
Полная версия
Глоссариум по искусственному интеллекту: 2500 терминов. Том 2
Computational cybernetics is the integration of cybernetics and computational intelligence techniques246.
Computational efficiency of an agent or a trained model is the amount of computational resources required by the agent to solve a problem at the inference stage247.
Computational efficiency of an intelligent system is the amount of computing resources required to train an intelligent system with a certain level of performance on a given volume of tasks248.
Computational Graphics Processing Unit (computational GPU, cGPU) – graphic processor-computer, GPU-computer, multi-core GPU used in hybrid supercomputers to perform parallel mathematical calculations; for example, one of the first GPUs in this category contains more than 3 billion transistors – 512 CUDA cores and up to 6 GB of memory249.
Computational humor is a branch of computational linguistics and artificial intelligence which uses computers in humor research250.
Computational intelligence (CI) usually refers to the ability of a computer to learn a specific task from data or experimental observation251.
Computational learning theory (COLT) in computer science, is a subfield of artificial intelligence devoted to studying the design and analysis of machine learning algorithms252.
Computational linguistics is an interdisciplinary field concerned with the statistical or rule-based modeling of natural language from a computational perspective, as well as the study of appropriate computational approaches to linguistic questions253.
Computational mathematics is the mathematical research in areas of science where computing plays an essential role254.
Computational neuroscience (also known as theoretical neuroscience or mathematical neuroscience) is a branch of neuroscience which employs mathematical models, theoretical analysis and abstractions of the brain to understand the principles that govern the development, structure, physiology, and cognitive abilities of the nervous system255,256.
Computational number theory (also algorithmic number theory) – the study of algorithms for performing number theoretic computations257,,258.
Computational problem in theoretical computer science is a mathematical object representing a collection of questions that computers might be able to solve259.
Computational statistics (or statistical computing) is the application of computer science and software engineering principles to solving scientific problems. It involves the use of computing hardware, networking, algorithms, programming, databases and other domain-specific knowledge to design simulations of physical phenomena to run on computers. Computational science crosses disciplines and can even involve the humanities260,261.
Computer engineering — technologies for digital modeling and design of objects and production processes throughout the life cycle262.
Computer incident is a fact of violation and (or) cessation of the operation of a critical information infrastructure object, a telecommunication network used to organize the interaction of such objects, and (or) a violation of the security of information processed by such an object, including as a result of a computer attack263.
Computer science – the theory, experimentation, and engineering that form the basis for the design and use of computers. It involves the study of algorithms that process, store, and communicate digital information. A computer scientist specializes in the theory of computation and the design of computational systems. Computer science is the study of computation, automation, and information. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to practical disciplines (including the design and implementation of hardware and software). Computer science is generally considered an area of academic research and distinct from computer programming264.
Computer simulation is the process of mathematical modelling, performed on a computer, which is designed to predict the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be determined by comparing their results to the real-world outcomes they aim to predict. Computer simulations have become a useful tool for the mathematical modeling of many natural systems in physics (computational physics), astrophysics, climatology, chemistry, biology and manufacturing, as well as human systems in economics, psychology, social science, health care and engineering265.
Computer vision (CV) is scientific discipline, field of technology and the direction of artificial intelligence (AI), which deals with computer processing, recognition, analysis and classification of dynamic images of reality. It is widely used in video surveillance systems, in robotics and in modern industry to improve product quality and production efficiency, comply with legal requirements, etc. In computer vision, the following areas are distinguished: face recognition (face recognition), image recognition (image recognition), augmented reality (augmented reality (AR) and optical character recognition (OCR). Synonyms – artificial vision, machine vision266.
Computer vision processing (CVP) is the processing of images (signals) in a computer vision system, in computer vision systems – about algorithms (computer vision processing algorithms), processors (computer vision processing unit, CVPU), convolutional neural networks (convolutional neural network), which are used for image processing and implementation of visual functions in robotics, real-time systems, smart video surveillance systems, etc.267.
Computer-Aided Detection/Diagnosis (CAD), uses computer programs to assist radiologists in the interpretation of medical images. CAD systems process digital images for typical appearances and highlight suspicious regions in order to support a decision taken by a professional268.
