 полная версия
полная версияBible Animals
Even the bivalves, which can shut themselves up between two shells, fare no better, the tongue of the Dog-Whelk rasping a hole in the hard shell in eight-and-forty hours.
Any of my readers who desire to obtain a very fair specimen of the old imperial purple can do so without difficulty.
Let him go down to the sea-shore, and collect a number of Dog-Whelks—a task of no difficulty, as a bushel may be obtained in a very short time. Let him provide himself with a piece of perfectly clean linen, or pure white woollen fabric, and a pair of fine scissors or a sharp knife.
In order to procure the animal, the shell must be broken with a sharp blow of a small hammer, and the receptacle of the colouring matter can then be seen behind the head, and recognised by its lighter hue.
When it is opened, a creamy sort of matter exudes. It is yellowish, and gives no promise of its future richness of hue. There is only one drop of this matter in each animal, and it is about sufficient in quantity to stain a piece of linen the size of a sixpence.
The best mode of seeing the full beauty of the purple is to take a number of the Molluscs, and to stain as large a surface as possible. The piece of linen should then be exposed to the rays of the sun, when it will go through a most curious series of colours. The yellow begins to turn green, and, after a while, the stained portions of the linen will be entirely green, the yellow having been vanquished by the blue. By degrees the blue predominates more and more over the yellow, until the linen is no more green, but blue. Then, just as the yellow yielded to the blue, the blue yields to red, and becomes first violet, then purple, and lastly assumes the blood-red hue of royalty.
The colour is very permanent, and, instead of fading by time, seems rather to brighten. Some two hundred years ago there was an established trade in this dye in Ireland; but it has long ago been crushed by the cheaper, though less permanent, dyes which have since been invented.
In some cases the ancients appear not to have troubled themselves with the complicated operation of taking the animal out of the shell, opening the receptacle, and squeezing the contents on the fabric to be dyed, but simply crushed the whole of the Mollusc, so as to set the colouring matter free, and steeped the cloth in the pulp. Tyre was one of the most celebrated spots for this manufacture, the "Tyrian dye" being celebrated for its richness. Heaps of broken shells remain to the present day as memorials of the long-perished manufacture.
The value which the ancients set upon this dye is shown by many passages in various books. Among others we may refer to Herodotus.
Cambyses, it appears, had a design to make war upon three nations, the Ammonians, the Carthaginians, and the Ethiopians. He determined to invade the first by land, and the second by sea; but, being ignorant of the best method of reaching the Ethiopians, he dispatched messengers to them, nominally as ambassadors, but practically as spies. He sent to the King of Ethiopia valuable presents—namely, a purple mantle, a golden necklace and bracelet, an elaborate box of perfumed ointment, and a cask of palm-wine, these evidently being considered a proof of imperial magnificence.
The Ethiopian king ridiculed the jewels, praised the wine, and asked curiously concerning the dye with which the purple mantle was stained. On being told the mode of preparation, he refused to believe the visitors, and, referring to the changing hues of the mantle and to the perfume of the ointment, he showed his appreciation of their real character by saying that the goods were deceptive, and so were the bearers.
This curious narrative occurs in the third book, chaps. 19-22.
The same historian has in another place a passing allusion to the trade of catching the purple-producing whelks. In his fourth book, chap. 151, he mentions a man who was a purple-dyer by trade, the word signifying equally one who procures the Molluscs as one who dyes the threads of which the purple fabrics are woven.
The dye-producing power is not restricted to the whelks, but is shared by other Molluscs. For example, the Diadem Staircase Shell (Scalaria diadema) secretes a substance which produces a purple hue, and the Cerithium telescopium produces a dye which retains its green hue, instead of passing into blue and red.
The Hebrew word argaman, which signifies the regal purple, occurs several times in Scripture, and takes a slightly different form according to the Chaldaic or Hebraic idiom.
For example, we find it in Exod. xxv. 4: "This is the offering which ye shall take of them: gold, and silver, and brass,
"And blue, and purple, and scarlet, and fine linen," &c. &c.
It occurs again in 2 Chron. ii. 7: "Send me now therefore a man cunning to work in gold, and in silver, and in brass, and in iron, and in purple, and crimson, and blue." These words are repeated in ver. 14.
