 полная версия
полная версияThe Crown of Wild Olive
Book III.
Who the Hohenzollerns were, and how they came to power in Nüremberg, is told in Chap. v. of Book II.
Their succession in Brandenburg is given in brief at page 377 (269). I copy it, in absolute barrenness of enumeration, for our momentary convenience, here:
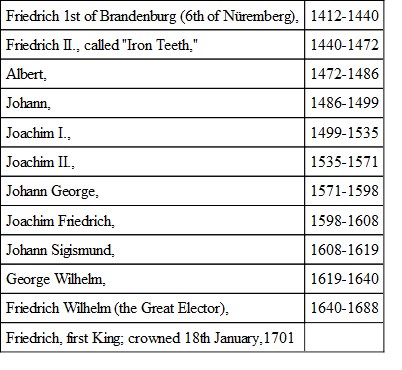
Of this line of princes we have to say they followed generally in their ancestor's steps, and had success of the like kind more or less; Hohenzollerns all of them, by character and behaviour as well as by descent. No lack of quiet energy, of thrift, sound sense. There was likewise solid fair-play in general, no founding of yourself on ground that will not carry, and there was instant, gentle, but inexorable crushing of mutiny, if it showed itself, which after the Second Elector, or at most the Third, it had altogether ceased to do.
This is the general account of them; of special matters note the following:—
II. Friedrich, called "Iron-teeth," from his firmness, proves a notable manager and governor. Builds the palace at Berlin in its first form, and makes it his chief residence. Buys Neumark from the fallen Teutsch Ritters, and generally establishes things on securer footing.
III. Albert, "a fiery, tough old Gentlemen," called the Achilles of Germany in his day; has half-a-century of fighting with his own Nürembergers, with Bavaria, France, Burgundy, and its fiery Charles, besides being head constable to the Kaiser among any disorderly persons in the East. His skull, long shown on his tomb, "marvellous for strength and with no visible sutures."
IV. John, the orator of his race; (but the orations unrecorded). His second son, Archbishop of Maintz, for whose piece of memorable work see page 223 (143) and read in connection with that the history of Margraf George, pp. 237-241 (152-154), and the 8th chapter of the third book.
V. Joachim I., of little note; thinks there has been enough Reformation, and checks proceedings in a dull stubbornness, causing him at least grave domestic difficulties.—Page 271 (173).
VI. Joachim II. Again active in the Reformation, and staunch,
though generally in a cautious, weighty, never in a rash, swift way, to the great cause of Protestantism and to all good causes. He was himself a solemnly devout man; deep, awe-stricken reverence dwelling in his view of this universe. Most serious, though with a jocose dialect, commonly having a cheerful wit in speaking to men. Luther's books he called his Seelenschatz, (soul's treasure); Luther and the Bible were his chief reading. Fond of profane learning, too, and of the useful or ornamental arts; given to music, and "would himself sing aloud" when he had a melodious leisure hour.
VII. Johann George, a prudent thrifty Herr; no mistresses, no luxuries allowed; at the sight of a new-fashioned coat he would fly out on an unhappy youth and pack him from his presence. Very strict in point of justice; a peasant once appealing to him in one of his inspection journeys through the country—
"Grant me justice, Durchlaucht, against so and so; I am your Highness's born subject." "Thou shouldst have it, man, wert thou a born Turk!" answered Johann George.
Thus, generally, we find this line of Electors representing in Europe the Puritan mind of England in a somewhat duller, but less dangerous, form; receiving what Protestantism could teach of honesty and common sense, but not its anti-Catholic fury, or its selfish spiritual anxiety. Pardon of sins is not to be had from Tetzel; neither, the Hohenzollern mind advises with itself, from even Tetzel's master, for either the buying, or the asking. On the whole, we had better commit as few as possible, and live just lives and plain ones.
A conspicuous thrift, veracity, modest solidity, looks through the conduct of this Herr; a determined Protestant he too, as indeed all the following were and are.
VIII. Joachim Friedrich. Gets hold of Prussia, which hitherto, you observe, has always been spoken of as a separate country from Brandenburg. March 11, 1605—"squeezed his way into the actual guardianship of Preussen and its imbecile Duke, which was his by right."
