
Полная версия
Agatha Christie: A Biography
I am especially grateful to those who have allowed me to quote from letters to or from Agatha Christie and from family papers. Mrs Anthony Hicks, Mr and Mrs Mathew Prichard, John Mallowan and Peter Mallowan have been immensely helpful and I am also indebted to Edmund Cork and his family. I would also like to thank: Anthony Fleming, for permitting me to quote from the letters of his mother, Miss Dorothy L. Sayers; Mrs Frankfort, for an extract from a letter from her father, Professor Stephen Glanville; Lord Hardinge of Penshurst, whose reports to Collins are quoted here; Lady Kirwan, for quotations from letters from Agatha and Max; Mrs Anne McMurphy, formerly Miss Marple, whose letter from Agatha revealed the origins of that heroine’s name; James Paterson, for extracts from his correspondence about the Churston window; Miss Dorothy Olding, whose exchanges with Edmund Cork I have plundered; Sir Peter Saunders, for quotations from letters and telegrams about plays; Professor Harry Smith, for allowing me to quote from a letter from his father, Professor Sidney Smith; and Miss Barbara Toy, whose correspondence I have cited in writing about Murder at the Vicarage.
I also wish to thank the directors of Agatha Christie Ltd, and the board of Booker McConnell Ltd, for allowing me to use their records; the BBC Written Archives Centre, and Mrs J. Kavanagh, Neil Somerville and Jeff Walden, for permission to quote from their records; the British Red Cross, and the archivist, Miss Margaret Wade, for details of Agatha Christie’s service in the First World War; the directors of William Collins Ltd, for opening their files and allowing me to quote from them; Harrods Press Office, for their efforts to trace a letter Agatha Christie sent them in 1926; the Harrogate Advertiser and Herald, whose archive gave an illuminating picture of the town and its visitors in the ‘twenties; the Home Office Library and the Departmental Records Officer, for their invaluable help in my search through the accounts of Agatha’s disappearance; Hughes Massie Ltd, for permission to examine the records of Agatha’s dealings with her agent; the Imperial War Museum for giving me access to the tape-recording Agatha made for their oral archive; the Trustees of the Allen Lane Foundation, and Dr Michael Rhodes, the archivist, for allowing me to cite extracts from Agatha’s correspondence with The Bodley Head; the Trustees of the Mountbatten Foundation, for enabling me to quote from Earl Mountbatten’s correspondence with Agatha about The Murder of Roger Ackroyd; the trustees of the Harold Ober estate, who made the correspondence of Agatha’s American agent available to me, the Rare Books and Manuscripts Section of the Firestone Library at Princeton University, which houses it, and Miss Jane Snedeker, who guided me to it; the Surrey Record Office, and Dr Robinson, for their help in disentangling the events of 1926; and the University of Manchester Library, and Miss J. Sen, for supplying details of the careers of the doctors who attended Agatha in 1926.
There are others who, out of enthusiasm, curiosity or both, contributed to this book by producing new ideas and surprising references. I particularly wish to thank: Dr Marilyn Butler; Professor John Carey; Christopher Campbell; Stephen Hearst; Leofranc Holford-Strevens; Miss Frances Irwin; Edward Jospé; Mrs Cécil Jospé; Gordon Lee; Douglas Matthews; Mrs Alexandra Nicol; Miss Olivia Stewart; and Miss Anne Willis. I am equally grateful to those who interpreted, typed, arranged and copied my manuscript as I moved from one house, hotel, office and country to the next: Mrs Rigby Allen; Mrs Berry; Miss Michelle Cooper; Vincent Jones; Mrs Daisy Sasso; Mrs Jean Smith; and, as choreographers, Mrs Sheila George and Ray Walters. I would also like to thank Mr Bobby Burns and the Hon. Mrs Burns for their patience and hospitality while I cut and shuffled the text in their house in Jamaica.
The encouragement and guidance of my publishers have been indispensable and I am grateful to Bob Gottlieb of Alfred A. Knopf, Philip Ziegler of William Collins, Elizabeth Burke, Elizabeth Bowes Lyon and Elizabeth Walter.
This book is not only for people who like detective stories but also for those who are interested in a writer’s development and experience, in Agatha Christie’s character and the instinct which made her work a success. Like the lives of many writers, hers changed pace as she reached middle age. There was less incident, more consolidation. She was, moreover, quiet and reflective by temperament, and increasing age and fame made her more so. Though her energy remained immense, she gave most of it to her work. This book looks at the way in which she distilled her experience in her novels, plays and detective stories. Only in one case, however, does it reveal the solution to a plot and then only where Agatha Christie has done so in her own memoirs.
