 полная версия
полная версияBuried Cities: Pompeii, Olympia, Mycenae (Complete)
That earthquake frightened the people away, and they left Olympia alone again. Hermes was still there, but he looked out upon ruins. Victory lay in a heap of fragments. Apollo was there, but broken and buried in earth with the other people of the pediments. Zeus and all the hundreds of heroes and athletes were gone. So it was for a while. Then a new race of people came and built another little town upon the earth-covered ruins. They little guessed what lay below their poor houses. But for some reason this town, also, died and left the ruins alone. Then dusty winds and flooding rivers began to cover up what was left. Kladeos piled up sand fifteen feet deep. Alpheios swung out of its banks and washed away the race-course for chariots. Under the rains and floods the sun-dried bricks of Hera’s walls melted again into clay and covered the floor. Again the earth quaked, and Hermes fell forward on his face, and little was left of the beautiful old Olympia. Grass and flowers crept in from the sides. Seeds blew in and shrubs and trees took the place of columns. Soon the flowers and the animals had Olympia to themselves. A few gray stones thrust up through the soil. So it was for hundreds of years. Greece was conquered by the men of Venice and then by the Turks. But Olympia, in its far corner, was forgotten and untouched except when a Turkish officer or farmer went there to dig a few stones out of the ground. And they knew nothing of the ancient gods and the ancient festival and the old story of the place, for they were foreigners and new people.
But about a hundred years ago Englishmen and Germans and Frenchmen began to visit Greece. They went to see, not her new Turkish houses or her Venetian castles or the strange dress of her new people, but her old ruins and the signs of her old glory. These men had read of Olympia in ancient Greek books and they knew what statues and buildings had once stood there. They wrote back to their friends things like this:
“I saw a piece of a huge column lying on top of the ground. It was seven feet across. It must have belonged to the temple of Zeus.”
“To-day I saw a long, low place in the ground where I think must have been the stadion in ancient days.”
At last, about thirty years ago, Ernst Curtius and several other Germans went there. They were men who had studied Greek history and Greek art and they planned to excavate Olympia.
“We will uncover the sacred enclosure again. Men shall see again the ancient temples and altars, the stadion, the statues.”
Germany had given them money for the work, and at last Greece allowed them to begin. In October they started their digging. Workmen up-rooted shrubs and dug away dirt. Excavators watched every spadeful. They were always measuring, making maps, taking notes. They found a few vases, terra cotta figures, pieces of bronze statues, swords and armor. They cleared off temple floors and were able to make out the plans of the old buildings. They found the empty pedestals of many statues. Yet they were disappointed. Olympia had been a beautiful place, a rich place. They were finding only the hints of these things. The beauty was gone. Of the three thousand statues that had been there should they not find one?
Then they uncovered the fallen statues of the pediments of Zeus’ temple. Thirty or more there were—Apollo, Zeus, heroes, women, centaurs, horses. Arms were gone, heads were broken, legs were lost. The excavators fitted together all the pieces and set the mended statues up side by side as they had been in the gable. They found, too, the carved marble slabs that showed the labors of Herakles. But even these were not the lovely things that people had hoped to see from Olympia. They were rather stiff and ungraceful. They had not been made by the greatest artists. In the temple of Hera one day men were digging in clay. Over all the rest of Olympia was only sand. The excavators wondered for a long time why this one spot should have clay. Where could it have come from? They read their old books over and over. They thought and studied. At last they said:
“The walls of the temple must have been made of sun-dried brick. In the old days they must have been covered with plaster. This and the roof kept them dry. But the plaster cracked off, and the roof fell in, and the rain and the floods turned the bricks back to clay again.”
Then one May morning, when the men were digging in the clay, a workman lifted off his spadeful of dirt, and white marble gleamed out. After that there was careful work, with all the excavators standing about to watch. What would it be? They thought over all the statues that the ancient books said had stood in Hera’s temple. Then were slowly uncovered, a smooth back, a carved shoulder, a curly head. A white statue of a young man lay face down in the gray clay. The legs were gone. The right arm was missing. From his left hung carved drapery. On his left shoulder lay a tiny marble hand.