For my own part, I do not trouble myself much about these rights, never being able to make out any single one, to begin with, except the right to keep everything and every place about you in as good order as you can—Prussia, Poland, or what else. I should much like, for instance, just now, to hear of any honest Cornish gentleman of the old Drake breed taking a fancy to land in Spain, and trying what he could make of his rights as far round Gibraltar as he could enforce them. At all events, Master Joachim has somehow got hold of Prussia; and means to keep it.
IX. Johann Sigismund. Only notable for our economical purposes, as getting the "guardianship" of Prussia confirmed to him. The story at page 317 (226), "a strong flame of choler," indicates a new order of things among the knights of Europe—"princely etiquettes melting all into smoke." Too literally so, that being one of the calamitous functions of the plain lives we are living, and of the busy life our country is living. In the Duchy of Cleve, especially, concerning which legal dispute begins in Sigismund's time. And it is well worth the lawyers' trouble, it seems.
It amounted, perhaps, to two Yorkshires in extent. A naturally opulent country of fertile meadows, shipping capabilities, metalliferous hills, and at this time, in consequence of the Dutch-Spanish war, and the multitude of Protestant refugees, it was getting filled with ingenious industries, and rising to be what it still is, the busiest quarter of Germany. A country lowing with kine; the hum of the flax-spindle heard in its cottages in those old days—"much of the linen called Hollands is made in Jülich, and only bleached, stamped, and sold by the Dutch," says Büsching. A country in our days which is shrouded at short intervals with the due canopy of coal-smoke, and loud with sounds of the anvil and the loom.
The lawyers took two hundred and six years to settle the question concerning this Duchy, and the thing Johann Sigismund had claimed legally in 1609 was actually handed over to Johann Sigismund's descendant in the seventh generation. "These litigated duchies are now the Prussian provinces, Jülich, Berg, Cleve, and the nucleus of Prussia's possessions in the Rhine country."
X. George Wilhelm. Read pp. 325 to 327 (231, 233) on this Elector and German Protestantism, now fallen cold, and somewhat too little dangerous. But George Wilhelm is the only weak prince of all the twelve. For another example how the heart and life of a country depend upon its prince, not on its council, read this, of Gustavus Adolphus, demanding the cession of Spandau and Küstrin:
Which cession Kurfürst George Wilhelm, though giving all his prayers to the good cause, could by no means grant. Gustav had to insist, with more and more emphasis, advancing at last with military menace upon Berlin itself. He was met by George Wilhelm and his Council, "in the woods of Cöpenick," short way to the east of that city; there George Wilhelm and his Council wandered about, sending messages, hopelessly consulting, saying among each other, "Que faire? ils ont des canons." For many hours so, round the inflexible Gustav, who was there like a fixed mile-stone, and to all questions and comers had only one answer.
On our special question of war and its consequences, read this of the Thirty Years' one:
But on the whole, the grand weapon in it, and towards the latter times, the exclusive one, was hunger. The opposing armies tried to starve one another; at lowest, tried each not to starve. Each trying to eat the country or, at any rate, to leave nothing eatable in it; what that will mean for the country we may consider. As the armies too frequently, and the Kaiser's armies habitually, lived without commissariat, often enough without pay, all horrors of war and of being a seat of war, that have been since heard of, are poor to those then practised, the detail of which is still horrible to read. Germany, in all eatable quarters of it, had to undergo the process; tortured, torn to pieces, wrecked, and brayed as in a mortar, under the iron mace of war. Brandenburg saw its towns seized and sacked, its country populations driven to despair by the one party and the other. Three times—first in the Wallenstein-Mecklenburg times, while fire and sword were the weapons, and again, twice over, in the ultimate stages of the struggle, when starvation had become the method—Brandenburg fell to be the principal theatre of conflict, where all forms of the dismal were at their height. In 1638, three years after that precious "Peace of Prag,"… the ravages of the starving Gallas and his Imperialists excelled all precedent,… men ate human flesh, nay, human creatures ate their own children. "Que faire? ils ont des canons!"
"We have now arrived at the lowest nadir point" (says Carlyle) "of the history of Brandenburg under the Hohenzollerns." Is this then all that Heavy Peg and our nine Kurfürsts have done for us?
Carlyle does not mean that; but even he, greatest of historians since Tacitus, is not enough careful to mark for us the growth of national character, as distinct from the prosperity of dynasties.
