 полная версия
полная версияThe Stones of Venice, Volume 1 (of 3)
The extreme diameter of the circle is 3 ,, 10½; its field is slightly raised above the red marbles, as shown in the section at A, on the left. A a is part of the red marble field; a b the section of the dentil moulding let into it; b c the entire breadth of the rayed zone, represented on the other side of the spandril by the line C f; c d is the white marble band let in, with the dogtooth on the face of it; b c is 7¾ inches across; c d 3¾; and at B are given two joints of the dentil (mentioned above, in the chapter on dentils, as unique in Venice) of their actual size. At C is given one of the inlaid leaves; its measure being (in inches) C f 7¾; C h ¾; f g ¾; f e 4¾, the base of the smaller leaves being of course f e – f g = 4. The pattern which occupies the other spandril is similar, except that the field b c, instead of the intersecting arcs, has only triangles of grey marble, arranged like rays, with their bases towards the centre. There being twenty round the circle, the reader can of course draw them for himself; they being isosceles, touching the dentil with their points, and being in contact at their bases: it has lost its central boss. The marbles are, in both, covered with a rusty coating, through which it is excessively difficult to distinguish the colors (another proof of the age of the ornament). But the white marbles are certainly, in places (except only the sugary dentil), veined with purple, and the grey seem warmed with green.
A trace of another of these ornaments may be seen over the 21st capital; but I doubt if the marbles have ever been inserted in the other spandrils, and their want of ornament occasions the slight meagreness in the effect of the lower story, which is almost the only fault of the building.
This decoration by discs, or shield-like ornaments, is a marked characteristic of Venetian architecture in its earlier ages, and is carried into later times by the Byzantine Renaissance, already distinguished from the more corrupt forms of Renaissance, in Appendix 6. Of the disc decoration, so borrowed, we have already an example in Plate I. In Plate VII. we have an earlier condition of it, one of the discs being there sculptured, the others surrounded by sculptured bands: here we have, on the Ducal Palace, the most characteristic of all, because likest to the shield, which was probably the origin of the same ornament among the Arabs, and assuredly among the Greeks. In Mr. Donaldson’s restoration of the gate of the treasury of Atreus, this ornament is conjecturally employed, and it occurs constantly on the Arabian buildings of Cairo.
21. ANCIENT REPRESENTATIONS OF WATER
I have long been desirous of devoting some time to an enquiry into the effect of natural scenery upon the pagan, and especially the Greek, mind, and knowing that my friend, Mr. C. Newton, had devoted much thought to the elucidation of the figurative and symbolic language of ancient art, I asked him to draw up for me a few notes of the facts which he considered most interesting, as illustrative of its methods of representing nature. I suggested to him, for an initiative subject, the representation of water; because this is one of the natural objects whose portraiture may most easily be made a test of treatment, for it is one of universal interest, and of more closely similar aspect in all parts of the world than any other. Waves, currents, and eddies are much liker each other, everywhere, than either land or vegetation. Rivers and lakes, indeed, differ widely from the sea, and the clear Pacific from the angry Northern ocean; but the Nile is liker the Danube than a knot of Nubian palms is to a glade of the Black Forest; and the Mediterranean is liker the Atlantic than the Campo Felice is like Solway moss.
Mr. Newton has accordingly most kindly furnished me with the following data. One or two of the types which he describes have been already noticed in the main text; but it is well that the reader should again contemplate them in the position which they here occupy in a general system. I recommend his special attention to Mr. Newton’s definitions of the terms “figurative” and “symbolic,” as applied to art, in the beginning of the paper.
In ancient art, that is to say, in the art of the Egyptian, Assyrian, Greek, and Roman races, water is, for the most part, represented conventionally rather than naturally.
By natural representation is here meant as just and perfect an imitation of nature as the technical means of art will allow: on the other hand, representation is said to be conventional, either when a confessedly inadequate imitation is accepted in default of a better, or when imitation is not attempted at all, and it is agreed that other modes of representation, those by figures or by symbols, shall be its substitute and equivalent.
In figurative representation there is always impersonation; the sensible form, borrowed by the artist from organic life, is conceived to be actuated by a will, and invested with such mental attributes as constitute personality.