A very important use of this word is found in Dan. v. 7: "And the king spake, and said to the wise men of Babylon, Whosoever shall read this writing, and show me the interpretation thereof, shall be clothed with scarlet" ("purple" in margin), "and have a chain of gold about his neck, and shall be the third ruler in the kingdom." Here we find that the dye in question was a regal one, that the wearing it was a matter of sumptuary law, and that the fact of being allowed to wear it was a sign that the wearer was of the very highest rank.
The Jewish Bible invariably translates the word as "red-purple."
That the preparers of the precious purple colour took care to preserve their art a secret, is evident from the writings of the Talmudists, who had the very vaguest ideas respecting the dye. They knew that it was obtained from a marine Mollusc, but thought that the creature only made its appearance once in seventy years, and that this scarcity was the cause of its costliness. They said that the dye obtained from one sea was blackish, evidently referring to the ink of the cuttle; that when it was obtained from another it was violet, and that the Phœnician waters alone produced the true red-purple hue.
They accounted for its colour by saying that the animal took the colour of the sea which it inhabited: the sea was like the sky which it reflected, the sky was like the throne of God, and the throne of God was like the sapphire. Therefore, the dye was like the sapphire. It is not impossible even that the dyers exhibited specimens of the Violet Snail, or Janthina, which is of a rich blue colour, and which would readily be accepted as the source of the Tyrian dye.
THE SNAIL
The Snail which melteth—Rendering of the Jewish Bible—Theory respecting the track of the Snail—The Hebrew word Shablul—Various Snails of Palestine.
There is a very remarkable and not very intelligible passage in Ps. lviii. 8: "As a snail which melteth, let every one of them pass away." The Jewish Bible renders the passage in a way which explains the idea which evidently prevailed at the time when the Psalms were composed: "As a snail let him melt as he passeth on."
The ancients had an idea that the slimy track made by a Snail as it crawled along was subtracted from the substance of its body, and that in consequence the farther it crept, the smaller it became, until at last it wasted entirely away. The commentators on the Talmud took this view of the case. The Hebrew word shablul, which undoubtedly does signify a Snail of some kind, is thus explained: "The Shablul is a creeping thing: when it comes out of its shell, saliva pours from itself, until it becomes liquid, and so dies."
Other explanations of this passage have been offered, but there is no doubt that the view taken by these commentators is the correct one, and that the Psalmist, when he wrote the terrible series of denunciations in which the passage in question occurs, had in his mind the popular belief regarding the gradual wasting away of the Snail as it "passeth on."
It is needless to say that no particular species of Snail is mentioned, and almost as needless to state that in Palestine there are many species of Snails, to any or all of which these words are equally applicable.
THE ONYCHA
Ingredients of the sacred incense—The Onyx, or Onycha—Derivation of the word—The Arabic Dofr—The Doofu of Abyssinia—Odour of the perfume.
In Exod. xxx. 34 there occurs a remarkable word, shecheleth, which is used to describe one of the ingredients of the incense to be used in Divine worship. The Jewish Bible renders the word rightly, "onycha," while Buxtorf renders it by "onyx," a word which is likely to mislead the reader, and to cause him to believe it to be a mineral, and not an animal substance.
The Onycha is the operculum of one of the Strombi or Wing-shells, and derives its name from the resemblance which it bears in those shells to a nail or claw. The Greek word onyx primarily signifies a nail, and is indeed the origin of our own word. Secondarily, it is used to denote a precious stone, partly because the white bands of the sardonyx bear some resemblance to the white semi-lunar marks at the base of human nails. In consequence of the resemblance of the operculum to a claw or nail, the Arabs call the Wing-shell "Dofr-el-afrit," or Afrit's (i.e. demon's) claw.
The operculum of the Wing-shells has a sharp and powerful scent when burned, and, when mixed with substances more fragrant but less powerful, it has the effect of adding to their potency if not to their fragrance.
A remarkable corroboration of this rendering occurs in Mr. Mansfield Parkyns's valuable "Life in Abyssinia." In the Appendix to vol. i. in which the commerce of Abyssinia and the Red Sea is described, the following entry occurs:—"October 5, 1848. Sailed for Suakim in a native boat. Cargo: muslins, marawdi, Surat tobacco, sandal-wood, and doofu. This article is the operculum or horny substance with which some species of shell-fish are furnished to protect the mouth of their shells. These in some parts of Nubia are used for perfume, being burnt with sandal-wood."
