 полная версия
полная версияThe Eighteen Christian Centuries
The degraded prætorians then elevated one of the companions of Nero’s guilty excesses to the throne in the person of Otho, but resistance was made to their selection.
|A.D. 69.|
The forces in Germany nominated Vitellius to the supreme authority; and Otho, either a voluptuary tired of life, or a craven incapable of exertion, committed suicide to save the miseries of civil war. But this calamity was averted by a nobler hand. Vitellius had only time to show that, in addition to the usual vices of the throne, he was addicted to the animal enjoyments of eating and drinking to an almost incredible degree, when he heard a voice from the walls of Jerusalem which hurled him from the seat he had so lately taken; for the legions engaged in that most memorable of sieges had decided on giving the empire of the world to the man who deserved it best, and had proclaimed their general, Flavius Vespasian, Imperator and Master of Rome.
|A.D. 70.|
Now we will pause, for we have come to the year seventy of this century, and a fit breathing-time to look round us and see what condition mankind has fallen into within a hundred years of the end of the Republic. We leave out of view the great empires of the farther East, where battles were won, and dynasties established on the plains of Hindostan, and within the Chinese Wall. The extent of our knowledge of Oriental affairs is limited to the circumference of the Roman power. Following that vast circle, we see it on all sides surrounded by tribes and nations who derive their sole illumination from its light, for unless the Roman conquests had extended to the confines of those barbaric states, we should have known nothing of their existence. Beyond that ring of fire it is almost matter of conjecture what must have been going on. Yet we learn from the traditions of many peoples, and can guess with some accuracy from the occurrences of a later period, what was the condition of those “outsiders,” and what were their feelings and intentions with regard to the civilized portions of the world. Bend your eyes in any direction you please, and what names, what thoughts, suggest themselves to our minds! We see swarms of wild adventurers with wives and cattle traversing with no definite object the uncultivated districts beyond the Danube; occasionally pitching their tents, or even forming more permanent establishments, around the roots of Caucasus and north of the Caspian Sea, where grass was more plentiful, and hills or marshes formed an easily defended barrier against enemies as uncivilized as themselves. Coming from no certain region—that is, forgetting in a few years of wandering the precise point from which they set out, pushed forward by the advancing waves of great national migrations in their rear—moving onward across the upper fields of Europe, but keeping themselves still cautiously from actual contact with the Roman limits, from those hordes of homeless, lawless savages are derived the most polished and greatest nations of the present day. Forming into newer combinations, and taking different names, their identity is scarcely to be recognised when, three or four centuries after this, they come into the daylight of history; but nobody can doubt that, during these preliminary ages, they were gathering their power together, hereafter, under the impulse of fresh additions, to be hurled like a dammed-up river upon the prostrate realm, carrying ruin and destruction in their course, but no less certainly than the overflowing Nile leaving the germs of future fertility, and enriching with newer vegetation the fields they had so ruthlessly submerged. And year by year the mighty mass goes on accumulating. The northern plains become peopled no one knows how. The vast forests eastward of the Rhine receive new accessions of warriors, who rapidly assimilate with the old. United in one common object of retaining the wild freedom of their tribe, and the possession of the lands they have seized, they have opposed the advance of the Roman legions into the uncultivated districts they call their own; they have even succeeded in destroying the military forces which guarded the Rhine, and have with difficulty been restrained from crossing the great river by a strong line of forts and castles, of which the remains astonish the traveller of the present day, as, with Murray’s Guide-Book in his hand, he gazes upon their ruins between Bingen and Aix-la-Chapelle.
