 полная версия
полная версияThe Lenâpé and their Legends
That it was an Algonkin dialect, closely akin to the Nanticoke, is clear from the words and proper names preserved in the early records and locally to this day. The only word which has created doubts has been the name of "a certain imaginary spirit called Ochre."[35] It has been supposed that this was the Huron oki. But it is pure Algonkin. It is the Cree oki-sikow (être du ciel, ange, Lacombe), the Abnaki ooskoo (katini ooskoo, Bon Esprit, matsini ooskoo, Mauvais Esprit, Rasles).
It was nearly allied to that spoken in Virginia among Powhatan's subjects, as an English boy who had lived with that chieftain served as an interpreter between the settlers and the Patuxent and neighboring Indians.[36]
The Conoys were removed, before 1743, from Conejoholo to Conoy town, further up the Susquehanna, and in 1744 they joined several other fragmentary bands at Shamokin (where Sunbury, Pa., now stands). Later, they became merged with the Nanticokes.[37]
The ShawneesThe wanderings of the unstable and migratory Shawnees have occupied the attention of several writers, but it cannot be said that either their history or their affiliations have been satisfactorily worked out.[38]
Their dialect is more akin to the Mohegan than to the Delaware, and when, in 1692, they first appeared in the area of the Eastern Algonkin Confederacy, they came as the friends and relatives of the former.[39]
They were divided into four bands, as follows: —
1. Piqua, properly Pikoweu, "he comes from the ashes."
2. Mequachake, "a fat man filled," signifying completion or perfection. This band held the privilege of the hereditary priesthood.
3. Kiscapocoke.
4. Chilicothe.[40]
Of these, that which settled in Pennsylvania was the Pikoweu, who occupied and gave their name to the Pequa valley in Lancaster county.[41]
According to ancient Mohegan tradition, the New England Pequods were members of this band. These moved eastwardly from the Hudson river, and extended their conquests over the greater part of the area of Connecticut. Dr. Trumbull, however,[42] assigns a different meaning to their name, and a more appropriate one —Peguitóog, the Destroyers. Some countenance is given to the tradition by the similarity of the Shawnee to the Mohegan, standing, as it does, more closely related to it than to the Unami Delaware.
It has been argued that a band of the Shawnees lived in Southern New Jersey when that territory first came to the knowledge of the whites. On a Dutch map, drawn in 1614 or thereabouts, a tribe called Saw wanew is located on the left bank of the Delaware river, near the Bay;[43] and DeLaet speaks of the Sawanoos as living there.
I am inclined to believe that, in both these cases, the term was used by the natives around New York Bay in its simple geographical sense of "south" or "southern," and not as a tribal designation. It frequently appears with this original meaning in the Waluam Olum.
The SapooneesA tribe called the Sapoonees, or Saponies, is mentioned as living in Pennsylvania, attached to the Delawares, about the middle of the last century.[44]
They are no doubt the Saponas who once dwelt on a branch of the Great Pedee river in North Carolina, and who moved north about the year 1720.[45]
They were said to have joined the Tuscaroras, but the Pennsylvania records class them with the Delawares. Others, impressed by the similarity of Sa-po-nees to Pa-nis, have imagined they were the Pawnees, now of the west. There is not the slightest importance to be attached to this casual similarity of names.
They were called, by the Iroquois, Tadirighrones, and were distinctly identified by them with the nation known to the English as the Catawbas.[46] For a long time the two nations carried on a bitter warfare.
The AssiwikalesThis band of about fifty families, or one hundred men (about three hundred souls), are stated to have come from South Carolina to the Potomac late in the seventeenth century, and in 1731 were settled partly on the Susquehanna and partly on the upper Ohio or Alleghany. Their chief was named Aqueioma, or Achequeloma.
Their name appears to be a compound of assin, stone; and wikwam, house, and they were probably Algonkin neighbors of the Shawnees in their southern homes, and united with them in their northern migration.[47]
CHAPTER III
The Lenape or Delawares
Derivation of the Name Lenape. – The Three Sub-Tribes the Minsi or Wolf, the Unami or Turtle, and the Unalachtgo or Turkey Tribes – Their Totems – The New Jersey Tribes the Wapings, Sanhicans and Mantas – Political Constitution of the Lenape – Vegetable Food Resources – Domestic Architecture – Manufactures. – Paints and Dyes. – Dogs – Interments – Computation of Time – Picture Writing – Record Sticks – Moral and Mental Character – Religious Belief. – Doctrine of the Soul. – The Native Priests. – Religious Ceremonies.
