 полная версия
полная версияThe Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction. Volume 10, No. 271, September 1, 1827

Various
The Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction / Volume 10, No. 271, September 1, 1827
The New Prison, Norwich
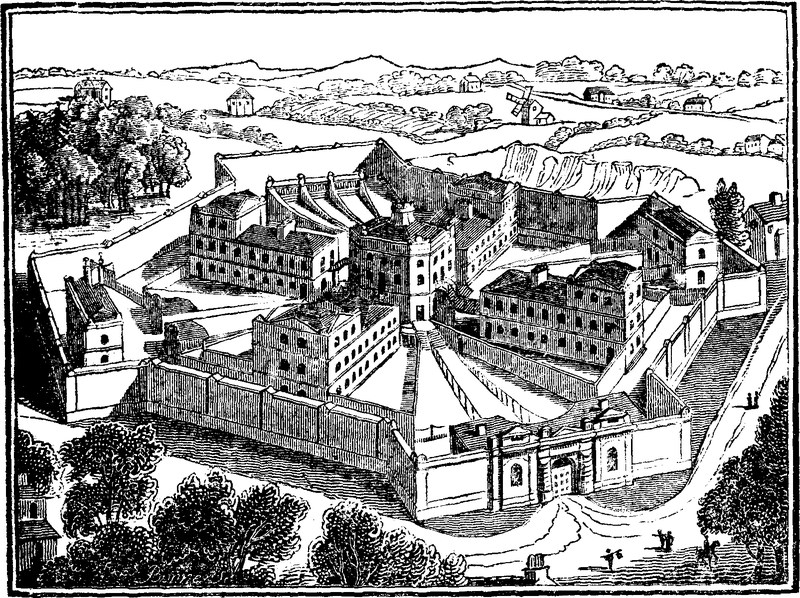
The old gaol in the city of Norwich, in the year 1823, being found no longer secure, nor according to the new act of parliament, admitting of sufficient room for the classification of the prisoners, the magistrates came to a resolution of erecting a new one outside the city, near St. Giles's gates; the same was accordingly advertised in the Norwich papers, in which architects were requested to send plans, elevations, and sections, (in competition,) accompanied with an estimate of the total expense of the new building. A great number of designs were in consequence submitted, when the plan sent by Mr. Brown, of Wells-street, Oxford-street, London, was adjudged to be the best: his plan was therefore adopted and carried into execution, of which the annexed engraving is a faithful representation, taken from the tower of St. Giles's Church, in the city of Norwich. The foundation stone was laid in 1824, and the building finished this year, 1827. It is designed to hold 120 prisoners, besides the necessary turnkeys and servants, and has cost the city £23,000; the boundary wall is quadrangular, but is cut off at the junction of the four angles by bastions, thereby giving to the wall a greater stability; the whole circumference is 1,220 feet, and encloses an area of one acre, two roods, and thirty-four poles, being nearly one acre and three quarters of ground.
The bastion at the entrance contains on the ground floor a porter's room, press room, hot and cold baths, and a room with an oven for the purpose of purifying foul linen. The upper story contains over the entrance gate the drop room: on each side are receiving cells, two for males and two for females, a searching room for the surgeon, and the prison wardrobe; directly over the drop room on the lead flat is the place where the more heinous malefactors expiate their crimes. The bastion on the right hand contains a building, on the ground floor and in the centre of which is the wash-house and laundry, and in front the drying ground; at each end of this building are the airing grounds for the sick prisoners, and on the second floor are the male and female infirmaries, separated by a strong partition wall. The left hand bastion contains the millhouse, stable, and a room for the van which takes the prisoners to the town hall in the assize time; over these three rooms are the mill chamber and hay-loft. The horizontal wind vane on the roof of this building is to assist the prisoners when there is not a sufficiency of them sentenced to the tread-wheels; by shutting the louvre boards of the arms it then produces employment for the prisoners when there is no corn in the mill to grind. In the remote bastion are seen the tread-wheels on which the prisoners are employed in keeping up a constant retrograde motion, which works the machinery in the millhouse by means of an iron shaft with universal joints concealed below the surface of the ground.
