
Полная версия
Theory of vortex creation and control
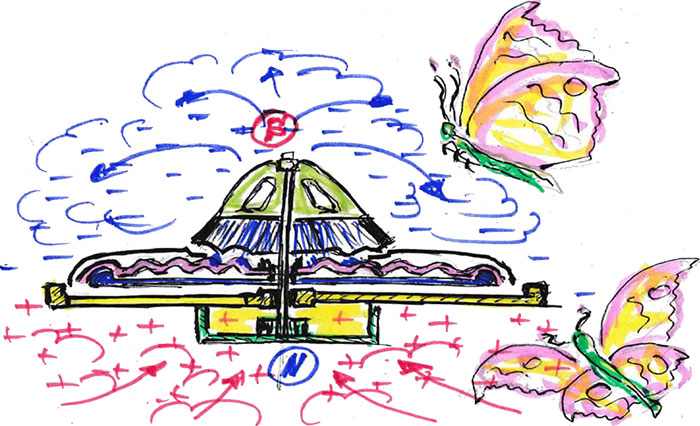
Fig. 2. Diagram of a levitating platform on wave disks
Through the slots made on the inner surfaces of the two rings of the upper disk, the air jets enter the inter disc zone, where they collide with the inner profiles of the lower disk, are compressed and, supported by the next portion of air, rotate in a vortex and slide out through a narrow slit from the compression zone to the expansion zone towards the periphery, where the gaps to the edge of the disks are critically narrowed. It should be noted that with such a sharp expansion of the volume of cooled air, a certain increase in temperature occurs and the effect of absorption (rarefaction) occurs, which accelerates the process of centrifugal movement of air from the previous zone. The higher the difference in the volume of air squeezed between the waves of the disks during centrifugal motion, the more effective the formation of numerous radially directed vortices in them. Which, with the simultaneous rotation of both disks (or separately, which is more efficient), spin with acceleration around their own axis with some derivation and move in a continuous sequence to the periphery, simultaneously rotating around the common axis of the installation, and activating the processes of formation of a single toroidal vortex. Recall that the profile of the space between the disks forces these vortices to rhythmically contract and expand, increasingly densifying the flows of strongly ionized atmospheric air from the center to the periphery. A kind of modulated wave. As a result, vortex arms are formed from twisted, rigid discrete "pigtails" of elementary particles of matter in air (or a water-air mixture), i.e. charges. More precisely, when water is supplied through a hole in the central axis, ionization processes are accelerated. In addition, in the inner cavity of the installation, there should be some roughness of the disc surfaces at the level of primary young corrosion on the surface of the iron.
Thus, the concept of alternation of events adopted by us: decrease-condensation during compression and increase-expansion during rarefaction of cooled air, which is inevitably realized here in dynamics, significantly, cyclically and constantly accelerates processes in time, breaking up and releasing both carbon and oxygen (plus hydrogen) from the flow of the medium. Thus, ionizing the flow at the outlet in the periphery of the rotating disks in order to accelerate the formation and separation of charges. Here it is important to disrupt as much as possible in the molecules and atoms of the substance of the environment of space not only electromagnetic connections, but also weak interactions between elementary particles of atoms and molecules. When this stage is reached, negative charges are formed above the disks, which are associated with the processes of temperature increase and expansion of cooled flows of the ionized medium of space, and positive charges are created below the disks, supporting the processes of temperature decrease and condensation of the gas medium.
However, this is not enough to fulfill the goal. It is necessary to achieve the occurrence of the phenomenon of resonance in standing waves by initiating centripetal actions, to make the properties of diamagnets work and, if possible, to use the effect of wing lift in the design as much as possible. Thus, there is a need for a third, support disk, rigidly fixed to the common hub of the axis of rotation from below, but with a larger diameter for 2.5 wave periods. Its profile is not only a support for the lower wave disk, but also structurally plays the role of a peripheral turbine. It is made of paramagnet (for example, aluminum), the flat surface of which to the wave disk along the edge is framed by turbine blades no higher than the outermost wave of the lower disk and one and a quarter wide of the wave period in the form of through, alternating, inclined (at an angle of 30-40 degrees) slits in the direction of rotation. The profile of each blade of the peripheral turbine resembles a plano-convex model of an airplane wing.
