 полная версия
полная версияThrough Three Campaigns: A Story of Chitral, Tirah and Ashanti
"No further resistance was met with, though two more stockades were passed. This want of enterprise, on the part of the enemy, was due to a short armistice that had been arranged with the beleaguered garrison.
"Major Morris's force was the third reinforcement which had reached the garrison. The first to come up was a party of Gold Coasters from the south. This was the only contingent permitted by the Ashantis to enter Coomassie unopposed. The next was a detachment from Lagos, composed of two hundred and fifty men of that colony's Hausa force, with four British officers and a doctor, under the command of Captain Alpin. The Adansis, who occupy the country between the Prah and the recognized Ashanti boundary, had revolted; so that for part of the way they were unopposed but, as soon as they reached the first village in the Ashanti country, they were heavily attacked. After a couple of hours' fighting, however, the advance guard took the village, at the point of the bayonet.
"Next day they reached the Ordah River. Here the enemy made a determined stand, entrenched behind a stockade. The fight lasted for four hours, and then the situation became critical. The Maxim had jammed, the ammunition of the seven-pounder was exhausted, and a great proportion of the small-arm ammunition had been expended. Captain Cox and thirty men went into the bush, to turn the enemy's position. When they reached a point where they took the enemy in rear, they charged the stockade. The enemy fled, and were kept at a run until Coomassie was reached, before dark.
"The list of casualties showed how hard had been the fighting. All the white officers had been wounded, and there were a hundred and thirty casualties among the two hundred and fifty British soldiers. The garrison now consisted of seven hundred rank and file, and about a dozen British officers; two hundred and fifty native levies, and nearly four thousand Fanti and Hausa refugees.
"The next force to move forward was the first contingent from Northern Nigeria, consisting of two companies under the command of Captain Hall, with one gun. In traversing the Adansi country Captain Hall drew up a treaty, and got the Adansi king to sign it. Then he marched on to Bekwai, the chief town of a friendly tribe; and took up his quarters at Esumeja, a day's march from Coomassie. The border of Bekwai lay a short distance on one side, that of Kokofu was half a mile to the east.
"These were an Ashanti tribe, very fierce and warlike; and the occupation of Esumeja both kept them in check, and inspired the loyal Bekwais with confidence. Here Captain Hall was joined by a second contingent from Lagos, a hundred strong; and fifty men of the Sierra Leone frontier police. The force has got no farther, but its position on the main line of march is of vital service; as it overawes the Kokofu, and facilitates the advance of further relief.
"That, gentlemen, is the situation, at present. So far as I know, the garrison of Coomassie is amply sufficient to defend the fort; but we know that they are short of ammunition, and also of supplies to maintain the large number of people shut up there.
"I am expecting the vessel with the main Nigerian contingent tomorrow, or next day; and I hope that this reinforcement will enable an advance to be made."
"Thank you, sir! It is evident that we are in for some tough fighting, and shall have all our work cut out for us."
"There can be no doubt of that," the commissioner said, gravely. "The difficulties have been greatly increased by the erection of these stockades, a new feature in these Ashanti wars. When the Bekwais put themselves under our protection, instructions were given them in stockading, so that they might resist any force that the Ashantis might send against them and, doubtless, the latter inspected these defences and adopted the idea. The worst of it is that they are generally so covered, by the bush, that they are not seen by our troops till they arrive in front of them."
Chapter 14: Forest Fighting
Early the next morning the transport with the Nigerian troops anchored off the town. The work of disembarkation began at once. Five of the newly-arrived officers were appointed to the commissariat transport service. The three others–of whom Lisle, to his great satisfaction, was one–were appointed to the command of companies in the Nigerian force. This distinction, the commissioner frankly informed him, was due to his being the possessor of the V.C.
Having nothing to do that day, Lisle strolled about the town. There were a few European houses, the property of the natives who formed the elite of the place; men for the most part possessing white blood in their veins, being the descendants of British merchants who, knowing that white women could not live in the place, had taken Negro wives. These men were distinguished by their hair, rather than by their more European features. Their colour was as dark as that of other natives. Lisle learned that such light-coloured children as were born of these mixed marriages uniformly died, but that the dark offspring generally lived.
