really valuable, and what you need only or becomes obsolete at the moment of appearance.
– Resistance to change and company culture
In the process of transforming your business, you will inevitably encounter staff resistance to innovation and in a favourable scenario you will lose 10—15% of employees.
There are many reasons for this. A special chapter will be devoted to working with resistance. It is worth noting the issue of culture, because culture has a strategy for breakfast. If you don’t know how to work with change and teamwork, nothing good can come of it.
– Terms
When implemented correctly, when changes are introduced from the top, from top, and supported by ordinary employees, digital transformation takes 2.5—3 years. In large companies this period may extend to 4—5 years.
Even the first results will be visible only after 9—12 months, but most managers lay 6—9 months for the entire transformation. For this period, you will have time to implement only 1—2 projects on digitalization or automation.
– Non-streamlined processes
This is one of the key elements of digital transformation. You can go the classic way – first automate what you have, and then reengineer processes. However, automation without prior optimization is not feasible. You will spend a lot of time and resources, but in the end, you will create a very heavy and clumsy system. Optimization is the most important step in the transition from manual labor to automated labor.
– Unstructured data
If you can’t structure data, transform it into useful information, then everything else is meaningless.
– Staff competencies
Digital technologies place a new level of demands on the knowledge and competencies of both the people adopting these technologies and the users. Large-scale measures are needed to educate and retrain, motivate and overcome resistance to innovation.
At the same time, research of one of the federal projects showed that in Russia only 26% of people have advanced digital skills. According to DICE, in Europe, this figure reaches 57%.
– Costs and people overburdened
Digital transformation is a high-cost initiative without guarantees of success.
According to research, only 20% of the changes are implemented successfully. Others fail for various reasons, including because of its redundancy. If there are 250 changes per person per year, you can hardly expect a positive result.
– Technology Disappointment
Gartner’s Gartner Hype Curve, a consulting agency, issues a report every August. This is a graph of public expectations about a particular technology. According to the agency, in the ideal case, the technology successively passes five stages: the launch of the technology, the peak of elevated expectations, the bottom of frustration, the slope of education, the plateau of productivity. However, it also happens that technology doesn’t make it past stage three – the bottom of disappointment.
Of course, it should be remembered that the Gartner chart is just a forecast, there are exceptions to it, but it still helps to assess the risks of early use of new technologies.
In summary, the most common causes of failure are:
– the unpreparedness of the IT systems used;
– data quality and availability;
– poor quality work with change management;
– Poor quality project management.
We will discuss this issue in a separate chapter.
Chapter summary
– The introduction of digital technologies is one of the tasks of digitalization. The global challenge is digital transformation, with a redefinition of processes, goals, models and strategies.
– Digital transformation is only a tool. More important is the overall quality of management, team. You cannot focus only on numbers.
You need highly qualified employees. Additionally, this means that policy management and aggressive management will no longer be applicable. Such employees are highly mobile, with mismanagement you will have to constantly recruit new personnel, teach them, and then lose them, and so on.
– In the Gartner diagram, many digital technologies are near the peak of high expectations. Disappointment will follow, and only after we learn how to use all these tools will there be value.
– There are no employees on the market with full set of necessary competencies. Team members are likely to have one or two strong competencies to use.
– Basic digital literacy increases the likelihood of digital transformation succeeding.
When implementing digital projects, a large number of users are affected, and the level of their basic IT training can vary. The accumulated statistics showed that «tightening» of basic PC skills significantly increases the probability of successful implementation of digital solutions in general.
– Basic for all competences are the ability to solve poorly structured problems, system and critical thinking, digital skills.
– The introduction of technologies and transformation can be carried out independently: allocate resources and people, work according to a matrix.
Your chances of success are 20 to 30%, at least 10% of your employees will be gone, you will have to bear a huge cost and the implementation period will be 2.5—3 years.
I recommend finding a company that specializes in digital transformation and will communicate with people while remaining independent of domestic policy. It will digitize the project, prepare proposals for optimization and necessary changes in culture, processes, necessary training programs for employees and will implement everything gradually. Then you won’t have to get rid of the time team on this project.
– To understand whether you need digitalization and digital transformation, ask yourself a few questions:
– how competitive is your industry?
– is it possible to replace your product or service with a digital one?
– do you have market preferences that are not available to other members?
– what is the threshold of entry?
Answers to them will already give an idea of how far you need to move forward. Additionally, the main criterion – it is necessary to deal with digitization if your revenue depends on a few key customers.
Chapter 2. Technology. Pros, Cons, Personal Opinions
I’m sure many of you at first thought this was going to be a major section. However, since this book is not for techs, I’m going to try to make it simple. After all, our task is to see the essence and begin to navigate the digital technologies, to understand how to use them for business.