The sensible symbol, whether borrowed from organic or from inorganic nature, is not a personification at all, but the conventional sign or equivalent of some object or notion, to which it may perhaps bear no visible resemblance, but with which the intellect or the imagination has in some way associated it.
For instance, a city may be figuratively represented as a woman crowned with towers; here the artist has selected for the expression of his idea a human form animated with a will and motives of action analogous to those of humanity generally. Or, again, as in Greek art, a bull may be a figurative representation of a river, and, in the conception of the artist, this animal form may contain, and be ennobled by, a human mind.
This is still impersonation; the form only in which personality is embodied is changed.
Again, a dolphin may be used as a symbol of the sea; a man ploughing with two oxen is a well-known symbol of a Roman colony. In neither of these instances is there impersonation. The dolphin is not invested, like the figure of Neptune, with any of the attributes of the human mind; it has animal instincts, but no will; it represents to us its native element, only as a part may be taken for a whole.
Again, the man ploughing does not, like the turreted female figure, personify, but rather typifies the town, standing as the visible representation of a real event, its first foundation. To our mental perceptions, as to our bodily senses, this figure seems no more than man; there is no blending of his personal nature with the impersonal nature of the colony, no transfer of attributes from the one to the other.
Though the conventionally imitative, the figurative, and the symbolic, are three distinct kinds of representation, they are constantly combined in one composition, as we shall see in the following examples, cited from the art of successive races in chronological order.
In Egyptian art the general representation of water is the conventionally imitative. In the British Museum are two frescoes from tombs at Thebes, Nos. 177 and 170: the subject of the first of these is an oblong pond, ground-plan and elevation being strangely confused in the design. In this pond water is represented by parallel zigzag lines, in which fish are swimming about. On the surface are birds and lotos flowers; the herbage at the edge of the pond is represented by a border of symmetrical fan-shaped flowers; the field beyond by rows of trees, arranged round the sides of the pond at right angles to each other, and in defiance of all laws of perspective.
Fig. LXXI.
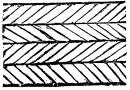
In the fresco, No. 170, we have the representation of a river with papyrus on its bank. Here the water is rendered by zigzag lines arranged vertically and in parallel lines, so as to resemble herring-bone masonry, thus. There are fish in this fresco as in the preceding, and in both each fish is drawn very distinctly, not as it would appear to the eye viewed through water. The mode of representing this element in Egyptian painting is further abbreviated in their hieroglyphic writing, where the sign of water is a zigzag line; this line is, so to speak, a picture of water written in short hand. In the Egyptian Pantheon there was but one aquatic deity, the god of the Nile; his type is, therefore, the only figurative representation of water in Egyptian art. (Birch, “Gallery of British Museum Antiquities,” Pl. 13.) In Assyrian sculpture we have very curious conventionally imitative representations of water. On several of the friezes from Nimroud and Khorsabad, men are seen crossing a river in boats, or in skins, accompanied by horses swimming (see Layard, ii. p. 381). In these scenes water is represented by masses of wavy lines somewhat resembling tresses of hair, and terminating in curls or volutes; these wavy lines express the general character of a deep and rapid current, like that of the Tigris. Fish are but sparingly introduced, the idea of surface being sufficiently expressed by the floating figures and boats. In the representation of these there is the same want of perspective as in the Egyptian fresco which we have just cited.
In the Assyrian Pantheon one aquatic deity has been discovered, the god Dagon, whose human form terminates in a fish’s tail. Of the character and attributes of this deity we know but little.
The more abbreviated mode of representing water, the zigzag line, occurs on the large silver coins with the type of a city or a war galley (see Layard, ii. p. 386). These coins were probably struck in Assyria, not long after the conquest of it by the Persians.
In Greek art the modes of representing water are far more varied. Two conventional imitations, the wave moulding and the Mæander, are well known. Both are probably of the most remote antiquity; both have been largely employed as an architectural ornament, and subordinately as a decoration of vases, costume, furniture and implements. In the wave moulding we have a conventional representation of the small crisping waves which break upon the shore of the Mediterranean, the sea of the Greeks.