All the small shops in the town were kept by this class. With the exception of the buildings belonging to them, the houses of the town were merely mud erections, with a door and a window or two. The roofs were flat, and composed of bamboos and other branches; overlaid by a thick mud which, Lisle learned, not unfrequently collapsed in the rainy season. Nothing could be done at that time to repair them, and their inhabitants took refuge in the houses of their friends, until the dry season permitted them to renew their own roofs.
The women were of very superior physique to the men. The latter considered that their only duty was to stroll about with a gun or a spear; and the whole work of cultivating the ground, and of carrying burdens, fell to the lot of the women. Many of these had splendid figures, which might have been the envy of an English belle. Their great defect is that their heels, instead of going straight to the leg, project an inch or more behind it. From their custom of always carrying their burdens on their heads, their carriage is as upright as a dart. Whether the load was a heavy barrel, or two or three bananas, Lisle noticed that they placed it on the head; and even tiny girls carried any small article of which they might become possessed in this manner.
Curiously enough, the men had no excuse for posing as warriors; for the Fantis were the only cowardly race on the coast, and had several times shown themselves worthless as fighters, when the Ashantis made their expeditions against them.
A narrow valley ran up from the sea, in one part of the town, and terminated in a swamp behind it. Here the refuse of the place was thrown, and the stench in itself was sufficient to account for the prevalence of fever. Here were the accumulations of centuries; for the Dutch governors, who were frequently relieved, had made no effort whatever towards draining the marsh, nor improving the sanitary condition of the place; nor had the British governors who followed them shown any more energy in that direction. Doubtless the means were wanting, for the revenue of the place was insufficient to pay for the expenses of the garrison; and so the town which, at a very moderate expenditure, might have been rendered comparatively healthy, remained a death trap.
As soon as the Nigerian troops had landed, Lisle reported himself to their commander. He was at once put in charge of a company, and began his duties. When, two days later, they marched up the country, he felt well pleased with his command; for the men were for the most part lithe, active fellows; very obedient to orders and ready for any work, and evidently very proud of their position as British soldiers. They had for the most part had very little practice in shooting; but this was of comparatively little consequence, as what fighting they would have to do would be in the forests, against a hidden enemy, where individual shooting would be next to impossible.
The Adansi had risen, three days after signing the treaty. Two Englishmen, going from Bekwai to Kwisa, on their way were fired upon, and the terror-stricken carriers fled. Their loads were lost, and they themselves just succeeded in escaping to Kwisa.
Captain Slater, who was in command there, was much surprised to hear of such hostility, so soon after the signing of the treaty; and he started with twenty-six men to investigate the cause. He was attacked at the same place–one soldier being killed and ten wounded, while two were missing–and he was obliged to retire to Kwisa. Sixty Englishmen of the Obuasi gold mines, on the western frontier of the Adansi, sent down for arms, and were supplied without any mishap.
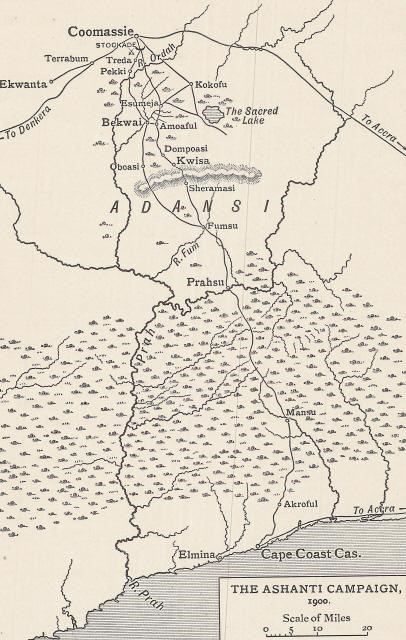
Colonel Wilkinson telegraphed orders to a force, which had started two days before, to halt at Fumsu until he joined them with the newly-arrived contingents. Colonel Willcocks now had four hundred and fifty men, under Captain Hall, at Kwisa and Bekwai; Captain Slater a handful of men at Kwisa; Colonel Wilkinson a company at Fumsu; Colonel Carter the two hundred soldiers just landed on the line of march, and three hundred men from Northern Nigeria. Nine hundred reinforcements were known to be on their way. The force was scattered over a hundred and forty miles, and numerically only equal to the garrison they were going to relieve. The carriers were utterly insufficient for the transport.