Well, for those who think this topic is the main one, I suggest clicking on the QR code or the link below. There you will find a large number of visualizations, links and videos.

An overview of digital technologies. Part 1
Internet of Things (IoT, IIoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT – Internet of Things, IIoT – Industry Internet of Things – industrial Internet of Things) is a network of interconnected Internet devices. These are so-called «smart devices», although this name is not quite correct.
What is it for?
First, to collect and share data that can be analysed and based on such analysis, to make decisions. And secondly, to remotely control connected objects or devices.
According to Strategy Analytics, in 2018 there were 23 billion devices connected to the Internet of things worldwide. And by 2025, about 80 billion IoT devices are expected.
The IoT development was made possible by the reduction of the cost of the Internet (it has decreased several times in 10 years), as well as the reduction of computing power and sensors.
At the same time, it must be understood that the Internet of things is not so much a conditionally «smart» kettle, socket and so on, as a big data generator (which we will talk about a little later), something that analysts and data will work with later Scientists to form new proposals and generate ideas.
IoT, for example, will allow:
– to develop predictive analysis and prevent accidents or catastrophes at industrial facilities;
– adjust road traffic according to traffic density;
– make recommendations for improving efficiency.
Application scenarios here are limited only to imagination.
The main advantages are mobility and generation of «pure» data, that is, the exclusion of errors that occur when you enter data.
I believe that the Internet of things, including the Internet of Industrial Things, is one of those technologies that will fundamentally affect all aspects of our lives. Only in 5—10 years.
Now it is necessary to discuss how the Internet of things works. Do you have to pull cables everywhere or put routers?
Nay.
Different wireless communication systems can be used to organize data exchange, not necessarily mobile networks, but depending on goals and objectives.
First, consider LPWAN – long-range networks.
LPWAN
LPWAN (Low-power Wide-area Network, long-range energy efficient network) is a technology for the wireless transmission of small volumes of data over long distances. Since the volumes are small, the low data transmission rate is enough to achieve a longer range of reception.
This technology is designed to collect telemetry and interaction between machines (M2M). In fact, it is one of the key wireless technologies for IoT systems.
The LPWAN network approach is similar to that of mobile networks. A device or modem with an LPWAN module sends data via a radio channel to the base station. The station receives signals from all devices within its range, digitizes and transmits to a remote server using an accessible communication channel: wired Internet or cellular.
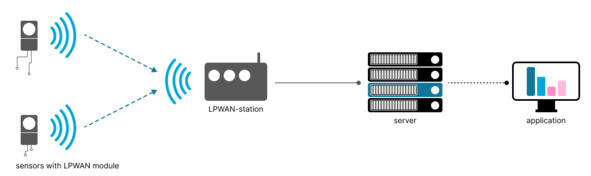
LPWAN data collection and processing scheme LPWAN data collection and processing scheme
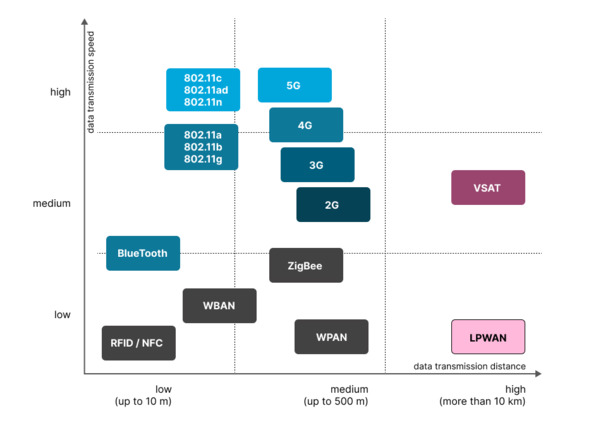
Comparison of different communication standards
Benefits of LPWAN
– Long range – from 10 to 15 km
– Low power consumption in sensors
– Relatively high range even in the city
– It’s easy to build networks and add new objects
– Easy to use – can be done without permits and pay for radio frequency spectrum
Drawbacks of LPWAN
– Low speed – only necessary data can be transferred
– High delay between data transfer sessions
– There is no single standard for creating compatible solutions from different manufacturers
There are two main options for implementing the LPWAN network:
• licensed frequency range (increased power, relatively high speed, no interference);
• unlicensed frequency range (low power, low speed, limited transmission cycle, possible interference from other participants).
3 main technologies of construction of LPWAN-networks:
• NB-IoT – evolution of cellular communication;
• UNB (unlicensed LPWAN) – SigFox in the world;
• LoRa is a broadband unlicensed LPWAN.