Computer-automated design (CAutoD) – design automation usually refers to electronic design automation, or Design Automation which is a Product Configurator. Extending Computer-Aided Design (CAD), automated design and computer-automated designare concerned with a broader range of applications, such as automotive engineering, civil engineering, composite material design, control engineering, dynamic system identification and optimization, financial systems, industrial equipment, mechatronic systems, steel construction, structural optimisation, and the invention of novel systems. More recently, traditional CAD simulation is seen to be transformed to CAutoD by biologically inspired machine learning, including heuristic search techniques such as evolutionary computation, and swarm intelligence algorithms269.
Computing modules are plug-in specialized computers designed to solve narrowly focused tasks, such as accelerating the work of artificial neural networks algorithms, computer vision, voice recognition, machine learning and other artificial intelligence methods, built on the basis of a neural processor – a specialized class of microprocessors and coprocessors (processor, memory, data transfer).
Computing system is a software and hardware complex intended for solving problems and processing data (including calculations) or several interconnected complexes that form a single infrastructure270.
Computing units are blocks that work like a filter that transforms packets according to certain rules. The instruction set of the calculator can be limited, which guarantees a simple internal structure and a sufficiently high speed of operation271.
Сoncept drift in predictive analytics and machine learning, the concept drift means that the statistical properties of the target variable, which the model is trying to predict, change over time in unforeseen ways. This causes problems because the predictions become less accurate as time passes272.
Сonnectionism is an approach in the fields of cognitive science, that hopes to explain mental phenomena using artificial neural networks273,274.
Сonsistent heuristic in the study of path-finding problems in artificial intelligence, a heuristic function is said to be consistent, or monotone, if its estimate is always less than or equal to the estimated distance from any neighboring vertex to the goal, plus the cost of reaching that neighbor275.
Сonstrained conditional model (CCM) is a machine learning and inference framework that augments the learning of conditional (probabilistic or discriminative) models with declarative сonstraints276.
Constraint logic programming is a form of constraint programming, in which logic programming is extended to include concepts from constraint satisfaction. A constraint logic program is a logic program that contains constraints in the body of clauses277.
Constraint programming is a programming paradigm wherein relations between variables are stated in the form of constraints. Constraints differ from the common primitives of imperative programming languages in that they do not specify a step or sequence of steps to execute, but rather the properties of a solution to be found278.
Constructed language (also conlang) is a language whose phonology, grammar, and vocabulary are consciously devised, instead of having developed naturally. Constructed languages may also be referred to as artificial, planned, or invented languages279.
Control theory in control systems engineering, is a subfield of mathematics that deals with the control of continuously operating dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a control model for controlling such systems using a control action in an optimum manner without delay or overshoot and ensuring control stability280.
Convolutional neural network (CNN, or ConvNet) in deep learning, is a class of deep neural networks, most commonly applied to analyzing visual imagery. CNNs use a variation of multilayer perceptrons designed to require minimal preprocessing. They are also known as shift invariant or space invariant artificial neural networks (SIANN), based on their shared-weights architecture and translation invariance characteristics. Сonvolutional neural network is a class of artificial neural network most commonly used to analyze visual images. They are also known as Invariant or Spatial Invariant Artificial Neural Networks (SIANN) based on an architecture with a common weight of convolution kernels or filters that slide over input features and provide equivalent translation responses known as feature maps281.
Confidentiality of information is a mandatory requirement for a person who has access to certain information not to transfer such information to third parties without the consent of its owner282.
Confirmation Bias – the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms one’s own beliefs or hypotheses while giving disproportionately less attention to information that contradicts it283.
Confusion matrix is a situational analysis table that summarizes the prediction results of a classification model in machine learning. The records in the dataset are summarized in a matrix according to the real category and the classification score made by the classification model284,285.
Consumer artificial intelligence is specialized artificial intelligence programs embedded in consumer devices and processes286.
Continuous feature is a floating-point feature with an infinite range of possible values. Contrast with discrete feature287,288.
Contributor is a human worker providing annotations on the Appen data annotation platform289.
Convenience sampling – using a dataset not gathered scientifically in order to run quick experiments. Later on, it’s essential to switch to a scientifically gathered dataset290.
Convergence – informally, often refers to a state reached during training in which training loss and validation loss change very little or not at all with each iteration after a certain number of iterations. In other words, a model reaches convergence when additional training on the current data will not improve the model. In deep learning, loss values sometimes stay constant or nearly so for many iterations before finally descending, temporarily producing a false sense of convergence. See also early stopping291,292.