The newly-arrived troops, with Colonel Willcocks and his staff in front, rode out of the town on the morning of the 5th of June. A drizzling rain was falling, but this soon ceased and the sun broke out. The road lay over low scrub-covered sand hills. It was a fair one, with the exception of bad bits, at intervals. The first day's march was a short one, as much time had been lost in getting the carriers together, and loading them up.
They halted that evening at Akroful. The place afforded but little accommodation. Five white officers slept together in one small room. There was a storm during the night, but the sky had cleared by the time the troops started in the morning.
They now entered a very different country. It was the belt of forest, three hundred miles wide, which ran across the whole country. Great as had been the heat, the day before, the gloom of the forest was more trying to the nerves. Except where the road had been cleared, the advance was impeded by the thick undergrowth of bush and small trees, through which it was impossible to pass without cutting a path with a sword. Above the bush towered the giants of the forest–great cotton trees, thirty or forty feet in circumference, and rising to the height of from two to three hundred feet. Round the tops of these many birds were flitting, but in the underbrush there was no sign or sound of life. Thorny creepers bound the trees together.
In the small clearings, where deserted and ruined villages stood, a few flowers were to be found. Here, also, great butterflies flew about.
The moist air, tainted with decaying vegetation; the entire absence of wind, or of movement among the leaves; the profound silence, broken only by the occasional dropping of water, weighed heavily on the spirits of the troops. Under foot the soil was converted into mire by the recent rains; and glad, indeed, were all, when they reached Mansu.
From this village, as had been the case at the previous halt, numbers of the carriers deserted. In order to get on, therefore, it was necessary to send out to the surrounding villages, to gather in men to take their places; and at the same time a telegram was sent down to Cape Coast, requesting the commandant there to arrest all the men who came in, and try to punish them as deserters. It was some satisfaction to know that they would be flogged, though this did not obviate the inconvenience caused by their desertion.
Mansu was a pleasanter halting place than the two preceding ones. It was surrounded by a clearing of considerable size; and contained two bungalows, which served as quarters for the officers. The soldiers got abundance of firewood from the forest, and the place presented a picturesque appearance, after nightfall, with its blazing fires and their reflection on the deep circle of foliage.
The march had been a depressing one, to the officers; but the native troops did not seem to find it so, and chattered, sang, and danced by their fires. Three of the officers found it difficult to swallow their food; but Lisle and another young officer, named Hallett, with whom he had been a special chum on board ship, made a hearty meal and, after it was finished, set out together for a tour round the camp, to assure themselves that everything was going on satisfactorily.
"This must be very different from your experience in the Tirah," Hallett said.
"Yes; to begin with, it was generally so cold at night, even in the valley, that we were glad of both our blankets and cloaks; while among the passes it was bitter, indeed. Then, too, the greater portion of the troops were white and, though they were cheerful enough, their spirits were nothing to the merriment of these natives. Then the camps were crowded with animals, while here there are only these wretched carriers; and almost every night we were saluted with bullets from the heights, and lay down in readiness to oppose any sudden attack.
"I suppose we shall have to do the same, when we get into the enemy's country, here. That is really the only similarity between the two expeditions. The country, too, was mountainous and, except in the valleys, there were few trees; while here we tramp along in single file, through what is little better than a swamp, and only get an occasional glimpse of the sky through the overhanging foliage. Of course it is hot in Northern India, very hot sometimes; but it is generally dry heat, quite different from the close, muggy heat of the forest. However, they say that when we have once ascended the Adansi hills, matters will be better."
"I hope so, Bullen. I found it so close today that I would gladly have got rid of all my clothes, which were so drenched with perspiration that I could have wrung them. We shall have other things to think about, however, when we get across the river; for you don't think of minor inconveniences when, at any moment, a volley may be poured into you from the bushes."