NB-IoT
NB-IoT (Narrow Band Internet of Things) is a cellular communication standard for low-volume telemetry devices: medical sensors, resource meters, smart home devices, etc.
NB-IoT is one of three IoT standards developed for cellular networks:
– eMTC (improved machine-type communication) – has the highest capacity and is deployed on LTE (4G) hardware;
– NB-IoT – can be deployed both on LTE cellular network hardware and separately, including on top of GSM;
– EC-GSM-IoT – provides the least bandwidth and deploys over GSM networks.
– Advantages of NB-IoT
– Flexible power management of devices (up to 10 years in a network with a capacity of 5 W*h)
– High network bandwidth (hundreds of thousands of connections to the base station)
– Low cost of devices
LoRaWAN
LoRaWAN is an open communication protocol that defines the system architecture. It was designed to link low-cost devices that can run on batteries (batteries).
According to IoT Analytics, it was the most widely used low-power global network (LPWAN) technology in the second half of 2020.
The LoRa technology is primarily required for machine-to-machine interaction, and can service up to 1 million devices in a single network, giving them a 10-year autonomy from a single AA battery (a regular palm battery).
For the review to be objective, disadvantages and limitations must be addressed.
The most important limitation for organizations wishing to implement IoT is the cost and time of project implementation. Another factor was the limited expertise of the staff.
Technological shortcomings include the following:
– power supply (either have low speed and frequency of data, or need to arrange power supply);
– dimensions (not all sensors can be miniature);
– equipment calibration (reliability of readings);
– dependence on the data network;
– lack of common protocols and standards for transmitted data, which may make it difficult to process, integrate, and analyze data even on a single production scale (in February 2022, the new ISO/IEC 30162:2022 standard was released, but the transition to uniform rules will still be difficult);
– vulnerability to external attacks and subsequent data leaks or intruders gaining access to hardware management.
5G
You’ve probably heard of the 5G. That this is a breakthrough in communications, and no new flagship can be a breakthrough without the 5G. After all, without it it is impossible to look at the smartphone new series at 4 or 8K. Therefore, you need to buy smartphones only with this module and pay 100—150$ more than the version with the 4G module.
However, very few know that the standard itself was not designed for video in YouTube or TikTok, but for the scale development and implementation of digital services. Its «chip» is flexible combination of ultralow latency (URLLC), high speed (eMBB) and reliability of the communication channel (mMTC), depending on what is needed by a particular subscriber.
Basically, it’s a connection for the IoT. It may not be entirely suitable for an industrial IoT, but for a smart city, healthcare, and industrial enterprises in the city it is the ideal option.
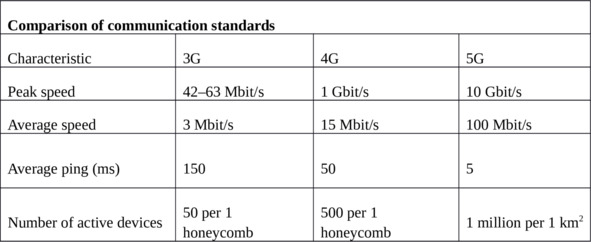
So, what is the difference between 5G and 4G/LTE?
– Eight times better energy efficiency
– 10—100 times the speed
– 100 times more subscribers per base station
All those who are engaged in digitalization in production, and even just implementing ACS TP, know that the main problem is to organize data transmission to or from sensors. The solution of this issue in accordance with all the rules of the company is sometimes several times more expensive than «iron» and software.
Additionally, I hope that with the development of 5G technology, this problem will become less and less relevant.
In addition, the development of this technology will also help the implementation of more advanced IT systems, especially MES, APS, EAM, BIM. More about them – in the next chapter. All these systems need information from sensors without human intervention.
However, there is an unpleasant moment for many. All this will require other competencies from the employees. This means that the «optimization» of the organizational structure and the increase of social tension will begin.
6G
China and the US are already developing standards for 6th generation networks. However, why?
To ensure further growth of smart device deployment! 5G still has limited capacity.
Some sources suggest peak speeds of up to 1 Tbit/s. Average speed of several hundred Mbit/s. The average signal latency is 1 ms, which is useful for applications that require minimal latency, such as autopilots and virtual reality. The number of active devices that can connect to 6G per unit time will also be several times higher than 5G.
«The 6G Era will offer new possibilities for creating brain-computer interfaces», says Dr Mahyar Shirvanimogaddam of Sydney University. An example of such development is the electronic chip for paralyzed and people with CNS disorders, which is created by Elon Musk’s startup.
In this case, the 6G has one great advantage – it is possible to upgrade the existing 5G towers for its implementation, while the 5G had to build new base stations.