Here we have one or two points worthy of notice. In the first place, it is evident that the Doofu of the Abyssinians is identical with the Dofr of the Arabs. In the second place we find that it is not used alone as a perfume, but is burned together with the fragrant sandal-wood. Lastly, we find that the materials of the incense which were ordained for the special use of the Jewish worship were derived from North-Eastern Africa, and were in all probability familiar to the Jews from their long residence in Egypt.
The opercula of all the Strombidæ possess this powerful, though not very fragrant odour, which has been compared to that of spices, or castoreum, and probably acts the part which is played in many modern perfumes by materials which in themselves possess an odour the reverse of fragrant.
The mineral onyx is represented by a different Hebrew word, namely, shoham.
THE PEARL
The Pearl of Scripture—Wisdom compared to Pearl—Different renderings of the Hebrew word—Opinions of the Talmudists—Structure of Pearls—The Pearls of the marine and aquatic mussels—Pearl-fisheries of the Conway—Metaphorical uses of the Pearl—The Pearl of great price—Casting Pearls before swine—An ancient proverb.
There is only one passage in the Old Testament in which can be found the word which is translated as Pearl, and it is certain that the word in question may have another interpretation.
The word in question is gabish, and occurs in Job xxviii. 18. Treating of wisdom, in that magnificent passage beginning, "But where shall Wisdom be found, and where is the place of understanding?" the sacred writer uses these words, "No mention shall be made of coral, or of pearls: for the price of wisdom is above rubies." This is the only passage in the Bible which contains the word in its simple form, but there are two others in which it is found with the addition of the syllable el, connected with the word abne, or stone. In this form, it is translated in the Authorized Version as "hailstones."
See Ezek. xiii. 11: "Say unto them which daub it with untempered morter, that it shall fall: there shall be an overflowing shower; and ye, O great Hailstones, shall fall; and a stormy wind shall rend it." Also xxxviii. 22: "And I will plead against him with pestilence and with blood; and I will rain upon him, and upon his bands, and upon the many people that are with him, an overflowing rain, and great Hailstones, fire, and brimstone."
The Jewish Bible accepts the rendering of "hailstones" in both these passages, but affixes the mark of doubt to the word, whereas in Job xxviii. 18 it translates the word gabish as "pearls" without using any mark of doubt. In Buxtorfs Hebrew Lexicon, the word is translated as "Unio, Margarita pretiosa." It is not, however, difficult to see that the word gabish may primarily signify either ice or Pearl, and that the one may have been used metaphorically for the other.
The Talmudical writers had much to say on the subject of Pearls, but, before proceeding to their curious disquisitions, it will be as well to describe briefly the Pearl and its origin.
We are all familiar with the shining inner coating or "nacre" possessed by many bivalve molluscs, such as the common mussels and oysters. This coating is sometimes found upon extraneous substances deposited on the "mantle" of the animal, and then takes the name of "Pearl." Sometimes these are found in the common oyster.
For example, I have before me some Pearls about as large as No. 5 shot, that I took out of a single plateful of oysters. They are dull in colour and irregular in form, but they are perfect Pearls.
Then the common edible mussel frequently contains Pearls, which, however, are almost invariably small, and comparatively valueless. It is mentioned by Pliny that Julius Cæsar obtained in Britain a sufficient number of Pearls to cover a breastplate, which he dedicated to Venus, and hung in her temple. It is evident from Pliny's account that the Pearls in question were small and comparatively valueless, and it has been shrewdly suggested that Cæsar only presented them to the goddess because the Roman ladies would not have worn them.
These Pearls were in all probability obtained from the common edible mussel which grows so abundantly on our coasts, and not, as has been generally thought, from the river Pearl-mussel, which really produces Pearls of considerable value. The celebrated pearl-fishers of the Conway employ the edible mussel, and sell the Pearls at a certain price per ounce.
The scientific name of the river Pearl-shell is Unio margaritiferus, which is found in best condition in rapid mountain streams. It is plentiful in many of the Irish rivers, from which Pearls of considerable value have been procured. One of these Pearls, seen by Sir R. Redding set in a necklace, was purchased for thirty pounds by the owner, who had refused nearly three times the sum for it.
