
Полная версия
Самоучитель английского языка для менеджеров фармбизнеса. PharmEnglish for pharm career
• What did the physician start to do?
• What product did the physician start to use?
• Why did the physician start to use the new product?
6. The physician got the right patients within two weeks.
• Who got the right patients within two weeks?
• What patients did the physician get within two weeks?
• Within what time did the physician get the right patients?
7. One month’s initial treatment was enough for the patient to feel some progress.
• What was enough for the patient to feel some progress?
• What initial treatment was enough for the patient to feel some progress?
• For whom was one month’s initial treatment enough to feel some progress?
8. The Sales Rep must in advance prepare promotional literature.
• Who must in advance prepare promotional literature?
• What must the Sales Rep do in advance?
• What must the Sales Rep prepare in advance?
• What literature must the Sales Rep prepare in advance?
9. Physicians always like to see proof of the benefits.
• Who always like to see proof of the benefits?
• What do physicians always like to do?
• What proof do physicians always like to see?
10. It is important to have a copy of the clinical paper for the call.
• What is it important to have for the call?
• What paper is it important to have for the call?
11. Every sales call also needs a good opening.
• What needs a good opening?
• What does every sales call need?
• What opening does every sales call need?
12. Both the salesperson and the customer will gain benefits from the call.
• Who will gain benefits from the call?
• What will both the salesperson and the customer gain from the call?
13. The skill of opening will enable a Sales Rep to get his customer’s interest.
• What will enable a Sales Rep to get his customer’s interest?
• What skill will enable a Sales Rep to get his customer’s interest?
• Whose interest will the skill of opening enable a Sales Rep to get?
14. Every customer wants to see value in spending time with a Sales Rep.
• Who wants to see value in spending time with a Sales Rep?
• What customer wants to see value in spending time with a Sales Rep?
• What does every customer want to do?
• What does every customer want to see?
15. A Sales Rep needs to recognize the appropriate time to open.
• Who needs to recognize the appropriate time to open?
• What does a Sales Rep need?
• What time to open does a Sales Rep need to recognize?
16. An effective sales person must always state the purpose of the call.
• Who must always state the purpose of the call?
• What sales person must always state the purpose of the call?
• What must an effective sales person always state?
• What purpose must an effective sales person always state?
17. He explained what the customer would get from the call.
• Who explained what the customer would get from the call?
• What did he do?
• What did he explain?
18. Exploring is the most effective skill in selling.
• What is the most effective skill in selling?
• Where is exploring the most effective skill?
19. By asking questions, the Sales Rep has discovered the customer’s buying needs.
• Who has discovered the customer’s buying needs?
• How has the Sales Rep discovered the customer’s buying needs?
20. By asking open questions you can make your customer respond freely.
• How can you make your customer respond by asking open questions?
• By asking what questions can you make your customer respond freely?
21. By asking closed questions you can gain «yes» or «no» responses.
• By asking what questions can you gain «yes» or «no» responses?
• What responses can you gain by asking closed questions?
22. The Sales Rep has proceeded very effectively through the sales call.
• Who has proceeded very effectively through the sales call?
• How has the Sales Rep proceeded through the sales call?
23. The experienced Sales Rep has uncovered the customer’s needs.
• Who has uncovered the customer’s needs?
• What Sales Rep has uncovered the customer’s needs?
24. After exploring the customer’s needs the Sale Rep provided the information about the relevant features, advantages and benefits of the product.
• Who provided the information about the relevant features, advantages and benefits of the product after exploring the customer’s needs?
• About what did the Sale Rep provide the information after exploring the customer’s needs?
• When did the Sale Rep provide the information about the relevant features, advantages and benefits of the product?
• About what features, advantages and benefits of the product did Sale Rep provide the information?
25. During the call the Sales Rep faced some real challenges.
• Who faced some real challenges during the call?
• What did the Sales Rep face during the call?
• What challenges did the Sales Rep face during the call?
26. He explored the challenges and listened carefully.
• Who explored the challenges and listened carefully?
• What did he explore?
• How did he listen?
27. The Sales Reps must respect the customer’s point of view.
• Who must respect the customer’s point of view?
• What must the Sales Reps do?
• What must the Sales Reps respect?
• Whose point of view must the Sales Reps respect?
28. Doubts and misconceptions can occur at every stage of the call.
• What can occur at every stage of the call?
• When can doubts and misconceptions occur?
• At what stage of the call can doubts and misconceptions occur?
29. The customer doubted whether your product really had the features or benefits.
• Who doubted whether your product really had the features or benefits?
• What did the customer doubt about?
30. After your call the customer had incomplete or inaccurate information.
• Who had incomplete or inaccurate information after the call?