Derivation of Lenni LenapeThe proper name of the Delaware Indians was and is Lenapé, (a as in father, é as a in mate). Dr. J. Hammond Trumbull[48] is quite wide of the mark both in calling this a "misnomer," and in attributing its introduction to Mr. Heckewelder.
Long before that worthy missionary was born, the name was in use in the official documents of the commonwealth of Pennsylvania as the synonym in the native tongue for the Delaware Indians,[49] and it is still retained by their remnant in Kansas as the proper term to designate their collective nation, embracing its sub-tribes.[50]
The derivation of Lenape has been discussed with no little learning, as well as the adjective lenni, which often precedes it (Lenni Lenape). Mr. Heckewelder stated that lenni means "original, pure," and that Lenape signifies "people."[51] Dr. Trumbull, in the course of a long examination of the words for "man" in the Algonkin dialects, reaches the conclusion that "Len-âpé" denotes "a common adult male," i. e., an Indian man; lenno lenâpé, an Indian of our tribe or nation, and, consequently, vir, "a man of men."[52] He derives these two words from the roots len (= nen), a pronominal possessive, and ape, an inseparable generic particle, "denoting an adult male."
I differ, with hesitation, from such an eminent authority; but this explanation does not, to my mind, give the precise meaning of the term. No doubt, both lenno, which in Delaware means man, and len, in Lenape, are from the pronominal radicle of the first person né, I, we, mine, our. As the native considered his tribe the oldest, as well as the most important of created beings, "ours" with him came to be synonymous with what was esteemed ancient, indigenous, primeval, as well as human, man-like, par excellence. "We" and "men" were to him the same. The initial l is but a slight modification of the n sound, and is given by Campanius as an r, "rhenus, homo."
Lenape, therefore, does not mean "a common adult male," but rather "a male of our kind," or "our men."[53]
The termination apé is said by Heckewelder to convey the idea of "walking or being in an erect posture." A comparison of the various Algonkin dialects indicates that it was originally a locative, signifying staying in a place, abiding or sitting. Thus, in Cree, apú, he is there; in Chipeway, abi, he is at home; in Delaware, n'dappin, I am here. The transfer of this idea to the male sex is seen in the Cree, ap, to sit upon, to place oneself on top, apa, to cover (animate and active); Chipeway, nabe, the male of quadrupeds. Baraga says that for a Chipeway woman to call her husband nin nabem (lit. my coverer, comp. French, femme couverte), is coarse.
The Lenape Sub-TribesThe Lenape were divided into three sub-tribes: —
1. The Minsi, Monseys, Montheys, Munsees, or Minisinks.
2. The Unami, or Wonameys.
3. The Unalachtigo.
No explanation of these designations will be found in Heckewelder or the older writers. From investigations among living Delawares, carried out at my request by Mr. Horatio Hale, it is evident that they are wholly geographical, and refer to the locations of these sub-tribes on the Delaware river.
Minsi, properly Minsiu, and formerly Minassiniu, means "people of the stony country," or briefly, "mountaineers." It is a synthesis of minthiu, to be scattered, and achsin, stone, according to the best living native authorities.[54]
Unami, or W'nãmiu, means "people down the river," from naheu, down-stream.
Unalachtigo, properly W'nalãchtko, means "people who live near the ocean," from wunalawat, to go towards, and t'kow or t'kou, wave.
Historically, such were the positions of these sub-tribes when they first came to the knowledge of Europeans.
The Minsi lived in the mountainous region at the head waters of the Delaware, above the Forks, or junction of the Lehigh river. One of their principal fires was on the Minisink plains, above the Water Gap, and another on the East Branch of the Delaware, which they called Namaes Sipu, Fish River. Their hunting grounds embraced lands now in the three colonies of Pennsylvania, New York and New Jersey. The last mentioned extinguished their title in 1758, by the payment of one thousand pounds.