A republican historian would think of this development only, and suppose it to be possible without any dynasties.
Which is indeed in a measure so, and the work now chiefly needed in moral philosophy, as well as history, is an analysis of the constant and prevalent, yet unthought of, influences, which, without any external help from kings, and in a silent and entirely necessary manner, form, in Sweden, in Bavaria, in the Tyrol, in the Scottish border, and on the French sea-coast, races of noble peasants; pacific, poetic, heroic, Christian-hearted in the deepest sense, who may indeed perish by sword or famine in any cruel thirty years' war, or ignoble thirty years' peace, and yet leave such strength to their children that the country, apparently ravaged into hopeless ruin, revives, under any prudent king, as the cultivated fields do under the spring rain. How the rock to which no seed can cling, and which no rain can soften, is subdued into the good ground which can bring forth its hundredfold, we forget to watch, while we follow the footsteps of the sower, or mourn the catastrophes of storm. All this while, the Prussian earth—the Prussian soul—has been thus dealt upon by successive fate; and now, though laid, as it seems, utterly desolate, it can be revived by a few years of wisdom and of peace.
Vol. I. Book III. Chap, xviii.—The Great Elector, Friedrich Wilhelm. Eleventh of the dynasty:—
There hardly ever came to sovereign power a young man of twenty under more distressing, hopeless-looking circumstances. Political significance Brandenburg had none; a mere Protestant appendage, dragged about by a Papist Kaiser. His father's Prime Minister, as we have seen, was in the interest of his enemies; not Brandenburg's servant, but Austria's. The very commandants of his fortresses, Commandant of Spandau more especially, refused to obey Friedrich Wilhelm on his accession; "were bound to obey the Kaiser in the first place."
For twenty years past Brandenburg had been scoured by hostile armies, which, especially the Kaiser's part of which, committed outrages new in human history. In a year or two hence, Brandenburg became again the theatre of business, Austrian Gallas advancing thither again (1644) with intent "to shut up Torstenson and his Swedes in Jutland." Gallas could by no means do what he intended; on the contrary, he had to run from Torstenson—what feet could do; was hunted, he and his Merode Brüder (beautiful inventors of the "marauding" art), till they pretty much all died (crepirten) says Köhler. No great loss to society, the death of these artists, but we can fancy what their life, and especially what the process of their dying, may have cost poor Brandenburg again!
Friedrich Wilhelm's aim, in this as in other emergencies, was sun-clear to himself, but for most part dim to everybody else. He had to walk very warily, Sweden on one hand of him, suspicious Kaiser on the other: he had to wear semblances, to be ready with evasive words, and advance noiselessly by many circuits. More delicate operation could not be imagined. But advance he did; advance and arrive. With extraordinary talent, diligence, and felicity the young man wound himself out of this first fatal position, got those foreign armies pushed out of his country, and kept them out. His first concern had been to find some vestige of revenue, to put that upon a clear footing, and by loans or otherwise to scrape a little ready-money together. On the strength of which a small body of soldiers could be collected about him, and drilled into real ability to fight and obey. This as a basis: on this followed all manner of things, freedom from Swedish-Austrian invasions, as the first thing. He was himself, as appeared by-and-by, a fighter of the first quality, when it came to that; but never was willing to fight if he could help it. Preferred rather to shift, manœuvre, and negotiate, which he did in most vigilant, adroit, and masterly manner. But by degrees he had grown to have, and could maintain it, an army of twenty-four thousand men, among the best troops then in being.
To wear semblances, to be ready with evasive words, how is this, Mr. Carlyle? thinks perhaps the rightly thoughtful reader.
Yes, such things have to be; There are lies and lies, and there are truths and truths. Ulysses cannot ride on the ram's back, like Phryxus; but must ride under his belly. Read also this, presently following:
Shortly after which, Friedrich Wilhelm, who had shone much in the battle of Warsaw, into which he was dragged against his will, changed sides. An inconsistent, treacherous man? Perhaps not, O reader! perhaps a man advancing "in circuits," the only way he has; spirally, face now to east, now to west, with his own reasonable private aim sun-clear to him all the while?