• After whose call did the customer have incomplete or inaccurate information?
• What information did the customer have after the call?
• When did the customer have incomplete or inaccurate information?
31. It is not surprising that the customer was questioning you in depth.
• Who was questioning you in depth?
• What was the customer doing?
• How was the customer questioning you?
32. They wanted to be sure that you really could deliver what you claimed.
• Who wanted to be sure that you really could deliver what you claimed?
• What did they want to be sure?
33. Every product has its limitations.
• What has its limitations?
• What does every product have?
34. A limitation is something that can be offered or satisfied by that product.
• What is a limitation?
35. You will need to explore the limitation fully.
• Who will need to explore the limitation fully?
• What will you need?
• How will you need to explore the limitation?
36. You must put the limitation into perspective.
• Who must put the limitation into perspective?
• What must put into perspective?
• Where must you put the limitation?
37. He balanced the limitation with relevant accepted benefits.
Who balanced the limitation with relevant accepted benefits?
• What did he balance with relevant accepted benefits?
• With what did he balance the limitation?/What did he balance the limitation with?
• With what benefit did he balance the limitation?/What benefit did he balance the limitation with?
38. In the end of the call he has gained the customer’s agreement.
• Who has gained the customer’s agreement?
• What has he gained in the end of the call?
• Whose agreement has he gained in the end of the call?
39. The customer was not at all interested in what you were saying.
• Who was not at all interested in what you were saying?
• In what wasn’t the customer interested at all?
40. He doesn’t want your product.
• Who doesn’t want your product?
• What doesn’t he want?
• Whose product doesn’t he want?
41. He feels that the product will add some value to his practice.
• Who feels that the product will add some value to his practice?
• What value will he feel the product add to his practice?
• To whose practice will the product add some value?
42. The Sales Rep has uncovered all opportunities.
• Who has uncovered all opportunities?
• What has the Sales Rep done?
• What has the Sales Rep uncovered?
• What opportunities has the Sales Rep uncovered?
43. He has found implications and needs arising out of that situation.
• Who has found implications and needs arising out of that situation?
• What has he found?
• What needs has he found?
44. Many Sales Reps are afraid to ask for commitment.
• Who is afraid to ask for commitment?
• How many Sales Reps are afraid to ask for commitment?
• What are many Sales Reps afraid of?
45. He feared that the customer would say «No!»
• Who feared that the customer would say «No!»?
• What did he fear?
46. The Sales Rep has failed to close the call.
• Who has failed to close the call?
• What has he failed to do?
• What has he failed to close?
47. During his last call he recognized the appropriate time to close.
• Who recognized the appropriate time to close during the last call?
• What did he recognize?
• What time did recognize to close during the last call?
48. The customer has given a buying signal.
• Who has given a buying signal?
• What has the customer done?
• What signal has the customer given?
49. The Sales Rep has reminded the customer of the accepted benefits.
• Who has reminded the customer of the accepted benefits?
• Whom has the customer reminded of the accepted benefits?
• Of what benefits has the Sales Rep reminded the customer?
50. Tomorrow you will need to suggest an action-plan.
• Who will need to suggest an action-plan tomorrow?
• What will you need to do tomorrow?
• What plan will you need to suggest tomorrow?
• When will you need to suggest an action-plan?
Задание 8 b) Письменно переведите предложения на английский язык:
1. She works as a physician. But she doesn’t! She works as a Sales Rep in a pharmaceutical company.
2. Doctor Sergeeva has not returned from from the international congress yet. But she has! She returned a month ago.
3. Andrey Teetov will go to the cycle conference in Turkey. Yes, that is right.
4. Medical Reps usually work in the office. But they don’t! They always work in the field with their customers.
5. Few Medical Reps work in big pharmaceutical companies. It is not correct! Many Medical Reps work in I big pharmaceutical companies.
6. As a rule, Medical Reps don’t have cars. But they do! Medical Reps usually have cars.
7. Medical Reps buy mobile phones for themselves. But they don’t the company buys mobile phones for them.
Задание №12: Письменно, ответьте, что Вы не знаете ответа на заданный вопрос, используя приведенные ниже модели:
• I am afraid I don’t know…
• I am afraid I can’t say…
• I have no idea…
1. I am afraid I don’t know what a special technique is that the Sales Reps use to prepare for the call.
2. I am afraid I can’t say what SMART means.
3. I have no idea what Specific means in SMART.
4. I am afraid I don’t know what Measurable means in SMART.
5. I am afraid I can’t say what Ambitious means in SMART.
6. I have no idea what Timed means in SMART.
7. I am afraid I don’t know why Sales Reps prepare promotional literature for a call.
8. I am afraid I can’t say why a good opening is so important for sales call.
9. I have no idea what the skill of opening enables a Sales Rep.
10. I am afraid I don’t know what the skill of opening includes.
11. I am afraid I can’t say why exploring is the most powerful and effective skill in selling.
12. I have no idea what exploring helps a Sales Rep to discover.
13. I am afraid I don’t know what a Sales Rep can achieve by asking open questions.
14. I am afraid I can’t say what a Sales Rep can achieve by asking close questions.
15. I have no idea what the most effective and well known technique of exploring customer’s needs is.
16. I am afraid I can’t say what SPIN means.
17. I am afraid I can’t say what S means in SPIN.
18. I have no idea what P means in SPIN.
19. I am afraid I don’t know what I means in SPIN.
20. I am afraid I can’t say what N means in SPIN.
21. I have no idea why it is important to ask a customer situation questions.
22. I am afraid I don’t know why it is important to ask a customer problem questions.
23. I am afraid I can’t say why it is important to ask a customer implication questions.
24. I have no idea why it is important to ask a customer navigation questions.
25. I am afraid I don’t know when a Sales Rep must provide the information about the relevant features, advantages and benefits of your product.
26. I have no idea why it is important to provide the information about the relevant features, advantages and benefits of your product.
27. I have no idea what a Sales Rep can achieve by providing the information about the relevant features, advantages and benefits of your product.
28. I am afraid I don’t know what Sales Reps often face during the call.
29. I am afraid I can’t say why Sales Reps often face challanges during the call.
30. I have no idea what challenges include.
31. I am afraid I don’t know what a Sales Rep must do to manage these challenges.
32. I am afraid I can’t say why doubts and misconceptions occur.
33. I have no idea why indifference occur.
34. I am afraid I don’t know why limitations occur.
35. I am afraid I can’t say what a Sales Rep must do to manage the product limitation.
36. I have no idea what it means to balance the limitation with a relevant accepted benefit.
37. I am afraid I don’t know what makes indifference the most difficult challenge for a Sales Rep.
38. I have no idea what a Sales Rep must do to manage a customer indifference.
39. I am afraid I can’t say why closing can be a real challenge for many Sales Reps.
40. I am afraid I don’t know what call closing includes.
41. I have no idea why closing is so important for a sales call.
«Ключ» для проверки контрольной работы по теме №2:
1. I am not sure that every Medical Rep does some pre-call planning.
2. What is a special technique that the Sales Reps use to prepare for the call?
3. What does SMART mean?
4. I am not sure that Sales Reps use promotional literature in every call.
5. Why is a good opening so important for a sales call?
6. What does the skill of opening enable a Sales Rep to do?
7. I am afraid you are wrong when you say that the skill of exploring includes active listening.
8. I don’t agree with you that Sales Reps achieve nothing by asking open questions.
9. What is the most effective and well known technique of exploring customer’s needs?
10. Why is it important to ask a customer problem questions?
11. Why did the Sales Rep provide/present the information about the product before exploring the customer’s needs?
12. I am afraid I don’t know why Sales Reps often face challenges during the call.
13. What do challenges include?
14. What has the Sales Rep done to manage these challenges?
15. Why do doubts and misconceptions occur?
16. How did the Sales Rep manage the product limitation?
17. What makes indifference the most difficult challenge for a Sales Rep?
18. What will you do to manage a customer indifference?
19. Why has he failed to sale?
20. I don’t think closing is so important for a sales call.
Тема №3: Определение менеджером стратегий работы на территории и постановка бизнес цели на основе анализа ее потенциала
Учебный модуль №1. Грамматика:
Модальные глаголы английского языка
Модальность – выражение отношения говорящего к происходящим действиям. Модальные глаголы – одно из средств выражения отношения к происходящему. Модальные глаголы выражают:
В английском языке модальные глаголы can и must не имеют формы будущего времени.
Значение глагола can в будущем времени передается его эквивалентом to be able to, обозначающим «быть в состоянии сделать что-либо».

Для выражения необходимости совершить какое-либо действие в будущем вместо must употребляется глагол -to have to.

В общении с руководителями следует иметь в виду, что формы прошедшего времени глаголов can = could и may = might не только служат для выражения собственно прошедшего времени, но и используются для придания вашим обращениями и просьбам дополнительной вежливости и большей деликатности.
Например:
Can I take it? Мне можно это взять? (формальная просьба)
Could you do me a favour? Не могли бы Вы оказать мне услугу?
(большая степень вежливости).
