 полная версия
полная версияBlackwood's Edinburgh Magazine, Volume 54, No. 334, August 1843
Nevertheless, before the title of Switzerland Felix be fully conceded, the legitimacy of its derivation remains to be investigated. The concession can only be registered upon three conditions fulfilled. It must be shown, firstly, that manufacturing industry was not fostered in its early stages by the governing power; secondly, that if it had attained a large development unprotected, the proportions of such development shall have been at the least equal, as upon the theory of free trade they should be superior, to the ratio of progression manifested in other countries where protection has been the ruling principle; thirdly, that free trade was not a necessity imposed by circumstances and position, not the result of a barter of value for value, but of free and spontaneous choice, and as the result of the profound conviction of the superior excellency and adaptability of the abstract principle. We shall deal briefly with the subject, because it has been discussed more at length heretofore in those special articles in which we have treated of the rise and progress of the cotton manufacture in this and other countries. In regard to the first condition, it was established on a former occasion, that the ruling powers of one or more of the Cantons, did advance large capitals, and offered more, in order to encourage and assist in the establishment of cotton-spinning mills, with machinery of the most perfect construction, under the superintendence, and with a share in the profits, of persons duly skilled from England. Happily, one of the individuals to whom such offers (on the basis of a £100,000 capital) were made, and by whom declined, then and subsequently one of the largest exporting merchants of Lancashire to Switzerland, and the Continent generally, still lives, and we have had the statement confirmed by himself within the last two or three years. This was somewhere between 1795 and 1800, further our memory does not serve for the precise date at present, nor is it indispensable. A manufacture thus, as may be said, artificially created and bolstered up, we do not say unwisely, does not assuredly answer the first condition required. With respect to the measure of the manufacturing development, the data are unfortunately wanting for precise verification; for Switzerland possesses no returns of foreign trade at all, nor can any satisfactory approximation be arrived at from inspection of the official tables of the foreign and transit commerce now before us of Holland, Belgium, and France, through which all the transmarine intercourse of Switzerland must necessarily pass. The exports and imports of Holland, by the Rhine, are not so classed as to show what proportion appertains to Germany and what to Switzerland, as both stand under the one head of Germany and the Rhine. In the Belgian tables, Switzerland does not enter at all until 1841, therefore they can afford no materials for the comparison with former years. From the French tables, more scientifically constructed, correct information may be gathered, so far as the commerce with and through France. But we are wanting nearly altogether in materials for estimating the land traffic of Switzerland with Germany and Italy. Taking the French tables alone, it may be collected, however, that the commerce of Switzerland has been considerably on the increase with and through France. In the cotton trade, for example, the imports of raw cotton in transit through Havre, for Switzerland, had already augmented from 2,973,159 kilogrammes in 1830, to 6,446,703 kilogrammes in 1836; and again, from the latter term, to 104,842 metrical quintals in 1840, which declined to 77,534 in 1841. Our returns do not enable us to state with exactitude whether the whole, or what portion, of the transit of cotton for the two latter years was destined for Switzerland, because our French tables do not, as up to 1836, embrace the details of the separate transit trade to each country, but only the total quantities. The increase of imports by way of France must not, however, be taken to all the extent as an absolute increase, nor can we conclude, with any assurance, that it was an increase upon the whole. For, in consequence of some important reductions in the dues agreed to by France in order to favour and attract the entire transit trade of Switzerland through its territory, the cottons formerly passed to Switzerland through Rotterdam and Antwerp by the Rhine, have been sent by way of Havre. Thus, on consulting Mr Porter's Tables of Trade, we find that the twenty-one millions of lbs. of cotton re-exported to Holland and Belgium in 1837, had decreased, in 1840, to little more than twelve millions. What proportion of the twenty-one millions was destined for Switzerland, there are no means of ascertaining, except from the returns in detail of the Rhine navigation, the existence of which, in any available shape, may be doubted. Assuming that the whole of the cotton passing in transit through France was for Switzerland, we find a quantity equal to about seventeen millions of pounds, in 1841, as required for the supply