
Полная версия
Think Like a Monk

CURATE YOUR VALUES
Doing a self-audit tells you the values that have crept into your life by default. The next step is to decide what your values are and whether your choices are in alignment with them. Contemplating monk values may help you identify your own. Our teachers at the ashram explained that there are higher and lower values. Higher values propel and elevate us toward happiness, fulfillment, and meaning. Lower values demote us toward anxiety, depression, and suffering. According to the Gita, these are the higher values and qualities: fearlessness, purity of mind, gratitude, service and charity, acceptance, performing sacrifice, deep study, austerity, straightforwardness, nonviolence, truthfulness, absence of anger, renunciation, perspective, restraint from fault finding, compassion toward all living beings, satisfaction, gentleness/kindness, integrity, determination. (Notice that happiness and success are not among these values. These are not values, they are rewards—the end game—and we will address them further in Chapter Four.)
The six lower values are greed, lust, anger, ego, illusion, and envy. The downside of the lower values is that they so readily take us over when we give them space to do so, but the upside is that there are a lot fewer of them. Or, as my teacher Gauranga Das reminded us, there are always more ways to be pulled up than to be pulled down.
We can’t pull a set of values out of thin air and make sweeping changes overnight. Instead, we want to let go of the false values that fill the space in our lives. The ashram gave us monks the opportunity to observe nature, and our teachers called our attention to the cycles of all living things. Leaves sprout, transform, and drop. Reptiles, birds, and mammals shed their skins, feathers, fur. Letting go is a big part of the rhythm of nature, as is rebirth. We humans cling to stuff—people, ideas, material possessions, copies of Marie Kondo’s book—thinking it’s unnatural to purge, but letting go is a direct route to space (literally) and stillness. We separate ourselves—emotionally if not physically—from the people and ideas who fill up our lives, and then we take time to observe the natural inclinations that compel us.
Choices come along every day, and we can begin to weave values into them. Whenever we make a choice, whether it’s as big as getting married or as small as an argument with a friend, we are driven by our values, whether they are high or low. If these choices work out well for us, then our values are in alignment with our actions. But when things don’t work out, it’s worth revisiting what drove the decision you made.
TRY THIS: PAST VALUES
Reflect on the three best and three worst choices you’ve ever made. Why did you make them? What have you learned? How would you have done it differently?
Take a close look at your answers to the Try This above—buried in them are your values. Why did you make a choice? You may have been with the right or wrong person for the same reason: because you value love. Or maybe you moved across the country because you wanted a change. The underlying value may be adventure. Now do the same thing for the future. Look at your biggest goals to see if they’re driven by other people, tradition, or media-driven ideas of how we should live.
TRY THIS: VALUE-DRIVEN DECISIONS
For the next week, whenever you spend money on a nonnecessity or make a plan for how you will spend your free time, pause, and think: What is the value behind this choice? It only takes a second, a flash of consideration. Ideally, this momentary pause becomes instinctive, so that you are making conscious choices about what matters to you and how much energy you devote to it.
FILTER OEOS, DON’T BLOCK THEM
Once you filter out the noise of opinions, expectations, and obligations (OEOs), you will see the world through different eyes. The next step is inviting the world back in. When I ask you to strip away outside influences, I don’t want you to tune out the whole world indefinitely. Your monk mind can and must learn from other people. The challenge is to do so consciously by asking ourselves simple questions: What qualities do I look for/admire in family, friends, or colleagues? Are they trust, confidence, determination, honesty? Whatever they may be, these qualities are, in fact, our own values—the very landmarks we should use to guide ourselves through our own lives.
When you are not alone, surround yourself with people who fit well with your values. It helps to find a community that reflects who you want to be. A community that looks like the future you want. Remember how hard it was for me to start living like a monk during my final year of college? And now, it’s hard for me to live in London. Surrounded by the people I grew up with and their ways of living, I’m tempted to sleep in, gossip, judge others. A new culture helped me redefine myself, and another new culture helped me continue on my path.
Every time you move homes or take a different job or embark on a new relationship, you have a golden opportunity to reinvent yourself. Multiple studies show that the way we relate to the world around us is contagious. A twenty-year study of people living in a Massachusetts town showed that both happiness and depression spread within social circles. If a friend who lives within a mile of you becomes happier, then the chance that you are also happy increases by 25 percent. The effect jumps higher with next-door neighbors.