Repelled by these barriers, they cluster thicker than ever in the woods and valleys, to which the Romans have no means of penetrating. Southern Gaul submits, and becomes a civilized outpost of the central power; but far up in the wild regions of the north, and even to the eastward of the Gulfs of Bothnia and Finland, the assemblage goes on. Scandinavia itself becomes over-crowded by the perpetual arrival of thousands of these armed and expatriated families, and sends her teeming populations to the east and south. But all these incidents, I must remind you, are occurring in darkness. We only know that the desert is becoming peopled with crowded millions, and that among them all there floats a confused notion of the greatness of the Roman power, the wealth of the cities and plains of Italy; and that, clustering in thicker swarms on the confines of civil government, the watchful eyes of unnumbered savage warriors are fixed on the territories lying rich and beautiful within the protection of the Roman name. So the whole Roman boundary gets gradually surrounded by barbaric hosts. Their trampings may be heard as they marshal their myriads and skirt the upper boundaries of Thrace; but as yet no actual conflict has occurred. A commotion may become observable among some of the farthest distant of the half intimidated of the German tribes; or an enterprising Roman settler beyond the frontier, or travelling merchant, who has penetrated to the neighbourhood of the Baltic, may bring back amazing reports of the fresh accumulations of unknown hordes of strange and threatening aspect; but the luxurious public in Rome receive them merely as interesting anecdotes to amuse their leisure or gratify their curiosity: they have no apprehension of what may be the result of those multitudinous arrivals. They do not foresee the gradual drawing closer to their outward defences—the struggle to get within their guarded lines—the fight that is surely coming between a sated, dull, degraded civilization on the one side, and a hungry, bold, ambitious savagery on the other. They trust every thing to the dignity of the Eternal City, and the watchfulness of the Emperor: for to this, his one idea of irresistible power equally for good or evil, the heart of the Roman was sure to turn. And for the eleven years of the reigns of Vespasian and Titus, the Roman did not appeal for protection against a foreign enemy in vain. Rome itself was compensated by shows and buildings—with a triumph and an arch—for the degradation in which it was held. But prætor and proconsul still pursued their course of oppressing the lands committed to their defence; and the subject, stripped of his goods, and hopeless of getting his wrongs redressed, had only the satisfaction of feeling that the sword he trembled at was in the hand of a man and not of an incarnate demon. A poor consolation this when the blow was equally fatal. Vespasian, in fact, was fonder of money than of blood, and the empire rejoiced in having exchanged the agony of being murdered for the luxury of being fleeced.
|A.D. 79.|
With Titus, whom the fond gratitude of his subjects named the Delight of the human race, a new age of happiness was about to open on the world; but all the old horrors of the Cæsars were revived and magnified when he was succeeded, after a reign of two years, by his brother, the savage and cowardly Domitian.
|A.D. 81.|
With the exception of the brief period between the years 70 and 81, the whole century was spent in suffering and inflicting pain. The worst excesses of Nero and Caligula were now imitated and surpassed. The bonds of society became rapidly loosened. As in a shipwreck, the law of self-preservation was the only rule. No man could rely upon his neighbour, or his friend, or his nearest of kin. There were spies in every house, and an executioner at every door. An unconsidered word maliciously reported, or an accusation entirely false, brought death to the rich and great. To the unhappy class of men who in other times are called the favourites of fortune, because they are born to the possession of great ancestral names and hereditary estates, there was no escape from the jealous and avaricious hatred of the Emperor. If a patrician of this description lived in the splendour befitting his rank—he was currying favour with the mob! If he lived retired—he was trying to gain reputation by a pretence of giving up the world! If he had great talents—he was dangerous to the state! If he was dull and stupid—oh! don’t believe it—he was only an imitative Brutus, concealing his deep designs under the semblance of fatuity! If a man of distinguished birth was rich, it was not a fitting condition for a subject—if he was poor, he was likely to be seduced into the wildest enterprises. So the prisons were filled by calumny and suspicion, and emptied by the executioner. A dreadful century this—the worst that ever entered into tale or history; for the memory of former glories and comparative freedom was still recent. A man who was sixty years old, in the midst of the terrors of Tiberius, had associated in his youth with the survivors of the Civil War, with men who had embraced Brutus and Cassius; he had seen the mild administration of Augustus, and perhaps had supped with Virgil and Horace in the house of Mæcenas. And now he was tortured till he named a slave or freedman of the Emperor his heir, and then executed to expedite the succession. There was a hideous jocularity in some of these imperial proceedings, which, however, was no laughing-matter at the time. When a senator was very wealthy, it was no unusual thing for Tiberius and his successors to create themselves the rich man’s nearest relations by a decree of the Senate. The person so honoured by this graft upon his family tree seldom survived the operation many days. The emperor took possession of the property as heir-at-law and next of kin; and mourned for his uncle or brother—as the case might be—with the most edifying decorum.