Their regular succession, and equality of force and volume, are generalised in this moulding, while the minuter varieties which distinguish one wave from another are merged in the general type. The character of ocean waves is to be “for ever changing, yet the same for ever;” it is this eternity of recurrence which the early artist has expressed in this hieroglyphic.
With this profile representation of water may be compared the sculptured waves out of which the head and arms of Hyperion are rising in the pediment of the Parthenon (Elgin Room, No. (65) 91, Museum Marbles, vi. pl. 1). Phidias has represented these waves like a mass of overlapping tiles, thus generalising their rippling movement. In the Mæander pattern the graceful curves of nature are represented by angles, as in the Egyptian hieroglyphic of water: so again the earliest representation of the labyrinth on the coins of the Cnossus is rectangular; on later coins we find the curvilinear form introduced.
In the language of Greek mythography, the wave pattern and the Mæander are sometimes used singly for the idea of water, but more frequently combined with figurative representation. The number of aquatic deities in the Greek Pantheon led to the invention of a great variety of beautiful types. Some of these are very well known. Everybody is familiar with the general form of Poseidon (Neptune), the Nereids, the Nymphs and River Gods; but the modes in which these types were combined with conventional imitation and with accessory symbols deserve careful study, if we would appreciate the surpassing richness and beauty of the language of art formed out of these elements.
This class of representations may be divided into two principal groups, those relating to the sea, and those relating to fresh water.
The power of the ocean and the great features of marine scenery are embodied in such types as Poseidon, Nereus and the Nereids, that is to say, in human forms moving through the liquid element in chariots, or on the back of dolphins, or who combine the human form with that of the fish-like Tritons. The sea-monsters who draw these chariots are called Hippocamps, being composed of the tail of a fish and the fore-part of a horse, the legs terminating in web-feet: this union seems to express speed and power under perfect control, such as would characterise the movements of sea deities. A few examples have been here selected to show how these types were combined with symbols and conventional imitation.
In the British Museum is a vase, No. 1257, engraved (Lenormant et De Witte, Mon. Céram., i. pl. 27), of which the subject is, Europa crossing the sea on the back of the bull. In this design the sea is represented by a variety of expedients. First, the swimming action of the bull suggests the idea of the liquid medium through which he moves. Behind him stands Nereus, his staff held perpendicularly in his hand; the top of his staff comes nearly to the level of the bull’s back, and is probably meant as the measure of the whole depth of the sea. Towards the surface line thus indicated a dolphin is rising; in the middle depth is another dolphin; below a shrimp and a cuttle-fish, and the bottom is indicated by a jagged line of rocks, on which are two echini.
On a mosaic found at Oudnah in Algeria (Revue Archéol., iii. pl. 50), we have a representation of the sea, remarkable for the fulness of details with which it is made out.
This, though of the Roman period, is so thoroughly Greek in feeling, that it may be cited as an example of the class of mythography now under consideration. The mosaic lines the floor and sides of a bath, and, as was commonly the case in the baths of the ancients, serves as a figurative representation of the water it contained.
On the sides are hippocamps, figures riding on dolphins, and islands on which fishermen stand; on the floor are fish, crabs, and shrimps.
These, as in the vase with Europa, indicate the bottom of the sea: the same symbols of the submarine world appear on many other ancient designs. Thus in vase pictures, when Poseidon upheaves the island of Cos to overwhelm the Giant Polydotes, the island is represented as an immense mass of rock; the parts which have been under water are indicated by a dolphin, a shrimp, and a sepia, the parts above the water by a goat and a serpent (Lenormant et De Witte, i., tav. 5).
Sometimes these symbols occur singly in Greek art, as the types, for instance, of coins. In such cases they cannot be interpreted without being viewed in relation to the whole context of mythography to which they belong. If we find, for example, on one coin of Tarentum a shell, on another a dolphin, on a third a figure of Tarus, the mythic founder of the town, riding on a dolphin in the midst of the waves, and this latter group expresses the idea of the town itself and its position on the coast, then we know the two former types to be but portions of the greater design, having been detached from it, as we may detach words from sentences.
The study of the fuller and clearer examples, such as we have cited above, enables us to explain many more compendious forms of expression. We have, for instance, on coins several representations of ancient harbors.