Here are four prison wings in the building, the right hand one contains in one ward common debtors, and in the other unconvicted men felons, not capital. The second wing on the right contains on one side unconvicted men felons, and unconvicted women felons for capital offences on the other. In the first left hand wing there is on the first side the master debtors, and on the other the court of conscience debtors; the second wing on the left contains on one side men misdemeanors, and on the other convicted men felons. There are two day-rooms in each of the four wings, and four condemned cells and four solitary ones in the back towers; there is also fourteen airing yards between the four wings, six of which are sunk three feet below the others, to enable the governor from the inspection gallery of his house to overlook the tread-wheels, millhouse, and infirmary; those yards are descended by stone steps, in each there is a day room, and they are appropriated to the following prisoners, namely, women debtors, unconvicted women felons, not capital; convicted women felons, women fines, men fines, and boys for misdemeanors. There is also a level passage between each two of the sunk yards, one leading to the infirmary, one to the millhouse, and the other to the tread-wheels.
In the governor's house there is in the basement story a kitchen, scullery, and bakehouse, store room, beer-cellar, and coal cellar; on the ground floor is the governor's office, living room, committee room, and matron's room; on the second floor are two bedrooms and the lower part of the chapel; and on the third floor are two bedrooms and the gallery of the chapel. There are likewise four bridge staircases, one from each prison wing leading to passages in the governor's house, which communicates with the chapel; the prisoners are not here able to see each others' class, as they are separated by fourteen partitions, being as many as there are yards in the prison, yet the governor and minister have from their seats a complete view of every person and every part. Around the governor's house is an enclosed area, and above an inspection gallery, from which the governor is enabled to see into every part of the prison. On the towers of the four prison wings there are reservoirs for containing water, which is thrown up by a pump worked by the prisoners at the tread-wheel, whenever water is required, and by means of lead pipes, it is then conveyed to every part of the prison. The whole gaol is fire-proof, the floors being of stone, and the doors and windows of iron.
There is certainly a peculiar arrangement in the plan of this gaol not to be met with in any other in the kingdom; there are four yards between each of the wings excepting those two in the approach to the governor's house; the middle yards which are divided by a passage, have, as before stated, each of them a day-room. The prisoners allotted to these yards have their sleeping cells in the main wing, to which they are conducted along a passage, at the end of those upper yards which join the prison wing; the prisoners are therefore in their passage to and from the sleeping cells, concealed from the others; should there at any time be a greater number of prisoners belonging to the ward on the ground floor than there are sleeping cells they are then taken to the spare cells in the wards above through a door at the end of the upper yard, and yet concealed from those classes in the sunk yards. All our prison buildings hitherto erected are hid from the sight by the high boundary wall that encloses them, producing nothing interesting to the citizen or the traveller but a monotonous façade. Mr. Brown has obviated this in the gaol before us, by having raised towers on the ends of the four wings, which, with the top of the governor's house, mill, and infirmary, being seen rising above the boundary wall and entrance front, produces to the eye of the spectator on approaching the prison a tout ensemble truly imposing and grand.
ARCHITECTUS.
LIVING AUTHORS
BERNARD BARTON
"Sheltered, but not to social duties lost;Secluded, but not buried; and with songCheering his days."The productions of Mr. Barton are doubtless familiar to most of our readers, and from them they have learnt much of the amiable turn of the poet's character. Mr. Barton's compositions afford indications of genuine feeling, of deep affection, of benevolence, sympathy, taste, and integrity; he seems to have an ear ever on the listen for the accents of charity, patriotism, and religion; where human anguish causes the tear to start, there he would fain be to soothe and alleviate. Such is the character of the poet, and in the following sketch such will be proved to be the character of the man.
