 полная версия
полная версияOur Cats and All About Them
The foregoing is by way of advice; in buying a white cat—or, in fact, any other—ascertain for a certainty that it is not deaf.
A short time since I saw a white Persian cat with deep blue eyes sitting at the door of a tobacconist's, at the corner of the Haymarket, London. On inquiry I found that the cat could hear perfectly, and was in no way deficient of health and strength; and this is by no means a solitary instance.
MISS SAUNDERS' "TIGER."
THE ANGORA
The Angora cat, as its name indicates, comes from Angora, in Western Asia, a province that is also celebrated for its goats with long hair, which is of extremely fine quality. It is said that this deteriorates when the animal leaves that locality. This may be so, but that I have no means of proving; yet, if so, do the Angora cats also deteriorate in the silky qualities of their fur? Or does it get shorter? Certain it is that many of the imported cats have finer and longer hair than those bred in this country; but when are the latter true bred? Even some a little cross-bred will often have long hair, but not of the texture as regards length and silkiness which is to be noted in the pure breed. The Angora cats, I am told, are great favourites with the Turks and Armenians, and the best are of high value, a pure white, with blue eyes, being thought the perfection of cats, all other points being good, and its hearing by no means defective. The points are a small head, with not too long a nose, large full eyes of a colour in harmony with that of its fur, ears rather large than small and pointed, with a tuft of hair at the apex, the size not showing, as they are deeply set in the long hair on the forehead, with a very full flowing mane about the head and neck; this latter should not be short, neither the body, which should be long, graceful, and elegant, and covered with long, silky hair, with a slight admixture of woolliness; in this it differs from the Persian, and the longer the better. In texture it should be as fine as possible, and also not so woolly as that of the Russian; still it is more inclined to be so than the Persian. The legs to be of moderate length, and in proportion to the body; the tail long, and slightly curving upward towards the end. The hair should be very long at the base, less so toward the tip. When perfect, it is an extremely beautiful and elegant object, and no wonder that it has become a pet among the Orientals. The colours are varied; but the black which should have orange eyes, as should also the slate colours, and blues, and the white are the most esteemed, though the soft slates, blues, and the light fawns, deep reds, and mottled grays are shades of colour that blend well with the Eastern furniture and other surroundings. There are also light grays, and what is termed smoke colour; a beauty was shown at Brighton which was white with black tips to the hair, the white being scarcely visible, unless the hair was parted; this tinting had a marvellous effect. I have never seen imported strong-coloured tabbies of this breed, nor do I believe such are true Angoras. Fine specimens are even now rare in this country, and are extremely valuable. In manners and temper they are quiet, sociable, and docile, though given to roaming, especially in the country, where I have seen them far from their homes, hunting the hedgerows more like dogs than cats; nor do they appear to possess the keen intelligence of the short-haired European cat. They are not new to us, being mentioned by writers nearly a hundred years ago, if not more. I well remember white specimens of uncommon size on sale in Leadenhall Market, more than forty years since; the price usually was five guineas, though some of rare excellence would realise double that sum.
MISS MOORE'S "DINAH."
MISS SAUNDERS' "SYLVIE."
