 полная версия
полная версияA Gothic Grammar
Note 3. For s from t, þ, d, before consonants (t), s. § 69, n. 2; § 71, n. 3; § 75, n. 1.
Note 4. Concerning the fonetic distinction between the spirants s and þ, cp. IF., 342.
§ 77. The sign z corresponds in Greek words to ζ; as, Zaíbaídaius, Ζεβεδαῖος; azymus, ἄζυμος. Its sound, like that of the Gr. ζ both at Wulfila's time and in New Greek, was the corresponding soft sound of s, hense a voiced dental spirant (E. z).
§ 78. (a) In Goth. words z occurs never initially.
(b) Medial z is frequent. But final z becums s, the corresponding hard sound (cp. § 79). E. g.
azêts, easy; hazjan, to praise; hazeins, praise; dius, gen. diuzis, animal; hatis, gen. hatizis, hatred; hatizôn, to be angry; huzd, trezure; gazds, sting; mizdô, reward; azgô, ashes; marzjan, to offend; talzjan, to teach; – comparativs: maiza, 'major'; frôdôza, alþiza, etc.; – pronominal forms; as, izwara, þizôs, þizê, blindaizôs; 2nd pers. sing. midl: haitaza.
(c) Most of the Gothic final ss represent z, especially the inflectional s; this reappears as z when it becums medial by an enclitic addition, for exampl, the s of the nom. ƕas, who?, but ƕazuh; is, he, but izei, who; us, out, but uzuh, uzu; dis- (as in dizuhþansat; Mk. XVI, 8); þôs, nom. pl. f., but þôzuh; weis, we; weizuh; wileis, 2nd pers. sg., but wileizu; advs.: mais (compar. maiza), more; áiris, erlier (compar. áiriza), etc.
Note 1. z is but rarely employd for final s: minz, less; II. Cor. XII, 15 (Codex B), for mins elsewhere; riqiz (4 times), darkness, beside riqis, gen. riqizis; aiz, brass, muney (only Mk. VI, 8); mimz, flesh; I. Cor. VIII, 13. – For a different view of final s for z, s. Wilmanns, Dtsch. Gramm., I, p. 86.
Note 2. The s (z) of the nom. sg. is dropt (1) after s (ss, z): drus, m., gen. drusis, fall; swês, gen. swêsis, adj., one's own; laus, lausis, loose; us-stass, f., gen. usstassais, resurrection; (2) after r immediately preceded by a short vowel: waír, waíris, man; baúr, sun; kaisar, Cæsar; anþar, other; unsar, our; but s remains unchanged after a long syllabl: akrs, field; hôrs, whoremonger; skeirs, clear; swêrs, honord; gáurs, sorrowful. An exception is the onse occurring nom. stiur, steer, calf. Cp. Brgm., I, 516; II, 531; Wrede, 'Ostg.', 177 et seq. – At a later stage of development, especially in East-Gothic, the loss of the nominativ-s occurs more extensivly. So alredy in the Documents (Neap. Doc.: Gudilub, Ufitahari); cp. Wrede, loc. cit.
Note 3. z and s interchange in the prt. of slêpan; saíslêp; Mt. VIII, 24. Lu. VIII, 23. I. Thess. IV, 14; saízlêp; Jo. XI, 11. I. Cor. XV, 6; – in the neuters in -is (gen. agisis and gen. hatizis); s. 94, n. 5.
Note 4. The z (s. c, abuv) of the prep. us is in compounds assimilated to a following r (cp. § 24, n. 2); e. g., urruns, a running out; urreisan, to (a)rise; urrûmnan (beside usrûmnan, in Codex B, II. Cor. VI, 11), to expand; onse ur for the prep. us: ur riqiza; II. Cor. IV, 6. —us remains unchanged before other sounds in cpds.; as, usagjan, to frighten; usbeidan, to abide, expect (cp. § 56, n. 2). z for s before a vowel appears only in uzôn (prt. of *usanan, to expire); Mk. XV, 37. 39; and in uzêtin (dat. of *usêta, manger); Lu. II, 7. 12. 16.
Note 5. When us is affixt to a word beginning with st, only one s is sumtimes writn: ustaig (prt. of us-steigan); Mk. III, 13; ustôþ; Lu. VIII, 55. X, 25; ustandiþ (prt. and prs. of us-standan); Mk. X, 34; ustassai (nom. usstass); Lu. XIV, 14. – Cp. twistandans (in B = twis-standans in A); II. Cor. II, 13; diskritnan (for dis-skritnan); Mt. XXVII, 51; there is no analogon for sp.
APPENDIX
GENERAL REMARKS ON THE CONSONANTS
§ 79. The Gothic soft spirants, b, d, z, finally and before the s of the nom. (cp. §§ 56. 74. 78) ar changed into the corresponding hard sounds, f, þ, s, while the fourth soft spirant, medial g, remains unchanged when final (§ 66; § 65, n. 2).