That, at any time, as Heckewelder asserts, their territory extended up the Hudson as far as tide-water, and westward "far beyond the Susquehannah," is surely incorrect. Only after the beginning of the eighteenth century, when they had been long subject to the Iroquois, have we any historic evidence that they had a settlement on the last named river.
The Unamis' territory on the right bank of the Delaware river extended from the Lehigh valley southward. It was with them and their southern neighbors, the Unalachtigos, that Penn dealt for the land ceded him in the Indian Deed of 1682. The Minsis did not take part in the transaction, and it was not until 1737 that the Colonial authorities treated directly with the latter for the cession of their territory.[55]
The Unalachtigo or Turkey totem had its principal seat on the affluents of the Delaware near where Wilmington now stands. About this point, Captain John Smith, on his map (1609,) locates the Chikahokin. In later writers this name is spelled Chihohockies, Chiholacki and Chikolacki, and is stated by the historians Proud and Smith to be synonymous with Delawares.[56] The correct form is Chikelaki, from chik'eno, turkey, the modern form as given by Whipple,[57] and aki land. The n, l and r were alternating letters in this dialect.
The population was, however, very sparse, owing to the predatory incursions of the Susquehannocks, whose trails, leading up the Octorara and Conestoga, and down the Christina and Brandywine Creeks, were followed by war parties annually, and desolated the west shores of the Bay and lower river. When, in 1634, Captain Thomas Young explored the river, the few natives he found on the west side told him (through the medium of his Algonkin Virginian interpreter) that the "Minquaos" had killed their people, burnt their villages, and destroyed their crops, so that "the Indians had wholly left that side of the river which was next their enemies, and had retired themselves on the other side farre up into the woods."[58]
North of the Chikelaki, Smith's map locates the Macovks. This name does not appear in later authors, but near that site were the Okahoki band, who occupied the shores of Ridley and Crum creeks and the land between them. There they remained until 1703, when they were removed to a small reservation of 500 acres in what is now Willistown township, Chester county.[59]
The Totemic AnimalsThese three sub-tribes had each its totemic animal, from which it claimed a mystical descent. The Minsi had the Wolf, the Unami the Turtle, and the Unalachtigo the Turkey. The Unamis claimed and were conceded the precedence of the others, because their ancestor, the Turtle, was not the common animal, so-called, but the great original tortoise which bears the world on its back, and was the first of living beings, as I shall explain on a later page.
In referring to the totemic animals the common names were not used, but metaphorical expressions. Thus the Wolf was referred to as Ptuksit, Round Foot (ptuk, round, sit, foot, from the shape of its paws;) the turtle was Pakoango, the Crawler; and the turkey was Pullaeu, he does not chew,[60] referring to the bird's manner of swallowing food.
The signs of these animals were employed in their picture writing, painted on their houses or inscribed on rocks, to designate the respective sub-tribes. But only in the case of the Unamis was the whole animal represented. The Turkey tribe painted only one foot of their totemic bird, and the Minsi the extended foot of the wolf, though they sometimes added an outline of the rest of the animal.[61]
These three divisions of the Lenape were neither "gentes" nor "phratries," though Mr. Morgan has endeavored to force them into his system by stating that they were "of the nature of phratries."[62] Each was divided into twelve families bearing female names, and hence probably referring to some unexplained matriarchal system. They were, as I have called them, sub-tribes. In their own orations they referred to each other as "playmates." (Heckewelder.)
The New Jersey LenapeThe native name of New Jersey is given as Shã'akbee (English orthography: ã as in fate); or as the German missionaries wrote it, Sche'jachbi. It is a compound of bi, water, aki, land, and the adjective prefix schey, which means something long and narrow (scheyek, a string of wampum; schajelinquall, the edge of the eyes, the eyelids, etc.) This would be equivalent to "long-land water," and, according to the rules of Delaware grammar, which place the noun used in the genitive sense before the noun which governs it, the term would be more suitable to some body of water, Delaware bay or the ocean, than to the main land.