Of these, the earliest occurs on the coins of Zancle, the modern Messina in Sicily. The ancients likened the form of this harbor to a sickle, and on the coins of the town we find a curved object, within the area of which is a dolphin. On this curve are four square elevations placed at equal distances. It has been conjectured that these projections are either towers or the large stones to which galleys were moored still to be seen in ancient harbors (see Burgon, Numismatic Chronicle, iii. p. 40). With this archaic representation of a harbor may be compared some examples of the Roman period. On a coin of Sept. Severus struck at Corinth (Millingen, Sylloge of Uned. Coins, 1837, p. 57, Pl. II., No. 30) we have a female figure standing on a rock between two recumbent male figures holding rudders. From an arch at the foot of the rock a stream is flowing: this is a representation of the rock of the Acropolis of Corinth: the female figure is a statue of Aphrodite, whose temple surmounted the rock. The stream is the fountain Pirene. The two recumbent figures are impersonations of the two harbors, Lechreum and Cenchreia, between which Corinth was situated. Philostratus (Icon. ii., c. 16) describes a similar picture of the Isthmus between the two harbors, one of which was in the form of a youth, the other of a nymph.
On another coin of Corinth we have one of the harbors in a semicircular form, the whole arc being marked with small equal divisions, to denote the archways under which the ancient galleys were drawn, subductæ; at the either horn or extremity of the harbor is a temple; in the centre of the mouth, a statue of Neptune. (Millingen, Médailles Inéd., Pl. II., No. 19. Compare also Millingen, Ancient Coins of Cities and Kings, 1831, pp. 50-61, Pl. IV., No. 15; Mionnet, Suppl. vii. p. 79, No. 246; and the harbor of Ostium, on the large brass coins of Nero, in which there is a representation of the Roman fleet and a reclining figure of Neptune.)
In vase pictures we have occasionally an attempt to represent water naturally. On a vase in the British Museum (No. 785), of which the subject is Ulysses and the Sirens, the Sea is rendered by wavy lines drawn in black on a red ground, and something like the effect of light playing on the surface of the water is given. On each side of the ship are shapeless masses of rock on which the Sirens stand.
One of the most beautiful of the figurative representations of the sea is the well-known type of Scylla. She has a beautiful body, terminating in two barking dogs and two serpent tails. Sometimes drowning men, the rari nantes in gurgite vasto, appear caught up in the coils of these tails. Below are dolphins. Scylla generally brandishes a rudder to show the manner in which she twists the course of ships. For varieties of her type see Monum. dell’Inst. Archeol. Rom., iii. Tavv. 52-3.
The representations of fresh water may be arranged under the following heads—rivers, lakes, fountains.
There are several figurative modes of representing rivers very frequently employed in ancient mythography.
In the type which occurs earliest we have the human form combined with that of the bull in several ways. On an archaic coin of Metapontum in Lucania, (see frontispiece to Millingen, Ancient Coins of Greek Cities and Kings,) the river Achelous is represented with the figure of a man with a shaggy beard and bull’s horns and ears. On a vase of the best period of Greek art (Brit. Mus. No. 789; Birch, Trans. Roy. Soc. of Lit., New Series, Lond. 1843, i. p. 100) the same river is represented with a satyr’s head and long bull’s horns on the forehead; his form, human to the waist, terminates in a fish’s tail; his hair falls down his back; his beard is long and shaggy. In this type we see a combination of the three forms separately enumerated by Sophocles, in the commencement of the Trachiniæ.