Perhaps the most celebrated Pearl-mussel is that of the Chinese, Dipsas plicatus. This species attains a considerable size, a specimen in my possession being seven inches in length and five in width.
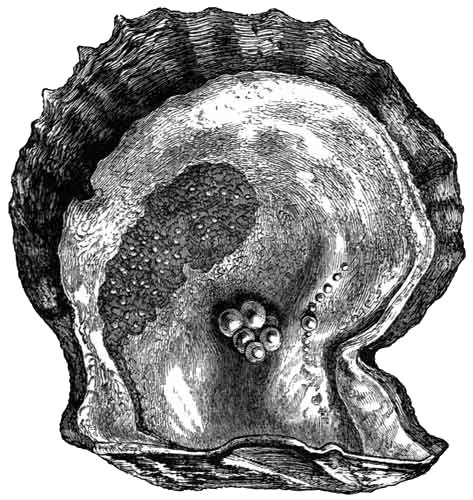
PEARL OYSTER.
"And the twelve gates were twelve pearls."—Rev. xxi. 21.
The Chinese make a singular use of this mussel. They string a number of globular pellets, and introduce them between the valves of the mussel, so that in course of time the creature deposits a coating of pearly substance upon them, and forms a very good imitation of real Pearls. They also stamp little images, popularly called josses, out of metal, and force the animal to cover them with nacre in a similar manner. Six such josses are in my specimen. Frequently, however, these incorrigible imitators actually counterfeit the sham pearls, merely taking the josses and pellets, laying them in shells from which the animal has been removed, and washing them with a solution which, when dry, looks so like nacre that it cannot be distinguished from that substance without much difficulty.
The best Pearls are those which are procured from the well-known Pearl Oyster (Meleagrina margaritifera), which is found in several parts of the world, and which constitutes the principal source of wealth to the localities where it most abounds.
The Talmudical commentators wrote rather copiously about the Pearl, respecting the nature of which they were somewhat perplexed, as it was a gem and yet not a mineral. They thought that it lay at the bottom of the sea, under flat, slab-like stones some of which had Pearls beneath them, but the greater part were without them. In consequence of the difficulty of diving and the precariousness of the search, a number of proverbs were current. For example, a person who persevered in some fruitless search was said to be a diver who brought up stones without Pearls. If one person laboured and another took the credit, it was said that the one would not have found the Pearl if the other had not brought up the stone.
In consequence of the labour and research required for seeking wisdom, it was proverbially likened to a Pearl, and in this sense we must understand the warning of our Lord, not to cast Pearls before swine. The "pearl of great price" is another form of the same metaphor.
This metaphor holds good in almost all Oriental languages.
There is also a proverb which bears a curious resemblance to the well-known "painting the lily and gilding refined gold:" "Whoso praises a priceless pearl undervalues it."
INSECTS
Insects—Beetles not mentioned in Scripture—The Locust—Various species of the insect, and different words used to signify it—The Arbeh of Scripture, and its derivation—The two migratory Locusts at rest and on the wing—The Locust swarms—Gordon Cumming's account—Progress of the insect hosts—Vain attempts to check them—Tossed up and down as a Locust—Effect of the winds on the insect—The east and the west winds—Locusts used for food—Ancient and modern travellers—The food of St. John.
Considering the vast variety of insects which are found in Egypt, Syria, and Palestine, it is somewhat remarkable that so few should be mentioned by name. Not one single coleopteran is mentioned; for, although the Hebrew word chargol, which occurs in Lev. xi. 21, 22, is rendered in the Authorized Version as "beetle," the context shows that it could not have been a coleopterous insect at all, but must have belonged to the locusts. We will therefore pass to the insect next in order.
THE LOCUST
Of the Locusts there are several species in Palestine, two of which are represented in the accompanying plate. Those on the ground are the common Migratory Locusts (Œdipoda migratoria), while those on the wing, which have long heads, are a species of Truxalis.
At least four species of Locust are mentioned in the Scriptures, one of them being the beetle of the Authorized Version; and it is probable that one or two words which are differently rendered in the Authorized Version are either names of different species of Locusts, or are synonyms for the same species.
We will first take the different Hebrew words which are translated as "Locust," and then proceed to the description of the insects themselves.