В разговорной речи вместо глагола -have to часто употребляется выражение have got to (с последующим инфинитивом=неопределенной формой глагола), которое обычно передает действие, относящееся к будущему.

Учебный модуль №2. Текст:
Тerritory management: promotional strategies and business objectives
An effective management of the territory for the regional manager starts with an objective evaluation of territory potential. The first thing to do is to compare with each other several key marketing indicators reflecting the territory potential in terms of sales and market share growth. They are:
• relevant* market growth (relevant* means a specific therapy group segment for our product);
• our product sales growth;
• our product market share growth.
Each of the key market indicators mentioned above must be compared in terms of time (for example 2020 vs 2019) and in terms of territory (for example region vs region/or region vs country) for better understanding of a territory potential.
At this stage of territory analysis a regional manager is recommended to use BCG-Matrix (developed by Boston Consulting Group specialists) to visualize potential business strategy for a product/business in a territory (see picture below). A Business Strategy – is a justified concentration of promotional resources to reach the appropriate objectives in the appropriate market environment.
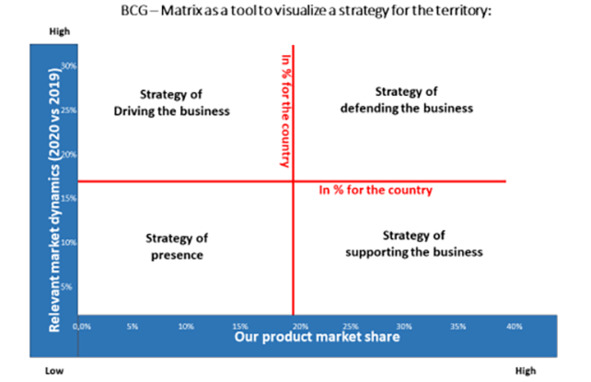
As you can see BCG-Matrix has two scales where a vertical one represents relevant market dynamics in percent (for example, 2020 vs 2019) and horizontal scale represents our product market share (for example, for 2020) also in percent. The lines marked red in the BCG-Matrix dividing it into four segments are relevant market dynamics for the country and our product market share for the country. They give us the benchmark for further analysis of our territory potential vs the country potential.
As you can see in the picture above there are basically four main business strategies for a territory:
1. The strategy of driving the business (upper left segment of BCG-Matrix) is chosen when the relevant business grows up (above the country) while our market share is small (lower than in the country). Under these circumstances, it is reasonable for the company to invest high promotional resources to drive the market share and to boost our sales. The strategy of driving the business requires very high resources because it is aimed at reaching high coverage of A and B customers (with low loyalty to our products) high call frequency and big number of group promotional activities (medical conferences, round table discussions, group presentations). The average balance between individual calls and group promotional activities is not less than 6+2 for each physician where the first number (6) reflects individual calls and the second – participation of each physician in group promotional activities. This balance (6+2) is calculated for a promotional cycle equal to three months.
2. The strategy of defending the business (upper right segment of BCG-Martix) is chosen when the relevant business dynamics in the territory is growing or standing still while our market share is high. In such circumstances our business objective is to aim the necessary promotional resources at active defense of the gained market share against our competitors. The strategy of defending our business means a certain limitation of individual calls to high potential customers with high loyalty to our products in favor of group promotional activities: medical conferences, round table discussions and group presentations. The average balance between individual contacts and participation of customers in group promotional activities does not exceed 2+3 per promotional cycle (three months).
3. The strategy of supporting the business (the low right segment of the BCG-Matrix) is chosen when the relevant business dynamics in the territory is standing still or falling (below country level) while our market share is still high. In such circumstances our business objective is to aim the necessary promotional resources at the defense of the gained market share against our competitors. But unlike previous strategy (=defending business) the strategy of supporting business means even bigger limitation of individual calls to high potential customers with high loyalty to our products in favor of group promotional activities: medical conferences, round table discussions and group presentations. The average balance between individual contacts and participation of customers in group promotional activities does not exceed 1—2+3 per promotional cycle (three months).
4. The strategy of presence in the territory (low left segment of BCG-Matris) is usually chosen when the relevant market in the territory stagnates or is falling while our market share is low. Under these circumstances the investment of significant resources in the territory in terms of return of investment (ROI indicator) is not justified. The objective of this strategy is to limit the promotional resources to a reasonable minimum of less expensive promotional activities to ensure high coverage. When business environment in the territory changes, for example it starts to grow up the business strategy changes accordingly, for example from presence to driving the business. Thus following the strategy of presence the MRs and KAMs call on customers with low coverage and frequency and concentrate their attention to group activities to detail the company products. The average balance between individual contacts and participation of customers in group promotional activities is close to 1+1 or even 0+1.