Agatha Christie lived to a great age and she was prolific. I have not given a chronological list of her work at the end of this book, for it is already long and readers who would like such a bibliography may find it in one of the interesting critical accounts of Agatha’s writing. The Agatha Christie Chronology by Nancy Blue Wynne (New York: Ace Books, 1976) is particularly useful; less accurate but more daring is Charles Osborne’s The Life and Crimes of Agatha Christie (Collins, 1982). Robert Barnard has published an excellent study in A Talent to Deceive (Collins, 1980); Gordon C. Ramsey’s Agatha Christie: Mistress of Mystery (Collins, 1972) is thoughtful and was examined before publication by Agatha Christie herself. Sir Peter Saunders’s autobiography, The Mousetrap Man (Collins 1972), gives a producer’s perspective on her work for the theatre, while Tom Adams and Julian Symons have compiled a volume that is stimulating to look at as well as to read, by writing about the jacket designs for some of her paperbacks, in Tom Adams’s Agatha Christie Cover Story (Paper Tiger, 1982). Those who need assistance in keeping track of the characters in Agatha Christie’s work will find, as I have done, that Randall Toy’s The Agatha Christie Who’s Who (Muller, 1980) is painstaking and invaluable. Citations from the reviews of books and plays may be found in many books about Agatha Christie, notably Dennis Sanders and Len Lovallo’s Agatha Christie Companion (Delacorte Press, NY 1984), which is devoted to this theme. I have preferred, however, not to draw greatly on such material, for, apart from their remarkable geographical spread, reviews of Agatha Christie’s work are interesting mainly for their predictability.
There is one more group whom, at the end of this preface, I would like to thank: the secret army of those who gave good advice, pursued elusive references and raided libraries and bookshops across the world, so that they could telephone to Devon – and remoter spots – with answers to questions I thought urgent. Though these friends are anonymous here, I will write their names, with gratitude and affection, in their copies of this biography.
Janet Morgan
1 ‘… the Millers – a family’
Even the beginnings were deceptive. To comfortable middle-class households in Torquay, the airy coastal resort in Devon where Agatha was born, the end of the nineteenth century seemed to be a Victorian afternoon. They did not notice that twilight was stealing over the terraces, the gardens and the pier. Agatha’s own family, the Millers, looked equally prosperous and secure, but their fortunes, too, were imperceptibly growing shakier. And, like most families, the Millers were not as ordinary as they first appeared. In fact, they were decidedly unconventional.
Agatha was the youngest of three children. Madge, her sister, had a passion for disguise that exasperated her teachers and, eventually, her husband, as much as it entertained her friends and bewildered her visitors. Monty, Agatha’s brother, had a different if related talent – for hitting on wild schemes into which he would draw harmless bystanders, to no one’s profit but everyone’s delight, particularly that of the women. Frederick, Agatha’s father, was a charming, nonchalant American, keen on amateur theatricals, fussy about his health but not, until too late, about his investments; her mother, Clarissa, known always as Clara, was capricious, enchanting, and said to be psychic. She was also prone to spiritual and intellectual recklessness. Agatha adored them all.
Frederick and Clara had a romantic and complicated history. Clara’s childhood was a mixture of comfort and insecurity that made her an especially possessive mother; this, in turn, fed Agatha’s devotion, which for a time was to become obsessive. To understand Agatha, it is necessary to know her parents and, equally important, the two women who shaped their lives: her grandmother and step-grandmother, Mary Ann and Margaret.
The family was connected as neatly as characters in a detective story. These links are clearer if they are described like the settings for Agatha’s plots, with the help of a plan:
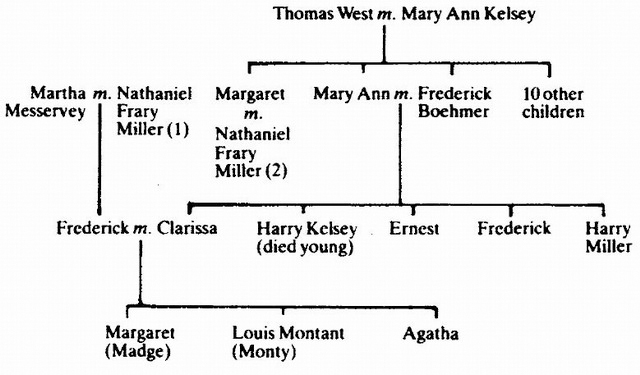
Mary Ann and Margaret West and their ten brothers and sisters were orphans and were brought up on a farm in Sussex by childless relations. In 1851 Mary Ann met Captain Frederick Boehmer of the Argyll Highlanders, who pressed her to marry him. Since he was thirty-six and she sixteen, her family demurred but Captain Boehmer argued that, as his regiment was about to be sent abroad, the wedding should take place at once – and it did. Mary Ann and Frederick had five children in quick succession (one died as a baby) of whom the only daughter, Clara, was born in Belfast in 1854.
