 полная версия
полная версияThe Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction. Volume 19, No. 552, June 16, 1832

Various
The Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction / Volume 19, No. 552, June 16, 1832
THE BRAHMIN BULL, IN THE ZOOLOGICAL GARDENS, REGENT'S PARK
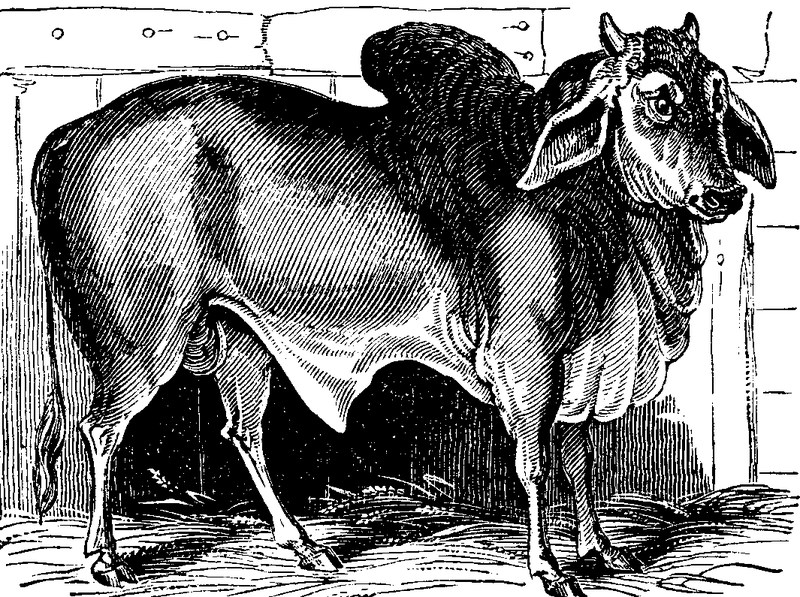
The Zoological Society possess several Zebus, or Indian oxen. These were formerly considered a distinct species, but zoologists are now of opinion that the Zebu is merely a variety of the common ox, "although," as Mr. Bennett observes, "it is difficult to ascertain the causes by which the distinctive characters of the two races have been in the process of time gradually produced."1 Their anatomical structure is precisely the same, and the only circumstances in which the two animals differ consist in the fatty hump on the shoulders of the Zebu, and in the somewhat more slender and delicate make of its legs.
The object of the Zoological Society in their collection of Zebus is the introduction of an improved breed of oxen. The larger specimens are kept at the farm at Kingston Hill, and only a pair of small ones are reserved for the Gardens, in addition to the Brahmin Bull, who occupies the central division of the Cattle Shed.

Brahmin Bull in Cattle Shed.
The specimen before us has been received by the Society from India, and is one of the largest that has ever been seen in Europe. It is equal in size to the larger breeds of our native oxen, and is of a slaty grey on the body and head; with cream-coloured legs and dewlap, the latter exceedingly long and pendulous; very short horns directed upwards and outwards; and ears of great proportional magnitude, and so flexible and obedient to the animal's will as to be moved in all directions with the greatest facility. Although a full-grown male, he is perfectly quiet, good-tempered, and submissive, and receives the caresses of strangers with apparent satisfaction.
The whole of the breeds of Zebus are treated with great veneration by the Hindoos, who hold it sinful to deprive them of life under any pretext whatever. They are in general used as beasts of draft, principally for purposes of husbandry, but a select number (of which the specimen before us is one,) are exempted from all services, and even idolized.
Bishop Heber,2 calls them Brahminy Bulls, and tells us they are turned out when calves, on different solemn occasions by wealthy Hindoos, as an acceptable offering to Siva. It would be a mortal sin to strike or injure them. They feed where they choose, and devout persons take great delight in pampering them. They are exceeding pests in the villages near Calcutta, breaking into gardens, thrusting their noses into the stalls of fruiterers and pastry-cook's shops, and helping themselves without ceremony. Like other petted animals, they are sometimes mischievous, and are said to resent with a push of their horns any delay in gratifying their wishes.