of the cotton manufacture; or say, on a rough average of 1840 and 1841, nineteen and a half millions of pounds. Now, considering that the cotton manufacture has been established in Switzerland above a century, these figures certainly demonstrate any thing but an extraordinary rate of progress. The cotton manufacture of Russia does not number half the years of existence, and yet the average consumption of raw cotton, in 1840 and 1841, was nearly thirteen millions of pounds, and of cotton yarn, rendered into cotton,10 about twenty-three millions more. It must be noted, moreover, that whereas subsequently to the inventions of Arkwright and Crompton, Switzerland drew nearly the whole of her yarns for making into cloths from England, not possessing herself any spinning machinery until the commencement of the present century, and then but to a trivial extent, with scarcely any augmentation of importance, until some years after the general peace of 1815; yet that, within the last twenty years, the use of machinery has been extensively introduced, cotton factories have spread on all sides, for working which water-power in abundance afforded every facility, so that she now spins nearly all the yarns necessary for her fabrics, and imports from England but a very slender quantity of the higher counts still required for her finest muslins. Those imports do not perhaps exceed, if they reach to, one million pounds per annum. Of many merchants in Manchester, thirty or forty years ago, extensively engaged in furnishing that supply, but one or two at present are to be found. It remains, therefore, doubtful whether there has been any material progress in the cotton manufactures of Switzerland, so far as the quantities of fabrics produced, and the weight of cotton consumed, for many years past. Through the commercial arrangements before referred to, her special trade with France in all commodities has been on the increase; but, as the usual result of the commercial treaties of France, all to the advantage of France. Thus, for 1841, the imports (special trade of internal consumption) of France from Switzerland are stated at twenty-two millions of francs only, whilst the exports of France to Switzerland amounted to thirty-nine millions. This, be it observed, is the result of one-sided free trade, which opens its gates to all, whilst partially favoured only in return, when at all. Switzerland, for example, is free to the import of French cottons; France hermetically sealed against those of Switzerland. The general trade, that is, inclusive of transit and special, had also materially improved; the aggregate imports representing eighty-three millions of imports into, against eighty-nine millions of exports from Switzerland; or that the general trade with France had rather more than doubled since 1832, imports and exports together. The transit portion of this general trade, representing all the transmarine movement of Switzerland, is that rather, it may be said, carried on with the United States Spanish America, Brazil, &c., in which the greatest improvement of her foreign trade had taken place. She has, on the contrary, very largely lost ground in Germany, where she enjoyed marts for her manufactures, before the establishment of the Commercial Union, of an extensive and profitable description, from the advantages of her geographical position; and it is probable, that from the same cause she will have lost no inconsiderable portion of the share her merchants had in the supply of Turkey, Persia, and other countries on the shores of the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. With Holland and Belgium, her commercial relations would seem to have been sensibly on the decline, so far as the returns, available and comparative, enable us to form an opinion. Upon a balance, therefore, of increase, upon one side, and decrease on the other, there is reasonable ground to question any progress in Switzerland, at all commensurate with the general accelerated movement in manufactures and commerce of other industrial countries about her, and beyond the seas; in exemplification of which, we have on other occasions presented, as we shall continue to present, evidence which may not be questioned.
Therefore, it results, that the second condition in proof of the superiority of the free, or one-sided free trade principle, as represented in Switzerland, the embodied beau idéal of the theory, is not fulfilled. It were easy, indeed, to show the absurdity of a pretension to the rigorous reign of a principle, in a country where, though the federal government levies are merely nominal duties on imported commodities, for other than which it is and must ever be powerless, whatever the will, yet in the separate cantons or chief towns with barriers, scarcely any article enters and escapes without payment of an octroi impost, equal to a moderate state duty on importation at the ports or frontiers of other states. What would be said in this country, if wool, cotton, or any commodity entering free, or at merely nominal rates, at London or Liverpool, were to be taxed on arrival at Leeds or Manchester, for purposes of local revenue or local protection?