The first of those words is arbeh, about the rendering of which there is no doubt whatever. It occurs many times in the Scriptures, and, even if its signification were doubtful, the context would be sufficient to denote the proper rendering of the word. Take, for example, the account in Exod. x. of the threatened plague of Locusts. Nothing can be more terse and graphic than the description of the Arbeh, its vast multitudes, its sudden arrival, and its destructive power.
In Judges vi. 5 the word is translated as "grasshopper." "For they came up with their cattle and their tents, and they came as grasshoppers for multitude; for both they and their camels were without number: and they entered into the land to destroy it." Translating the word rightly as "Locust," we see the real force of this passage. Grasshoppers may inhabit a spot, and do no great harm, but the Locusts invade whole districts, coming like destructive armies upon it, and causing utter destruction as long as they remain.
In 1 Kings viii. 37, Solomon speaks of the presence of the Arbeh among the most terrible calamities that can befall a country, and classes it with famine, drought, pestilence, and siege. In Prov. xxx. 27 the same writer remarks on the curious fact that these creatures are gregarious and migratory, and yet have no leader, as is mostly the case with gregarious animals. "The locusts have no king, yet go they forth all of them by hands."
Allusion is made to the vast number of the Arbeh in Jer. xlvi.: "They shall cut down her forest, saith the Lord, though it cannot be searched; because they are more than the grasshoppers, and are innumerable." The voracity of the Arbeh is mentioned in Joel i. 4 and ii. 25. These are but a few passages selected out of the many in which the Arbeh is mentioned, in order to show how completely the word corresponds with the character of the Locust. The word is derived from a Hebrew root signifying multitudes, and is therefore appropriately used for these insects, which singly are so feeble, and collectively are so terrible.
Next comes the word chagab, which evidently signifies some migratory and gregarious Locust, though we cannot say precisely to which species it refers. The word is mostly translated as "grasshopper," and, from the context of several passages, it seems to have been less in size than the Arbeh, inasmuch as it is used as a metaphor to express smallness. See, for example, Numb. xiii. 31-33, where is recorded the false report of the spies whom Moses sent to inspect the land. "The men that went up said, We be not able to go up against the people; for they are stronger than we.
"And they brought up an evil report of the land which they had searched unto the children of Israel, saying, The land, through which we have gone to search it, is a land that eateth up the inhabitants thereof; and all the people that we saw in it are men of a great stature.
"And there we saw the giants, the sons of Anak, which come of the giants: and we were in our own sight as grasshoppers" (chagabim), "and so we were in their sight."
A similar metaphor is employed by the Prophet Isaiah: "It is He that sitteth upon the circle of the earth, and the inhabitants thereof are as grasshoppers" (xl. 22). And in Eccles. xii. 5 extreme weakness is forcibly indicated by the words, "the grasshopper" (chagab) "shall be a burden."
Now the two principal species of Locust which travel in bands and devastate the country are the common Migratory Locust (Œdipoda migratoria) and the Acridium peregrinum. If, therefore, the word arbeh expresses one of these insects, it is probable that the word chagab signifies the other.
The Bald Locust of Lev. xi. 22 is probably some species of Truxalis, the insects belonging to this genus having long and smooth heads. The Hebrew word is sallom, and the Jewish Bible leaves it untranslated. The word chargol which also occurs in the same passage, and is translated in the Authorized Version as "beetle," is in all probability a species of Locust, as it is classed with those insects which have "legs above their feet to leap withal."
Besides these words, we find that others translated as "caterpillar," "palmerworm," and "cankerworm" may be synonyms for the Locust, either different species, or as expressing the same species in its various stages of development. (See Lepidoptera, page 632.)
We will now pass on to the insect and its habits, taking the Migratory Locust as the type of its family.
The Locust belongs to the great order of Orthoptera, or straight-winged insects. They have, when fully developed, four wings, the two front being thick and membraneous, while the two hinder wings are large, delicate, translucent, and folded longitudinally under the front pair of wings when the insect is at rest. In the Locusts these characteristics are admirably shown. The appearance of a Locust when at rest and when flying is so different that the creature is at first sight scarcely recognisable as the same creature. When at rest, it is a compact and tolerably stout insect, with a dull though delicately coloured body; but when it takes flight it appears to attain twice its previous dimensions.