We may here in connexion with the Zoological Gardens, not inappropriately introduce the following graphic passage from the concluding Number of Mr. Landseer's "Characteristic Sketches of Animals." It appears as a "Note by the Editor," Mr. John Barrow, and represents the labours of the Zoological Society as very gratifying to the subscribers and the public.3
"By the spirit and perseverance with which they have succeeded in domiciling their magnificent collection of living animals in the Regent's Park—by the knowledge and experience they have evinced in the arrangements adopted in that establishment, and the good taste, skill, and industry, they have employed in carrying into effect its multiplied details—they have accomplished a task of far higher importance, and of infinitely nobler character, than that of merely providing for all classes of an enlightened metropolis an additional source of amusement and recreation. Such a collection, so maintained and so displayed, advances—slowly but certainly—the best interests of morals and philosophy. The curiosity which it excites, the gratification it affords, operate, though with differing degrees of intensity, on the most uncultivated and the best informed of those who visit it, to beget inquiry and awaken reflection; and in what can inquiry and reflection, thus originated, determine, but in producing or extending the most sublime impressions of the beneficence, the power, and the providence, of the Great Author of Creation? The physical mechanism of birds, the muscular energies of brutes, strike us at first with wonder, or move us with mingled terror and delight; but the activity of the human mind will not suffer us long to remain at this point of simple excitement. We involuntarily begin to analyze the properties of animals, the relations of their structure to those properties, the adaptation of the parts to the whole of that structure, and the conformity of their physical endowment and their instincts to the various habitats or regions in which they respectively exist. Whether we reason from causes to effects, as from instinct to habit; or endeavour, upon an inverted process, to arrive from the consideration of effects at causes, as from habit to instinct; or attempt, upon the analysis and analogies of admitted facts in the natural history of one animal, to deduce a theory of the history of another,—we shall find this mysterious but beautiful chain of relation and adaptation unbroken, impassable, perpetual.
"Observe how this infant colony, of which we are especially speaking, has already been peopled! The majestic rusa, captured in the sultry forests of Bengal, and the elegant gazelle, which has once bounded over the parching deserts of Barbary, have become intimate and make their couch with the white reindeer, brought from the icy wastes of Lapland. The misshapen but harmless kangaroo of New Holland is a fellow-lodger with the ferocious gnu of Southern Africa; and the patient llama, who has left the snowy sides and precipitous defiles of the Andes, contemplates without terror its formidable neighbours, the wolf of the Pyrenees, and the bear of the stupendous mountains of Thibet. In the immediate vicinity of the sacred bull, whose consecrated life has heretofore been passed in luxurious freedom or insolent enjoyment on the banks of the Ganges or the Jumna—feeds the gaunt and shaggy bison, which crops with sullen tranquillity a herbage more nutritious but less grateful to him than he loved to cull among the stony pastures of the Alleghany range, or of the howling solitudes surrounding Hudson's Bay. Though thousands of leagues have interposed between the arid sands from which they have been imported into this peaceful and common home, the camel of the Thebais, as he ruminates in his grassy parterre, surveys with composed surprise the wild dog of the Tierra del Fuego and the sharp-eyed dingo of Australia. Around the ghastly sloth-bear, disentombed from his burrows in the gloomiest woods of Mysore or Canara—and his more lively congener of Russia—the armadillo of Brazil and the pine marten of Norway display a vivacity of action and a cheerfulness of gesture which captivity seems powerless to repress. The elephant of Ceylon, and the noble wapiti of the Canadas, repose beneath the same roof; and from his bath, or his pavilion, the Arctic bear contemplates—not his native rocks and solitudes, the crashing of icebergs, and the Polar seas, alternately lashed into terrific fury or hemmed in by accumulating precipices of ice; but—monkeys of almost every size, form, and family, which gambol in the woods of Numidia or Gundwana; in the loftiest trees of Sumatra; on the mountains of Java; by the rivers of Paraguay and Hindustan; of South America and South Asia; among the jungly banks of the Godavery and the woody shores of the Pamoni, of the Oroonoko, and the Bramahputra—in short, in every sunny clime and region where the rigours of his own winter are not only unknown, but inconceivable. There is something sublime in the mere consideration of the prodigious remoteness from one another of the various points from which these animals have thus been collected; something gratifying to human pride, in the thought that neither the freezing atmosphere of the countries which surround the Pole, nor the fierce heats of those which lie beneath the Line, or are enclosed between the Tropics—neither destructive climates, nor trackless deserts, nor stormy oceans, can interpose obstacles powerful enough to quell the enterprise of man!