The battle of Warsaw, three days long, fought with Gustavus, the grandfather of Charles XII., against the Poles, virtually ends the Polish power:
Old Johann Casimir, not long after that peace of Oliva, getting tired of his unruly Polish chivalry and their ways, abdicated—retired to Paris, and "and lived much with Ninon de l'Enclos and her circle," for the rest of his life. He used to complain of his Polish chivalry, that there was no solidity in them; nothing but outside glitter, with tumult and anarchic noise; fatal want of one essential talent, the talent of obeying; and has been heard to prophesy that a glorious Republic, persisting in such courses, would arrive at results which would surprise it.
Onward from this time, Friedrich Wilhelm figures in the world; public men watching his procedure; kings anxious to secure him—Dutch print-sellers sticking up his portraits for a hero-worshipping public. Fighting hero, had the public known it, was not his essential character, though he had to fight a great deal. He was essentially an industrial man; great in organizing, regulating, in constraining chaotic heaps to become cosmic for him. He drains bogs, settles colonies in the waste places of his dominions, cuts canals; unweariedly encourages trade and work. The Friedrich Wilhelm's Canal, which still carries tonnage from the Oder to the Spree, is a monument of his zeal in this way; creditable with the means he had. To the poor French Protestants in the Edict-of-Nantes affair, he was like an express benefit of Heaven; one helper appointed to whom the help itself was profitable. He munificently welcomed them to Brandenburg; showed really a noble piety and human pity, as well as judgment; nor did Brandenburg and he want their reward. Some twenty thousand nimble French souls, evidently of the best French quality, found a home there; made "waste sands about Berlin into potherb gardens;" and in spiritual Brandenburg, too, did something of horticulture which is still noticeable.
Now read carefully the description of the man, p. 352 (224-5); the story of the battle of Fehrbellin, "the Marathon of Brandenburg," p. 354 (225); and of the winter campaign of 1679, p. 356 (227), beginning with its week's marches at sixty miles a day; his wife, as always, being with him;
Louisa, honest and loving Dutch girl, aunt to our William of Orange, who trimmed up her own "Orange-burg" (country-house), twenty miles north of Berlin, into a little jewel of the Dutch type, potherb gardens, training-schools for young girls, and the like, a favorite abode of hers when she was at liberty for recreation. But her life was busy and earnest; she was helpmate, not in name only, to an ever busy man. They were married young; a marriage of love withal. Young Friedrich Wilhelm's courtship; wedding in Holland; the honest, trustful walk and conversation of the two sovereign spouses, their journeyings together, their mutual hopes, fears, and manifold vicissitudes, till death, with stern beauty, shut it in; all is human, true, and wholesome in it, interesting to look upon, and rare among sovereign persons.
Louisa died in 1667, twenty-one years before her husband, who married again—(little to his contentment)—died in 1688; and Louisa's second son, Friedrich, ten years old at his mother's death, and now therefore thirty-one, succeeds, becoming afterwards Friedrich I. of Prussia.
And here we pause on two great questions. Prussia is assuredly at this point a happier and better country than it was, when inhabited by Wends. But is Friedrich I. a happier and better man than Henry the Fowler? Have all these kings thus improved their country, but never themselves? Is this somewhat expensive and ambitious Herr, Friedrich I. buttoned in diamonds, indeed the best that Protestantism can produce, as against Fowlers, Bears, and Red Beards? Much more, Friedrich Wilhelm, orthodox on predestination; most of all, his less orthodox son;—have we, in these, the highest results which Dr. Martin Luther can produce for the present, in the first circles of society? And if not, how is it that the country, having gained so much in intelligence and strength, lies more passively in their power than the baser country did under that of nobler men?
These, and collateral questions, I mean to work out as I can, with Carlyle's good help;—but must pause for this time; in doubt, as heretofore. Only of this one thing I doubt not, that the name of all great kings, set over Christian nations, must at last be, in fufilment, the hereditary one of these German princes, "Rich in Peace;" and that their coronation will be with Wild olive, not with gold.