Please note that the upper wave disk is made in such a way that its extreme wave is followed by another wave, which coincides in profile with the "wave" of the peripheral turbine, and covers it from above by three quarters of the height of the blades. To create the rigidity of the system, this turbine shelter is fastened along the circumference with evenly spaced bolted joints (10-12 pcs.), through holes in the blades of the peripheral turbine. Let us clarify that the profile of the blades, as well as the external recesses on them, which additionally twist the flow, can be selected individually. The thickness of the support disk does not play a role and is selected from the structural rigidity. On the hub and on the periphery up to the turbine blades, all disks along the ring through holes are evenly tightened with bolts (5-6 pcs.). For this purpose, along the edge of the lower disk, after the last wave with duplication on the rest, an overlap of the base metal in the form of a fastening ring is provided. At the same time, there should be no threshold at the junction of the lower ring with the support ring and the flow outlet to the blades of the peripheral turbine. In addition, a common casing of the structure is required, dividing the spaces into zones. It is made of any diamagnet (for example, copper) in the form of a bell with a central hole in diameter equal to the beginning of the depression of the third (without slits) wave of the upper disk, with the formation of a protrusion on it with the continuation of the profile to its internal wave, as a place for support and centering in the axis of the central turbine. This is where the central turbine is installed, on which the central air intake housing is mounted and all this is pressed by a bolt screwed into a threaded sleeve in the center of the hub. The external size of the general casing should be sufficient to cover the contours of all disks, with a rounding along the outer diameter of the profile of the blades of the peripheral turbine, with an extension to the lower cut of the support disk. This entire structure is connected to a circular frame made of ferromagnet (for example, iron), in the center of which a bearing unit for rotation is made, in which the axle is fixed in such a way as to provide sufficient clearance between the bed and the support disk. The diameter of the bed should exceed the diameter of the general casing and through slots should be made in it. The bed itself is connected to the drive unit via a sliding clutch for take-off or to the generator shaft to generate power. It is also possible to trigger the phenomenon from a rechargeable battery located directly on the platform of the structure with a device for its recharging. It is important that between the discs and casings made of various materials, both on the hub and on the insulated fasteners, in order to connect them to each other and adjust the technological clearances in the area between the discs, it is necessary to install dielectric gaskets made of a layer of dense rubber or polymer.
What will happen next to the flow of rotating vortices when it meets the peripheral turbine? And then centrifugal influences direct compacted, ionized air flows directly to the blades of the peripheral turbine, where they are not only dissected and pushed down and to the side, as if from a nozzle, but also reflected back, creating centripetal effects.
This effect is calculated and tuned constructively in terms of antinodes and nodes, period and waves to achieve a stable resonance between the atoms of the diamagnetic disks, as a result of the action of the formed standing waves. In the intervals between the waves, a number of other phenomena that are interesting to us arise. For example, an increase in the effect of negative magnetic susceptibility in the material of disks, also during the creation of resonance phenomena, but in each separate wave period, as a consequence of the deceleration of the air flow during vortex compressions. In this case, part of the centrifugal flows is reflected from the frontal profile of the wave of the lower disk, forming centripetal effects with the formation of standing waves, which leads to the resonance of the disk material in different frequency ranges. The formation of vortex magnetic fields associated with electric radial and ring currents of charges in the intermediate zone should not be overlooked. As a result, fields with zero magnetic and electric strength periodically arise.