But besides giving the general likeness of a period, it is necessary to individualize it still further by introducing, in the background of the picture, some incident by which it is peculiarly known, as we find Nelson generally represented with Trafalgar going on at the horizon, and Wellington sitting thoughtful on horseback in the foreground of the fire of Waterloo. Now, there cannot be a more distinguishing mark than a certain great military achievement which happened in the year 70 of this century, and is brought home to us, not only as a great historical event in itself, but as the commencement of a new era in human affairs, and the completion of a long line of threats and prophecies. This was the capture and destruction of Jerusalem. The accounts given us of this siege transcend in horror all other records of human sorrow. It was at the great annual feast of the Passover, when Jews from all parts of the world flocked to the capital of their nation to worship in the Temple, which to them was the earthly dwelling-place of Jehovah. The time was come, and they did not know it, when God was to be worshipped in spirit and in truth. More than a million strangers were resident within the walls. There was no room in house or hall for so vast a multitude; so they bivouacked in the streets, and lay thick as leaves in the courts of the holy place. Suddenly the Roman trumpets blew. The Jews became inspired with fanatical hatred of the enemy, and insane confidence that some miracle would be wrought for their deliverance. They deliberated, and chose for their leaders the wildest and most enthusiastic of the crowd. They refused the offers of mercy and reconciliation made to them by Titus. They sent back insulting messages to the Roman general, and stood expectant on the walls to see the idolatrous legions smitten by lightning or swallowed up by an earthquake. But Titus advanced his forces and hemmed in the countless multitude of men, and women, and children—few able to resist, but all requiring to be fed. Famine and pestilence came on; but still the mad fanatics of the Temple determined to persevere. They occasionally opened a gate and rushed out with the cry of “The sword of the Lord and of Gideon!” and were slaughtered by the unpitying hatred of the Roman soldiers. Their cruelty to their prisoners, when they succeeded in carrying off a few of their enemies, was great; but the patience of Titus at last gave way, and he soon bettered the instruction they gave him in pitilessness and blood. He drew a line of circumvallation closer round the city, and intercepted every supply; when deserters came over, he crucified them all round the trenches; when the worn-out people came forth, imploring to be suffered to pass through his ranks, he drove them back, that they might increase the scarcity by their lives, or the pestilence by adding to the heaps of unburied dead. Dissensions were raging all this time among the defenders themselves. They fought in the streets, in the houses, and heaped the floor and outcourts of the Temple with thousands of the slain. There was no help either from heaven or earth; eleven hundred thousand people had died of plague and the sword; and the rest were doomed to perish by more lingering torments. Nearest relations—sisters, brothers, fathers, wives—all forgot the ties of natural affection under this great necessity, and fought for a handful of meal, or the possession of some reptile’s body if they were lucky enough to trace it to its hiding-place; and at last—the crown of all horrors—the daughter of Eleazer killed her own child and converted it into food. The measure of man’s wrong and Heaven’s vengeance was now full. The daily sacrifice ceased to be offered; voices were audible to the popular ear uttering in the Holy of Holies, “Let us go hence.” The Romans rushed on—climbed over the neglected walls—forced their way into the upper Temple, and the gore flowed in streams so rapid and so deep that it seemed like a purple river! Large conduits had been made for the rapid conveyance away of the blood of bulls and goats offered in sacrifice; they all became choked now with the blood of the slaughtered people. At last the city was taken; the inhabitants were either dead or dying. Many were crushed as they lay expiring in the great tramplings of the triumphant Romans; many were recovered by food and shelter, and sold into slavery. The Temple and walls were levelled with the ground, and not one stone was left upon another. The plough passed over where palace and tower had been, and the Jewish dispensation was brought to a close.