It is now believed that 6G may be introduced in the early 2030s.
Neural networks, machine and deep learning (ML & DL), speech and text recognition systems
So, we’re getting to the future – neural networks, artificial intelligence, machine revolutions and other horror stories.
Neural networks are perhaps the most interesting technology. With the support of the Internet of Things, 5G and Big Data, it will bring revolutionary changes to our lives.
Additionally, artificial intelligence is any mathematical method that can simulate human intelligence.
Oh as our favorite advertisers and marketers are satisfied… Now any, the simplest neuronetwork can proudly be called «Artificial Intelligence».
However, artificial intelligence is still divided into strong and weak. In 2019, scientists came close to creating a strong AI, the equivalent of human consciousness. This ability not only to distinguish a pen from a pencil or a cat from a dog (according to this principle all neural networks work, it is weak AI), but also to navigate changing conditions, choose specific solutions, model and predict the development of the situation.
A strong AI will be indispensable in intelligent transportation and transportation systems, cognitive assistants. However, this is the future, and what is now?
Now there are learning neural networks. An artificial neural network is a mathematical model modeled on the neural networks that make up the brains of living things. Such systems learn to perform tasks by treating them without specific programming for specific applications. This can be found in Yandex Music, Tesla autopilots, referral systems for doctors and managers.
Therefore, here are the two main trends:
– machine learning (ML – machine learning);
– deep learning (DL – deep learning).
Machine learning is statistical methods that enable computers to improve the quality of the task with experience and training. So it’s about how the neural networks of living organisms work.
Deep learning is not only learning a machine with the help of a person who says what is right and what is not, but also self-learning systems. This is the simultaneous use of different methods of training and data analysis.
However, how do these neural networks teach? What’s the magic?
Actually, in fact, nothing. It’s like training a dog. Neuronetworks show, for example, a picture and say that it is depicted. The neural network must then respond, and if the answer is wrong, it is corrected. An approximate algorithm is given below.
As a result, it turns out that each «neuron» of such a network learns to recognize, refers to it this picture, or rather its part, or not.
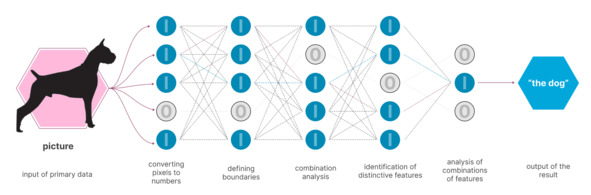
Example of neural network operation in image recognition
Neural networks and machine learning apply:
– for forecasting and decision making;
– image recognition and generation, including «pictures» and voice recordings;
– complex data analysis without clear relationships;
– process streamlining.
The application value of this can be seen in the examples of the creation of unmanned cars (decision-making), the search for illegal content (data analysis), the prediction of diseases (pattern recognition and linkage search). At the same time, on the haip it is pattern recognition and generative models (chatGPT, midjourney, etc.). However, business problems are still poorly solved. At the same time, 9 out of 10 students now go to study exactly on pattern recognition and machine vision.
The AI + IoT link deserves special attention:
– AI receives net big data (about them in the next section) in which there are no human factor errors to learn and search relationships;
– IoT’s effectiveness increases as it becomes possible to create predictive (predictive) analytics and early detection of deviations.
Okay, this is all a theory. I want to share a real example of how neuronetworks can be used in business.
In the summer of 2021, I was approached by an entrepreneur from the realtor sector. He is engaged in the rental of real estate, including daily rent. Its goal is to increase the pool of rented apartments and change the status of an entrepreneur to a full-fledged organization. The nearest plans are to launch the site and mobile application.
I happen to be a client myself. And at our meeting I noticed a very big problem – the long preparation of the contract: it takes up to 30 minutes for the registration of all the details and signing. This is both the limitation of the loss generating system and the inconvenience for the customer.
Imagine that you want to spend time with a girl, but you have to wait half an hour for your passport details to be entered into the contract, checked and signed.
Now there is only one option to eliminate this inconvenience – ask for passport photos in advance and manually enter all the data into the template of the contract. As you can imagine, that’s not very convenient either.
How can digital tools help solve this problem, but also provide the basis for working with data and analytics?
Neural networks. The client sends photo passports, the neural network recognizes data and enters the template or database. It remains only to print out the ready contract or to sign in electronic form. Additionally, the advantage here is that all passports are standardized. The series and the number are always printed in the same color and font, the division code too, and the list of issuing units is not very large. To teach such a neuronetwork can be easy and fast. Cope even student in the thesis. As a result, the business saves on development, and the student gets a current thesis. Besides, every time we make a mistake, the neural net gets smarter.