The Lenape distinctly claimed the whole of the present area of New Jersey. Their great chief, Tedyuscung, stated at the Conference at Easton (1757), that their lands reached eastward to the shore of the sea. The New Jersey tribes fully recognized their unity. As early as 1694, at an interview with Governor Markham at Philadelphia, when the famous Tamany and other Lenape chieftains were present, Mohocksey, a chief of the Jersey Indians, said: "Though we live on the other side of the water (i. e., the Delaware river), yet we reckon ourselves all one, because," he added, giving a characteristically native reason, "because we drink one water."[63]
The names, number and position of the Jersey tribes have not been very clearly made out. A pamphlet published in London, in 1648, states that there were twenty-three Indian kinglets in its area, with about 2000 warriors in all. Of these, Master Robert Evelin, a surveyor, who spent several years in the Province about 1635, names nine on the left bank of the Delaware, between Cape May and the Falls. The names are extremely corrupt, but it may be worth while giving them.[64]
1. Kechemeches, 500 men, five miles above Cape May.
2. Manteses, 100 bowmen, twelve leagues above the former.
3. Sikonesses.
4. Asomoches, 100 men.
5. Eriwoneck, 40 men.
6. Ramcock, 100 men.
7. Axion, 200 men.
8. Calcefar, 150 men.
9. Mosilian, 200 men, at the Falls.
Of these, the Mantes lived on Salem creek; Ramcock is Rancocas creek; the Eriwoneck are evidently the Ermomex of Van der Donck's map of 1656; Axion may be for Assiscunk creek, above Burlington, from Del. assiscu, mud; assiscunk, a muddy place. Lindstrom and Van der Donck name the most Southern tribe in New Jersey Naraticons. They were on and near Raccoon creek, which on Lindstrom's map is Narraticon Sipu, the Naraticon river. Probably the English name is simply a translation of the Del. nachenum, raccoon.
In 1675 the number of sachems in Jersey of sufficient importance for the then Governor Andros to treat with were four. It is noted that when he had made them the presents customary on such occasions, "They return thanks and fall a kintacoying, singing kenon, kenon."[65] This was the Delaware genan (genama, thank ye him. Zeis).
The total number in New Jersey a few years before this (1671) were estimated by the authorities at "about a thousand persons, besides women and children."[66]
The "Wakings, Opings or Pomptons," as they are named in the old records, were the tribe which dwelt on the west shore of New York harbor and southwardly, or, more exactly, "from Roeloff Jansen's Kill to the sea."[67] They were of the Minsi totem, and were the earliest of the Lenape who saw white men, when, in 1524, the keel of Verrazano was the first to plough the waters of New York harbor.
The name Waping or Oping is derived from Wapan, east, and was applied to them as the easternmost of the Lenape nation.[68] Their other name, Pompton, Mr Heckewelder identifies with pihm-tom, crooked-mouthed, though its applicability is not obvious.[69]
In the middle of the eighteenth century the remains of the Pompton Indians resided on the Raritan river. The boundaries of their territory were defined in 1756, at the Treaty of Crosswicks.
The Sanhicans occupied the Delaware shore at the Falls, near where Trenton now stands, and extended eastward along the upper Indian path quite to New York bay. Heckewelder says that this name, Sankhicani, means a gun lock, and was applied by the Lenape to the Mohawks who were first furnished with muskets by the Europeans. This has led some writers to locate a band of Mohawks at the Falls.
The Sanhicans were, however, undoubtedly Lenape. Campanius, who quotes the name of the place in 1642, classes them as such. In Van der Donck's map, of 1656, they are marked as possessing the land at the Falls and Manhattan Bay; and De Laet gives the numerals and a number of words from their dialect, which are all pure Delaware, as: —
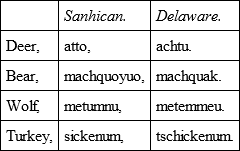
Their name has lost its first syllable. It should be assanhican. This means not merely and not originally a gun-flint, but any stone implement, from achsin, or, in the New Jersey dialect, assun, a stone, and hican, an instrument. They were distinctively "the stone-implement people."
This is plainly with reference to their manufactures near Trenton. The great deposit of post-glacial gravels at this point abound with quartzite fragments suitable for working into stone implements, and to what extent they were utilized by the natives is shown by the enormous collection, numbering over thirty thousand specimens, which Dr. Charles C. Abbott, of Trenton, has made in that immediate vicinity. A horde of over 125 beautifully chipped lance heads of quartz and jasper, and the remains of a workshop of remarkable magnitude, were evidences of the extensive manufacture that once prevailed there.