We may afford to dismiss the third condition in the smallest space. Free trade in Switzerland, such as it is, is not an affair of principle, of conviction, therefore of choice, as ridiculously pretended, but a necessity arising out of her geographical position. On all sides she is surrounded enclavée, amidst states which hold the gates of ingress and egress. Close the Rhine and the Seine against her, and she must surrender commercially at discretion, as she politically does, to such terms as may be dictated. A heavy péage upon river or land transit, ruins her manufactories, her industry, root and branch. She is too happy only, therefore, to be tolerated with a passage to the sea, on the hard terms of surrendering the just rights of her own industry to the free invasion of foreign competing products; she makes, ex necessitate, the sacrifice of a large portion, in order to save the remainder. Would you have the commentary? Read it in the miserable fare, the low wages, the toil unremitting and uncompensated, of the operative masses; in the depressed rate of profits, the strict, painful, but indispensable frugality of master manufacturers and capitalists, when perchance capitalists may be found, of Switzerland surnamed Felix, over-borne by foreign competition, as depicted in the Report of that romance writer, Mr John Bowring himself, who, of all men, in his own particular case, would be the last to advocate short commons, shabby salaries, or petty profits. Switzerland, therefore, answers none of the conditions required for the demonstration of the free trade theory upon the greatest profit, or even upon the greatest happiness principle, the verba ardentia of anti-corn-law declaimers, and utilitarian poetasters, notwithstanding. But if the case of the free and one-sided trade theory breaks down in its one only deceptive personification, the proofs are strong and abundant in behalf the cause of the legitimate principle of protection to industry, or of the reciprocity principle well understood, which involves essentially the principle of protection. Let us discursively range over Europe, in further addition to the evidence, which, in respect of Russia, has already been assigned; and, as with regard to Spain, and Russia as well, we shall not hesitate to signalize the abuse of a righteous principle, where in practice it degenerates into the Japanese barbarism of almost absolute prohibition and isolation. A comparison betwixt Switzerland and Japan, two nearly stationary states, where all around is in progress in the industrial sense, ruled upon economical principles so opposite and conflicting, would be a labour both amusing and profitable; but unfortunately the adequate materials are wanting in the one case as in the other; state-books of account and custom-house returns, are as rare and unheard of in Nangasaki as in Helvetia. Fiscal exactions, however, are not unknown in either, the difference being, that the despotic majesty of Japan undertakes them upon his own account, whilst the people of the Alps, as intractable, with better right, impose and levy for their own use and behoof. Withal, to the one-idea'd philosophy of your absolute theory, systematic, uniformity men of the present day, it should seem an extraordinary paradox, putting all speculation to rout, that despotic Japan should be as prosperous, more powerful, more free from intestine convulsion, although more ancient of standing, therefore to be presumed enjoying at least as much happiness as free and unfettered Switzerland, rioting betimes in all the freaks of liberty and revolution.
We do not propose to extend our enquiries into the history of industrial progress in other lands further on the present occasion, than to such external demonstrations, as measured by imports and exports, as may with most convenient brevity and fidelity answer the purpose in view. The possession of authentic documents in ample degree, expository of the past and present conditions of social and material interests in almost all the civilized states of the world, would enable us to follow out, in minute detail, the rise, the career, the vicissitudes of each; but although, on future and suitable occasions, we may be induced to resume and pursue the task already commenced in former numbers, it is not necessary now, and would far outstrip any possible space at our disposal. Commencing with Austria, it may be shown, that even with an ill-considered economical régime of, until of late years, general prohibitions and restrictions, with the incessant and ill-judged policy of forcing manufacturing industry, for the hasty development of which the natural foundations were not previously laid, whilst neglecting the cultivation and encouragement of those varied agricultural and mining treasures, with which, through the length and breadth of her territory, she is so abundantly stored, the advance of Austria, commercial and manufacturing, need not assuredly fear comparison with that of free-trading Switzerland. The following are the returns of the foreign trade of the Austrian empire, excepting for Hungary and Transylvania, which will be found hereafter for the years cited. Other documents are in our possession, bringing the information down to 1840, but as not entirely complete in respect of a portion of the traffic by the land frontiers, whilst in results they differ little from the last year of the table here given, it is not worth while to make the addition.
