
Полная версия
The fourth industrial revolution glossarium: over 1500 of the hottest terms you will use to create the future
DeepMind is an artificial intelligence company founded in 2010 and later acquired by Google in 2014. DeepMind developed AlphaGo program that beat a human professional Go player for the first time.
Default access controls – the access controls that apply where a registered individual has not set controls on the registered healthcare provider organizations or nominated representatives who may access the individual’s My Health Record. This means that any registered healthcare provider organisation involved in your healthcare can access your record389.
Degree of maturity is the degree of clarity (clarity) of the definition, management, measurement, control and implementation of a specific technological process.
De-identification – process of rendering data pseudonymized or anonymized. general term for any process of removing the association between a set of identifying data and the data subject390.
Denial of Service (DoS) prevents unauthorized access to resources. It also prevents time-critical operation delays391.
Depersonalization of personal data is actions as a result of which it is impossible to determine, without the use of additional information, the belonging of personal data to a specific User or other personal data subject392.
Depthwise separable convolutional neural network (sepCNN) – a convolutional neural network architecture based on Inception, but where Inception modules are replaced with depthwise separable convolutions. Also known as Xception. A depthwise separable convolution (also abbreviated as separable convolution) factors a standard 3-D convolution into two separate convolution operations that are more computationally efficient: first, a depthwise convolution, with a depth of 1 (n ✕ n ✕ 1), and then second, a pointwise convolution, with length and width of 1 (1 ✕ 1 ✕ n). To learn more, see Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions.
Design Center – an organizational unit (the entire organization or its subdivision) that performs a full range or part of the work on creating products up to the stage of its mass production, and also has the necessary personnel, equipment and technologies for this.
Design thinking is an iterative process in which we seek to understand the user, challenge assumptions, and redefine problems in an attempt to identify alternative strategies and solutions that might not be instantly apparent with our initial level of understanding. At the same time, it provides a solution-based approach to solving problems. It is a way of thinking and working as well as a collection of hands-on methods393.
Destruction of personal data – actions, as a result of which it becomes impossible to restore the content of personal data in the personal data information system and (or) as a result of which material carriers of personal data are destroyed.
Developer Experience (DX) is a type of user experience that has been targeted at software professionals, such as software developers. An excellent DX is a central business objective, for instance, for SaaS and platform economy operators394.
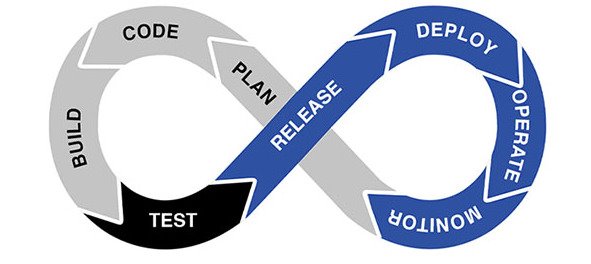
DevOps (development & operations) is a set of practices, tools, and culture philosophies that automate and integrate the processes of software development teams and IT teams. DevOps emphasizes team empowerment, collaboration and collaboration, and technology automation. The term DevOps is also understood as a special approach to organizing development teams. Its essence is that developers, testers and administrators work in a single thread – they are not each responsible for their own stage, but work together on the release of the product and try to automate the tasks of their departments so that the code moves between stages without delay. In DevOps, responsibility for the result is distributed among the entire team. Devops is an agile operational model for producing electronic services. DevOps focuses on the communication between software developers, maintenance and production personnel. DevOps aims to build an environment in which building, testing and publishing software can happen quickly, often and reliably. DevOps relies on the practices of agile development and tools that automate infrastructure management. DevOps is a particularly central term in modern SaaS software development395,396,397.
DHE Funding Database – an overview of open relevant calls to support the large-scale deployment of person-centred digital solutions. The database includes Horizon Europe, EU4Health and the Digital Europe Program398.
Diagnostic analysis is a form of advanced analytics which examines data or content to answer the question «Why did it happen?», and is characterized by techniques such as drill-down, data discovery, data mining and correlations. Diagnostic analytics takes a deeper look at data to attempt to understand the causes of events and behaviors399.