The left bank of the Delaware, from the vicinity of Burlington quite to and below Salem, was held by a warlike tribe known to the settlers as the Mantas, or Mantos, or Mandes, otherwise named the Frog Indians. They extended eastward along the main or southern Indian path, which led from the Delaware, below the mouth of Rancocas Creek, to the extensive Indian plantations or corn fields near Sandy Hook, mentioned by Campanius and Lindstrom.[70]
Mr. Henry has derived their name from mangi, great,[71] and others have suggested menatey, an island; but I do not think either of these is tenable. I have no doubt that mante is simply a mis-spelling of monthee, which is the form given by the East Jersey and Stockbridge Indians to the name of the Minsi or Monsey sub-tribe of the Delawares.[72] This is further indicated by the fact that toward the beginning of the eighteenth century they incorporated themselves wholly with the two other Lenape sub-tribes.[73] We thus find that the Minsis were not confined to the North and Northwest, as Heckewelder and others wrote, but had pressed southward in New Jersey, quite to the shores of Delaware Bay.
The New Jersey Indians disappeared rapidly. As early as 1721 an official document states that they were "but few, and very innocent and friendly."[74] When, in 1745, the missionary Brainerd visited their settlement at Crosweeksung, Burlington county, he found some "who had lived with the white people under gospel light, had learned to read, were civil, etc."[75] Those with whom he labored at this place subsequently removed to New Stockbridge, Mass., and united with the Mohegans and others there.[76]
The Swedish traveler, Peter Kalm, who spent about a year in New Jersey in 1749, observes that the disappearance of the native population was principally due to two agencies. Smallpox destroyed "incredible numbers", "but brandy has killed most of the Indians."[77]
The dialect of the New Jersey Indians was soft and vocalic, avoiding the gutturals of their northern relatives, and without the frequent unpleasant forcible expirations of the Nanticoke. A vocabulary of it, obtained for Mr. Thomas Jefferson, in 1792, at the village of Edgpiihik, West New Jersey, is in MS. in the library of the American Philosophical Society.
Political ConstitutionEach totem of the Lenape recognized a chieftain, called sachem, sakima, a word found in most Algonkin dialects, with slight variations (Chip. ogima, Cree, okimaw, Pequot, sachimma), and derived from a root ôki, signifying above in space, and by a transfer frequent in all languages, above in power. Thus, in Cree,[78] we have sâkamow, "il projecte, il montre la tête," and in Delaware, w'ochgitschi, the part above, the upper part (Zeisberger), etc.
It appears from Mr. Morgan's inquiries, that at present and of later years, "the office of sachem is hereditary in the gens, but elective among its members."[79] Loskiel, however, writing on the excellent authority of Zeisberger, states explicitly that the chief of each totem was selected and inaugurated by those of the remaining two.[80] By common and ancient consent, the chief selected from the Turtle totem was head chief of the whole Lenape nation.
These chieftains were the "peace chiefs." They could neither go to war themselves, nor send nor receive the war belt – the ominous string of dark wampum, which indicated that the tempest of strife was to be let loose. Their proper badge was the wampum belt, with a diamond-shaped figure in the centre, worked in white beads, which was the symbol of the peaceful council fire, and was called by that name.
War was declared by the people at the instigation of the "war captains," valorous braves of any birth or family who had distinguished themselves by personal prowess, and especially by good success in forays against the enemy.[81]
Nor did the authority of the chiefs extend to any infringement on the traditional rights of the gens, as, for instance, that of blood revenge. The ignorance of this limitation of the central power led to various misunderstandings at the time, on the part of the colonial authorities, and since then, by later historians. Thus, in 1728, "the Delaware Indians on Brandywine" were summoned by the Governor to answer about a murder. Their chief, Civility, answered that it was committed by the Minisinks, "over whom they had no authority."[82] This did not mean but that in some matters authority could be exerted, but not in a question relating to a feud of blood.
Agriculture and Food ResourcesThe Lenape did not depend solely on the chase for subsistence. They were largely agricultural, and raised a variety of edible plants. Indian corn was, as usual, the staple; but in addition to that, they had extensive fields of squashes, beans and sweet potatoes.[83] The hardy variety of tobacco was also freely cultivated.









