 полная версия
полная версияThe Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction. Volume 19, No. 538, March 17, 1832

Various
The Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction / Volume 19, No. 538, March 17, 1832
THE ARBALEST, OR CROSS-BOW
THE ARBALEST, OR CROSS-BOW
The Bow would appear to have been in most ancient nations the principal implement of war; and to keep alive this "mystery of murder," archery, or the art of shooting with a bow and arrow, seems to have been a favourite pastime in days of peace. In no country, however, has archery been more encouraged than in this island; wherefore the English archers became the best in Europe, and procured many signal victories. Tributary as have been the bow and arrow to some of the brightest scenes in our history, it is not surprising that its exercise should have become cherished among us as an amusement. Strutt tells us that in the early ages of chivalry, the usage of the bow was considered as an essential part of the education of a young man who wished to make a figure in life. Hence the long-bow and cross-bow have been and are playthings in the hands of youth; and would that they had only been the toys of the playground instead of leading men to slaughter each other for the costly toys of the game of life. It is chiefly to the use of the cross-bow that we propose to confine ourselves upon the present occasion.
The arbalest, or cross-bow, was not only much shorter than the long-bow, but fastened also upon a stock, and discharged by means of a catch or trigger, which Mr. Strutt reasonably enough thinks gave rise to the lock on the modern musket. The old logicians illustrate the distinction in their quaintest fashion. Bayle, explaining the difference between testimony and argument, uses this laconic simile, "Testimony is like the shot of a long-bow, which owes its efficacy to the force of the shooter; argument is like the shot of the cross-bow, equally forcible, whether discharged by a dwarf or a giant."
The arbalest is said by some writers to be of Italian origin. Verstegan says it was introduced here by the Saxons, but was neglected till again brought into use by William the Conqueror, at the battle of Hastings. No mention is made of bowmen among the troops of Harold; but we read that the Norman army was fronted by "footmen clothed in light armour, worn over a gilted cassock, and bearing either long-bows or steel cross-bows." Harold himself had his eye struck by an arrow, notwithstanding which he continued to fight at the head of his army. Cross-bows were afterwards prohibited by the second Lateran Council, anno 1139, as hateful to God, and unfit to be used among Christians; in consequence whereof they were laid aside till the reign of Richard the First, who again introduced them, and was himself killed by an arrow or quarrel, discharged from a cross-bow at the siege of the Castle of Chalus. 1
Cross-bows shot darts called quarrels, or quarreaux, or quadrels, and in English bolts: they were headed with solid, square pyramids of iron, and sometimes trimmed with brass instead of feathers. According to Sir John Smith a cross-bow would kill point blank 60 yards, and if elevated above 160. There was an officer styled Balistrarius Regius; and several estates were held by the service of delivering a cross-bow and thread to make the string, when the king passed through certain districts. These you will find in Blount's Tenures and Jacob's Law Dictionary. 2
We find that the pay of a cross-bowman, in the reign of Edward II., was sixpence per diem. 3 Few notices of archery are, however, upon record till an order by Edward III. in the 15th year of his reign, to the sheriffs of most of the English counties, to provide bows and arrows for the intended war against France: these orders, however, relate to the long-bow. In the famous battle of Crecy, fought in 1346, our chroniclers state that we had 2,800 archers, who were opposed to about the same number of the French; which, together with a circumstance to be immediately mentioned, seems to prove that by this time we used the long-bow whilst the French archers shot with the arbalest. The circumstance alluded to is as follows:—Previously to the engagement there fell a heavy rain, which is said to have much damaged the bows of the French, or rather the strings of them. Now, the long-bow, when unstrung, may be conveniently covered, so as to prevent the rain injuring it; nor is there scarcely any addition to the weight from a case; whereas the arbalest is of a most inconvenient form to be sheltered from the weather. It is also stated 4 that, at Crecy, "the Genoese archers, fatigued by their heavy cross-bows, in a sultry and tempestuous march, rushed forward with loud cries to attack the English bowmen, who were the strength of Edward's army. These last stood still; even on the second charge they stirred not one foot! When they got within shot of their foes, they let fly their arrows so quickly that they came like snow. The Genoese fled, and some of the heavy-armed troops were involved in their confusion." At Crecy the English ascribed their victory to their archers. The battle of Poictiers, fought in 1356, was gained by the same means. In 1417, Henry V. attributed his splendid victory at Agincourt to the archers, and directed the sheriffs of many counties to pluck from every goose six wing-feathers for the purpose of improving arrows, which were to be paid for by the King. In 1421, though the French had been defeated at Crecy, Poictiers, and Agincourt, by the English archers, yet they still continued the use of the cross-bow; for which reason Henry V., as Duke of Normandy, confirms the charters and privileges of the balistarii, who had been long established as a fraternity in his city of Rouen.