Note 1. Also the final b, d, z hav sumtimes remaind unchanged, i. e. z rarely (§ 78, n. 1), but b and d especially often in certain parts where also other forms show a later stage of development. Cp. § 56, n. 1; § 74, n. 1, and Zs. fda., 25, 226 et seq.
Note 2. Interchange between f and b, þ and d, h and g, s and z, which had taken place in proethnic Germanic according to definit laws and is better preservd in other Germanic languages ('Grammatical Change'; s. ahd. gr., § 100 et seq.), occurs in Gothic only in derivativ words; cp. g-h, § 66, n. 1; d-þ, § 74, n. 3; (z – s, § 78, n. 3); and traces of it ar seen in the inflection of the verbs þarf (§ 56, n. 3), áih (§ 203, n. 1).
§ 80. Gemination of the Gothic liquids and nasals, l, m, n, r, is frequent; also ss and a few instances of kk (§ 58, n. 1), tt (§ 69, n. 1), þþ (§ 71, n. 1), dd (§ 73, n. 1); – the more frequent exampls of gg (§§ 67. 68) ar in part of another kind.
The geminated consonants remain unchanged when final and before the s of the nominativ: skatts, full, kann, rann, wamm, gawiss; likewise before j (as in fulljan, skattja, kannjan, etc.), but ar as a rule simplified before other consonants: kant, kunþa (cp. kann); rant, 2nd pers. sg. prt., ur-runs, m., a running out (cp. rinnan); swumfsl, pond (cp. *swimman); – but uzually fullnan, only a few times fulnan.
Note. Sum instances of gemination as wel as of simplified gemination in the MSS. ar merely orthografic errors; as, allh for alh; Lu. II, 46; wisêdun (s for ss); inbranjada (nj for nnj); Jo. XV, 6; swam for swamm; Mk. XV, 36. – Such errors ar mostly corrected by the editors. Cp. Bernhardt, 'Vulfila', p. LVII.
§ 81. The changes of consonants before dentals may, as far as the Gothic is concernd, be embraced in the following rule:
Before the dentals, d, þ, t, all labial stops and spirants ar changed into f, all gutturals into h, all dentals into s, the second dental appearing always as t. E. g.
skapjan, gaskafts (§ 51, n. 2); þaúrban (*þaúrbda), þaúrfta; giban, gifts (§ 56, n. 4); —siuks, saúhts; þagkjan, þâhta (§ 58, n. 2); magan, mahta (§ 66, n. 1); —wait, waist (§ 69, n. 2); waírþan, warst (§ 71, n. 3); biudan, baust (§ 75, n. 1).
Note 1. Exceptions ar magt (2nd pers. sg.; 1st mag, § 201) and gahugds, mind.
Note 2. st often becums ss by assimilation; as, wissa, prt. of witan (§ 76, n. 1). Cp. Beitr., 7, 171 et seq.; 9, 150 et seq.; IF., 4, 341 et seq.
Note 3. The rule givn abuv from a practical standpoint of the Gothic grammar must be formulated differently from a comparativ-historical standpoint, because the discust sound-shiftings hav not originated in the Gothic language, but ar reflections of proethnic Germanic and Indo-Germanic relations of sounds. S. Brgm., I, 381 et seq.; 403 et seq.
§ 82. Assimilations occur only in combination with h (s. § 62, n. 3) and us (§ 78, n. 4).
INFLECTION
CHAP. I. DECLENSION OF SUBSTANTIVS
GENERAL PRELIMINARY REMARKS
(a) On declension in general§ 83. The Gothic declension, like that of the remaining Old-Germanic dialects, comprises three genders: the masculin, neuter and feminin.
Note 1. The neuter of all declensions resembls in form very closely the masculin; a distinction occurs in the nom. and acc. sg. and pl. only.
Note 2. A distinction of gender is wanting only with the personal prn. of the 1st and 2nd persons, with the reflexiv prn. (§ 150), and with the numeral adjectivs 4-19 (§ 141).
§ 84. The Goth. declension has two numbers: singular and plural.
Note. The dual which originally existed in all Indg. languages, is preservd in the Goth. decl. in the 1st and 2nd pers. of the personal prn. only (§ 150).
§ 85. The Goth. declension has four complete cases: nominativ, genitiv, dativ, accusativ. The vocativ is mostly identical with the nominativ, only in the singular of sum classes of declension the vocativ is different from the nominativ, but then it is always identical with the accusativ.
Note. The Goth. dativ represents several Indg. cases (dativ, locativ, ablativ, instrumental). Relics of the neuter instrumental ar stil present in the pronominal declension: þê (§ 153), ƕê (§ 159).