Convex function is a function in which the region above the graph of the function is a convex set. The prototypical convex function is shaped something like the letter U. For example, the following are all convex functions:
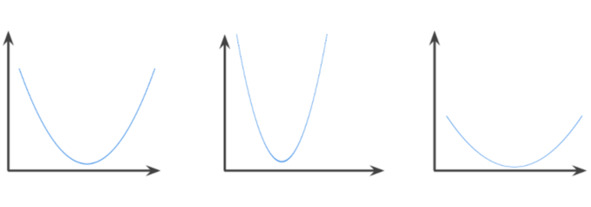
By contrast, the following function is not convex. Notice how the region above the graph is not a convex set:
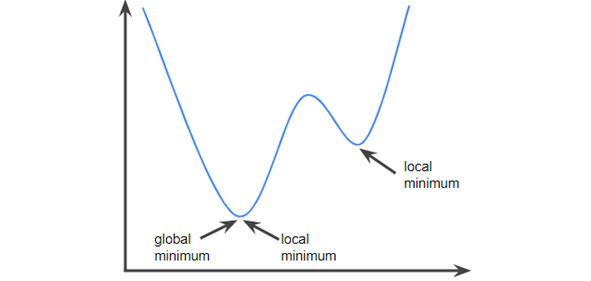
A strictly convex function has exactly one local minimum point, which is also the global minimum point. The classic U-shaped functions are strictly convex functions. However, some convex functions (for example, straight lines) are not U-shaped. A lot of the common loss functions, including the following, are convex functions: L2 loss; Log Loss; L1 regularization; L2 regularization. Many variations of gradient descent are guaranteed to find a point close to the minimum of a strictly convex function. Similarly, many variations of stochastic gradient descent have a high probability (though, not a guarantee) of finding a point close to the minimum of a strictly convex function. The sum of two convex functions (for example, L2 loss + L1 regularization) is a convex function. Deep models are never convex functions. Remarkably, algorithms designed for convex optimization tend to find reasonably good solutions on deep networks anyway, even though those solutions are not guaranteed to be a global minimum293,294.
Convex optimization – the process of using mathematical techniques such as gradient descent to find the minimum of a convex function. A great deal of research in machine learning has focused on formulating various problems as convex optimization problems and in solving those problems more efficiently. For complete details, see Boyd and Vandenberghe, Convex Optimization295.
Convex set is a subset of Euclidean space such that a line drawn between any two points in the subset remains completely within the subset.296.
Convolution — the process of filtering. A filter (or equivalently: a kernel or a template) is shifted over an input image. The pixels of the output image are the summed product of the values in the filter pixels and the corresponding values in the underlying image297.
Convolutional filter – one of the two actors in a convolutional operation. (The other actor is a slice of an input matrix). A convolutional filter is a matrix having the same rank as the input matrix, but a smaller shape298.
Convolutional layer is a layer of a deep neural network in which a convolutional filter passes along an input matrix299.
Convolutional neural network (CNN) is a type of neural network that identifies and interprets images300,301.
Convolutional operation – the following two-step mathematical operation: Element-wise multiplication of the convolutional filter and a slice of an input matrix. (The slice of the input matrix has the same rank and size as the convolutional filter); Summation of all the values in the resulting product matrix302.
Corelet programming environment (CPE) is a scalable environment that allows programmers to set the functional behavior of a neural network by adjusting its parameters and communication characteristics303.
Corpus of texts is a large dataset of written or spoken material that can be used to train a machine to perform linguistic tasks304.
Correlation analysis is a statistical data processing method that measures the strength of the relationship between two or more variables. Thus, it determines whether there is a connection between the phenomena and how strong the connection between these phenomena is305.
Correlation is a statistical relationship between two or more random variables306.
Cost – synonym for loss. A measure of how far a model’s predictions are from its label. Or, to put it more pessimistically, a measure of how bad a model is. To determine this value, the model must define a loss function. For example, linear regression models typically use the standard error for the loss function, while logistic regression models use the log loss307,308.
Co-training essentially amplifies independent signals into a stronger signal. For instance, consider a classification model that categorizes individual used cars as either Good or Bad. One set of predictive features might focus on aggregate characteristics such as the year, make, and model of the car; another set of predictive features might focus on the previous owner’s driving record and the car’s maintenance history. The seminal paper on co-training is Combining Labeled and Unlabeled Data with Co-Training by Blum and Mitchell309.