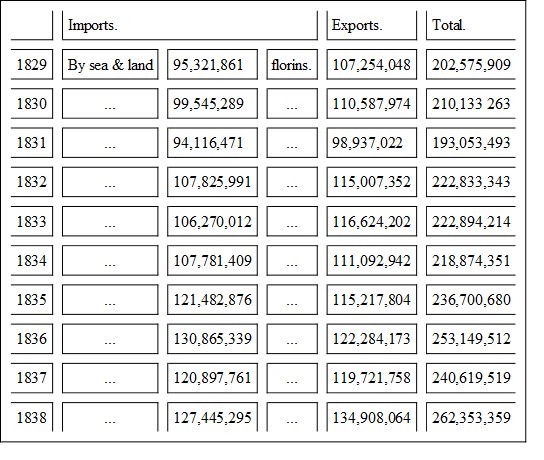
The florin is equal to 2s. 0d. 4-10 sterling. The increase under the head of importations within the ten years was equal, therefore, to nearly 33 per cent, and on exportations about 24 per cent. Amongst the imports may be remarked raw cotton to the value of about L.1,273,000; among the exports, raw silk, for about L.2,400,000; linens, for about L.770,000; woollens, for L.2,268,000; glass and earthen-ware, L.584,000; round numbers all. A mean value, imports and exports together, from 1835 to 1838 inclusive, of about twenty-five millions sterling annually, does not certainly represent a commercial movement so large as might be expected in an empire of the territorial extent, numerous population, and rich natural products of Austria. But, as appears, its progression is onwards; and seeing that, in 1836, she entered on the laudable undertaking of revising and reforming her prohibitory and restrictive system; that, in 1838, another not inconsiderable step in advance was taken by further relaxations of the tariff; and that she is at the present moment occupied with, and may shortly announce, fiscal improvements and tariff reductions of a more wisely liberal spirit still, it is not to be doubted that, with the accompanying extension of agricultural and mining industry, Austria is destined to take a much higher rank in the commercial world than she has yet attained.
The values of the external relations of Hungary and Transylvania with foreign nations direct, are of little importance. The bulk of the traffic with them doubtless passes through the Austrian dominions, properly so called. Thus their joint foreign traffic direct, was in—
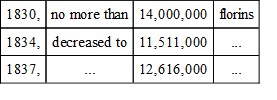
The imports, only once, in 1836, surpassed those of 1830, within the eight years. The foreign exports were, in

But the commercial relations of Hungary and Transylvania, with the other provinces of the Austrian monarchy, were, on the contrary, satisfactorily extending. The returns before us, never before published here, it is believed, do not date further back than 1835, and exhibit the following results:—
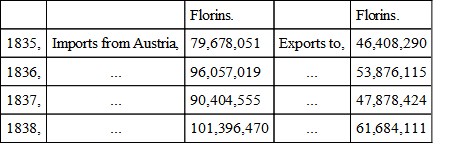
The value of manufactured cottons alone, imported from the other Austrian provinces, amounted, in 1838, to the almost incredible sum of sixty-four millions of florins, or say not far short of six and a half millions sterling; of woollens, the import was nearly to the value of eighteen millions of florins. It is difficult to conceive that such a mass of cottons could be destined for internal consumption alone; and therefore the suggestion naturally occurs, that a considerable portion at least must pass only in transit to the ports for re-exportation to the coasts of the Black Sea and the Levant; but on reference to the exports, we find cottons entered only for 31,296 florins. The proportions in which the different leading articles of importation and exportation enter into the total amounts of each may be thus stated:—
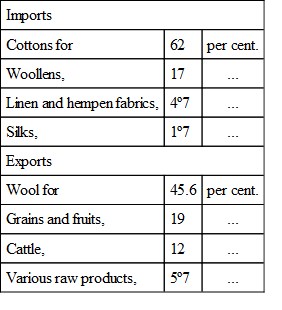
The great bulk of this commerce with Hungary and Transylvania is carried on with the three great provinces of the empire—Lower Austria, which alone absorbs about two-thirds of the total; Moravia and Austrian Silesia, one-fourth; and Gallicia and Austrian Poland, the imports from whence represent above one-tenth, and the exports to which form one-twentieth of the whole.