THE PERSIAN CAT
This differs somewhat from the Angora, the tail being generally longer, more like a table brush in point of form, and is generally slightly turned upwards, the hair being more full and coarser at the end, while at the base it is somewhat longer. The head is rather larger, with less pointed ears, although these should not be devoid of the tuft at the apex, and also well furnished with long hair within, and of moderate size. The eyes should be large, full, and round, with a soft expression; the hair on the forehead is generally rather short in comparison to the other parts of the body, which ought to be clothed with long silky hair, very long about the neck, giving the appearance of the mane of the lion. The legs, feet, and toes should be well clothed with long hair and have well-developed fringes on the toes, assuming the character of tufts between them. It is larger in body, and generally broader in the loins, and apparently stronger made, than the foregoing variety, though yet slender and elegant, with small bone, and exceedingly graceful in all its movements, there being a kind of languor observable in its walk, until roused, when it immediately assumes the quick motion of the ordinary short-haired cat, though not so alert. The colours vary very much, and comprise almost every tint obtainable in cats, though the tortoiseshell is not, nor is the dark marked tabby, in my opinion, a Persian cat colour, but has been got by crossing with the short-haired tortoiseshell, and also English tabby, and as generally shows pretty clearly unmistakable signs of such being the case. For a long time, if not now, the black was the most sought after and the most difficult to obtain. A good rich, deep black, with orange-coloured eyes and long flowing hair, grand in mane, large and with graceful carriage, with a mild expression, is truly a very beautiful object, and one very rare. The best I have hitherto seen was one that belonged to Mr. Edward Lloyd, the great authority on all matters relating to aquariums. It was called Mimie, and was a very fine specimen, usually carrying off the first prize wherever shown. It generally wore a handsome collar, on which was inscribed its name and victories. The collar, as Mr. Lloyd used jocosely to observe, really belonged to it, as it was bought out of its winnings; and, according to the accounts kept, was proved also to have paid for its food for some considerable period. It was, as its owner laughingly said, "his friend, and not his dependent," and generally used to sit on the table by his side while he was writing either his letters, articles, or planning those improvements regarding aquariums, for which he was so justly celebrated.

Next in value is the light slate or blue colour. This beautiful tint is very different in its shades. In some it verges towards a light purplish or lilac hue, and is very lovely; in others it tends to a much bluer tone, having a colder and harder appearance, still beautiful by way of contrast; in all the colour should be pure, even, and bright, not in any way mottled, which is a defect; and I may here remark that in these colours the hair is generally of a softer texture, as far as I have observed, than that of any other colour, not excepting the white, which is also in much request. Then follow the various shades of light tabbies, so light in the marking having scarcely a right to be called tabbies; in fact, tabby is not a Persian colour, nor have I ever seen an imported cat of that colour—I mean firmly, strongly marked with black on a brown-blue or gray ground, until they culminate in those of intense richness and density in the way of deep, harmonious browns and reds, yet still preserving throughout an extreme delicacy of line and tracery, never becoming harsh or hard in any of its arrangements or colour; not as the ordinary short-haired tabby. The eyes should be orange-yellow in the browns, reds, blues, grays, and blacks.

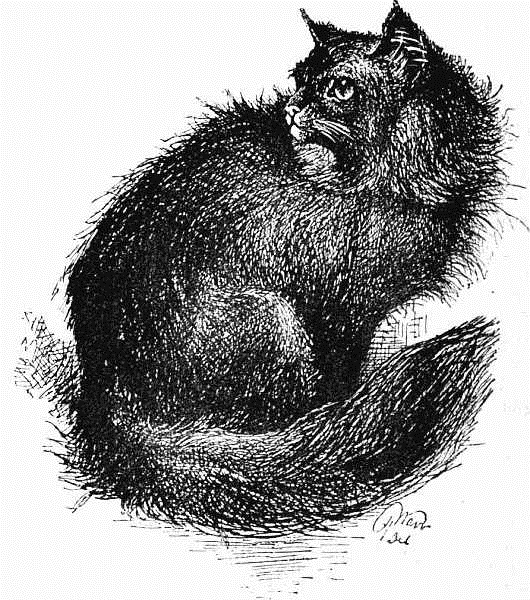
MR. A. A. CLARKE'S "TIM."
As far as my experience extends, and I have had numerous opportunities of noticing, I find this variety less reliable as regards temper than the short-haired cats, less also in the keen sense of observing, as in the Angora, and also of turning such observations to account, either as regards their comfort, their endeavour to help themselves, or in their efforts to escape from confinement.
In some few cases I have found them to be of almost a savage disposition, biting and snapping more like a dog than a cat, and using their claws less for protective purposes. Nor have I found them so "cossetty" in their ways as those of the "short-coats," though I have known exceptions in both.
They are much given to roam, as indeed are the Russian and Angora, especially in the country, going considerable distances either for their own pleasure or in search of food, or when "on the hunt." After mature consideration, I have come to the conclusion that this breed, and slightly so the preceding, are decidedly different in their habits to the short-haired English domestic cat, as it is now generally called.