In April 1863 Captain Boehmer, then stationed in Jersey, was thrown from his horse and killed, at the age of forty-eight, leaving Mary Ann, now twenty-seven, with four children to support as best she could. She was an excellent needlewoman and, by embroidering pictures and screens, slippers, pincushions and the like, augmented her husband’s tiny pension. As Frederick had lost what savings he had in some vague speculative venture, Mary Ann had a great struggle to make ends meet. It is little wonder that in an entry in a family ‘Album to Record Thoughts, Feelings, etc.’ known as the ‘Confessions’, written eight years after Frederick’s death, she gave her state of mind as ‘Anxious’.
Meanwhile, Mary Ann’s elder sister, Margaret, had been working in a large hotel in Portsmouth, a post found by an aunt who had for many years been its forceful and greatly respected receptionist. Margaret, already formidable herself, married when she was twenty-six, in April 1863. Her husband, Nathaniel Frary Miller, a widower, had been born in Easthampton, Massachusetts, and had become a successful businessman, a partner in the firm of H.B. Chaflin in New York City. Nathaniel and his first wife, a hospital nurse, had only one child, a son, Frederick Alvah Miller. After his mother’s death, Frederick was brought up mostly by his grandparents in America, but, after his father remarried and settled in England, where his firm had business in Manchester, Frederick visited Nathaniel and Margaret there. Here he met Clara.
It was a fortnight after Margaret’s marriage to Nathaniel that Mary Ann lost her husband. Margaret wrote immediately to her younger sister, offering to take one of the four children and bring it up as her own, and Mary Ann, now despairing, decided that Clara should go to live with her aunt and uncle in the North. The little nine-year-old was lonely and homesick in her new surroundings and Clara always believed Mary Ann had sent her away because she cared more for the boys, rather than, as seems likely, because she felt it would be less easy for a girl to make a career for herself. Clara’s chief consolation was her favourite book, The King of the Golden River, which she brought with her from Jersey. She would read aloud to her uncle Nathaniel the story of its hero, a lonely but determined little boy, who conquered his desolation by being sensible and considerate. Clara, quiet and imaginative, knowing her aunt and uncle were being kind to her but feeling bereft and misunderstood, treasured this book all her life, as Agatha did in her turn.
Clara’s upbringing and tastes were those of an intelligent but sheltered late-Victorian girl. When she was seventeen, she too listed her likes and dislikes in the ‘Confessions’. Her ‘favourite qualities in man’, she said, were ‘firmness, moral courage and honour’, and, in woman, ‘refinement, frankness and fidelity’. Her favourite occupation was reading and talking, her chief characteristic ‘a great love for children’, and ‘the fault for which she had most toleration’ (in this case her own), ‘reserve’. But the young woman whose ‘present state of mind’ was ‘wishing for a long dress’ and who admired Landseer and Mendelssohn, Tennyson, Miss Nightingale and the novels of Miss Mulock, nevertheless had a more robust and merry side. She gave her favourite food and drink as ‘Ice-cream; American soda water’, her favourite fictional heroine as Jo, the energetic tomboy in Little Women, and to the question ‘If not yourself, who would you be?’ she replied firmly, ‘A school-boy.’
When Clara came to live with the Millers, Frederick, Aunt Margaret’s American stepson, was seventeen years old and the cousins became fond of one another. Although there was only eight years’ difference between them, it seemed a larger gap: Clara lived quietly at home in England, while Frederick, after school in Switzerland, had enjoyed a lively, to Clara a dizzy, time in America. As one of his friends later told Agatha, ‘He was received by everyone in New York society, was a member of the Union Club, and was widely known, and there are scores of present members of the Union Club, mutual friends of ours, who knew him, and were very much attached to him.’ After Frederick’s marriage, his and Clara’s names appeared in the New York Social Register; in his own copy Frederick’s blue pencil ticked the names of his many New York friends and acquaintances and others in the best families of Philadelphia and Washington.