We now meet with several enactments by Edward IV. for the appointment of bowmen with the long-bow; but we pass over these and other records to the 19th year of the reign of Henry VII., who forbade the use of the cross-bow, because "the long-bow had been much used in this realme, whereby honour and victory had been gotten against outward enemies, the realm greatly defended, and much more the dread of all Christian princes by reason of the same." Statutes for the promotion of archery with the long-bow are now very frequent; but the cross-bow is proscribed in the same proportion: and, in the time of Henry VIII. a penalty of ten pounds was inflicted on every one who kept a cross-bow in his house.
Though archery continued to be encouraged by the king and legislature for more than two centuries after the first knowledge of the effects of gunpowder, yet by the latter end of the reign of Henry VIII., it seems to have been partly considered as a pastime.
From this period we pass to the date of the annexed CUTS, for which we are indebted to the research of an ingenious Correspondent, with the antiquarian subscription of "JONATHAN OLDBUCK," 5 who appends to his sketches the following historical notice:
"After the destruction of the Spanish Armada, fears being entertained lest the King of Spain should (out of revenge) send an emissary to attempt the life of Queen Elizabeth, a number of noblemen of the Court formed themselves into a body guard for the protection of her person, and under the denomination of the 'Companie of Liege Bowmen of the Queene,' had many privileges conferred upon them. The famous Dudley, Earl of Leicester, was captain of this company, which was distinguished by the splendour of its uniform and accoutrements. Upon the accession of James I. the company was disbanded, although those who composed it retained the privileges which had been conferred upon them by Elizabeth. Upon the breaking out of the Civil wars Charles reorganized this bodyguard which attended him against the Parliamentary forces, and afterwards emigrated with Charles II. At the Restoration this company was maintained, and under the title of 'Royal Company of Archers' received a new Charter, being the origin of the present 'Royal Artillery Company' of London. About the time of the institution of the Liege Bowmen of the Queen, a new kind of cross-bow was constructed in Holland, by one Vander Foheman, having many advantages over the old one. This he brought to England and it was purchased and adopted by the Company. 6
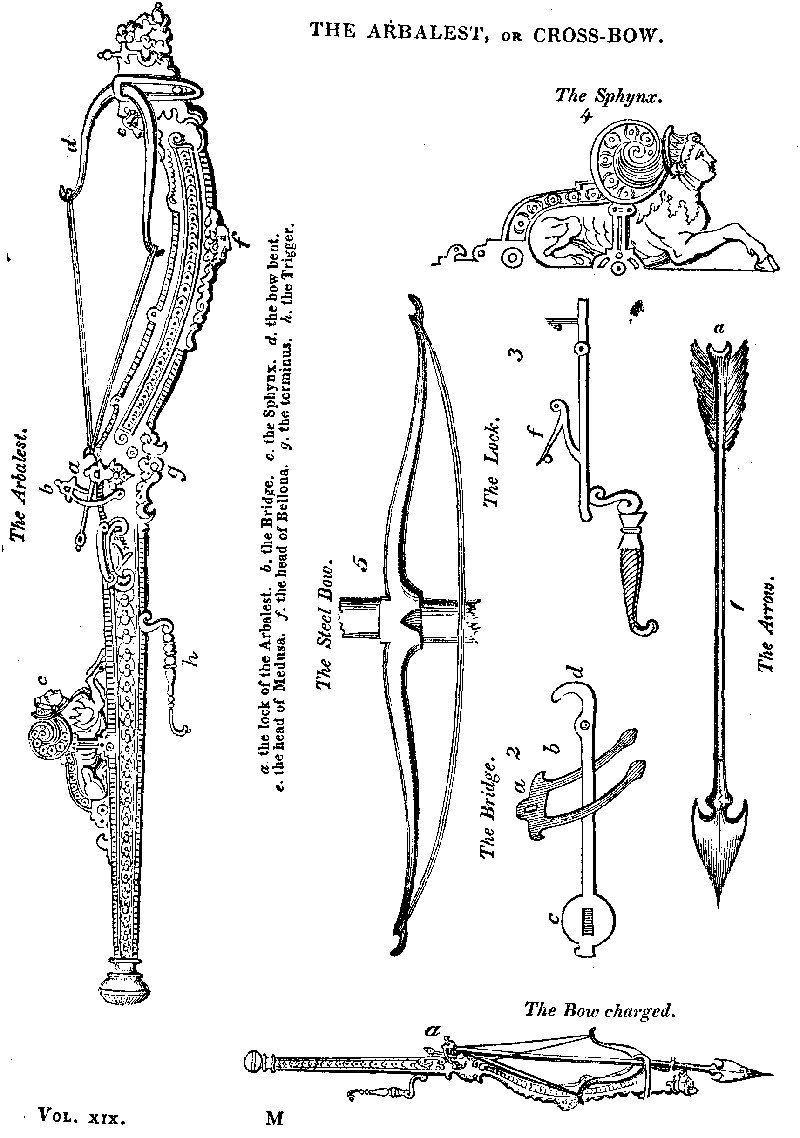
"An ARBALEST of Foheman's construction, bearing the date 1579, 3 feet 3 inches long, exquisitely carved out of black oak, is now in the possession of A. Nossoc, Esq., the proprietor of a rare and valuable collection of paintings by ancient masters. By this gentleman's kindness I have been able to take a sketch of it, a copy of which I enclose. In these instruments the impulse is not communicated to the arrow directly by the string, but by means of a movable iron bridge, placed behind the string. I subjoin outlines of the arrow used with this kind of bow, and also of its lock.—(See Cuts.)