Who you surround yourself with helps you stick to your values and achieve your goals. You grow together. If you want to run a 2:45 marathon, you don’t train with people who run a 4:45. If you want to be more spiritual, expand your practice with other spiritual people. If you want to grow your business, join a local chamber of commerce or an online group of business owners who are similarly driven toward that kind of success. If you’re an overworked parent who wants to make your kids your priority, cultivate relationships with other parents who prioritize their kids, so you can exchange support and advice. Better yet, where possible, cross groups: Foster relationships with family-oriented spiritual entrepreneurs who run marathons. Okay, I’m kidding, yet in today’s world where we have more ways to connect than ever, platforms like LinkedIn and Meetup and tools like Facebook groups make it easier than ever to find your tribe. If you’re looking for love, look in places that are value-driven, like service opportunities, fitness or sports activities, a series of lectures on a topic that interests you.
If you’re not sure where others fit in relation to your values, ask yourself a question: When I spend time with this person or group, do I feel like I’m getting closer to or further away from who I want to be? The answer could be clear-cut; it’s obvious if you’re spending four hours at a time playing FIFA soccer on PS2 (not that I’ve ever done that) versus engaging in meaningful interaction that improves the quality of your life. Or the answer could be more vague—a feeling like irritability or mental fuzziness after you spend time with them. It feels good to be around people who are good for us; it doesn’t feel good to be around people who don’t support us or bring out our bad habits.
TRY THIS: COMPANION AUDIT
Over the course of a week, make a list of the people with whom you spend the most time. List the values that you share next to each person. Are you giving the most time to the people who align most closely with your values?
Who you talk to, what you watch, what you do with your time: all of these sources push values and beliefs. If you’re just going from one day to the next without questioning your values, you’ll be swayed by what everyone else—from your family to hordes of marketing professionals—wants you to think. I remind myself of the moment in the storeroom all the time. A thought comes into my mind and I ask myself, Does this fit my chosen values or those that others have selected for me? Is this dust or is it me?
When you give yourself space and stillness, you can clear the dust and see yourself, not through others’ eyes, but from within. Identifying your values and letting them guide you will help you filter external influences. In the next chapter these skills will help you filter out unwanted attitudes and emotions.
TWO
NEGATIVITY
The Evil King Goes Hungry
It is impossible to build one’s own happiness on the unhappiness of others.
—Daisaku Ikeda
It is the summer after my third year of college. I have returned from spending a month at the ashram and am now interning for a finance firm. I’m at lunch with a couple of my colleagues—we’ve grabbed sandwiches and brought them to the concrete courtyard in front of the building, where low walls crisscross the hardscaping and young people in suits eat speedy lunches, defrosting in the summer sun before returning to the hyper-air-conditioned building. I am a monk out of water.
“Did you hear about Gabe?” one of my friends says in a loud whisper. “The partners tore apart his presentation.”
“That dude,” another friend says, shaking his head. “He’s sinking fast.”
I flash back to a class Gauranga Das taught called “Cancers of the Mind: Comparing, Complaining, Criticizing.” In the class, we talked about negative thought habits, including gossip. One of the exercises we did was keeping a tally of every criticism we spoke or thought. For each one, we had to write down ten good things about the person.
It was hard. We were living together, in close quarters. Issues came up, most of them petty. The average time for a monk’s shower was four minutes. When there was a line at the showers, we would take bets on who was taking too long. (This was the only betting we did. Because: monks.) And though the snorers were relegated to their own room, sometimes new practitioners emerged, and we rated their snores on a scale of motorcycles: this monk’s a Vespa; that one’s a Harley-Davidson.
I went through the exercise, dutifully noting every criticism I let slip. Next to each, I jotted down ten positive qualities. The point of the exercise wasn’t hard to figure out—every person was more good than bad—but seeing it on the page made the ratio sink in. This helped me see my own weaknesses differently. I tended to focus on my mistakes without balancing them against my strengths. When I found myself being self-critical, I reminded myself that I too had positive qualities. Putting my negative qualities in context helped me recognize the same ratio in myself, that I am more good than bad. We talked about this feedback loop in class: When we criticize others, we can’t help but notice the bad in ourselves. But when we look for the good in others, we start to see the best in ourselves too.
The guy sitting next to me on the wall nudges me out of my reverie. “So you think he’ll last?”
I’ve lost track of what we’re talking about. “Who?” I ask.
“Gabe—he shouldn’t have been hired in the first place, right?”
“Oh, I don’t know,” I say.