Diagnostic imaging report (or radiology) is primarily a written communication between the radiologist interpreting the imaging study (e.g. X-ray, MRI) and the clinician who requested the examination400.
Dialogflow API.AI is a platform that allows users to build brand-unique, natural language interactions for bots, applications, services, and devices. It features a Natural Language Understanding Tools to design unique conversation scenarios, design corresponding actions and analyze interactions with users.
DICOM (digital imaging and communications in medicine) is a standard protocol for the management and transmission of medical images and related data and is used in many healthcare facilities401.
Dictionary file is a special form of machine-readable codebook that contains information about the structure of a data file and the locations and, often, the names of variables in the data file. Typically, a researcher uses a dictionary file and a data file together with statistical software; the statistical software uses the dictionary to specify variables by name, rather than specifying their locations in the file402.
Digital Age is the time we live, characterized by people’s ability to transmit information without restriction and to have access to information in a way that was impossible in the past. It is also called the «informational era»403.
Digital Agenda represents the synthesis of the European Commission’s strategy for the usage of ICTs in order to achieve economic growth404.
Digital agriculture sometimes known as smart farming or e-agriculture, is tools that digitally collect, store, analyze, and share electronic data and/or information in agriculture. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations has described the digitalization process of agriculture as the digital agricultural revolution405.
Digital assets are electronic files of data that can be owned and transferred by individuals, and used as a currency to make transactions, or as a way of storing intangible content, such as computerized artworks, video or contract documents406.
Digital Body Language encompasses all the digital activities performed by an individual. Every time a person performs a Google search, visits a web page, opens a newsletter or downloads a guide, they contribute to their digital body language. Digital body language is used in building marketing automation407.
Digital Business Ecosystem it helps to support digital business models and local and regional development and growth encouraging cooperation between small organizations, entrepreneurs, local government, public administration, research, and innovation centers to promote the cohesion of local communities and enable new modes of sustainable e-business practices and open innovation408.
Digital Business Strategy is combination between IT strategy and business strategy409.
Digital Business, or Electronic Business is an activity that aims at gaining a competitive edge via (or with the help of) the web. The Internet has become one of the standard operational environments for electronic business, but there are alternatives. Digital business focusses on innovations related to the operational concept and realizes them through modern electronic solutions. On the strategic level, the core of operations is based on digitization, not merely on turning traditional processes electronic. This entire glossary of digital business can be understood as a group of things used to implement digital business strategies. Digital business is often linked to disruption-oriented approaches410.
Digital Capabilities is the term used to describe the skills and attitudes that individuals and organizations need if they are to thrive in today’s world. At an individual level we define digital capabilities as those which equip someone to live, learn and work in a digital society411.
Digital citizenship as the self-enactment of people’s role in society through the use of digital technologies, stressing the empowering and democratizing characteristics of the citizenship idea412.
Digital Company is companies, that offer digital brokerage services and advertising services without a fixed workplace413.
Digital consumer may be defined as someone using mobile devices, and in a broad sense, as e-consumer, looking for and purchasing products on the Internet, taking advantage of the content published on-line, aware of themselves and of their needs, and keen on simplifying the decisions they need to make414.
Digital contact tracing is a method of contact tracing relying on tracking systems, most often based on mobile devices, to determine contact between an infected patient and a user415.
Digital content refers to any type of media that an organization uses to engage with visitors, customers, or users of their website or applications, distributed by online delivery systems416.
Digital Curation is all about maintaining and adding value to a trusted body of digital information for future and current use; specifically, the active management and appraisal of data over the entire life cycle. Digital curation builds upon the underlying concepts of digital preservation whilst emphasizing opportunities for added value and knowledge through annotation and continuing resource management417.
Digital currency is a form of currency that is available only in digital or electronic form. It is also called digital money, electronic money, electronic currency, or cybercash418.
Digital Customer Experience is the sum of encounters experienced by the customer in various digital media. See also Customer experience419.
Digital disruption is an effect that changes the fundamental expectations and behaviors in a culture, market, industry or process that is caused by, or expressed through, digital capabilities, channels or assets420.