Counterfactual fairness is a fairness metric that checks whether a classifier produces the same result for one individual as it does for another individual who is identical to the first, except with respect to one or more sensitive attributes. Evaluating a classifier for counterfactual fairness is one method for surfacing potential sources of bias in a model. See «When Worlds Collide: Integrating Different Counterfactual Assumptions in Fairness» for a more detailed discussion of counterfactual fairness310.
Coverage bias – this bias means that the study sample is not representative and that the data set in the array has zero chance of being included in the sample311.
Crash blossom is a sentence or phrase with an ambiguous meaning. Crash blossoms present a significant problem in natural language understanding. For example, the headline Red Tape Holds Up Skyscraper is a crash blossom because an NLU model could interpret the headline literally or figuratively312.
Critic – synonym for Deep Q-Network313.
Critical information infrastructure – objects of critical information infrastructure, as well as telecommunication networks used to organize the interaction of such objects314.
Critical information infrastructure of the Russian Federation is a set of critical information infrastructure objects, as well as telecommunication networks used to organize the interaction of critical information infrastructure objects with each other315.
Cross-entropy is a generalization of Log Loss to multi-class classification problems. Cross-entropy quantifies the difference between two probability distributions. See also perplexity316.
Crossover (also recombination) in genetic algorithms and evolutionary computation, a genetic operator used to combine the genetic information of two parents to generate new offspring. It is one way to stochastically generate new solutions from an existing population, and analogous to the crossover that happens during sexual reproduction in biological organisms. Solutions can also be generated by cloning an existing solution, which is analogous to asexual reproduction. Newly generated solutions are typically mutated before being added to the population317.
Cross-Validation (k-fold Cross-Validation, Leave-p-out Cross-Validation) is a collection of processes designed to evaluate how the results of a predictive model will generalize to new data sets. k-fold Cross-Validation; Leave-p-out Cross-Validation318.
Cryogenic freezing (cryonics, human cryopreservation) is a technology of preserving in a state of deep cooling (using liquid nitrogen) the head or body of a person after his death with the intention to revive them in the future319.
Cyber-physical systems are intelligent networked systems with built-in sensors, processors and drives that are designed to interact with the physical environment and support the operation of computer information systems in real time320.
«D»
Darkforest is a computer go program, based on deep learning techniques using a convolutional neural network. Its updated version Darkforest2 combines the techniques of its predecessor with Monte Carlo tree search. The MCTS effectively takes tree search methods commonly seen in computer chess programs and randomizes them. With the update, the system is known as Darkforest3321.
Dartmouth workshop – the Dartmouth Summer Research Project on Artificial Intelligence was the name of a 1956 summer workshop now considered by many (though not all) to be the seminal event for artificial intelligence as a field322.
Data analysis is obtaining an understanding of data by considering samples, measurement, and visualization. Data analysis can be particularly useful when a dataset is first received, before one builds the first model. It is also crucial in understanding experiments and debugging problems with the system323.
Data analytics is the science of analyzing raw data to make conclusions about that information. Many of the techniques and processes of data analytics have been automated into mechanical processes and algorithms that work over raw data for human consumption324.
Data augmentation in data analysis are techniques used to increase the amount of data. It helps reduce overfitting when training a machine learning325.
Data Cleaning is the process of identifying, correcting, or removing inaccurate or corrupt data records326.
Data Curation – includes the processes related to the organization and management of data which is collected from various sources327.
Data entry – the process of converting verbal or written responses to electronic form328.
Data fusion — the process of integrating multiple data sources to produce more consistent, accurate, and useful information than that provided by any individual data source329.
Data Integration involves the combination of data residing in different resources and then the supply in a unified view to the users. Data integration is in high demand for both commercial and scientific domains in which they need to merge the data and research results from different repositories330.
Data is a collection of qualitative and quantitative variables. It contains the information that is represented numerically and needs to be analyzed.
Data Lake is a type of data repository that stores data in its natural format and relies on various schemata and structure to index the data331.
Data markup is the stage of processing structured and unstructured data, during which data (including text documents, photo and video images) are assigned identifiers that reflect the type of data (data classification), and (or) data is interpreted to solve a specific problem, in including using machine learning methods (National Strategy for the Development of Artificial Intelligence for the period up to 2030)332.