“It is the Hermes of Praxiteles,” the excavators whispered among themselves.
In his day Praxiteles had been almost as famous as Phidias. The old Greek world had rung with his praises. Modern men had dreamed of what his statues must have been and had longed to see them. How did he shape the head? How did his bodies curve? What expression was on his faces? All these things they had wished to know. But not one of his statues had ever been found. Now here lay one before the very eyes of these excavators. They put out their hands and lovingly touched the polished marble skin. But what would they find when they lifted it?—Perhaps the nose would be gone, the face flattened by the fall, the ears broken, the beautiful marble chipped. They almost feared to lift it. But at last they did so.
When they saw the face, they were struck dumb by its beauty, and I think tears sprang into the eyes of some of them. No such perfect piece of marble had ever been found before. There was not a scratch. The skin still glowed with the polishing that Praxiteles’ own hands had given it. There was even a hint of color on the lips. The soft clay bed had saved the falling statue. Here was a statue that the whole world would love. It would make the name of Olympia famous again. The excavators were proud and happy. That old ruined temple seemed indeed a sacred place to them as they gazed upon perhaps the most beautiful statue in the world.
“Surely we shall find nothing else so perfect,” they said.
Yet they went on with the work. Before long Hermes’ right foot was found imbedded in the clay. Its sandal still shone with the gilding put on two thousand years before. Workmen were tearing down one of the houses of the little town that had been built on the ancient ruins. Every stone in it had some old story. Pieces of fluted columns, carved capitals, broken pedestals, blocks from the temple of Zeus—all were cemented together to make these walls. The workmen pulled and chipped and lifted out piece after piece. The excavators studied each scrap to see whether it was valuable. And at last they found a baby’s body. They carefully broke off the mortar. It was of creamy marble, beautifully carved. They carried it to Hermes. It fitted upon the drapery over his arm. On a rubbish heap outside the temple they had found a little marble head. They put it upon this baby’s shoulders. It was badly broken, but they could see that it belonged there. So after two thousand years Hermes again smiled into the eyes of the baby Dionysus.
Other things were found. The shattered Victory was uncovered. Carefully the excavators fitted the pieces together. But the wide wings could never be made again, and the head was ruined. Even so, the statue is a beautiful thing, with its thin drapery flying in the wind.
After five years the work was finished. Now again hundreds of visitors journey to Olympia every year. They see no gleaming roofs and high-lifted statues and joyful games. They walk among sad ruins. But they can tread the gymnasium floor where Creon and many another victor wrestled. They can enter the gate of the grass-grown stadion. They can see the fallen columns of the temple of Zeus. In the museum they can see the statues of its pediments and, at the end of the long hall, they see Victory stepping toward them. They can wander on the banks of the Kladeos and the Alpheios. They can climb Mount Kronion and see the whole little plain and imagine it gay with tents and moving people.
All these things are interesting to those who like the old Greek life. But most people make the long journey only to see Hermes. In the museum, in a little room all alone, he stands, always calm and lovable, always dreaming of something beautiful, always half smiling at the coaxing baby.
PICTURES OF OLYMPIA
ENTRANCE TO STADION
This was not the gate where Charmides entered. This entrance was reserved for the judges, the competitors, and the heralds. Inside there were seats for forty-five thousand people. On one side the hill made a natural slope for seats. But on the other sides a ridge of earth had to be built up. The track was about two hundred yards long. Only the two ends have been excavated. The rest still lies deep under the sand.