History in ancient days was as exclusive as the court newsman in ours, and never published the movements of anybody below a senator or a consul. All the Browns and Smiths were left out of consideration; and yet to us who live in the days when those families—with the Joneses and Robinsons—form the great majority both in number and influence, it would be very interesting to have any certain intelligence of their predecessors during the first furies of the Empire. We have but faint descriptions even of the aristocracy, but what we hear of them shows, more clearly than any thing else, the frightful effect on morals and manliness of so uncontrolled a power as was vested in the Cæsars, and teaches us that the worst of despotisms is that which is established by the unholy union of the dregs of the population and the ruling power, against the peace and happiness and security of the middle class. You see how this combination of tyrant and mob succeeded in crushing all the layers of society which lay between them, till there were left only two agencies in all the world—the Emperor on his throne, and the millions fed by his bounty. The hereditary nobility—the safest bulwark of a people and least dangerous support of a throne—were extirpated before the end of the century, and impartiality makes us confess that they fell by their own fault. As if the restraints of shame had been thrown off with the last hope of liberty, the whole population broke forth into the most incredible licentiousness. If the luxury of Lucullus had offended the common sense of propriety in the later days of the republic, there were numbers now who looked back upon his feasts as paltry entertainments, and on the wealth of Crœsus as poverty. The last of the Pompeys, in the time of Caligula, had estates so vast, that navigable rivers larger than the Thames performed the whole of their course from their fountain-head to the sea without leaving his domain. There were spendthrifts in the time of Tiberius who lavished thousands of pounds upon a supper. The pillage of the world had fallen into the hands of a few favoured families, and their example had introduced a prodigality and ostentation unheard of before. No one who regarded appearances travelled anywhere without a troop of Numidian horsemen, and outriders to clear the way. He was followed by a train of mules and sumpter-horses loaded with his vases of crystal—his richly-carved cups and dishes of silver and gold. But this profusion had its natural result in debt and degradation. The patricians who had been rivals of the imperial splendour became dependants on the imperial gifts; and the grandson of the conqueror of a kingdom, or the proconsul of the half of Asia, sold his ancestral palace, lived for a while on the contemptuous bounty of his master, and sank in the next generation into the nameless mass. Others, more skilful, preserved or improved their fortunes while they rioted in expense. By threats or promises, they prevailed on the less powerful to constitute them their heirs; they traded on the strength, or talents, or the beauty of their slaves, and lent money at such usurious interest that the borrower tried in vain to escape the shackles of the law, and ended by becoming the bondsman of the kind-hearted gentleman who had induced him to accept the loan.
If these were the habits of the rich, how were the poor treated? The free and penniless citizens of the capital were degraded and gratified at the same time. The wealthy vied with each other in buying the favour of the mob by shows and other entertainments, by gifts of money and donations of food. But when these arts failed, and popularity could no longer be obtained by merely defraying the expense of a combat of gladiators, the descendants of the old patricians—of the men who had bought the land on which the Gauls were encamped outside the gates of Rome—went down into the arena themselves and fought for the public entertainment. Laws indeed were passed even in the reign of Tiberius, and renewed at intervals after that time, against this shameful degradation, and the stage was interdicted to all who were not previously declared infamous by sentence of a court. But all was in vain. Ladies of the highest rank, and the loftiest-born of the nobility, actually petitioned for a decree of defamation, that they might give themselves up undisturbed to their favourite amusement. This perhaps added a zest to their enjoyment, and rapturous applauses must have hailed the entrance of the beautiful grandchild of Anthony or Agrippa, in the character and drapery of a warlike amazon—the louder the applause and greater the admiration. Yet in order to gratify them with such a sight, she had descended to the level of the convict, and received the brand of qualifying disgrace from a legal tribunal. But the faint barrier of this useless prohibition was thrown down by the policy and example of Domitian. The emperor himself appeared in the arena, and all restraint was at an end. Rather, there was a fury of emulation to copy so great a model, and “Rome’s proud dames, whose garments swept the ground,” forgot more than ever their rank and sex, and were proud, like their lovers and brothers, not merely to mount the stage in the lascivious costume of nymph or dryad, but to descend into the blood-stained lists of the Coliseum and murder each other with sword and spear. There is something strangely horrible in this transaction, when we read that it occurred for the first time in celebration of the games of Flora—the goddess of flowers and gardens, who, in old times, was worshipped under the blossomed apple-trees in the little orchards surrounding each cottage within the walls, and was propitiated with children’s games and chaplets hung upon the boughs. But now the loveliest of the noble daughters of the city lay dead upon the trampled sand. What was the effect upon the populace of these extraordinary shows?
Always stern and cruel, the Roman was now never satisfied unless with the spectacle of death. Sometimes in the midst of a play or pantomime the fierce lust of blood would seize him, and he would cry out for a combat of gladiators or nobles, who instantly obeyed; and after the fight was over, and the corpses removed, the play would go on as if nothing had occurred. The banners of the empire still continued to bear the initial letters of the great words—the Senate and people of Rome. We have now, in this rapid survey, seen what both those great names have come to—the Senate crawling at the feet of the emperor, and the people living on charity and shows. The slaves fared worst of all, for they were despised by rich and poor. The sated voluptuary whose property they were sometimes found an excitement to his jaded spirits by having them tortured in his sight. They were allowed to die of starvation when they grew old, unless they were turned to use, as was done by one of their possessors, Vidius Pollio, who cast the fattest of his domestics into his fish-pond to feed his lampreys. The only other classes were the actors and musicians, the dwarfs and the philosophers. They contributed by their wit, or their uncouth shape, or their oracular sentences, to the amusement of their employers, and were safe. They were licensed characters, and could say what they chose, protected by the long-drawn countenance of the stoic, or the comic grimaces of the buffoon. So early as the time of Nero, the people he tyrannized and flattered were not less ruthless than himself. In his cruelty—in his vanity—in his frivolity, and his entire devotion to the gratification of his passions—he was a true representative of the men over whom he ruled. Emperor and subject had even then become fitted for each other, and flowers, we are credibly told by the historians, were hung for many years upon his tomb.