It may be, however, only a very close observer would notice the several peculiarities which I consider certainly exist. These cats attach themselves to places more than persons, and are indifferent to those who feed and have the care of them. They are beautiful and useful objects about the house, and generally very pleasant companions, and when kept with the short-haired varieties form an exceedingly pretty and interesting contrast; but, as I have stated, they certainly require more attention to their training, and more caution in their handling, than the latter. I may here remark, that during the time I have acted as judge at cat shows, which is now over eighteen years, it has been seldom there has been any display of temper in the short-haired breeds in comparison with the long; though some of the former, in some instances, have not comported themselves with that sweetness and amiability of disposition that is their usual characteristic. My attendant has been frequently wounded in our endeavour to examine the fur, dentition, etc., of the Angora, Persian, or Russian; and once severely by a "short-hair." Hitherto I have been so fortunate as to escape all injury, but this I attribute to my close observation of the countenance and expression of the cat about to be handled, so as to be perfectly on my guard, and to the knowledge of how to put my hands out of harm's way. If a vicious cat is to be taken from one pen to another, it must be carried by the loose skin at the back of the neck and that of the back with both hands, and held well away from the person who is carrying it.
THE RUSSIAN LONG-HAIRED CAT
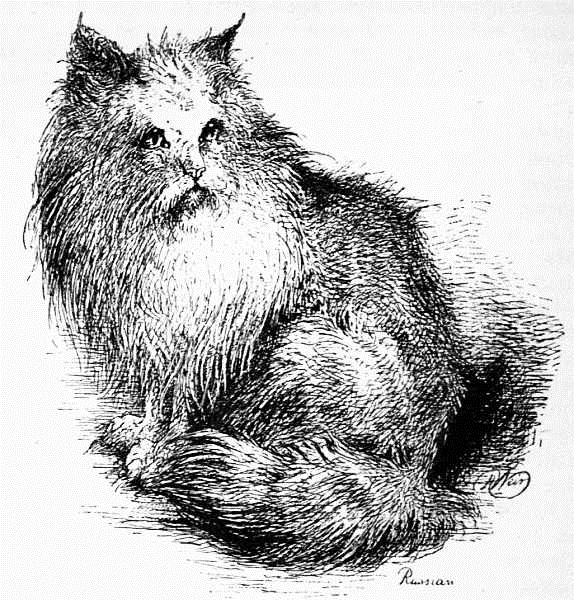
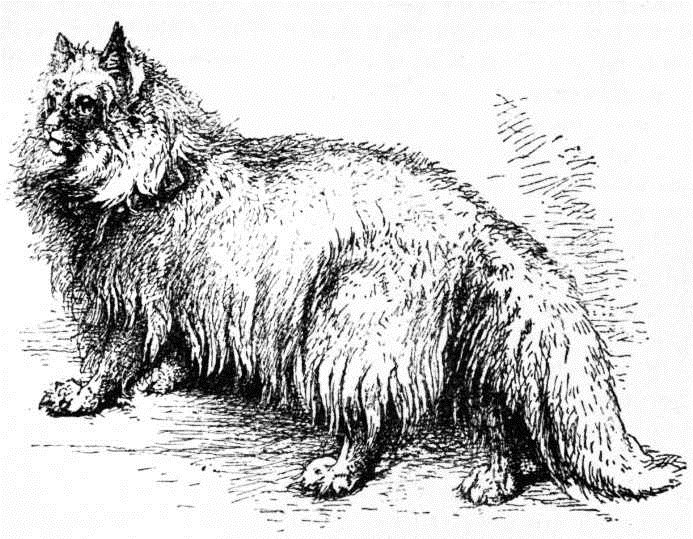
The above is a portrait of a cat given me many years ago, whose parents came from Russia, but from what part I could never ascertain. It differed from the Angora and the Persian in many respects. It was larger in the body with shorter legs. The mane or frill was very large, long, and dense, and more of a woolly texture, with coarse hairs among it; the colour was of dark tabby, though the markings were not a decided black, nor clear and distinct; the ground colour was wanting in that depth and richness possessed by the Persian, having a somewhat dull appearance. The eyes were large and prominent, of a bright orange, slightly tinted with green, the ears large by comparison, with small tufts, full of long, woolly hair, the limbs stout and short, the tail being very dissimilar, as it was short, very woolly, and thickly covered with hair the same length from the base to the tip, and much resembled in form that of the English wild cat. Its motion was not so agile as other cats, nor did it apparently care for warmth, as it liked being outdoors in the coldest weather. Another peculiarity being that it seemed to care little in the way of watching birds for the purpose of food, neither were its habits like those of the short-haired cats that were its companions. It attached itself to no person, as was the case with some of the others, but curiously took a particular fancy to one of my short-haired, silver-gray tabbies; the two appeared always together. In front of the fire they sat side by side. If one left the room the other followed. Adown the garden paths there they were, still companions; and at night slept in the same box; they drank milk from the same saucer, and fed from the same