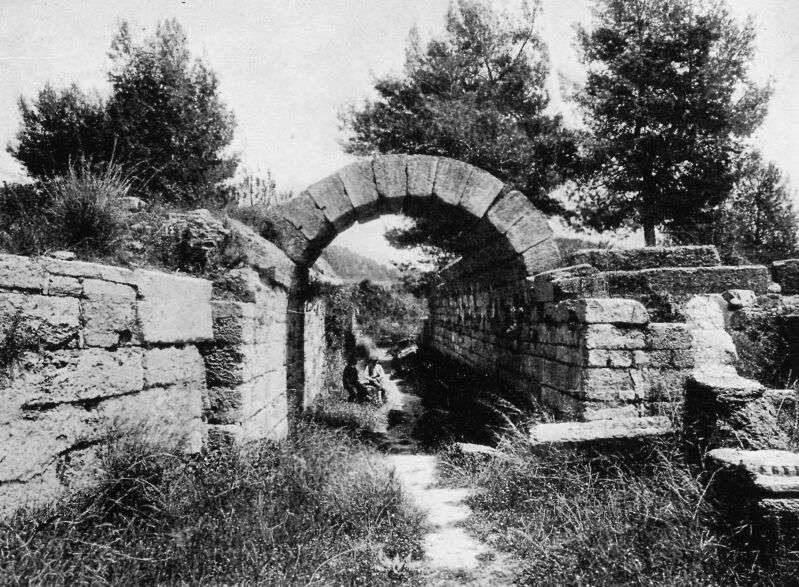

GYMNASIUM
Here Creon and the other boys spent a month in training before the games. The gymnasium had a covered portico as long as the track in the stadion, where the boys could run in bad weather. A Greek boy of to-day is playing on his shepherd’s pipes in the foreground, and they are the same kind of pipes on which the old Greeks played.

BOYS IN GYMNASIUM
From a vase painting. They are wrestling, jumping with weights, throwing the spear, throwing the discus, while their teachers watch them. One man is saying, “A beautiful boy, truly.”
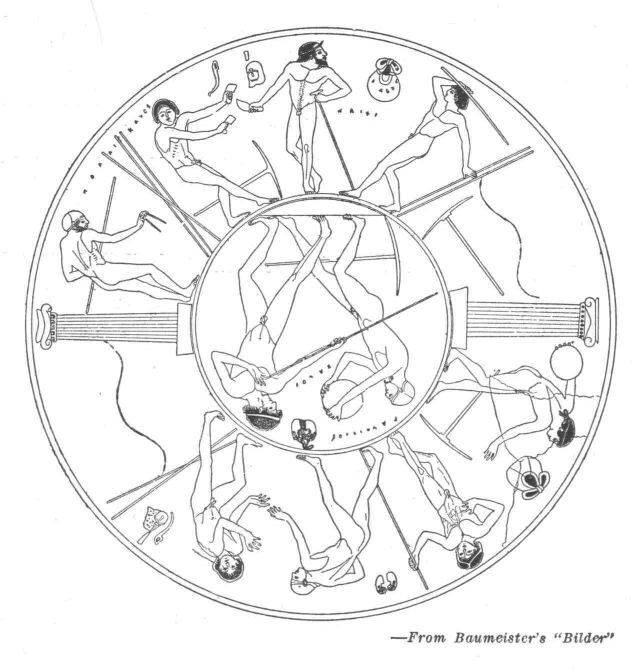
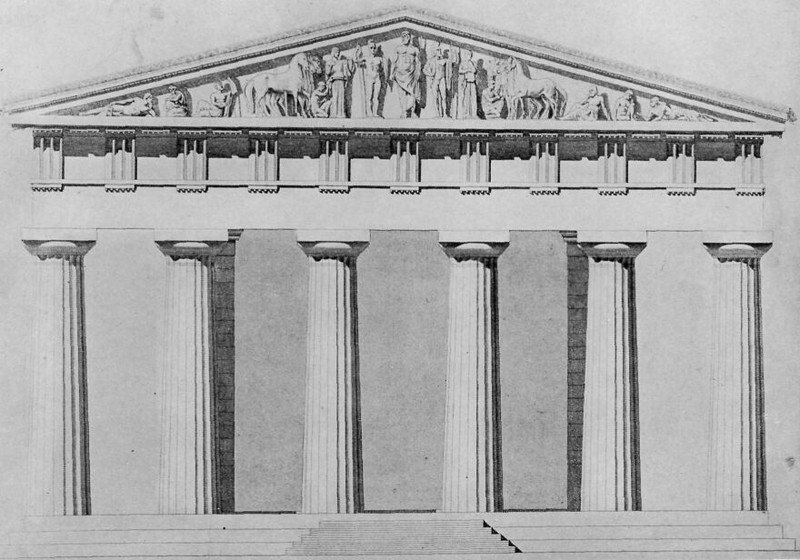
THE TEMPLE OF ZEUS
When we see a picture of fallen broken columns lying about a field in disorder, we try to learn how the original building looked and to imagine it in all its beauty. This, men believe, is the way the Temple of Zeus looked. The figures in the pediment were all of Parian marble. In the center stands Zeus himself. A chariot race is about to be run, and the contestants stand on either side of Zeus. Zeus gave the victory to Pelops, and Pelops became husband of Hippodameia, and king of Pisa, and founded the Olympic Games. These games were held every fourth year for more than a thousand years.