Once I’d spent time in the ashram, I became very sensitive to gossip. I’d gotten used to conversations with primarily positive energy. When I first arrived back in the world, I was awkwardly silent. I didn’t want to be the morality police, but I also didn’t want to participate. As the Buddha advised, “Do not give your attention to what others do or fail to do; give it to what you do or fail to do.” I quickly figured out to say things like “Oh, I’m not sure …” or “I haven’t heard anything.” Then I’d shift the conversation to something more positive. “Did you hear they’ve asked Max to stay on? I’m psyched for him.” Gossip has value in some situations: It helps society regulate what is acceptable behavior, and we often use it to see if others agree with our judgments about other people’s behavior and therefore our values. But there are kinder ways to negotiate these questions. More often, we use gossip to put others down, which can make us feel superior to them and/or bolster our status in a group.
Some of my friends and colleagues stopped trying to gossip with me altogether; we had real conversations instead. Some trusted me more, realizing that since I didn’t gossip with them, I wouldn’t gossip about them. If there were people who thought I was just plain boring, well, I have nothing bad to say about them.
NEGATIVITY IS EVERYWHERE
You wake up. Your hair looks terrible. Your partner complains that you’re out of coffee. On the way to work some driver who’s texting makes you miss the light. The news on the radio is worse than yesterday. Your coworker whispers to you that Candace is pretending to be sick again. … Every day we are assaulted by negativity. No wonder we can’t help but dish it out as well as receive it. We report the aches and pains of the day rather than the small joys. We compare ourselves to our neighbors, complain about our partners, say things about our friends behind their backs that we would never say to their faces, criticize people on social media, argue, deceive, even explode into anger.
This negative chatter even takes place throughout what we might consider to be a “good day,” and it’s not part of anyone’s plan. In my experience, nobody wakes up and thinks, How can I be mean to or about other people today? or How can I make myself feel better by making others feel worse today? Still, negativity often comes from within. We have three core emotional needs, which I like to think of as peace, love, and understanding (thanks Nick Lowe and Elvis Costello). Negativity—in conversation, emotions, and actions—often springs from a threat to one of the three needs: a fear that bad things are going to happen (loss of peace), a fear of not being loved (loss of love), or a fear of being disrespected (loss of understanding). From these fears stem all sorts of other emotions—feeling overwhelmed, insecure, hurt, competitive, needy, and so on. These negative feelings spring out of us as complaints, comparisons, and criticisms and other negative behaviors. Think of the trolls who dive onto social media, dumping ill will on their targets. Perhaps their fear is that they aren’t respected, and they turn to trolling to feel significant. Or perhaps their political beliefs are generating the fear that their world is unsafe. (Or maybe they’re just trying to build a following—fear certainly doesn’t motivate every troll in the world.)
For another example, we all have friends who turn a catch-up phone call into an interminable vent session describing their job, their partner, their family—what’s wrong, what’s unfair, what’s never going to change. For these people, nothing ever seems to go right. This person may be expressing their fear that bad things are going to happen—their core need for peace and security is threatened.
Bad things do happen. In our lives, we’re all victims at some point—whether we’re being racially profiled or being cut off in traffic. But if we adopt a victim mentality, we’re more likely to take on a sense of entitlement and to behave selfishly. Stanford psychologists took 104 subjects and assigned them to one of two groups—one told to write a short essay about a time they were bored, and the other to write about a time when life seemed unfair or when they felt “wronged or slighted by someone.” Afterward, the participants were asked if they wanted to help the researchers with an easy task. Those who’d written about a time they’d been wronged were 26 percent less likely to help the researchers. In a similar study, participants who identified with a victim mindset were not only more likely to express selfish attitudes afterward, they were also more likely to leave behind trash and even take the experimenters’ pens!
NEGATIVITY IS CONTAGIOUS
We’re social creatures who get most of what we want in life—peace, love, and understanding—from the group we gather around us. Our brains adjust automatically to both harmony and disagreement. We’ve already talked about how we unconsciously try to please others. Well, we also want to agree with others. Research has proven that most humans value social conformity so much that they’ll change their own responses—even their perceptions—to align with the group, even when the group is blatantly wrong.