Digital Divide is a term that refers to the gap between demographics and regions that have access to modern information and communications technology (ICT), and those that don’t or have restricted access. This technology can include the telephone, television, personal computers and internet connectivity. Digital Divide is a concept that has become especially widespread in the last decade due to the increased importance of introducing new digital technologies in society and overcoming existing differences in the field of information and knowledge that hinder the development of basic economic and social infrastructures, in particular the energy sector, telecommunications and education421.
Digital Economy is the worldwide network of economic activities, commercial transactions and professional interactions that are enabled by information and communications technologies (ICT). It can be succinctly summed up as the economy based on digital technologies. The digital economy is an economic activity in which digital data is a key factor in production, the processing of large volumes and the use of the analysis results of which, compared with traditional forms of management, can significantly increase the efficiency of various types of production, technologies, equipment, storage, sale, delivery of goods and services422.
Digital ecosystem is a group of interconnected information technology resources that can function as a unit. Digital ecosystems are made up of suppliers, customers, trading partners, applications, third-party data service providers and all respective technologies. Digital Ecosystem is an integrated information technology resource made up of suppliers, customers, trading partners, applications, third-party data service providers and all respective technologies with Interoperability being the key to its success423,424.
Digital educational environment is an open set of information systems designed to support various tasks of the educational process. The word «open» means the ability and the right to use different information systems as part of the DSP, replace them or add new ones at your own discretion.
Digital Entrepreneurship it is the branch of science or can even be placed within the administration and/or economics, which studies the specific characteristics of entrepreneurs in the current digital era425.
Digital ethics is a form of ethics that includes systems of values and moral principles of electronic interaction between people, organizations and things.
Digital Europe Program is a new EU funding program for the period 2021—2027 focused on bringing digital technology to businesses, citizens and public administrations426.
Digital Footprint refers to the presence of a company, an organization or an individual in the digital media. For example, blog marketing aims at growing the digital footprint of a company online. Digital Footprint – the information left behind as a result of digital activities and communications stated on the Internet427,428.
Digital goods are a general phrase used to describe any goods that are stored, delivered and used in its electronic format. Digital goods are shipped electronically to the consumer through email or download from the Internet429.
Digital government services (also called e-government) are defined as service delivery within government – as well as between government and the public – using information and communication technologies430.
Digital health (digital healthcare) is a broad, multidisciplinary concept that includes concepts from an intersection between technology and healthcare. Digital health and care refers to tools and services that use information and communication technology (ICT) to improve prevention, diagnosis, treatment, monitoring and management of health and lifestyle. Digital health and care has the potential to innovate and improve access to care, quality of care, and to increase the overall efficiency of the health sector431.
Digital health literacy refers to the ability to seek, find, understand and appraise health-related information from electronic resources and apply the knowledge gained to making appropriate health decisions in order to address or solve a health problem432.
Digital image processing is the use of a digital computer to process digital images through an algorithm. As a subcategory or field of digital signal processing, digital image processing has many advantages over analog image processing. It allows a much wider range of algorithms to be applied to the input data and can avoid problems such as the build-up of noise and distortion during processing. Since images are defined over two dimensions (perhaps more) digital image processing may be modeled in the form of multidimensional systems. The generation and development of digital image processing are mainly affected by three factors: first, the development of computers; second, the development of mathematics (especially the creation and improvement of discrete mathematics theory); third, the demand for a wide range of applications in environment, agriculture, military, industry and medical science has increased433.
Digital labor represents emergent forms of labor characterized by the production of value through interaction with information and communication technologies such as digital platforms or artificial intelligence434.
Digital Literacy – the American Library Association’s (ALA) task force on Digital Literacy defines it as the ability to effectively use information and communication technologies to «find, understand, evaluate, create and communicate» information (ALA, 2013). In the context of this chapter, digital literacy is a key skill required to fully participate in technologically advanced communities. Also, Digital Literacy is having the skills you need to live, learn, and work in a society where communication and access to information is increasingly through digital technologies like internet platforms, social media, and mobile devices. It involves knowing how to use a range of technologies to find information, solve problems or complete tasks. Digital literacy is also about knowing how to act safely and respectfully online. Digital literacy refers to the skills, knowledge, and attitudes necessary to successfully use digital solutions, effectively understand and utilize data outputs from such solutions as well as actively participate in the digital information society. Although digital competences are generally improving through increased utilization of digital technologies, there remain significant digital literacy gaps within and between population groups435,436,437.