As a result of our reasoning, we are convinced of the construction of a dynamic dipole structure with all its attributes of electromagnetic interactions with the environment based on electricity and magnetism. And we confirm that the basis for triggering the phenomena of levitation or conversion of charges of matter of the environment into a current of charges (or electric current) in such systems is the excitation of a sequence of processes of cold and heat, expansion and condensation of the medium, centripetal and centrifugal influences, or the change of fields of negative and positive charges. With one goal – to destroy as much as possible in molecules and atoms of the matter of the medium of space not only electromagnetic connections, but also weak interactions between elementary particles of atoms and molecules. In all this, one can see the formation of a stable undamped oscillatory system with energy consumption from the outside. Due to this, a tension or a gradient of charge densities arises in space, which lifts the object up by the force of a stable implosion, allowing the device to rotate at a certain resonant frequency on its own, that is, to levitate.
In many other well-known constructions, such as J. Searle or V. Grebennikov, similar phenomena are activated, but with a different order, other forms and structures of matter. They are based on the same charge gradient, which is excited by various manifestations of the fields of electricity and magnetism. But there is another wonderful view of the solution to the problem voiced above, and this is the interaction of charges in different media of space. We have already drawn your attention to the fact that objects made of superconductors or diamagnets, rotating with acceleration, when they reach resonance, generate their own magnetic (in fact, gravitational) field, directed against an external similar influence, amplifying it in relation to their own mass. That is, the effect of some body weight loss is created. So, can we state with certainty that weight is proportional to the charge of the substance? That is, the matter of the space of the environment, which forms a denser and thinner medium, in which elementary particles and other clumps of matter move at speeds close to the speed of light, will displace (repel the matter of the environment of the same space, but less dense, structurally larger (although fundamentally consisting of the same thing), but moving in the medium of sound (small) speeds.
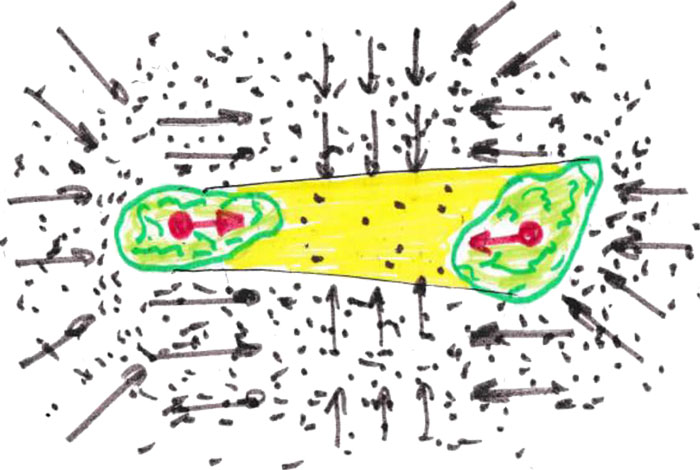
Fig. 3. Pushing 2 bodies in a dense medium
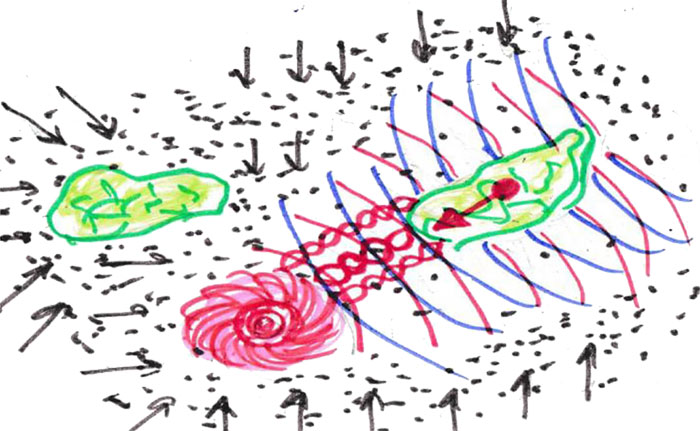
Fig. 4. Influence of charges on the motion of bodies the medium
Moreover, it can be displaced in the direction of attraction by a charge of a similar substance (see Fig. 3). Much like a lot of small air bubbles in water combine into larger ones. In the following chapters, we will analyze these interactions of objects in more detail with the matter of the structure of various media in space.