᾽Αχελῷον λέγω,ος μ᾽ ἐν τρισἰν μορφαῖσιν ἐξῄει πατρὸς,φοιτῶν ἐναργὴς αῦρος ἄλλοτ᾽ αἰόλος,δράκων ἑλικτὸς, ἄλλοτ᾽ ἄνδρειῳ κύτείβουπρῳρος, ἐκ δὲ δασκίου γενειάδοςκρουνοὶ διεῤῥαίνοντο κρηναίου ποτοῦ.In a third variety of this type the human-headed body is united at the waist with the shoulders of a bull’s body, in which it terminates. This occurs on an early vase. (Brit. Mus., No. 452.) On the coins of Œniadæ in Acarnia, and on those of Ambracia, all of the period after Alexander the Great, the Achelous has a bull’s body, and head with a human face. In this variety of the type the human element is almost absorbed, as in the first variety cited above, the coin of Metapontum, the bull portion of the type is only indicated by the addition of the horns and ears to the human head. On the analogy between these, varieties in the type of the Achelous and those under which the metamorphoses of the marine goddess Thetis are represented, see Gerhard, Auserl. Vasenb. ii. pp. 106-113. It is probable that, in the type of Thetis, of Proteus, and also of the Achelous, the singular combinations and transformations are intended to express the changeful nature of the element water.
Numerous other examples may be cited, where rivers are represented by this combination of the bull and human form, which maybe called, for convenience, the Androtauric type. On the coins of Sicily, of the archaic and also of the finest period of art, rivers are most usually represented by a youthful male figure, with small budding horns; the hair has the lank and matted form which characterises aquatic deities in Greek mythography. The name of the river is often inscribed round the head. When the whole figure occurs on the coin, it is always represented standing, never reclining.
The type of the bull on the coins of Sybaris and Thurium, in Magna Græcia, has been considered, with great probability, a representation of this kind. On the coins of Sybaris, which are of a very early period, the head of the bull is turned round; on those of Thurium, he stoops his head, butting: the first of these actions has been thought to symbolise the winding course of the river, the second, its headlong current. On the coins of Thurium, the idea of water is further suggested by the adjunct of dolphins and other fish in the exergue of the coin. The ground on which the bull stands is indicated by herbage or pebbles. This probably represents the river bank. Two bulls’ head occur on the coins of Sardis, and it has been ingeniously conjectured by Mr. Burgon that the two rivers of the place are expressed under this type.
The representation of river-gods as human figures in a reclining position, though probably not so much employed in earlier Greek art as the Androtauric type, is very much more familiar to us, from its subsequent adoption in Roman mythography. The earliest example we have of a reclining river-god is in the figure in the Elgin Room commonly called the Ilissus, but more probably the Cephissus. This occupied one angle in the western pediment of the Parthenon; the other Athenian river, the Ilissus, and the fountain Callirrhoe being represented by a male and female figure in the opposite angle; this group, now destroyed, is visible in the drawing made by Carrey in 1678.
It is probable that the necessities of pedimental composition first led the artist to place the river-god in a reclining position. The head of the Ilissus being broken off, we are not sure whether he had bull’s horns, like the Sicilian figures already described. His form is youthful, in the folds of the drapery behind him there is a flow like that of waves, but the idea of water is not suggested by any other symbol. When we compare this figure with that of the Nile (Visconti, Mus. Pio Clem., i., Pl. 38), and the figure of the Tiber in the Louvre, both of which are of the Roman period, we see how in these later types the artist multiplied symbols and accessories, ingrafting them on the original simple type of the river-god, as it was conceived by Phidias in the figure of the Ilissus. The Nile is represented as a colossal bearded figure reclining. At his side is a cornucopia, full of the vegetable produce of the Egyptian soil. Round his body are sixteen naked boys, who represent the sixteen cubits, the height to which the river rose in a favorable year. The statue is placed on a basement divided into three compartments, one above another. In the uppermost of these, waves are flowing over in one great sheet from the side of the river-god. In the other two compartments are the animals and plants of the river; the bas-reliefs on this basement are, in fact, a kind of abbreviated symbolic panorama of the Nile.
The Tiber is represented in a very similar manner. On the base are, in two compartments, scenes taken from the early Roman myths; flocks, herds, and other objects on the banks of the river. (Visconti, Mus. P. Cl. i., Pl. 39; Millin, Galerie Mythol., i. p. 77, Pl. 74, Nos. 304, 308.)
In the types of the Greek coins of Camarina, we find two interesting representations of Lakes. On the obverse of one of these we have, within a circle of the wave pattern, a male head, full face, with dishevelled hair, and with a dolphin on either side; on the reverse a female figure sailing on a swan, below which a wave moulding, and above, a dolphin.