Digital Marketing means marketing that is carried out in digital media as opposed to so-called traditional marketing which focusses on media such as radio, television and newspapers. Digital marketing comprises all marketing taking place online, e-mail marketing, mobile marketing, keyword advertising, social media marketing and so on438.
Digital Maturity describes how holistically and efficiently an organization utilizes digital means in its core business. Improving digital maturity increases a company’s competitive advantage in its market. The Digital Business Maturity Model helps to roughly outline your starting situation, set goals that suit your strategy, and identify the means to raise the digital maturity level to meet those goals. The digital business maturity model also helps to distinguish between easily applicable actions and those that require profound change439.
Digital Multinational Enterprise is enterprises that perform activities primarily based on Internet and/or provide the enabling infrastructure supporting the Internet in more than one country440.
Digital object identifier (DOI) is a unique persistent identifier for a published digital object, such as an article or a study. DOIs are included in ICPSR citations to data collections. Digital Object Identifier (DOI) is a unique, persistent identifying number for a document published online. It appears on a document or in a bibliographic citation as an alphanumeric string of characters that that acts as an active link to the original digital object (journal article, report, etc.). Its purpose is to be a permanent, precise identifier for an individual document, regardless of its location on the Internet; a document retains its DOI even if its URL location changes. A publisher assigns a DOI to an article when it is published and becomes accessible online441,442.
Digital Platform is a group of technologies that are used as a basis for creating a specific and specialized system of digital interaction. Also, Digital Platform is an Internet-based software solution that brings the operators of a certain area together to form one single value network. A digital platform can be figuratively described as the heart of a platform economy operator. The central element of a digital platform is a well-documented and comprehensive API, through which the platform can receive data from or send data to the operators of the value network (or the platform databanks). APIs enable the linking together of several different digital platforms443.
Digital platform of the Institute of the Commissioner for Human Rights is a set of information technologies and systems that are used as the basis for the collection, processing, storage, exchange, statistical and predictive analysis of large structured and unstructured data on violations and measures taken to protect rights based on big data technologies, artificial intelligence, differential privacy and ensuring the creation and functioning of a specialized digital ecosystem for the protection of rights and freedoms. The term was first introduced by Alexander Chesalov in his book Digital Ecosystem of the Ombudsman Institute: Concept, Technologies, Practice (2021).
Digital platforms operator is an entity or person offering an online communication service to the public based on computer algorithms used to classify content, goods, or services offered online, or the connection of several parties for the sale of goods, the provision of a service, or the exchange or sharing of content, goods, and services444.
Digital Preservation is a term that encompasses all of the activities required to ensure that the digital content designated for long-term preservation is maintained in usable formats, for as long as access to that content is needed or desired, and can be made available in meaningful ways to current and future users445.
Digital representation – information that represents attributes and behaviors of an entity446.
Digital rights are the rights of individuals as it pertains to computer access and the ability to use, create and publish digital media. Digital rights can also refer to allowed permissions for fair use of digital copyrighted materials. Digital rights are extensions of human rights like freedom of expression and the right to privacy. The extent to which digital rights are recognized varies from country to country, but Internet access is a recognized right in several countries447.
Digital rights management (DRM) is the use of technology to control and manage access to copyrighted material. Another DRM meaning is taking control of digital content away from the person who possesses it and handing it to a computer program. DRM aims to protect the copyright holder’s rights and prevents content from unauthorized distribution and modification448.
Digital Service Environment is any environment where online activity takes place, without confrontation449.
Digital Services is all activities carried out in digital services environment or services offered by digital companies450.
Digital Services Tax is a tax on income from certain digital services or the taxation of income from the provision of certain digital services resulting from user value creation451.
Digital Shadow is a digital image of a real object. These data contain both the current status and the desired status of the object, the possible ways and processes for achieving the desired status, and the history of what the object has already gone through. It is only the combination of a digital shadow and a physical object that results in a smart thing. Every physical product can be manufactured more efficiently and with higher quality in the digitized production facility if a digital shadow has been created for it and it bears its own specific DNA452.