plate, and, in fact, only seemed to exist for each other. In all my experience I never knew a more devoted couple. I bred but one kitten from the Russian, and this was the offspring of the short-haired silver tabby. It was black-and-white, and resembled the Russian in a large degree, having a woolly coat, somewhat of a mane, and a short, very bushy tail. This, like his father, seemed also to be fonder of animals for food than birds, and, although very small, would without any hesitation attack and kill a full-grown rat. I have seen several Russian cats, yet never but on this occasion had the opportunity of comparing their habits and mode of life with those of the other varieties; neither have I seen any but those of a tabby colour, and they mostly of a dark brown. I am fully aware that many cross-bred cats are sold as Russian, Angora, and Persian, either between these or the short-haired, and some of these, of course, retain in large degree the distinctive peculiarities of each breed. Yet to the practised eye there is generally—I do not say always—a difference of some sort by which the particular breed may be clearly defined. When the prizes are given, as is the case even at our largest cat shows, for the best long-haired cat, there, of course, exists in the eye of the judge no distinction as regards breed. He selects, as he is bound to do, that which is the best long-haired cat in all points, the length of hair, colour, texture, and condition of the exhibit being that which commands his first attention. But if it were so put that the prize should be for the best Angora, Persian, Russian, etc., it would make the task rather more than difficult, for I have seen some "first-cross cats" that have possessed all, or nearly all, the points requisite for that of the Angora, Persian, or Russian, while others so bred have been very deficient, perhaps showing the Angora cross only by the tail and a slight and small frill. At the same time it must be noted, that, although from time to time some excellent specimens may be so bred, it is by no means desirable to buy and use such for stock purposes, for they will in all probability "throw back"—that is, after several generations, although allied with thoroughbred, they will possibly have a little family of quite "short-hairs." I have known this with rabbits, who, after breeding short-haired varieties for some time, suddenly reverted to a litter of "long-hairs"; but have not carried out the experiment with cats. At the same time I may state that I have little or no doubt that such would be the case; therefore I would urge on all those who are fond of cats—or, in fact, other animals—of any particular breed, to use when possible none but those of the purest pedigree, as this will tend to prevent much disappointment that might otherwise ensue. But I am digressing, and so back to my subject—the Russian long-haired cat. I advisedly say long-haired cat, for I shall hereafter have to treat of other cats coming from Russia that are short-haired, none which I have hitherto seen being tabbies, but whole colour. This is the more singular as all those of the long-hair have been brown tabbies, with only one or two exceptions, which were black. It is just possible these were the offspring of tabby or gray parents, as the wild rabbit has been known to have had black progeny. I have seen a black rabbit shot from amongst the gray on the South Downs.