"Yes, the idea is rather creepy; but they say that the Ashantis always shoot high–the effect of the enormous charges they put into their muskets–so that the harm done bears no proportion, whatever, to the noise. I expect our Maxims will come in very useful for clearing out the bush; and I doubt if the Ashantis will be able to stand for a moment, against our bayonets, as they have no weapons of the sort."
"No, but a good many of them are armed with spears, which are a deal longer than our muskets and bayonets. They are not accustomed, however, to work together. Each man fights for himself, and I feel convinced that they would not stand a determined charge," Hallett said.
"It is all very well to talk about a charge; but how are you going to charge through the bush, where every step has to be cut? However, I suppose our fellows can get through as well as they can."
"It would be horrid work, Bullen, for some of these creepers are a mass of spikes, which would pretty nearly tear a man to pieces, as he was forcing his way past them in a hurry."
"Yes, that is not a pleasant idea; but I own that, if what they say about the stockades they have formed is true, they will be even more formidable than the bush; for our little guns will make no impression upon them. They say that these are constructed with two rows of timber, eight feet apart; the intervening space being filled up with earth and stones so that, if they are well defended, they ought to cost us a lot of men before we carry them."
"Well, tomorrow we shall be at Prahsu. They say it is a fine open camp, as it was completely cleared by Wolseley's expedition. Of course, bushes will have sprung up again but, fast as things grow in this climate, they can hardly have attained any great height; and we shall have no difficulty in clearing the place again. There is a good rest house at the place, I hear, and we sha'n't be pigged in, as we were at Akroful."
"Why should they build a better house there than at the other stations?"
"Because, when the river is full, there is no way of getting across; and one may have to wait there for a fortnight, before it falls."
On the afternoon of the next day Prahsu was reached, after a march of twenty miles. The greater part of the house was found to be occupied by offices and stores. Fortunately, however, two or three tents had been brought along. The troops soon ran up huts of bamboos and palm leaves and, as there was a small native village close by, all were soon able to sleep in shelter.
The Prah was found to be full of water. It was here about a hundred and fifty yards wide, and circled round three sides of the position. There was no bridge, but two old wooden pontoons were found, relics of the last expedition; and these, with the aid of two old native canoes, were the only means of crossing.
On the morning after their arrival a despatch, dated May 24, was received from Captain Hall. It gave the details of his attack on Kokofu. Some thousands of the enemy were round that place and, in his opinion, no advance could be made to Coomassie till this force was destroyed.
An hour or two later another runner came in, this time from Kwisa. The despatch he brought gave details of the fighting the force at this place had had, in trying to effect a junction with Captain Hall.
The column advanced rapidly. In any place where the bush was particularly thick, volleys were fired into the undergrowth by a few men of the advance guard; for it had been found by experience in Nigeria that, if fired upon, natives generally disclosed their presence by replying.
They went on, unmolested, until they neared the village of Dompoasi. The natives of this town had sworn a solemn oath, to prevent any reinforcements from going up to Coomassie; and they had erected a stockade, six feet high. This was built in zigzag shape, so that a flanking fire could be kept up from it. It was about four hundred yards long, with both ends doubled backwards, to prevent an enemy from turning the position. In the rear was a trench, in which they could load in perfect shelter. Seats had been prepared on the neighbouring trees, for riflemen; and the undergrowth was left untouched, so that there should be nothing to excite suspicion.
The stockade did not run across the road, but parallel to it, the distance varying from twenty to thirty yards. Thus, anybody coming along the path would notice nothing unusual, though he himself would be easily seen by the defenders. A road had been cut, at the back of the entrenchments, so as to give a line of retreat to the defenders. On the northern side of the village, a similar stockade had been constructed.
Captain Roupell–who commanded the advance–became aware, from the numerous tracks and footprints, that the enemy must be in force in the neighbourhood, and advanced cautiously. He did not observe the stockade, however, so well was it hidden among the bushes. Just as they reached the farther end of it, a tremendous fire was opened. Captain Roupell was wounded, and many of the men also killed or wounded.
For a moment the troops were paralysed by the hail of lead. Then they replied with their rifles, and two Maxims and an eleven pounder were got to work. Captain Roupell, in spite of his wound, worked one of the Maxims, Lieutenant O'Malley the other, and Lieutenant Edwardes the gun. Captain Roupell was again dangerously wounded, and Lieutenant O'Malley so severely wounded that he was forced to discontinue fire.