Humanity itself seemed to be sunk beyond the possibility of restoration; but we see now how necessary it was that our nature should reach its lowest point of depression to give full force to the great reaction which Christianity introduced. Men were slavishly bending at the footstool of a despot, trembling for life, bowed down by fear and misery, when suddenly it was reported that a great teacher had appeared for a while upon earth, and declared that all men were equal in the sight of God, for that God was the Father of all. The slave heard this in the intervals of his torture—the captive in his dungeon—the widow and the orphan. To the poor the gospel, or good news, was preached. It was this which made the trembling courtiers of the worst of the emperors slip out noiselessly from the palace, and hear from Paul of Tarsus or his disciples the new prospect that was opening on mankind. It spread quickly among those oppressed and hopeless multitudes. The subjection of the Roman empire—its misery and degradation—were only a means to an end. The harsher the laws of the tyrant, the more gracious seemed the words of Christ. The two masters were plainly set before them, which to choose. And who could hesitate? One said, “Tremble! suffer! die!” The other said, “Come unto me, all ye that are weary and heavy laden, and I will give you rest!”
SECOND CENTURY
Pliny the Younger, Plutarch, Suetonius, Juvenal, Arrian, Ælian, Ptolemy, (Geographer,) Appian, Epictetus, Pausanias, Galen, (Physician,) Athenæus, Tertullian, Justin Martyr, Tatian, Irenæus, Athenagoras, Theophilus of Antioch, Clement Of Alexandria, Marcion, (Heretic.)
THE SECOND CENTURY
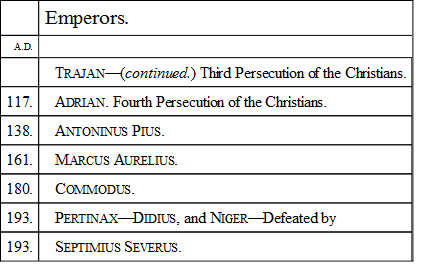
THE GOOD EMPERORSIn looking at the second century, we see a total difference in the expression, though the main features continue unchanged. There is still the central power at Rome, the same dependence everywhere else; but the central power is beneficent and wise. As if tired of the hereditary rule of succession which had ended in such a monster as Domitian, the world took refuge in a new system of appointing its chiefs, and perhaps thought it a recommendation of each successive emperor that he had no relationship to the last. We shall accordingly find that, after this period, the hereditary principle is excluded. It was remarked that, of the twelve first Cæsars, only two had died a natural death—for even in the case of Augustus the arts of the poisoner were suspected—and those two were Vespasian and Titus, men who had no claim to such an elevation in right of lofty birth. Birth, indeed, had ceased to be a recommendation. All the great names of the Republic had been carefully rooted out. Few people were inclined to boast of their ancestry when the proof of their pedigree acted as a sentence of death; for there was no surer passport to destruction in the times of the early emperors than a connection with the Julian line, or descent from a historic family. No one, therefore, took the trouble to inquire into the genealogy of Nerva, the old and generous man who succeeded the monster Domitian. |A.D. 96.|His nomination to the empire elevated him at once out of the sphere of these inquiries, for already the same superstitious reverence surrounded the name of Augustus which spreads its inviolable sanctity on the throne of Eastern monarchs. Whoever sits upon that, by whatever title, or however acquired, is the legitimate and unquestioned king. No rival, therefore, started up to contest the position either of Nerva himself, or of the stranger he nominated to succeed him. |A.D. 102.|Men bent in humble acquiescence when they knew, in the third year of this century, that their master was named Trajan,—that he was a Spaniard by birth, and the best general of Rome. For eighty years after that date the empire had rest. Life and property were comparatively secure, and society flowed on peaceably in deep and well-ascertained channels. A man might have been born at the end of the reign of Domitian, and die in extreme old age under the sway of the last of the Antonines, and never have known of insecurity or oppression—