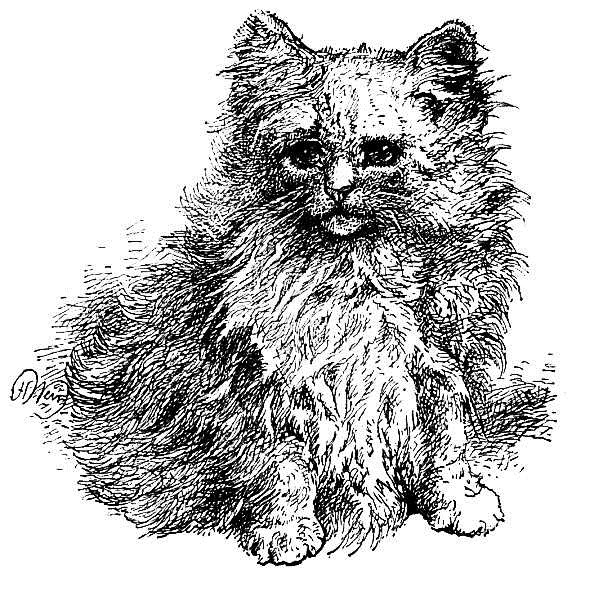

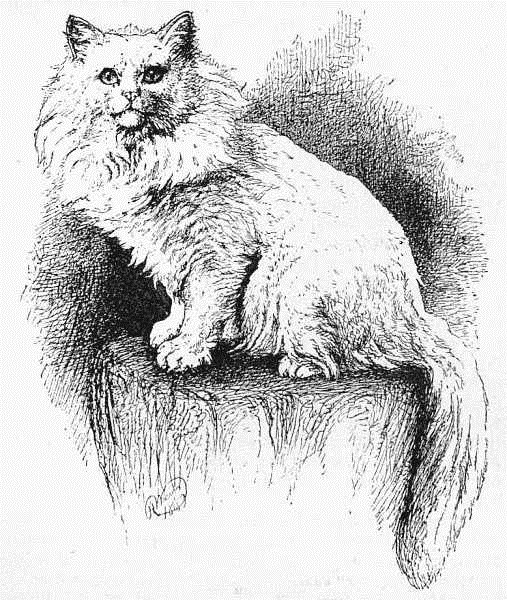
MISS MARY GRESHAM'S PERSIAN KITTEN, "LAMBKIN."
I do not remember having seen a white Russian "long-hair," and I should feel particularly obliged to any of my readers who could supply me with further information on this subject, or on any other relating to the various breeds of cats, cat-life and habits. I am fully aware that no two cats are exactly alike either in their form, colour, movements, or habits; but what I have given much study and attention to, and what I wish to arrive at is, the broad existing natural distinctions of the different varieties. In this way I shall feel grateful for any information.
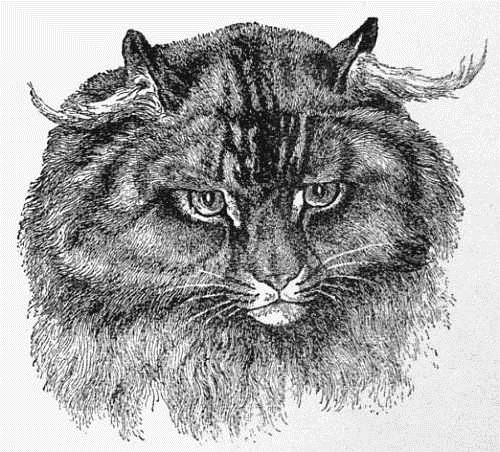

The above engraving and description of a very peculiar animal is from Daniel's "Rural Sports," 1813:
"This Cat was the Property of Mrs. Finch, of Maldon, Essex. In the Account of this Lusus Naturæ, for such it may be deemed, the Mother had no other Likeness to her Production, than her Colour, which is a tawny Sandy, in some parts lightly streaked with black; She had this, and another Kitten like it, about two Years since. The fellow Kitten was killed, in consequence of being troublesome, to the Mistress of the House, where it was presented. This is a Male, above the usual Size, with a shaggy Appearance round its Face, resembling that of the Lion's, in Miniature. The Hair protruding from the Ears, formerly grew, like what are termed Cork-screw Curls, and which are frequently seen, among the smart young Watermen, on the Thames; the Tail is perfectly distinct, from that of the Cat Species, and resembles the Brush of a Fox. The Mother, has at this time (1813), three Young ones, but without the least Difference to common Kittens, neither, indeed, has she ever had any before, or since, similar to That here described. The Proprietor has been offered, and refused One Hundred Pounds for this Animal."