The sort of life Frederick led is described in the novels of Henry James and Edith Wharton. The American upper-class society in which he moved was small and intimate – some nine hundred families only are listed in the Social Register of 1892 – and much time was taken up with visiting friends and relations, reading newspapers and writing notes at the Club, dining, dancing, going to the theatre and (less frequently for those who were not devotees) concerts and galleries, playing tennis, croquet and cards, smoking (a serious pastime) and watching horses racing or, alternatively, yachts. Frederick Miller was not, however, one of the moody young fellows depicted in novels of the time, but, in Agatha’s words, ‘a very agreeable man’. Indeed, in his own joking entry in the ‘Confessions’, written when he was twenty-six, he gave an accurate picture of his temperament – easy-going, philosophical, hardly energetic. His favourite occupation was described as ‘doing nothing’, his chief characteristic, ‘ditto’. The characters in history he most disliked were Richard III and Judas Iscariot, his favourite heroes in real life Richard Coeur de Lion and ‘a country curate’. His pet aversion was ‘Getting up in the morning’, his present state of mind ‘Extremely comfortable, thank you’, and to the question, ‘If not yourself, who would you be?’ he placidly replied, ‘Nobody.’ Only one question had a really enthusiastic answer and that concerned his favourite food and drink, where he crowded into a two-line reply: ‘Beefsteak, Chops, Apple Fritters, Peaches, Apples. All kinds of nuts. More peaches. More nuts, Irish stew. Roly Poly Pudding’, and, an asterisked afterthought, ‘Bitter Beer.’
In the same entry Frederick described the characteristics he most admired in women as ‘amenibility to reason’ (his spelling, like that of Madge and, especially, Clara and Agatha, was often erratic), ‘with a good temper’. These were his little cousin’s qualities. She was devoted to Cousin Fred, who had been the first person to compliment her, at the age of eleven or so, on her beautiful eyes, and who sent her when she was seventeen a volume of Southey’s poems, bound in blue and gold and inscribed: ‘To Clara, a token of love’. Clara, for her part, sent Frederick letters and poems and, later, notebooks embroidered with daisies, monograms in gold thread, inscriptions and, most ambitious, a red heart stuck with two arrows. She took pains over these tributes; she was a much less skilful needlewoman than her mother and in one piece of embroidery was obliged to leave off the last letter of Frederick’s name, having misjudged the space available. She also gave him serious and sentimental poetry; a maroon and gold album contains the verse, mostly about love and death, which she composed during their engagement. Occasional corrections in Frederick’s hand show that he not only conscientiously read his cousin’s poetry but here and there improved it.
The most lively verse in that collection was a satirical view of marriage, ‘The Modern Hymen’, which Clara described as being a purely egotistical arrangement: ‘For the Bride, fair beauty, For the Bridegroom, wealth. Two in one united, And that one is – Self.…’ Clara’s and Frederick’s marriage was not at all on these lines. She had refused his first proposal because she thought herself to be ‘dumpy’ and he, though believed to be rich because he was an American, enjoyed a comfortable but not enormous income.
The cousins were married in April 1878; Frederick was thirty-two and Clara twenty-four. A month later, in Switzerland, she wrote a long, rhapsodic poem for him, asking God to send her ‘an angel friend’, whom she could charge to protect and support ‘her darling’; the gift to Frederick is the more touching because it has at the foot a slightly botched attempt at a drawing of an angel and a request to ‘excuse this piece of paper … the only thin piece I had left’, as well as enclosing two dried edelweiss, a gentian, a violet and some clover. These, with the notebooks, Frederick always kept by him.
Margaret Frary Miller, Frederick and Clara’s first child, was born in January the following year, in Torquay, where the Millers had taken furnished lodgings. Soon after Madge’s birth her parents took her to America, so that Frederick could present his wife and baby daughter to his grandparents, and it was thus that the second child, a boy, was born in New York in June 1880. This was Louis Montant, named after Frederick’s greatest friend. The Millers and their two children then returned to England, where they expected to stay only a short time before going back to America to live. Frederick, however, was suddenly obliged to return to New York to see to various business matters and suggested that while he was away Clara should take a furnished house in Torquay. With the help of Aunt Margaret, now a widow, Clara accordingly inspected two or three dozen houses but the only one she liked was for sale, rather than for rent. Despite – or perhaps because of – the restrained and ordered environment in which she had been brought up, Clara was determined and impetuous, and she immediately bought the house, with the help of £2,000 which Nathaniel had left her. She had felt at ease in it at once and when its owner, a Quaker called Mrs Brown, had said, ‘I am happy to think of thee and thy children living here, my dear’, Clara felt it was a blessing. Frederick was somewhat taken aback to discover that his wife had bought a house in a place where he expected them to stay a year or so at most but, always good-natured, he fell in with her wishes.