"The end (a) of the arrow, Fig. 1., was placed against a small square plate of metal (a) of the bridge, and the other end of the arrow rested on the steel bow. The string pulled upon the hook, (d) Fig. 2, and the end (c) acting with a lever advantage communicated its impulse to the bridge, (b) against which was placed the arrow. The figure 3 will explain the rest of the contrivance, (f) being a spring to keep the trigger down.
"The wooden part of the arbalest is beautifully carved with figures; its front extremity is a lion's head holding in its mouth an acorn originally of gold, for which a wooden one is substituted, as is the round stock at the other extremity which was of silver; its lower side has a figure of Bellona, a terminus, &., carved out of it; its upper, a sphynx, head of Medusa, leaves, and numerous other ornaments upon it; the sides are also beautifully carved, and two steel escutcheons on its sides before the bridge have engraved on them a trophy, and two roses.
"As these cross-bows are now extremely rare, I should feel gratified if any correspondent could inform me whether an arbalest of this description is preserved in the Tower, or in any public or private collection of ancient armour; and whether it was used by the Company of Archers after the Restoration."
The Steel Bow is of the shape annexed, Fig. 5, being a resting-place for the fore end of the arrow.
We may here add that the Cross-bow was also called a Steel-bow, because the horns were usually made with steel; and others were called Stone-bows because they were modified to the purpose of discharging stones. The cross-bow makers used to exercise themselves in shooting at the popinjay, or artificial parrot, in a field called Tassal Close in London, from the number of thistles growing there, now called the Old Artillery Ground. 7
The following description of an archer, his bow, and accoutrements, is given in a MS. written in the time of Queen Elizabeth. "Captains and officers should be skilful of that most noble weapon, and to see that their soldiers according to their draught and strength have good bowes, well nocked, well strynged, every strynge whippe in their nocke, and in the myddes rubbed with wax, braser, and shuting glove, some spare strynges trymed as aforesaid, every man one shefe of arrows, with a case of leather defensible against the rayne, and in the same fower and twentie arrowes, whereof eight of them should be lighter than the residue, to gall or astoyne the enemye with the hail-shot of light arrows, before they shall come within the danger of the harquebuss shot. Let every man have a brigandine, or a little cote of plate, a skull or hufkyn, a mawle of leade of five foote in lengthe, and a pike, and the same hanging by his girdle, with a hook and a dagger; being thus furnished, teach them by musters to marche, shoote, and retire, keepinge their faces upon the enemy's. Sumtyme put them into great nowmbers, as to battell apparteyneth, and thus use them often times practised, till they be perfecte; ffor those men in battel ne skirmish can not be spared. None other weapon maye compare with the same noble weapon."