Lieutenant Edwardes, although he was hit early in the action, stuck to his gun. The gun team were all lying round, either killed or wounded, and he ran home the shells with a stick. He was, shortly afterwards, shot in the left arm. This incapacitated him from serving his gun; but he went and worked a Maxim, with his right arm, till a shot in the face compelled him to have his wounds dressed.
Colonel Carter was wounded in the head, and handed over the command to Colonel Wilkinson, who was himself slightly wounded at the back of the head. The men fell fast. The seven pounder and the other Maxim were completely isolated, some distance up the path. The existence of the stockade was only discovered as the undergrowth was cut away by the rain of bullets.
The officer commanding D company–which had been the rear guard all this time and, consequently, had not suffered–was in hammock with fever, and Colour Sergeant Mackenzie was in command. At this moment Mackenzie came up, and asked leave to charge the enemy. His proposal was at once sanctioned, and when half of his company had arrived they charged the stockade, other soldiers and officers near joining them. The enemy could not stand this determined attack, evacuated their position, and took to flight.
The force now prepared to retire, and this operation they performed in an orderly manner. Seven European officers had been wounded, and there were ninety casualties. Indeed, if the enemy had not fired too high, the column might have been annihilated.
Orders were sent, to Colonel Carter, telling him to remain where he was till reinforcements should arrive. A telegram was also sent to Captain Hall, instructing him to despatch a company to increase the garrison at Kwisa. In the meantime two companies of the troops on the Prah were ordered to proceed, instantly, to the relief of Kwisa, under the command of Captain Melliss and, to Lisle's satisfaction, some of his company were to form part of the force.
They started at two in the afternoon, but it was four before they got across the Prah; and they could only march ten miles that evening, which they did through a pouring rain. An early start was made, next morning. By eight o'clock they reached Fumsu, which was held by a company of soldiers under Quartermaster Sergeant Thomas; who informed them that all the troops ahead were perilously situated, short of food and ammunition, and crippled with casualties. He tried to dissuade them from going farther, saying:
"You are simply walking into a death trap. It is not fighting, it is murder. I am sure you will never get there, with only a hundred men and all these carriers."
However, orders had to be obeyed. The carriers were so limited in number that only a few days' food could be taken to the Kwisa garrison, if all the cartridges were to go on. A hundred extra rounds were served out to each man, in addition to the hundred he already had; so that there was no risk of running short, and the carriers would be relieved of much of the weight of the reserve, and could therefore carry up a larger amount of provisions. A hasty meal was eaten, and then they stepped forward for the twenty miles' march before them.
During the halt, they found out how the natives signalled. A gun was fired from the forest, the signal was repeated farther on, and continued to the next war camp. An estimate was given of the number and composition of an enemy by the number of guns fired. The force learned, afterwards, that their departure from Prahsu had been signalled in this way to the Adansis; and only the darkness and pouring rain, which delayed the enemy's movements, had saved the column from attack.
When the march was continued, therefore, the greatest precautions were taken against an ambush. A small party of twelve men marched ahead of the advance guard, and fired occasional volleys. Where the undergrowth was unusually thick, scouts moved abreast of them, cutting a way with their sword bayonets. The difficulties were so great that the column moved only three-quarters of a mile an hour. The carriers struggled on, carrying their burdens with surprising cheerfulness, staggering over the slippery mud, and frequently falling. The gun carriers had the worst time of all, for the parts into which these weapons divide are too heavy for single loads; and have to be carried, swung on bamboo poles, by four men–but often, at the acute bends in the path, the whole burden had to be supported by two.
Nevertheless, the column managed to advance. The river Fum was rising, but was still fordable, and they crossed it, with difficulty. It was now necessary to give up scouting, and depend entirely on the volleys of the men in front to discover ambuscades. One or two deserted or thinly populated villages were passed. Then, after two hours of this trying tramp, the advance guard came upon the Fum again; but at this point its volume and width were more than doubled. The river was rising rapidly, and there were no trees that could be cut down, with the sword bayonets, long enough to throw across.