Bernard Barton was born in the vicinity of London, on the 31st of January, 1784. His father was in trade in the metropolis, whither he had come from his native place, Carlisle. Bernard had the misfortune to lose his mother one month after his birth: her maiden name was Mary Done, and she was a native of Rockcliffe, Cumberland; she died at the early age of thirty-two. The following lines To a Profile evince the feelings with which our poet still cherishes her memory, or rather the recollection of what has been told him respecting her:—
"I knew thee not! then wherefore gazeUpon thy silent shadow there,Which so imperfectly portraysThe form thy features used to wear?Yet have I often looked at thee,As if those lips could speak to me.I knew thee not! and thou couldst know,At best, but little more of oneWhose pilgrimage on earth belowCommenced, just ere thy own was done;For few and fleeting days were thine,To hope or fear for lot of mine.Yet few and fleeting as they were,Fancy and feeling picture this,They prompted many a fervent prayer,Witnessed, perchance, a parting kiss;And might not kiss, and prayer, from thee,At such a period, profit me?Whether they did or not, I oweAt least this tribute to thy worth;Though little all I can bestow,Yet fond affection gives it birth;And prompts me, as thy shade I view,To bless thee, whom I never knew!"1His father died before Mr. Barton was seven years old; but his second marriage, which took place a few months before his death, provided an excellent parent for his children: to her, and to his two sisters,2 both several years older than himself, our author owed infinite obligations.
His education at one of the quaker seminaries was, of course, plain and circumscribed, being pretty much confined to useful, indeed necessary, branches of knowledge. But his father had been a man of greater natural and more cultivated intellect than many; he had read much, and on the abolition of slavery, in which he was one of Clarkson's earliest associates, he had, on several occasions, proved that he could write well, though, we believe, he was never avowedly an author. He had left no despicable collection of books, so that in his school vacations ample means were afforded to his son of indulging his taste for reading. A pleasing tribute to the memory of Mr. Barton's father will be found in his Napoleon and other Poems.
In the year 1806, Mr. Barton took up his residence in the pleasant town of Woodbridge, in Suffolk, and commenced business as a merchant; but an unlooked-for domestic affliction of the severest kind was about to visit him, and his wordly prospects were to receive an irrecoverable shock,—the loss of his amiable wife, before they had been married a twelvemonth, and soon after the birth of her child! This excellent woman, to whom our poet was, for so short a time, united, gave rise to some of his best pieces, particularly to the poem beginning, The heaven was cloudless,3 and that entitled A Portrait, in Napoleon and other Poems. In this last piece the poet no less beautifully than truly observes,—
To sympathies, which soothe and blessOur life from day to day,Which throw, with silent tenderness,Fresh flowers across our way,The heart must ever fondly cling:But can the poet's sweetest stringTheir loveliness display?No—nor could Titian's self supplyTheir living presence, once gone by.The air, in which we breathe and live,Eludes our touch and sight;The fairest flowers their fragrance giveTo stillness, and to night;The softest sounds that music flings,In passing, from her heaven-plumed wings,Are trackless in their flight!And thus life's sweetest bliss is knownTo silent, grateful thought alone.This mournful event, combined with discouraging prospects of a mercantile nature, induced our author to retire from commercial pursuits on his own behalf; and in 1810 he obtained a situation as a clerk in the Woodbridge bank, which he still holds.
Soon after Mr. Barton had entered upon his present situation, he began "to commit the sin of rhyme," and a new provincial paper being established about this time, it became the vehicle of his effusions: by degrees our young poet became bold enough to send a short piece now and then to a London paper, and at last, in 1812, ventured on an anonymous volume, entitled Metrical Effusions, 250 copies of which were printed by a bookseller of Woodbridge, and sold within the immediate circle of our author's acquaintance. In 1818, Mr. Barton printed, by subscription, an elegant volume, in elephant octavo, of Poems by an Amateur, of which 150 only were struck off, and none ever sold at the shops. Encouraged by the very flattering manner in which these impressions of his poems were received by his friends, our author at last ventured to publish, in a small volume, Poems, by Bernard Barton, which was very favourably noticed by the literary journals, and, being afterwards made still more known by an article in the Edinburgh Review, has now reached a third edition. He afterwards published, in a handsome octavo volume, his Napoleon and other Poems; and subsequently a volume of poems, entitled A Widow's Tale, which appeared in an early month of the present year.
Such has been the literary career of Bernard Barton. If it have not left behind it the brilliant track of other poetical comets, it has been less erratic in its course; and if it have not been irradiated by the full blaze of a noonday sun, it has nevertheless been illumined by the silver lustre of the queen of night; and his Parnassian vespers may be said to possess all the mild and soothing beauties of the evening star. If his muse have not always reached the sunward path of the soaring eagle, it is no extravagant praise to say, that she has often emulated the sublimity of his aërial flight. But the great charm thrown around the effusions of the Suffolk bard is that "lucid veil" of morality and religion which "covers but not conceals"—that "silver net-work," through which his poetic "apples of gold" shine with an adventitious beauty, which even the gorgeous ornaments so profusely lavished by a Byron or a Moore would fail to invest them.