—that the rocky caverns of the loneliest sea-coasts, and the deepest recesses of inland forests, are insufficient to protect from him the most terrible beasts of prey which inhabit them;—and that, in short, all the kingdoms of nature pay tribute to his sagacity or his power, his courage or his curiosity. This feeling is heightened, amidst the scene we have attempted to describe, by still more numerous representatives of the feathered race. Birds of the boldest wing and brightest hues—the denizens of the woods and the waters—of every variety of plumage, habit, song, and size—from the splendid macaw and toucan to the uncouth pelican and the shapeless puffin—from the gigantic ostrich to the beautiful but diminutive golden wren; in short, all the birds which are congregated in this spot come, literally, from every corner of our globe. The great alpine vulture may have sailed above the heights of Hohenlinden; the Egyptian vulture have roosted on the terraced roofs of Cairo, or among the sacred walls of Phylæ; the condor, have built in the ruined palaces of the Incas of Peru; the flamingo or the ibis have waded through the lakes and marshes which surround the desolation of Babylon; the eagle of America have ranged, perhaps daily, over those narrow straits which separate two worlds and bid defiance to all navigation! The emu has long since tracked the vast interior of that fifth continent whose inland rivers, tribes of mankind, quadrupeds, and mineral and vegetable productions, remain still, to us, sealed mysteries. The crowned crane has drawn its food from the waters of that vast lake of Tschad, in the search for which so many Europeans have perished; the little stormy petrel, borne on the surge, or wafted by the gale, has travelled to every shore that has been visited by the tempests in which it loves to rove; and the wandering stork, like the restless swallow, has nestled, indifferently, among the chimneys of Amsterdam, the campaniles of Rome or of Pisa, and on the housetops of Timbuctoo. In looking round upon these various birds and quadrupeds of all the regions of our globe—in considering the distant countries of their birth—their strangeness to us in feature or in form—the endless varieties of their instincts, their habits, their affections, their antipathies, their appetites—the several important offices they are destined to perform in what may be called the physical economy of the world,—in observing the powers of offence in some, of defence in others, and the astonishing means which have been supplied to certain classes of them destitute both of one and the other, of procuring their subsistence with equal facility,—it is surely impossible not to ascend to the contemplation of that all-wise and benevolent Power which has called all these creations into being, and thus informed and thus endowed them!"
ST. PANCRAS OLD CHURCH
(To the Editor.)In No. 546, of The Mirror, you gave a History of Old Saint Pancras Church. Will you allow me to say that it is not at a Church in the South of France, where prayers are said for the souls of those that are buried here, but at the Church of St. Peter, at Rome. A writer in the Morning Herald of August, 1825, states thus: "The History of the Old Church of Saint Pancras is not a little singular; it is one of the oldest in the county of Middlesex, and the parish it belongs to one of the largest, being eighteen miles in circumference. The name was sent from Rome by the Pope, expressly for this church, which has the only general Catholic burial ground in England; and mass is daily said in St. Peter's, at Rome, for the repose of the souls of the faithful, whose bodies are deposited therein; and it was also the last church in England whose bell tolled for mass, or in which any Catholic rites were celebrated. A few months ago an Italian showed me an Italian prayer-book, in which was a coloured drawing of St. Pancras Church; he told me it was held in great veneration at Rome, and prayers are said daily in St. Peter's, for its prosperity, and it is considered to be the oldest church now standing in Europe." A writer in the Gentleman's Magazine, 1749, states thus: "Christ's sacred altar here first Britain saw. Saint Pancras is included in that land granted by Ethelbert, the fifth King of Kent, to the Cathedral Church of St. Paul, London, about the year 603. The first mention that has been found to be made of this church, occurs in the year 1183; but it does not appear whether it was, or was not, of recent erection."
It is said there was a silver tomb in this church, which was probably taken away at the time of the commonwealth. About a mile from the church, in a field in Kentish Town, is the Gospel Oak, under which, tradition says, that Saint Austin, or one of his monks, preached. Near the church was a medicinal spa, which once attained some celebrity under the name of St. Pancras' Well, and was held in such estimation as to occasion great resort of company to it during the season. It is said the water was tasteless, but had a slight cathartic property.
Dr. Stukely, in a work published in 1756, says there was a Roman camp where St. Pancras Church stands.
The old church was repaired in 1827, when the old gallery was taken down. It was reopened under the name of St. Pancras Chapel, August 1828, by the Rev. James Moore, L.L.D., the Vicar; on which occasion he delivered a lecture, in which he gave a history of the church.