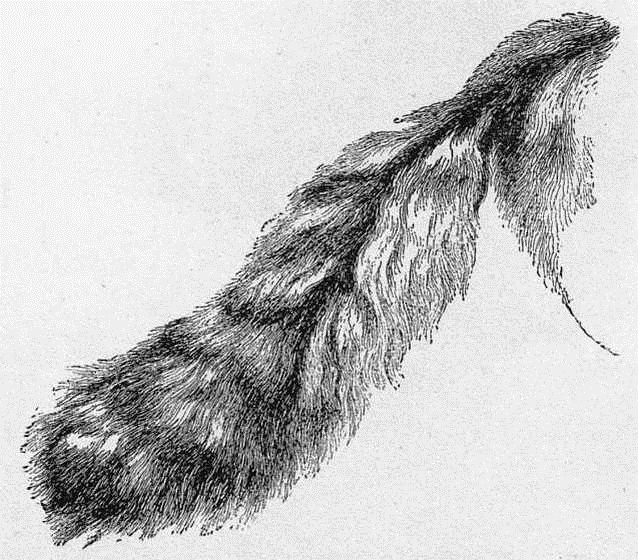

This was either a cross with the English wild cat, which sometimes has a mane, or it was an accidental variation of nature. I once bred a long-haired rabbit in a similar way, but at first I failed entirely to perpetuate the peculiarity. I think the above simply "a sport."

MISS MARY GRESHAM'S PERSIAN KITTEN, "LAMBKIN NO. 2."
MISS MOORE'S "BOGEY."
I have now concluded my remarks on the long-haired varieties of cats that I am at present acquainted with. They are an exceedingly interesting section; their habits, manners, forms, and colours form a by no means unprofitable study for those fond of animal life, as they, in my opinion, differ in many ways from those of their "short-haired" brethren. I shall not cease, however, in my endeavours to find out if any other long-haired breeds exist, and I am, therefore, making inquiries in every direction in which I deem it likely I shall get an increase of information on the subject, but hitherto without any success. Therefore, I am led to suppose that the three I have enumerated are the only domesticated long-haired varieties. The nearest approach, I believe, to these in the wild state is that of the British wild cat, which has in some instances a mane and a bushy tail, slightly resembling that of the Russian long-hair, with much of the same facial expression, and rather pointed tufts at the apex of the ears. It is also large, like some of the "long-haired" cats that I have seen; in fact, it far more resembles these breeds than those of the short hair. I was much struck with the many points of similitude on seeing the British wild cat exhibited by the Duke of Sutherland at the first cat show at the Crystal Palace in July, 1871. I merely offer this as an idea for further consideration. At the same time, allow me to say that I have had no opportunity of studying the anatomy of the British wild cat, in contradistinction to that of the Russian, or others with long hair. I only wish to point out what I term a general resemblance, far in excess of those with short hair. I am fully aware how difficult it is to trace any origin of the domestic cat, or from what breeds; it is also said, that the British wild cat is not one of them, still I urge there exists the similarity I mention; whether it is so apparent to others I know not.

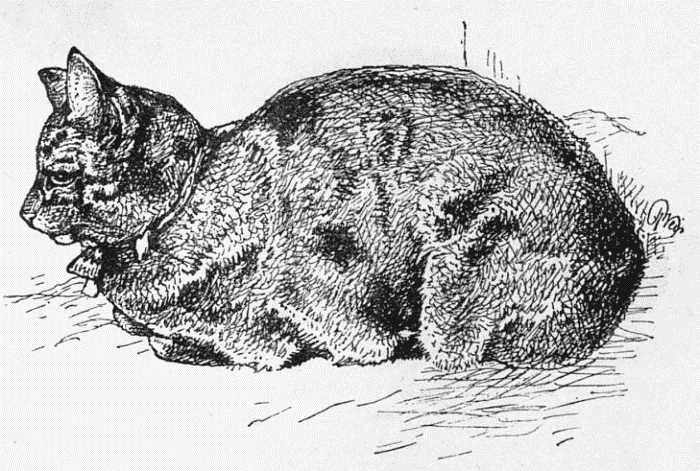
MR. SMITH'S PRIZE HE-CAT.