There is a fame which owes its spellTo popular applause alone;Which seems on lip and tongue to dwell,And finds—in others' breath—its own;For such the eager worldling sighs,And this the fickle world supplies.There is a nobler fame—which drawsIts purer essence from the heart;Which only seeks that calm applauseThe virtuous and the wise impart:Such fame beyond the grave shall live:But this the world can never give.—B. BARTON.We have alluded to the amiable character of our poet; that his modesty is equal to his merit, the following extract, from a letter to a friend, will afford a pleasing evidence. Speaking of his literary career, he says, "it has been marked by an indulgence on the part of the public, and the dispensers of literary fame, which I never anticipated. When I consider that only about three years have elapsed since I avowed myself an author, I am really surprised at the notice my trivial productions have received, and the numerous acquaintance to which they have, by correspondence, introduced me. Much of this, I dare say, is owing to my quakerism; and to that, unquestionably, I was indebted for the article in the Edinburgh Review, and the more recent passing notice in the Quarterly. Still, as I do not believe that any outré or adventitious source of attraction would have alone procured me the attention I have found, I would hope it may partly have arisen from their simple, unaffected appeal to those quiet, domestic, secluded feelings, which endear the still undercurrent of existence—in short, to my being content to make the best I could of the homely and confined materials to which my situation has given me access, without affecting scholarship, or aiming at romantic embellishment. There is nothing like simple truth and nature, after all; and he who is satisfied with simply and faithfully describing what he actually sees, feels, and, thinks, may always hope to appeal successfully to the unsophisticated heart."4
We here conclude our notice of the bard of Woodbridge; and should this brief account excite the interest of our readers to become better acquainted with this "living author," we refer them to the whole-length portrait painted by himself, and held up to view in every page of his poems.
RETROSPECTIVE GLEANINGS
THE GREAT FIRE OF 1666
The fire of London broke out on Sunday morning, September 2, 1666, O.S., and being impelled by strong winds, raged with irresistible fury nearly four days and nights; nor was it entirely mastered till the fifth morning after it began. The conflagration commenced at the house of one Farryner, a baker, in Pudding-lane, near [New] Fish-street-hill, and within ten houses of Thames-street, into which it spread within a few hours; nearly the whole of the contiguous buildings being of timber, lath, and plaster, and the whole neighbourhood presenting little else than closely confined passages and narrow alleys. The fire quickly spread, and was not to be conquered by any human means, "Then, (says a contemporary writer,) then the city did shake indeed, and the inhabitants did tremble, and flew away in great amazement from their houses, lest the flames should devour them: rattle, rattle, rattle, was the noise which the fire struck upon the ear round about, as if there had been a thousand iron chariots beating upon the stones. You might see the houses tumble, tumble, tumble, from one end of the street to the other, with a great crash, leaving the foundations open to the view of the heavens."5
The destructive fury of this conflagration was never, perhaps, exceeded in any part of the world, by any fire originating in accident. Within the walls, it consumed almost five-sixths of the whole city; and without the walls it cleared a space nearly as extensive as the one-sixth part left unburnt within. Scarcely a single building that came within the range of the flames was left standing. Public buildings, churches, and dwelling-houses, were alike involved in one common fate.
In the summary account of this vast devastation, given in one of the inscriptions on the Monument, and which was drawn up from the reports of the surveyors appointed after the fire, it is stated, that "The ruins of the city were 436 acres, [viz. 333 acres within the walls, and 63 in the liberties of the city;] that, of the six-and-twenty wards, it utterly destroyed fifteen, and left eight others shattered and half burnt; and that it consumed 400 streets, 13,200 dwelling-houses, 89 churches [besides chapels; 4 of] the city gates, Guildhall, many public structures, hospitals, schools, libraries, and a vast number of stately edifices." The immense property destroyed in this dreadful time cannot be estimated at less than ten millions sterling. Amid all the confusion and multiplied dangers that arose from the fire, it does not appear that more than six persons lost their lives. Calamitous as were the immediate consequences of this dreadful fire, its remote effects have proved an incalculable blessing to subsequent generations. To this conflagration may be attributed the complete destruction of the plague, which, the year before only, swept off 68,590 persons!! To this tremendous fire we owe most of our grand public structures—the regularity and beauty of our streets—and, finally, the great salubrity and extreme cleanliness of a large part of the city of London.