Since the year 1822, five new churches have been erected in this parish: the New St. Pancras Church, Euston-square; Regent Church, Sidmouth-street; Somers Church, Seymour-street; Camden Church, Pratt-street; and Highgate Church, on the Hill.
The first Bishop of Calcutta, the Rev. Thomas Fanshaw Middleton, D.D. was Vicar of St. Pancras. He died of a stroke of the sun, on the 8th of July, 1822. A Parishioner of St. Pancras.
MARY OF CAMBRIA.—A SONNET
(For the Mirror.)There was a maiden once would come and sitUpon our mountain, the long summer day;And watch'd the sun, till he had beauteous litThe mist-envelop'd rocks of Mona grey:Beneath whose base, the timid hinds would say,Her lover perish'd; and from that dread hour,Bereft of reason's mind ennobling ray,Poor Mary droop'd: Llanellian's fairest flower!Why gazeth she thus lone; can those soft eyesInterpret aught in each dim cloud above?Yes, there's more joy in her wild phantasiesThan reasons in its sober power could prove.List to her wild laugh now; she smiles and cries,It is my William's form; he beckons from you skies. The Author of a Tradesman's Lays 4This little metrical record is founded on fact. In the year 1808, a young female visited the grey, sterile mountain tract of Cefu Ogo, in Denbighshire, each day successively for two months. Her lover, who was a seaman on board one of the Welsh traders, had often met her there, and a tranquil, uninterrupted walk it afforded them, for exchanging the reciprocities of their mutual affection. He was lost not far from the iron-bound coast of Carnarvonshire, but nearer towards Anglesea. I saw her frequently, and her demeanour was most peaceable, except towards the evening, when her benighted fancy would conjure up a variety of pleasing expressions, which were uttered in the Welsh language; and were invariably directed towards her lover, whom she often fancied was present with her. I was happy to hear, that through the kind superintendence of the late Dr. Jones, of Denbigh, she in a great measure recovered her faculties, but died two or three years after at Liverpool.
SHAKSPERIANA
So much has been said, and said so well, respecting the writings of Shakspeare and the peculiar character of his genius, that it would be a hopeless as well as a presumptuous task to attempt adding anything to public information on that head. But I know not that any one has ventured to point out a few of those instances in which our great dramatist has stooped to plagiarize. That he must have done so, at least occasionally, is a matter of course, as no voluminous writings were ever given to the world that were not the result of study as well as original thought, for genius must ever be corrected by judgment, and what is judgment but the child of experience and study? Observation alone can tell us, that man is an imitative animal, and philosophy teaches us that his ideas are not innate; he must borrow them at first in a simple form from those around him, and though by the association of these ideas, and the gradual extension and improvement of them, he may eventually generate new ones, yet some traces cannot but remain of what was originally lodged in the mind, and will come into play as occasion may call them forth. Shakspeare was a perfect master of human nature, but he was a master of our language as well; he was indeed one of those who have improved it, but he could never have himself arrived at the degree of perfection in which he found it, had he not derived assistance from others, and made himself intimately acquainted with our purest national works of talent. Thus, he could never have been so ignorant as he is said to have been of English literature.
Little is known of Shakspeare's earlier years, except that he was sent to the free school at Stratford, where he acquired the rudiments of the learned languages; that he was never a distinguished classic is certain, but it is equally certain that he must have been acquainted with the Greek dramatists by the use of translations, though he may not have had scholarship enough to study them in the original. So many parallel passages might be drawn from this source, that the task would be an endless one; besides the fact is so well known and admitted, that it would be unnecessary. "We find him," says Mr. Pope, "very knowing in all the customs of antiquity." In Julius Caesar, Coriolanus, and other plays where the scene is laid at Rome, not only the spirit but the manners of the ancient Romans is exactly shown, and his reading in the ancient historians is no less conspicuous. It is well known at the universities of this country, that on any public examination, be the play either tragic or comic, the students are frequently required to produce parallel passages from the writings of Shakspeare: now it might indeed with some reason be supposed that occasionally the same ideas would present themselves to different minds, and where two writers are equally well acquainted with the nature of man, and equally skilled in analyzing his passions, it might well, I say, be supposed, that such true and acute observation would suggest similar ideas, and perhaps even the same method of defining them. Yet when this similarity is frequent instead of occasional, when the unusual peculiarity of the sentiment renders it startling and suspicious, then the above supposition becomes too extensive even for prejudice to admit. Such however is the case here, and so the matter stands between Shakspeare and the ancient dramatists. Even some of the machinery he has made use of is not his own. Thus, the seemingly ingenious introduction of "The Play" into Hamlet, is borrowed from an old Greek drama, where Alexander, the tyrant of Pharos, is struck with remorse for his crimes upon viewing similar cruelties to his own, practised upon the stage.