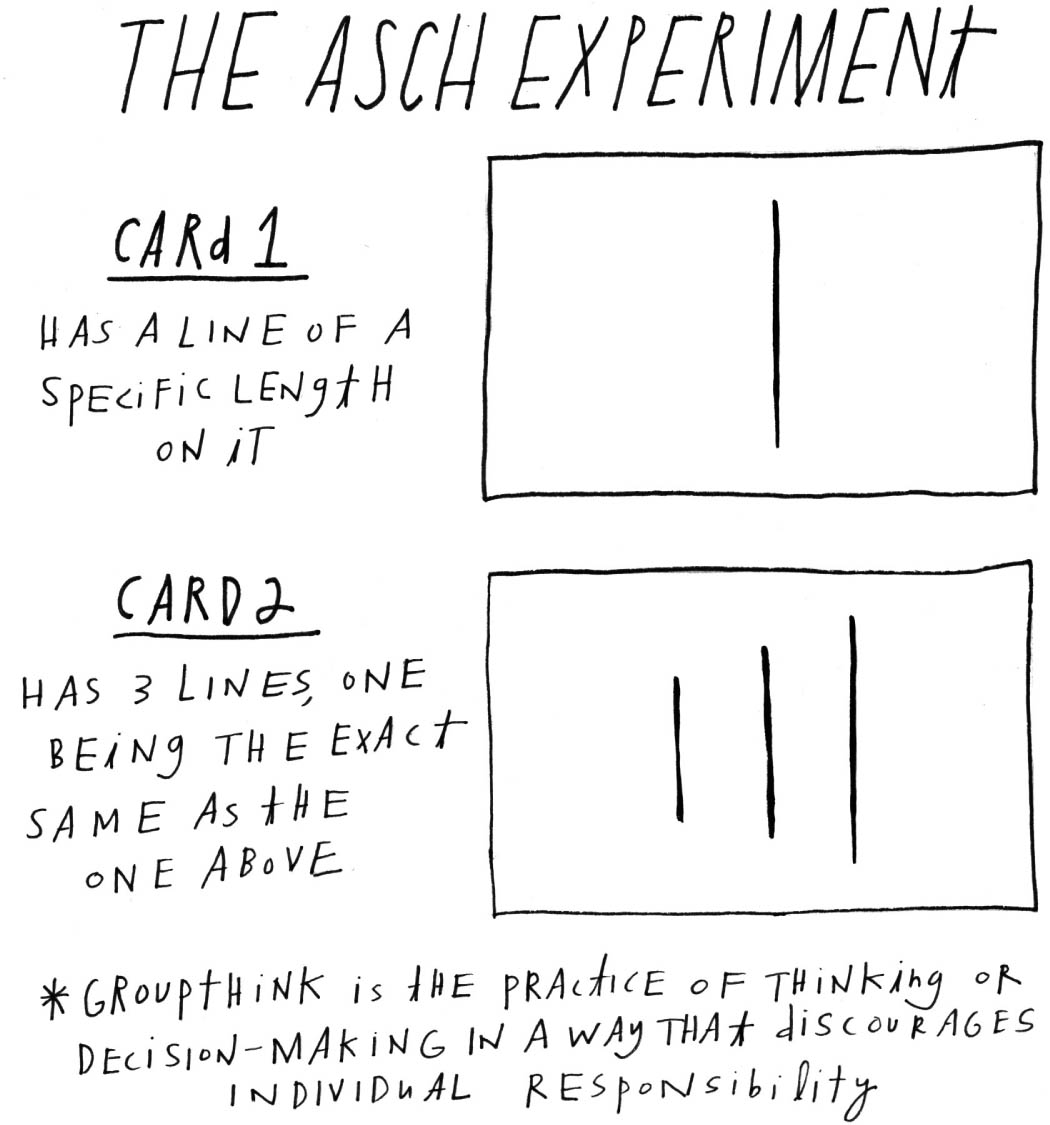
In the 1950s Solomon Asch gathered groups of college students and told them they were doing a vision test. The catch was that in each group, everyone was an actor except one person: the subject of the test.
Asch showed participants an image of a “target” line first, then of a series of three lines: one shorter, one longer, and one that was clearly the same length as the target line. The students were asked which line matched the length of the target line. Sometimes the actors gave correct answers, and sometimes they purposefully gave incorrect answers. In each case, the real study participant answered last. The correct answer should have been obvious. But, influenced by the actors, about 75 percent of the subjects followed the crowd to give an incorrect response at least once. This phenomenon has been called groupthink bias.
We’re wired to conform. Your brain would rather not deal with conflict and debate. It would much prefer to lounge in the comfort of like-mindedness. That’s not a bad thing if we’re surrounded by, say, monks. But if we’re surrounded by gossip, conflict, and negativity, we start to see the world in those terms, just like the people who went against their own eyes in Asch’s line experiment.
The instinct for agreement has a huge impact on our lives. It is one of the reasons why, in a culture of complaint, we join the fray.
And the more negativity that surrounds us, the more negative we become. We think that complaining will help us process our anger, but research confirms that even people who report feeling better after venting are still more aggressive post-gripe than people who did not engage in venting.