Even in Elizabeth's reign the bow was thought to be more advantageous than the musket; because the latter was at that period very cumbrous, and unskilful in contrivance, while archery had been carried to the highest perfection. Mr. Grose tells us that an archer could formerly shoot six arrows in the time necessary to charge and discharge a musket; and, as a specimen of the aim to be taken, even in modern days, a practised bowman has been known to shoot twelve arrows in a minute, into a circle not larger than the circumference of a man's hat, at the distance of forty yards.
THE GIPSEY FORTUNE-TELLER
(For the Mirror.)Augur only happy days,Gipsey, when thy glancing eye,Fain would dart its piercing rays,Through her future destiny.Life is yet without a shade,She has gathered flowers alone;Tell her not, that roses fade,When the ardent summer's gone.Sully not her early dream,With reality's cold hue,Let her morning brighter seem,Glittering with the early dew.Tell her not, that clouds o'ershading,Rainbows bright will darkly cover;Tell her not, that quickly fading,"All that's bright!" ere noon is over.Tell her not of memory's tear,And affection's broken chain;Tell her not, that every year,Brings but sorrow, care, and pain!Soon the mist will roll away,And the soft enchantment fly:Gipsey, hasten on thy way,Ne'er unrol her destiny!Tell her, if thou wilt, that never,'Neath the skies may be her home,And if thou that hope hadst ever,Tell her of a world to come!Kirton, Lindsey.ANNE R.FINE ARTS
THE BRITISH INSTITUTION
(From a Correspondent/)The admirers of modern painting invariably anticipate much delight prior to the opening of the Exhibition at this institution, and their hopes in the present instance have not been disappointed, as there certainly is a fine display of talent in almost every department of the art. There are nearly six hundred works.
No. 1. Portsmouth, from the King's Bastion; painted by command of his Majesty, by Clarkson Stanfield.
5. The Falconer; a brilliant little picture by A. Fraser.
6. Sabrina, from Milton's Comus; Mr. Etty delineates the female form with peculiar accuracy and delicacy, and in the subject before us he has displayed his usual ability.
28. A Lady of Rank of the fifteenth century taking the Veil; a work of considerable promise by a young artist—S. A. Hart.
30. The Rick Side; beautifully executed by T. Woodward.
47. A Man saved from Shipwreck; this is an interesting subject by Charles Hancock. Apropos, this gentleman paints much in the fascinating manner of Mr. Landseer.
61. Entrance to a Village; painted from nature in a pleasing style by C.R. Stanley.
75. Interior of a Highlander's House; E. Landseer, R.A.
248. Distant View of Goderich Church; Copley Fielding.
337. The Recruit; by H. Liversege. The principal group in this picture is treated in the following way: around a table are seated four persons, among whom are two soldiers—being the recruiting sergeant with one of his party. The recruit, a rustic looking youth, has a good deal of expression in his countenance; he seems extremely doubtful concerning the step he has taken, while an interesting young woman, apparently his sister, is fondly endeavouring to dissuade him from it. The sergeant complacently smokes his pipe, and smiles at her solicitude. This is, perhaps, the most unaffected picture in the whole collection, being a remarkably modest representation of nature. The composition is good, and the freedom and delicacy of the execution stands unrivalled.
386. Hunt the Slipper; A.E. Chalon, R.A. In this picture several figures are introduced seriatim, engaged at this old English, but now rather unfashionable, game. A little too much vulgarity is displayed, though in other respects the performance is highly praiseworthy.
413. Love the best Physician; painted at Paris by Monsieur Destouches. Although we disapprove of the colouring and some parts of the execution of this work, the subject is very interesting. A young man of fortune, who had fallen in love with a beautiful young girl, becomes sick in consequence of his hopeless passion. The physicians appear to have rendered him no service, and as a last alternative, his friends prevail on the girl to visit him, accompanied by her parents. The deep blushes with which her face is suffused, and her downcast eyes, indicate the violent agitation of her frame; while the sick man, having raised himself in bed, stretches out his arms, and eagerly feasts his eyes on the charming object of his love.—G.W.N.