The house was Ashfield, in Barton Road. It has long been demolished but some impression of it can be had from Agatha’s recollections and those of her contemporaries and from photographs taken at the turn of the century. Ashfield was large and spreading, like other Torquay villas of its kind, built for the sizeable families of the professional middle class, who needed plenty of spacious rooms to hang with draperies, cram with furniture and stuff with interesting objects which they liked, or liked to display. Such houses were no trouble to heat, because fuel was cheap, or to clean and maintain, because servants were inexpensive, with enterprising and ingenious plumbers, glaziers, carpenters and masons in abundant supply. Ashfield was an attractive and unusual house; a rectangular two-storey part, with wide sash windows, adjoined a squarish three-storey section, with tall windows, some of those on the ground floor having coloured glass in the upper part, while the lower sections opened on to the garden. There was a multiplicity of chimneys; trellis-work and climbing plants covered the walls. The porch, which was large and topped with window boxes, was entirely shrouded with creeper. Attached to the house was an airy conservatory, full of wicker furniture, palm trees and other spiky and exotic plants, and at ten-foot intervals along the edge of the lawn, where it bordered the gravel, were huge rounded pots of hyacinths, tulips and other plants in season. A second, smaller greenhouse, used for storing croquet mallets, hoops, broken garden furniture and the like, and known as ‘Kai Kai’, adjoined the house on the other side. (Towards the end of her life Agatha described this greenhouse in Postern of Fate.)
The garden seemed limitless to Agatha, most of whose childhood world it composed. She described it as being divided in her mind into three parts: the walled kitchen garden, with vegetables, soft fruit and apple trees; the main garden, a stretch of lawn full of trees – beech, cedar, fir, ilex, a tall Wellingtonia, a monkey-puzzle tree and something Agatha called ‘the Turpentine Tree’ because it exuded a sticky resin; and, last, a small wood of ash trees, through which a path led back to the tennis and croquet lawn near the house. Ashfield was, moreover, at the end of the older part of the town, so that Barton Road led into the lanes and fields of the rich Devon countryside. The houses and gardens seemed immense and that was how Agatha remembered them when she was grown up – but Ashfield was certainly big.
It was as well that the house was spacious, since Frederick had a mania for collecting. Torquay being a fashionable resort, patronised by people with money, taste and plenty of spare time, it had attracted a number of dealers, into whose smart shops he would make a detour on his daily walk to the Yacht Club. The shopkeeper who did best was J.O. Donoghue, of Higher Union Street, whose lengthy bills give a detailed picture of Frederick’s purchases of coffee tables, card cases, plaited baskets, salts, oriental jugs and jars, china plates, cut-glass candlesticks, paintings on rice paper, muffineers and innumerable pieces of Dresden china. The stack of bills preserved among Frederick’s papers also shows the extent of the Millers’ domestic establishment and hospitality. Five-course dinners were prepared daily by Jane, the cook, with a professional cook and butler hired for grand occasions, when at each course a choice of dishes would be presented. Clara kept a book of ‘receipts for Agatha’, which indicates the richness and expense of the food that was served: fish pies, for instance, were made of filleted sole layered with oysters (though there was a footnote saying ‘Best brand of tinned oysters “Imperial”’) and directions were given for preparing truffles to add to meat or chicken, for making breakfast dishes of cold salmon and of kidneys and mushrooms, for dishes of quail, splendid savouries, and various complicated salads, smooth creams and junkets. The only really economical recipe, for macaroni cheese, instructed the reader to ‘get the macaroni at a shop in Greek Street, Soho, kept by an Italian’ and carried the terse comment ‘Not very good.’
Into this well-equipped household Agatha was born on September 15, 1890. She was the much-loved ‘afterthought’; her mother was thirty-six, her father forty-four and there was a gap of eleven years between Agatha and Madge and ten between Agatha and Monty. Madge was by now a boarder at Miss Lawrence’s School in Brighton (later to become the celebrated girls’ boarding school Roedean) since this accorded with Clara’s current view of what should constitute female education. Madge’s letters to her baby sister – ‘My dear little chicken … Who do you get to make you a big bath of bricks in the schoolroom now that your two devoted slaves have left for school to learn their lessons?’ – reflected her gregarious and comic nature. She was a tumbling, bouncing girl, not beautiful but with an attractive, mobile face and an engaging grin. The only wistful note in her entry in ‘Confessions’ was her answer to: ‘If not yourself, who would you be?’ to which she replied, ‘A beautiful beauty.’