(b) On the declension of substantivs§ 86. The declension of substantivs in Gothic is divided into a vocalic and a consonantal declension, according as the stems of the substantivs end in a vowel or a consonant.
Note. The original form of the stem is in part unrecognizabl in the Gothic language, because the stem has blended with the endings, final vowels hav been lost, and the like, so that the division into a vocalic and a consonantal declension appears correct only in the light of the Comparativ Indo-Germanic Grammar, and but with reference to this it must be retaind. Such a division would never hav been made from an especially Gothic-Germanic standpoint.
§ 87. Of the consonantal stems in Gothic the n-stems (i. e. the stems in -an, -ôn, -ein), ar very numerous, while of other consonantal declensions but a few remains ar preservd (§ 114 et seq.). Sinse the time of Jac. Grimm the n-declension has also been calld Weak Declension.
§ 88. There ar four classes of the vocalic declension: stems in a, ô, i, u. Accordingly, we distinguish them as a-, ô-, i-, and u-declensions. The stem-characteristics ar stil clearly seen in all classes in the dat. and acc. pl.; e. g., dagam, dagans; – gibôm, gibôs; – gastim, gastins; – sunum, sununs. Sinse the time of Jacob Grimm the vocalic declension has also been calld Strong Declension.
Note 1. Of the four vocalic declensions the a- and ô-declensions ar closely connected, the a-declension containing only masculins and neuters (dags, waúrd), the ô-declension the corresponding feminins. Both classes ar therefore uzually givn as one, the a-declension.
Note 2. The Gothic a-declension corresponds to the second or o-declension in Greek and Latin (Gr. m. – ος, n. – ον; Lt. – us, – um), the Goth. ô-declension corresponds to the first or ā-declension in Gr. and Lt. Now sinse Comparativ Grammar teaches us that the Græco-Lt. vowels ar the more original ones, and that onse also the Germanic stems of the corresponding masculine and neuters must hav ended in o and those of the feminins in â, we often meet in Germanic Grammar with the term o-declension for the masculins and neuters, and with the term â-declension for the feminins.
(c) On the nominal composition§ 88a. Substantivs (and adjectivs) as the first parts of compounds end as a rule in a vowel, the connecting vowel of the components (or composition-vowel), which in the case of the vocalic stems is oftenest identical with the stem-vowel. Exampls: a-decl.: figgra-gulþ, hunsla-staþs, himina-kunds, fulla-tôjis; —i-decl.: gasti-gôþs, naudi-bandi; —u-decl.: fôtu-baúrd, hardu-haírtei, filu-waúrdei.
But the connecting vowel of the o-stems is always -a; as, aírþa-kunds, hleiþra-stakeins; the -ja of ja-stems persists when the stem is a short syllabl, but it becums i when the stem is long (cp. § 44); as, wadja-bôkôs, alja-kuns; arbi-numja, aglaiti-waúrdei; in like manner þûsundi-faþs, < stem in -jô-, nom. þûsundi (§ 145).
The n-stems hav simpl a insted of the thematic ending -an, -ôn; as, guma-kunds, fruma-baúr, wilja-halþei, qina-kunds, auga-daúrô; but mari-saiws (cp. Beitr., 8, 410).
Note 1. The composition-vowel was often dropt in Gothic, especially that of the a-stems; e. g., of a-stems: wein-drugkja (but weina-triu, weina-basi, etc.), gud-hûs, guþ-blôstreis (but guda-faúrhts, guda-laus, guþa-skaunei), laus-qiþrs, laus-handus (but lausa-waúrds), þiudan-gardi, háuh-þûhts, ain-falþs, þiu-magus (for þiwa-, § 91, n. 3); – of ja-stems: niuklahs (but niuja-satiþs), frei-hals, aglait-gastalds (but aglaiti-waúrdei); – of i-stems: brûþ-faþs, þut-haúrn (Beitr., 8, 411), twalib-wintrus (§ 141).
Note 2. Sum words show evasions of the composition-vowel: þiuþi-qiss (for þiuþa-); I. Cor. X, 16 (in Cod. A); anda-laus (for andja-); I. Tim. I, 4 (in A, but andi-laus in B); hrainja-haírts (for hraini-); Mt. V, 8; garda- in cpds. seems to be the normal form beside the stem gardi- (s. § 101): garda-waldands; Mt. X, 25. Lu. XIV, 21; miþgarda-waddjus; Eph. II, 14 (in B, but midgardi-w. in A); Beitr., 8, 432. Cp. also brôþra-lubô; Rom. XII, 10 (in A, but brôþru-lubô; I. Thess. IV, 9, in B). – The evasions occur mostly in Codex A and seem to be yunger East-Gothic forms; cp. the names in the Documents (e. g., Gudi-lub, in Ar. Doc.; Sunjai-friþas, in Neap. Doc.), and Wrede, 'Ostg.', 184.