SPIRIT OF THE PUBLIC JOURNALS
SCIENCE OF BURIAL
(From a piquant, rambling paper in Fraser's Magazine.)We arrived at Otaheite just in time to witness the funeral ceremonies of the pious chief Omaree. He was lying in state at his house above the harbour where we landed, and we were invited to assist at the obsequies. His viscera were removed, and his remains, properly speaking, were laid on an elegant palanquin or hanging bier, highly perfumed; around which, and through the apartment, odorous oils were burning. Several of his old friends came to see him, and complimented him highly on the state of his looks and his good condition in various respects. They presented him with numerous and tasteful gifts, which they assured him were sincere tokens of their esteem, and hoped he would accept them as such. Omaree replied by the mouth of an old priest who acted as master of the ceremonies—assuring the good company, in return, that he was "as well as could be expected," felt particularly flattered by the kind attentions of his friends and visiters, and hoped they would make themselves quite at home. "By the hand of my body," exclaimed the captain, sitting down to a bowl of fresh Palmetto wine, and lighting a pipe at the foot-lights, "this is the dacentest wake I ever came across out of Ireland! Noble sir, your good health and snug lying to you!"
After a conversation with Omaree on various interesting topics, his friends and family proposed taking him to see his property in another part of the island: he gratefully assented to the proposition, and requested the good company to avoid fatiguing themselves by travelling too rapidly, as he was in no hurry to leave them. He was then borne in state for some miles, preceded by dancers, singers, knuckle-drummers, strewers of flowers and leaves, &., to a pretty spot by the sea-side, where he had lately made a tobacco-plantation, and which, he remarked, "would be scarce worth the plucking, as he had not been able to attend to it of late;—however, he hoped his venerable and disinterested friend and spiritual comforter, the priest, would accept the crop, such as it was, as a slight testimony of his eternal gratitude." Hereupon the crowd clapped their hands with delight, the singers shouted, the drummers thumped, and the dancers vaulted their admiration of the piety and generosity of Omaree.
Here he was placed in an easy sitting posture, in a commodious arm-chair that commanded a view of the plantation and the Pacific; where, sheltered from the meridian sun by a lofty arbour of the climbing cobea and wild vine tastefully trained through a cluster of cocoa-palms, he was invited to witness a dramatic representation containing incidents which they knew his memory reverted to with pride and pleasure. This drama, in which a great company of performers took part, was carried on with much taste and spirit. The old priest undertook to translate the most interesting passages for my edification (still acting as the mouthpiece of his deceased friend), with the exception of a few "love-passages," as Queen Elizabeth would have called them, the import of which was sufficiently perspicuous without verbal comment.
Whilst remaining at Hayti, I took an excursion, on foot and alone, through the mountains one day, to visit this interesting spot. The ascent to the cavern was steep and toilsome. I was obliged frequently to change my course, and pursue a more lengthened route than what my eye had anticipated; but at length I reached the place, and, pausing a few minutes to rest after my weary journey, struck a light, and, with lantern in hand, entered the awful cave. A large stone had been so placed within the entrance that it might have served for a stopper occasionally. Even in its withdrawn position I passed it with difficulty. "Now," I exclaimed, "I shall behold with my own eyes the aboriginal style of burial in these sacred and almost inaccessible recesses, which that unsatisfactory historian, Ferdinand Colon, was too lazy to inspect with his own eyes, and which his father had never seen in all his hunting-matches. Indeed, I don't think his blood-hounds could climb the ascent to this cave." As I entered, I felt myself treading on bones! I looked around the narrow chamber of death, and every where bones—human bones covered the rocky floor; but no sign of art or trace of religious obsequies rewarded my scrutiny. "Bless me!" said I, "what a journey I have had for nothing! This is merely the ordinary HOTTENTOT-HOLE style, with a stone instead of a thorn-bush to exclude wild beasts!" So I hastened forth, blaming the easy credulity that drank in traditionary tales of aboriginal tombs. At the entrance I found a negro standing, leaning on his musket; a brace of pistols were stuck in his girdle, and a sword hung by his side. I was rather startled, for the man possessed a fierce and threatening aspect, and I was perfectly defenceless. Nevertheless there was are air of manly dignity about him which assured me that he was not likely to be unnecessarily savage. "Qui vive?" demanded he, sternly. I explained my views in coming to this secluded spot. He unbent his dark brow on hearing that I was an Englishman.