In relation to this awful calamity we add the following remarks:—Heaven be praised (says Mr. Malcolm6) old London was burnt. Good reader, turn to the ancient prints, in order to see what it has been; observe those hovels convulsed; imagine the chambers within them, and wonder why the plague, the leprosy, and the sweating-sickness raged. Turn then to the prints illustrative of our present dwellings, and be happy. The misery of 1665 must have operated on the minds of the legislature and the citizens, when they rebuilt and inhabited their houses. The former enacted many salutary clauses for the preservation of health, and would have done more, had not the public rejected that which was for their benefit; those who preferred high habitations and narrow dark streets had them. It is only to be lamented that we are compelled to suffer for their folly. These errors are now frequently partially removed by the exertion of the Corporation of London; but a complete reformation is impossible. It is to the improved dwellings composed of brick, the wainscot or papered walls, the high ceilings, the boarded floors, and large windows, and cleanliness, that we are indebted for the general preservation of health since 1666. From that auspicious year the very existence of the natives of London improved; their bodies moved in a large space of pure air; and, finding every thing clean and new around them, they determined to keep them so. Previously-unknown luxuries and improvements in furniture were suggested; and a man of moderate fortune saw his house vie with, nay, superior to, the old palaces of his governors. When he paced his streets, he felt the genial western breeze pass him, rich with the perfumes of the country, instead of the stench described by Erasmus; and looking upward, he beheld the beautiful blue of the air, variegated with fleecy clouds, in place of projecting black beams and plaster, obscured by vapour and smoke.
The streets of London must have been dangerously dark during the winter nights before it was burnt; lanterns with candles were very sparingly scattered, nor was light much better distributed even in the new streets previously to the 18th century. Globular lamps were introduced by Michael Cole, who obtained a patent in July, 1708.
We conclude the illustrations of this day with a singular opinion of the author just quoted. Speaking of the burning of London, he says, "This subject may be allowed to be familiar to me, and I have perhaps had more than common means of judging; and I now declare it to be my full and decided opinion, that London was burnt by government, to annihilate the plague, which was grafted in every crevice of the hateful old houses composing it."
THE SKETCH BOOK
BEHIND THE SCENES; OR, A BREAKFAST IN NEWGATE
(Concluded from page 134.)
No further delay was allowed. The sheriffs moved on, the ordinary, the culprits, and the officers did the same; and that class of attendants to which I belonged followed. I shall not easily forget the circumstances of this brief, but melancholy progress. The faltering step—the deep-drawn sigh—the mingling exclamations of anguish and devotion which marked the advance of the victims—the deep tones of the reverend gentleman who now commenced reading a portion of the burial service, and the tolling of the prison bell, which, as we proceeded through some of the most dreary passages of the gaol, burst on the ear, rendered the whole spectacle impressive beyond description. Few steps sufficed to conduct us to the small room, or entrance-hall, into which the debtor's door opens, and from this we saw the ladder which the criminals were to ascend, and the scaffold on which they were to die. I was on the alert to detect any sudden emotion which this spectacle might cause, but could not perceive that it had the slightest effect. The minds of the sufferers had been so prepared, that a partial view of the machine to which they were being conducted, seemed to give no additional shock. No further pause was deemed necessary. The clock was striking eight, and the ordinary and the youth first brought to the press-room, immediately passed up the ladder. To the two culprits that remained, the gentleman whom I have already mentioned offered his services, and filled up with a prayer the little interval which elapsed, before the second was conducted to the platform.
I heard from without the murmur of awe, of expectation, and pity, which ran through the crowd in front of the prison, and stepping on a small erection to the left of the door, gained a momentary glimpse of a portion of the immense multitude, who, uncovered, and in breathless silence, gazed on the operations of the executioners. I retreated just as the third halter had been adjusted. The finisher of the law was in the act of descending, when the under-sheriff addressed him—