At the Bhaktivedanta Manor, the temple’s London outpost, there was one monk who drove me crazy. If I asked him how he was in the morning, he’d tell me about how badly he’d slept and whose fault it was. He complained that the food was bad, and yet there was never enough. It was relentless verbal diarrhea, so negative that I never wanted to be around him.
Then I found myself complaining about him to the other monks. And so I became exactly what I was criticizing. Complaining is contagious, and he’d passed it on to me.
Studies show that negativity like mine can increase aggression toward random, uninvolved people, and that the more negative your attitude, the more likely you are to have a negative attitude in the future. Studies also show that long-term stress, like that generated by complaining, actually shrinks your hippocampus—that’s the region of your brain that affects reasoning and memory. Cortisol, the same stress hormone that takes a toll on the hippocampus, also impairs your immune system (and has loads of other harmful effects). I’m not blaming every illness on negativity, but if remaining positive can prevent even one of my winter colds, I’m all for it.

TYPES OF NEGATIVE PEOPLE
Negative behaviors surround us so constantly that we grow accustomed to them. Think about whether you have any of the following in your life:
Complainers, like the friend on the phone, who complain endlessly without looking for solutions. Life is a problem that will be hard if not impossible to solve.
Cancellers, who take a compliment and spin it: “You look good today” becomes “You mean I looked bad yesterday?”
Casualties, who think the world is against them and blame their problems on others.
Critics, who judge others for either having a different opinion or not having one, for any choices they’ve made that are different from what the critic would have done.
Commanders, who realize their own limits but pressure others to succeed. They’ll say, “You never have time for me,” even though they’re busy as well.
Competitors, who compare themselves to others, controlling and manipulating to make themselves or their choices look better. They are in so much pain that they want to bring others down. Often we have to play down our successes around these people because we know they can’t appreciate them.
Controllers, who monitor and try to direct how their friends or partners spend time, and with whom, and what choices they make.
You can have fun with this list, seeing if you can think of someone to fit each type. But the real point of it is to help you notice and frame these behaviors when they come at you. If you put everyone into the same box of negativity (“They’re so annoying!”), you aren’t any closer to deciding how to manage each relationship.
On the day I moved to the ashram with six other new monks traveling from England, they told us to think of our new home as a hospital, where we were all patients. Becoming a monk, detaching from material life, was not seen as an achievement in and of itself. It simply meant that we were ready to be admitted to a place of healing where we could work to overcome the illnesses of the soul that infected us and weakened us.
In a hospital, as we all know, even the doctors get sick. Nobody is immune. The senior monks reminded us that everyone had different sicknesses, everyone was still learning, and that, just as we would not judge anyone else’s health problems, we shouldn’t judge someone who sinned differently. Gauranga Das repeated this advice in brief metaphorical form that we often used to remind ourselves not to harbor negative thoughts toward others: Don’t judge someone with a different disease. Don’t expect anyone to be perfect. Don’t think you are perfect.
Instead of judging negative behavior, we try to neutralize the charge, or even reverse it to positive. Once you recognize a complainer isn’t looking for solutions, you realize you don’t have to provide them. If a commander says, “You’re too busy for me,” you can say, “Should we find a time that works for both of us?”
REVERSE EXTERNAL NEGATIVITY
The categories above help us step away from the negative person in order to make clearheaded decisions about our role in the situation. The monk way is to dig to the root, diagnose, and clarify a situation so you can explain it simply to yourself. Let’s use this approach to define strategies for dealing with negative people.
Become an Objective Observer
Monks lead with awareness. We approach negativity—any type of conflict, really—by taking a step back to remove ourselves from the emotional charge of the moment. Catholic monk Father Thomas Keating said, “There is no commandment that says we have to be upset by the way other people treat us. The reason we are upset is because we have an emotional program that says, ‘If someone is nasty to me, I cannot be happy or feel good about myself.’ … Instead of reacting compulsively and retaliating, we could enjoy our freedom as human beings and refuse to be upset.” We step away, not literally but emotionally, and look at the situation as if we are not in the middle of it. We will talk more about this distance, which is called detachment, in the next chapter. For now, I’ll say that it helps us find understanding without judgment. Negativity is a trait, not someone’s identity. A person’s true nature can be obscured by clouds, but, like the sun, it is always there. And clouds can overcome any of us. We have to understand this when we deal with people who exude negative energy. Just like we wouldn’t want someone to judge us by our worst moments, we must be careful not to do that to others. When someone hurts you, it’s because they’re hurt. Their hurt is simply spilling over. They need help. And as the Dalai Lama says, “If you can, help others; if you cannot do that, at least do not harm them.”