At that earlier period of literature when Shakspeare flourished, books were few in number, and consequently scarce; yet there can be no doubt that our author seized every opportunity of improving and strengthening his mind: whether he had any acquaintance with the modern languages is unknown, but he has certainly introduced many French scenes in his works, and he has taken several of his plots, such as that of Romeo and Juliet, from the Italians. As to his own language, he is said to have made the poems of Chaucer principally his study, so that it would not be quite fair to produce any plagiarisms from that writer; but I give the reader a few specimens of English literature taken from other quarters, which seem to have afforded Shakspeare ideas, or else matter, to work upon. The following passage is from one of our oldest dramas, and it will readily call to the recollection of the reader, the celebrated speech of Claudio in Measure for Measure:
"To die is sure to go we know not whither,We lie in silent darkness, and we rot.Perhaps the spirit, which is future life,Dwells, salamander-like, unharm'd in fire,Or else with wand'ring winds is blown aboutThe world; but if condemned like thoseWhom our uncertain thought imagines howling,Then the most loath'd and the most weary life,Which age, ache, penury or imprisonmentCan lay on nature, is a Paradise.To what we fear of death."The sentences that follow are from a small historical work I have fallen in with, written in old English, but without its date; about a fourth part of the matter contained in this little book is to be found woven into the different historical plays of Shakspeare, but the underwritten extracts are very nearly in his own words, allowing, of course, for the more poetical expression.
(Fall of Wolsey.) "Being near his end, he called Sir William Kingston to him, and said, 'Pray, present my duty to his majesty, who is a noble and gallant prince, and of a resolved mind, for he will venture the loss of his kingdom, rather than be contradicted in his desires. And now, Mr. Kingston, had I but served my God as diligently as I have served the king, he never would have forsaken me in my grey hairs!'" (Compare this with Cardinal Wolsey's speech to Cromwell, Henry VIII., Act iii.)
Amongst other particulars in this book, concerning Richard III. we have the following: "The Protector coming in council, seemed more than ordinarily merry, and after some other discourses, 'My lord (says he to the Bishop of Ely) you have very good strawberries in your garden in Holborn, pray let us have a dish of them.' 'With all my heart,' replied the bishop, and sent for some. Afterwards, the Protector knit his brows and his lips, and rising up in great wrath, he exclaimed, 'My lords, I have to tell you, that that old sorceress, my brother Edward's widow, and her partner, that common prostitute, Jane Shore, have by witchcraft and enchantment been contriving to take away my life, and though by God's mercy they have not been able to finish this villany, yet see the mischief they have done me; (and then he showed his left arm,) how they have caused this dear limb of mine to wither and grow useless.'" (Vide Richard III. Act iii. Scene 2.)
Shakspeare was contemporary with Bacon, and he no doubt valued and studied with attention, the writings of that great man. The working up of the splendid dialogue between Iago and Othello, may not impossibly have been suggested by this sentence of Lord Bacon: "Breaking off in the midst of what one was about to say, (as if he took himself up) breeds a greater appetite in him with whom you confer, to know more." (Vide Essays.)
But let us drop the tone of attempted criticism, which ill becomes an embryo writer at any time, and still less so when Shakspeare is the theme. Having mentioned Bacon, perhaps the following authenticated dialogue may not be uninteresting to the reader, especially as it is only to be met with in one or two scarce books:
(Shakspeare.) "I have heard, my lord, that a certain arch in Trinity College, Cambridge, would stand until a greater man than your lordship should pass through it."
(Bacon.) "Did you ever pass through it, Mr. Shakspeare?"
(Shakspeare.) "No, my lord, I never was at Cambridge."
(Bacon.) "Then we cannot decide which of us two is the greater man. I am told that most of the professors there pass under the arch without tear; which indeed shows a wise contempt of the superstition."