THE TORTOISESHELL CAT
I now come to the section of the short-haired domestic cat, a variety possessing sub-varieties. Whether these all came from the same origin is doubtful, although in breeding many of the different colours will breed back to the striped or tabby colour, and, per contra, white whole-coloured cats are often got from striped or spotted parents, and vice versâ. Those that have had any experience of breeding domesticated animals or birds, know perfectly well how difficult it is to keep certain peculiarities gained by years of perseverance of breeding for such points of variation, or what is termed excellence. Place a few fancy pigeons, for instance, in the country and let them match how they like, and one would be quite surprised, unless he were a naturalist, to note the great changes that occur in a few years, and the unmistakable signs of reversion towards their ancestral stock—that of the Rock pigeon. But with the cat this is somewhat different, as little or no attempts have been made, as far as I know of, until cat shows were instituted, to improve any particular breed either in form or colour. Nor has it even yet, with the exception of the long-haired cats. Why this is so I am at a loss to understand, but the fact remains. Good well-developed cats of certain colours fetch large prices, and are, if I may use the term, perpetual prize-winners. I will take as an instance the tortoiseshell tom, he, or male cat as one of the most scarce, and the red or yellow tabby she-cat as the next; and yet the possessor of either, with proper care and attention, I have little or no doubt, has it in his power to produce either variety ad libitum. It is now many years since I remember the first "tortoiseshell tom-cat;" nor can I now at this distance of time quite call to mind whether or not it was not a tortoiseshell-and-white, and not a tortoiseshell pure and simple. It was exhibited in Piccadilly. If I remember rightly, I made a drawing of it, but as it is about forty years ago, of this I am not certain, although I have lately been told that I did, and that the price asked for the cat was 100 guineas.
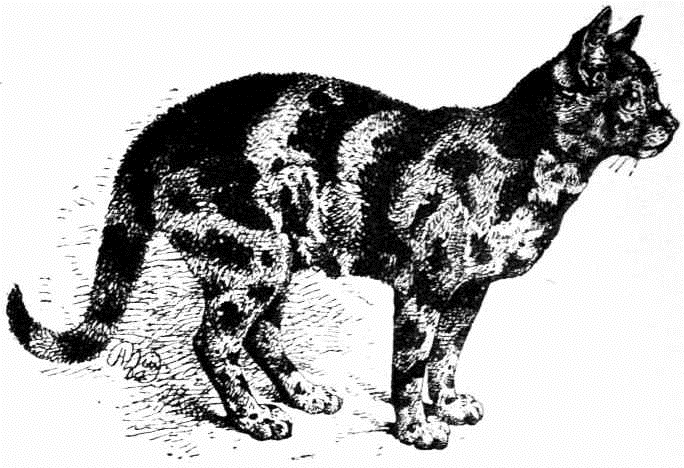
EXAMPLE OF TORTOISESHELL CAT, VERY DARK VARIETY.
This supposed scarcity was rudely put aside by the appearance, at the Crystal Palace Show of 1871, of no less than one tortoiseshell he-cat (exhibited by Mr. Smith) and three tortoiseshell-and-white he-cats, but it will be observed there was really but only one tortoiseshell he-cat, the others having white. On referring to the catalogues of the succeeding shows, no other pure tortoiseshell has been exhibited, and he ceased to appear after 1873; but tortoiseshell-and-white have been shown from 1871, varying in number from five to three until 1885. One of these, a tortoiseshell-and-white belonging to Mr. Hurry, gained no fewer than nine first prizes at the Crystal Palace, besides several firsts at other shows; this maintains my statement, that a really good scarce variety of cats is a valuable investment, Mr. Hurry's cat Totty keeping up his price of £100 till the end.