Such has been the progress of the Austrian empire even under the unwisely strained régime of prohibition and restriction. The absolute theory men will not gain much certainly by its comparison with the free trading elysium of Switzerland, although the most favourable for the latter which could well be selected, inasmuch as representing a principle carried to a prejudicial extreme.
We have not, however, done with our absolutists of the one-sided free-trade theory yet. We must traverse Belgium with them, but at railway speed; Belgium, of commercial system less restricted than Austria, yet more exclusive than England, where, however, some approach towards the juste milieu of the equitable principles of reciprocity, may be observed in progress. How then has she fared in the general mêlée of industrial strife, and what are her prospects for the future in despite of her stubborn resistance to the new lights? Let the figures which follow answer for her. The imports and exports by land and sea, were in—
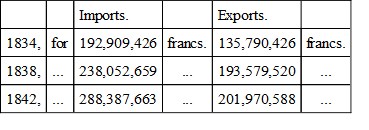
For commerce special, that is, of internal production and consumption alone, the returns show, in—
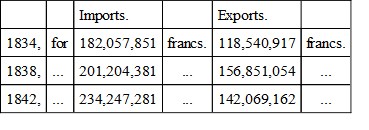
The commerce general comprises as well the imports and exports of the special commerce as the transit and deliveries in entrepot of foreign merchandise. From 1834 to 1842 the increase of imports and exports, combined under the special head, was equal to more than three millions sterling. Under the general head, the increase was nearly equal to six and a half millions sterling. The comparatively large and disadvantageous inequality betwixt the exports and imports, under both heads, results mainly from the loss of those markets in the Dutch colonies, and in Holland also, of which, during her connexion with Holland and under the rule of the same sovereign, Belgium was almost exclusively in possession. The formation of the German Commercial Union cannot have failed also to damage her intercourse with Germany, to the markets of which her contiguity afforded so easy and advantageous an access.
It was our intention to have reviewed at some length the progress of the German Customs Confederation since its complete formation, with some inconsiderable accessions subsequently in 1834; but space forbids. In brief, but conclusive, evidence of that progress under the rule of protection, we may afford, however, to cite the following returns of revenue accruing under the poundage system, representing, of course, the growing quantities imported. The alternate years only are given, to avoid the needless multiplication of figures:—

The Prussian thaler is 2s. 10-3/4d. sterling.
Year by year the rise has been uninterrupted; and with the growth of imported commodities thus represented by the revenue, have indigenous products multiplied, and native manufactures flourished and extended more rapidly and widely still.
In a review of protected nations it is impossible that France should be lost sight of. More rigorously protective than Belgium, prohibitive even in some essential parts of her system, whilst stimulating by bounties in others, the results of a policy so artificial and complicated can hardly fail to confound your dabblers in first principles and rigid uniformity. In the sense economical France has not hesitated to violate outrageously all these first principles, all that perfect theory, in the worship and application of which, politically and socially, her philosophers were wont to run raging mad, and her legislators, like frantic bacchanals, were in such sanguinary "haste to destroy." Singular as it may seem, and audaciously heretical as the consummation in defiance of the order inevitable of first causes and consequences invariable, the comparative freedom of commercial principles in the old régime of France allied with political despotism, was, however, ruthlessly condemned to the guillotine, along with the head of the Capets, never to be replaced by the ferocious spirit of democracy, revelling in the realization of all other visionary abstractions of perfect liberty, equality, levelling of distinctions and monopolies. With the reign of the rights of man was established, in the body politic, that of prohibition and restriction over the body industrial—gradually sobered down, as we find it now, to a system singularly made up of prohibition, restriction, protective, and stimulant, since the last great revolution of July. It is in vain to deny that, under the reign of that system, France has prospered and progressed beyond all former example; that whether freer Switzerland may have stood still or not, France, at least, has never retrograded one step, nor ceased to advance for one year, as thus may be concisely exemplified in the citation of three terms of her commercial career, faithfully indicative of the annual consecutive movement of the whole series:—