THE ETHICS OF THE DUST
PERSONÆ
PREFACE TO THE SECOND EDITION
I have seldom been more disappointed by the result of my best pains given to any of my books, than by the earnest request of my publisher, after the opinion of the public had been taken on the 'Ethics of the Dust,' that I would "write no more in dialogue!" However, I bowed to public judgment in this matter at once, (knowing also my inventive powers to be of the feeblest,); but in reprinting the book, (at the prevailing request of my kind friend, Mr. Henry Willett,) I would pray the readers whom it may at first offend by its disconnected method, to examine, nevertheless, with care, the passages in which the principal speaker sums the conclusions of any dialogue: for these summaries were written as introductions, for young people, to all that I have said on the same matters in my larger books; and, on re-reading them, they satisfy me better, and seem to me calculated to be more generally useful, than anything else I have done of the kind.
The summary of the contents of the whole book, beginning, "You may at least earnestly believe," at p. 130, is thus the clearest exposition I have ever yet given of the general conditions under which the Personal Creative Power manifests itself in the forms of matter; and the analysis of heathen conceptions of Deity, beginning at p. 131, and closing at p. 138, not only prefaces, but very nearly supersedes, all that in more lengthy terms I have since asserted, or pleaded for, in 'Aratra Pentelici,' and the 'Queen of the Air.'
And thus, however the book may fail in its intention of suggesting new occupations or interests to its younger readers, I think it worth reprinting, in the way I have also reprinted 'Unto this Last,'—page for page; that the students of my more advanced works may be able to refer to these as the original documents of them; of which the most essential in this book are these following.
I. The explanation of the baseness of the avaricious functions of the Lower Pthah, p. 39, with his beetle-gospel, p. 41, "that a nation can stand on its vices better than on its virtues," explains the main motive of all my books on Political Economy.
II. The examination of the connexion between stupidity and crime, pp. 57-62, anticipated all that I have had to urge in Fors Clavigera against the commonly alleged excuse for public wickedness,—"They don't mean it—they don't know any better."
III. The examination of the roots of Moral Power, pp. 90-92, is a summary of what is afterwards developed with utmost care in my inaugural lecture at Oxford on the relation of Art to Morals; compare in that lecture, §§ 83-85, with the sentence in p. 91 of this book, "Nothing is ever done so as really to please our Father, unless we would also have done it, though we had had no Father to know of it."
This sentence, however, it must be observed, regards only the general conditions of action in the children of God, in consequence of which it is foretold of them by Christ that they will say at the Judgment, "When saw we thee?" It does not refer to the distinct cases in which virtue consists in faith given to command, appearing to foolish human judgment inconsistent with the Moral Law, as in the sacrifice of Isaac; nor to those in which any directly-given command requires nothing more of virtue than obedience.
IV. The subsequent pages, 92-97, were written especially to check the dangerous impulses natural to the minds of many amiable young women, in the direction of narrow and selfish religious sentiment: and they contain, therefore, nearly everything which I believe it necessary that young people should be made to observe, respecting the errors of monastic life. But they in nowise enter on the reverse, or favourable side: of which indeed I did not, and as yet do not, feel myself able to speak with any decisiveness; the evidence on that side, as stated in the text, having "never yet been dispassionately examined."
V. The dialogue with Lucilla, beginning at p. 63, is, to my own fancy, the best bit of conversation in the book, and the issue of it, at p. 67, the most practically and immediately useful. For on the idea of the inevitable weakness and corruption of human nature, has logically followed, in our daily life, the horrible creed of modern "Social science," that all social action must be scientifically founded on vicious impulses. But on the habit of measuring and reverencing our powers and talents that we may kindly use them, will be founded a true Social science, developing, by the employment of them, all the real powers and honourable feelings of the race.
VI. Finally, the account given in the second and third lectures, of the real nature and marvellousness of the laws of crystallization, is necessary to the understanding of what farther teaching of the beauty of inorganic form I may be able to give, either in 'Deucalion,' or in my 'Elements of Drawing.' I wish however that the second lecture had been made the beginning of the book; and would fain now cancel the first altogether, which I perceive to be both obscure and dull. It was meant for a metaphorical description of the pleasures and dangers in the kingdom of Mammon, or of worldly wealth; its waters mixed with blood, its fruits entangled in thickets of trouble, and poisonous when gathered; and the final captivity of its inhabitants within frozen walls of cruelty and disdain. But the imagery is stupid and ineffective throughout; and I retain this chapter only because I am resolved to leave no room for any one to say that I have withdrawn, as erroneous in principle, so much as a single sentence of any of my books written since 1860.