Note 3. Beside the other consonantal stems there occur: brôþru-lubô (§ 114); cp. the preceding note; baúrgs-waddjus, a genitiv-composition (§ 116); nahta-mats (§ 116); beside mann- (§ 117) the stem mana- is found: mana-sêþs, mana-maúrþrja, unmana-riggws; and (probably according to note 1) man-leika. —sigis-laun and þruts-fill, which belong to old s-stems (s. § 94, n. 5. – Leo Meyer, Got. Spr., p. 174), may (by loss of a, according to note 1) also refer to a-stems.
Note 4. For more about the cpds. in Gothic, s. Beitr., 8, 371-460; Brgm., II, 73 et seq.; Wrede, 'Ostg.', 183 et seq.
A. VOCALIC (STRONG) DECLENSION
1. (a) A-Declension§ 89. The Gothic a-declension contains only masculins and neuters. We distinguish between pure a-stems and ja-stems.
Note. The wa-stems in Gothic differ but very litl from the pure a-stems. Their number is very small (§ 91, n. 3; § 93; § 94, n. 1).
Masculins§ 90. Paradims of the masculins. (a) Pure a-stems: dags, day (< an erlier *dagaz, proethnic Germanic *dago-z, § 88, n. 2); hlaifs, (loaf of) bred (proethnic Germanic *hlaibo-z). (b) ja-stems: haírdeis, herdsman (proethnic Germanic *herdio-z); harjis, army (proethnic Germanic *hario-z).
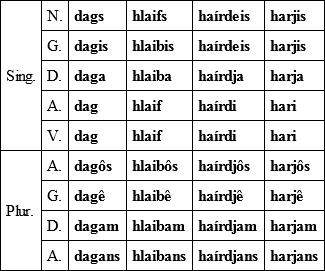
§ 91. Like dags decline many masculins; as, stains, stone; skalks, servant; tains, twig; himins, heven; fisks, fish; wigs, way; wulfs, wolf; fugls, bird (fowl); aiþs (gen. aiþis), oath.
hlaifs shows the hardening of the medial soft spirant when becuming final (cp. §§ 56. 79). So does laufs (nom. pl. laubôs), leaf.
Note 1. The declension of these masculins is identical with that of the masculin i-stems (100) in the hole sg. and in the gen. pl. Only the nom., acc., and dat. pl. can show to which declension they belong. Consequently, a number of masculins which ar not found in those pl. cases cannot with certainty be classified. The testimony of the other Germanic languages, however, wil in many cases enable us to decide. Thus akrs, field; mêgs, sun-in-law; maúrgins, morning; snaiws, snow; maiþms, present, etc., belong to the a-decl.
Note 2. Words which ar not found in the nom. sg. nor in the nom. acc. pl., may be neuter. Thus the nom. to the isolated gen. akeitis (vinegar) may be both akeits and akeit, that to the dat. staþa (shore) both staþs and staþ. Sum of such words ar undoutedly m., as is evident from the adjs. which modify them, or from the cognate dialects; e. g., slêps, sleep; wôkrs, uzury; aúhns, oven; tweifls, dout; môþs, anger (gen. môdis, § 74).
Note 3. According to the rules for final w (§ 42), þius and þiu ar givn, respectivly, as the nom. and voc. sg. to the nom. pl. þiwôs (servants), gen. þiwê– the only forms found. Cp. þiu-magus, servant, § 88a, n. 1.
Note 4. According to § 78, n. 2, the s of the nom. sg. is dropt in *ans (dat. anza), beam; *hals (halsis), neck; freihals, liberty; *ams (acc. pl. amsans), shoulder: waír, man; *gabaúr (n. pl. gabaúrôs), festiv meal; kaisar, emperor, Cæsar; stiur, steer (Neh. 5, 18; cp. Zs. fda., 37, 319).
Note 5. wêgs, wave (nom. pl. wêgôs, but dat. pl. wêgim); aiws, time (dat. pl. aiwam, acc. pl. aiwins), show a tendency to merge into the i-decl.
§ 92. The ja-stems ar subject to the rules concerning the contraction of the ji into ei (s. § 44, c and n. 1), according to which there is a distinction between the words with long and those with short stem-syllabls. Further exampls: (a) long-stemd and trisyllabic (polysyllabic): asneis, hired man; andeis, end; ƕaiteis, wheat; sipôneis, disciple; the words in -areis (Kluge, Stammbildung, §§ 8. 9; ahd. gr., § 200): laisareis, teacher; bôkareis, scribe, etc. (b) short stems: niþjis, cuzin; *andastaþjis, adversary.