"Behold that noble expanse!" said he, changing his tone and language together. "The guileless race whose bones whiten this rocky den once ranged over that lovely landscape in peace and freedom. The white savages came, and were received as brethren. They threw off the mask, and repaid friendship and love with bonds and tortures. The red man was too innocent, and too ignorant, and too feeble, to co-exist under the same sky with the cunning and ferocious white demon—and he retired to his caves to die! His race is extinct, for he knew not the use of arms!" He clasped his musket to his breast with emotion, and remained silent. "Who are you that feel so much for the exterminated Haytians?" I inquired. "Their avenger!" he replied, "and the champion of a darker race whose wrongs can never have vengeance enough. Christophe!"
"You shall see the 'Dead men's feast,'" said Logan. I followed him in silence, till we reached the southern bank of the Ohio, not far from his own residence. The tribe was seated in a beautiful and secluded prairie, that just afforded a vista of the river through the cypress swamp between. A number of men and women seemed busily engaged in the decoration of others with belts, beads, and brilliant-coloured garments; and these latter seemed passive or asleep. Logan laid down the load he carried in his blanket, and unwrapped the burden that had so long attracted my attention. "'Tis my grandsire!" said he: "he has only been two years buried:—I have brought him far. Aid me to cleanse the brave old limbs and skull from these worms, that his spirit may rejoice over the feast with his red children. Haste! my father yonder is painted and dressed already."
Before I quitted Kentucky, I made a point of visiting the celebrated and immense nitre caverns or catacombs of the limestone region. Here I found the mummies of the pigmy race that once inhabited the gigantic valley of the Mississippi, adorned with strings of shell-wampum and turkeys' feathers—seated in death like the ancient Naso-menes, grinning at me with their long inhuman fore-teeth—and came out as wise as I went in.
"O," said the captain, "a burial in Canada is no trifle in winter. Just before you arrived, our drummer died, and we mustered spades, picks, and shovels, to dig a grave for him; but the ground was one rock every where, and after trying twenty places we found—that we had spoiled our tools. It took the armourer next day to steel them all. The third day we got down four inches and a half, in the softest soil we could find; but it would only grind up pinch by pinch. The fourth day the armourer was at work again. The fifth day the whole company turned out in a rage with the ground, and having got under the frost in some degree, sunk the grave full nine inches more. This night another soldier, a corporal, died; and his comrades were almost dead with disappointment and vexation. The bodies would keep in the frost very well; but we had not a spare room in the barrack, and their comrades wanted to get them out of the way of a wedding. Well, sir, the sixth day I divided the garrison in two, and set them at separate graves; but, unluckily, they drank to keep up their spirits in the battle with the frost, and fought about the corporal's right of priority, and the freezing point of brandy. Worst of all, they forgot to cover the new picked surfaces with straw and blankets, so that when they came in the morning the points of attack were as invulnerable as ever. In despair they buried both in one grave—the corporal undermost—without further efforts to attain a decent depth. As to six feet, it was quite unfathomable. They heaped all the stones they could loosen over the bodies, and the chaplain read prayers at last, after a 'week's preparation' and suspense, 'snow to snow, and ice to ice.' That night a herd of wolves came prowling by, and carried the corporal and drummer along with them. The fifer—an Irish rascal—was laughing heartily the whole week; and it was he set up the corporal's claim to the deep grave, to have his joke out. When all was over, the sergeant reported him to me, for bragging 'that he could have buried them six feet deep himself in two hours, and have covered them up so nately after, that the devil couldn't stick a tooth in them; but he had kept the secret to be revenged of the corporal, who had 'listed him one day,' and of the drummer who had 'flogged him.' 'Please your honour,' said he, when called before me, 'I was sartain you wished to find work for us this cowld weather, and it wouldn't become me to say what your honour knew as well as myself—that a rousing fire would soften any frost; and sure, only I know you compassionated the poor starving wolves, I'd have thrown a few buckets of water through the grave-stones, and clinched 'em as tight as the bars of Newgate.'"