And in this case, in order to trigger the phenomenon of levitation, it is enough to neutralize the effect of the subtle matter medium on objects synchronized with the matter of the sound velocity medium itself. In other words, it is possible to influence the movement of bodies in space by acting on them with other charges, even reflected in the form of a standing wave in the opposite phase (see Fig. 4). We will consider the properties of various forms of matter during the interaction of their charges in a separate chapter, where it is important for us to understand charge as a measure of the intensity of rotation (spin).
Energy and Space
"As sad as it may be, physics is stagnant today – we still drive cars and still fly airplanes."
Mirco BashichLet's try to look at such a property of matter as energy a little differently. What is it in essence? Where does it come from in us and around us, and what processes nourish it? This will help us in the perception of many natural phenomena.
Such interactions as weak and strong, electrical, magnetic and gravitational interactions that have long been known to science are all "manifestations" of energy. Conventionally, energy in the Universe exists in two systems: closed and open. In nature, most energy systems are open, if we consider its production and consumption. Energy, in general perception, is the property of matter to do work. Therefore, the energy of any source is capable of exciting and influencing the energy of the environment and even creating conditions for its capture and transformation into the energy of electric current convenient for us. That is, open systems are interaction with energy from the outside.
But energy is the motion, for example, of elementary particles. Or any energy is the power of the movement of the vortex. That is, any flow of energy is a flow of their charges. And as we know, the charge from body to body is transmitted through the electromagnetic field, or the environment through the interaction of vortices, as dipoles of elementary particles. This means that we can safely assert that energy is the value of the charge gradient. Or the magnitude of the intensity of their motion, where "motion" is understood as both rotational (spin) and translational displacement. Obviously, if the charges have a dipole structure, for example, like the poles of the globe – "plus" and "minus" in one, then they are able to accumulate, transfer and modify energy.
Then what are charges? What if the carriers of charges in the microcosm are elementary particles known and unknown to us: electrons, ions, positrons, etc.? What if they all have a vortex structure with different directions of rotation of the torus disk? We already know that vortices are formed when conditions are created for the formation of low- or high-pressure zones. Inside the vortices, the pressure is always reduced, and outside there are centripetal oppositions of the surrounding environment, forming a zone of increased stress. In our case, each such vortex has three energy states in the form of positive, neutral and negative charges. If the presence of axial rotation, or the kinetic energy of the vortex, is responsible for the electric charge of the particle, then its polarity is determined by the orientation of the annular rotation relative to the toroidal rotation.
It is no secret that some laws of mechanics quite rightly describe phenomena occurring in both the micro and macrocosm. Then let's take advantage of this and, by analogy with the direction of rotation of the planets, assume that the negative charges rotate counterclockwise, and the positive ones rotate clockwise, if we look from the side where the torus turns inverted. We say that the energy of an object is conventionally designated as positive or negative, depending on the direction of rotation (spin) of the torus disk, its dipole. However, let us recall that the electron, like other similar dipoles, has both magnetic and electric components. Therefore, their vortex field is more complex than that of a permanent magnet, which simply creates the rotation of the surrounding environment.
How is the charge of the dipole (torus) formed and what is the difference from generally accepted views? In order not to get confused, we note that permanent magnets do not exist in nature. All of them are of artificial origin, they are obtained by sintering ferromagnets that have undergone a special heat treatment and the process of magnetization by an external magnetic field, in which the atoms of the substance are tightly packed in crystals. Such a magnet is able to retain magnetization for a long time and create a magnetic field in the absence of electric current. That is, elementary particles in the structure of permanent magnets with their vortex formations are compressed to such an extent that the central holes of the torus are closed, hence there is no electric current in them. Therefore, all the energy of the vortices of these particles is spent on the unwinding of the torus disk with the involvement of the medium in the rotation of matter in the form of a magnetic field. Where the direction of rotation of the medium in several single magnetic fields coincides, the speed of the joint flux increases, and the pressure decreases. Then the total flux has a unidirectional magnetic field. This is also confirmed by experiments with the combined poles of two permanent magnets. And vice versa, when the rotations do not coincide, the opposite action occurs, or deceleration and pressure increase.
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «Литрес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на Литрес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.