Note: This and the following plates of the Labors of Herakles and the statue of Victory, were photographed from Curtius and Adler’s “Olympia: Die Ergebnisse der von dem Deutschen Reich Veranstalteten Ausgrabung,” etc. This is one of the most beautiful books ever made for a buried city.
Boys and girls who can reach the Metropolitan Museum Library should not miss it. It is in many volumes, each almost as large as the top of the table, and you do not need to read German to appreciate the plates.

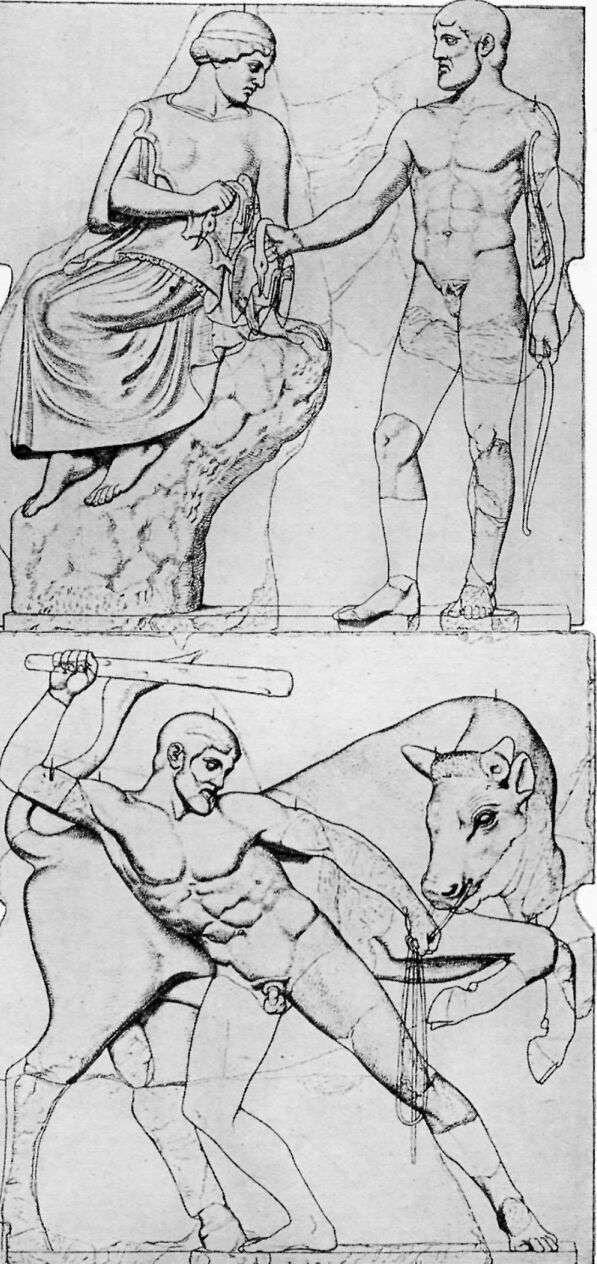
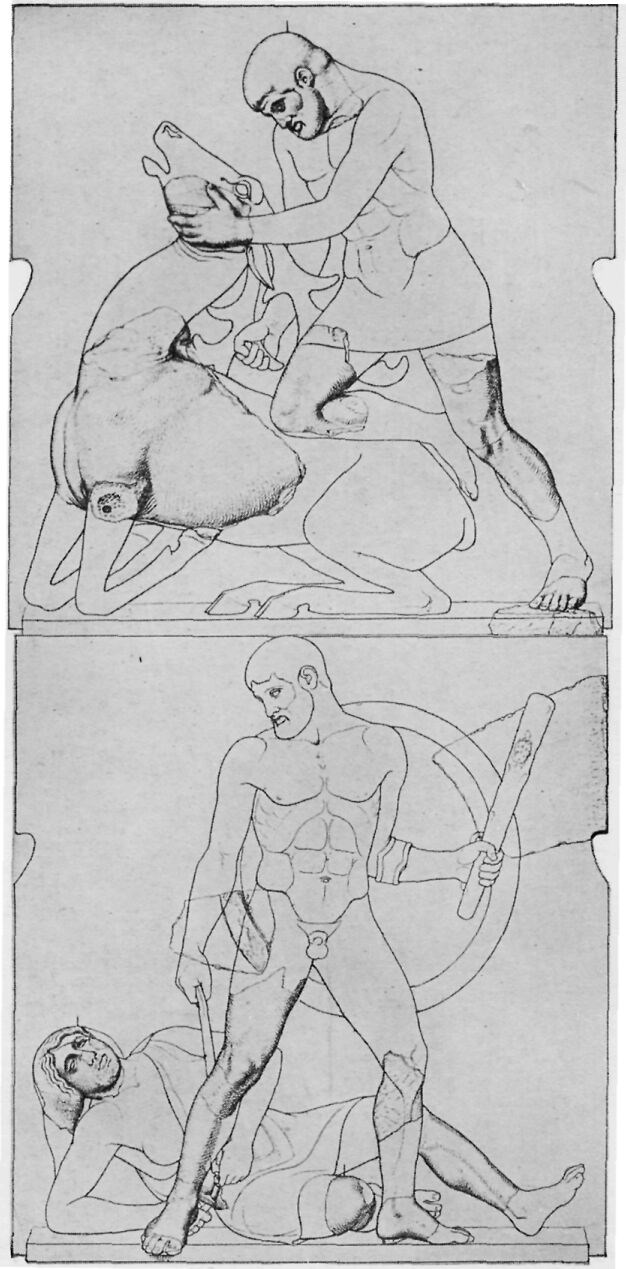
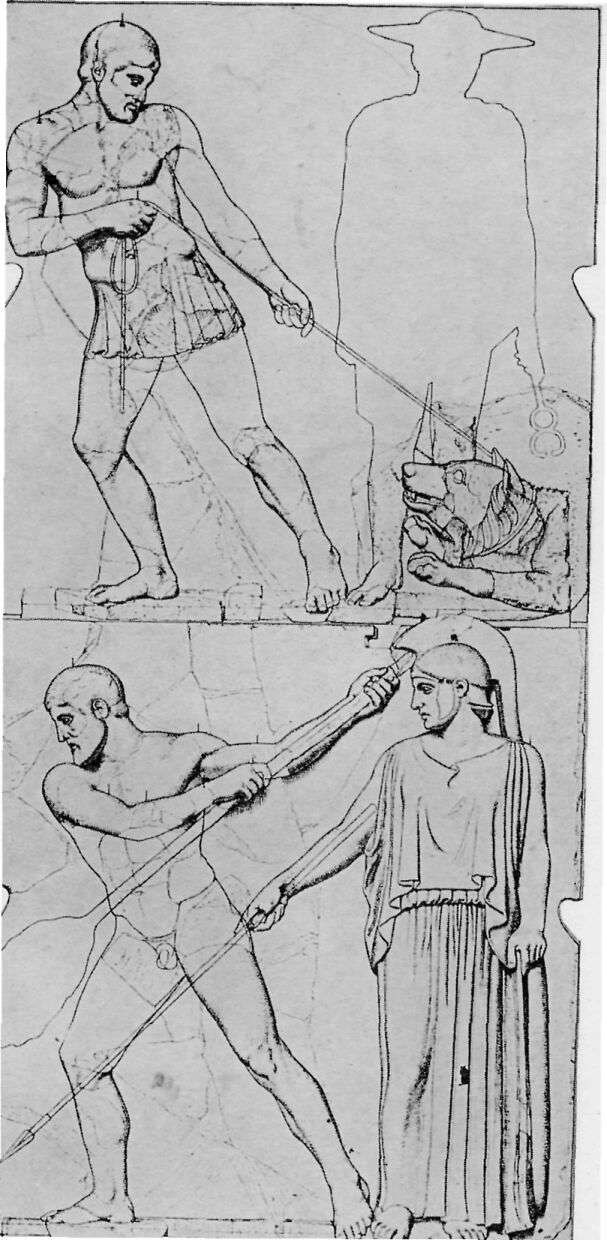
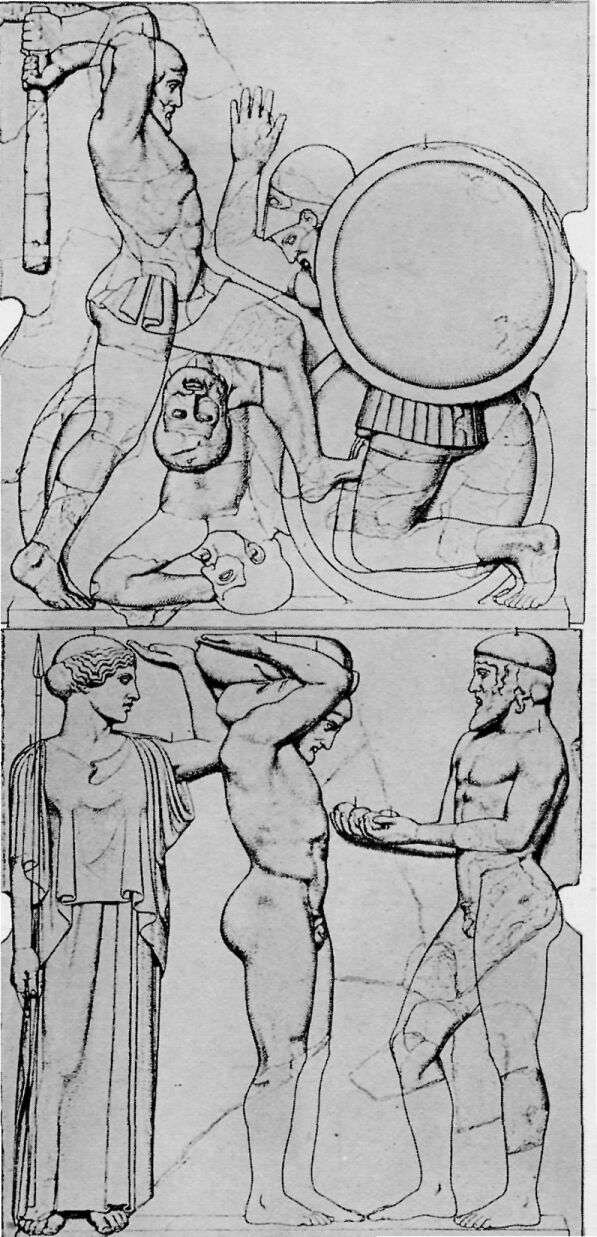
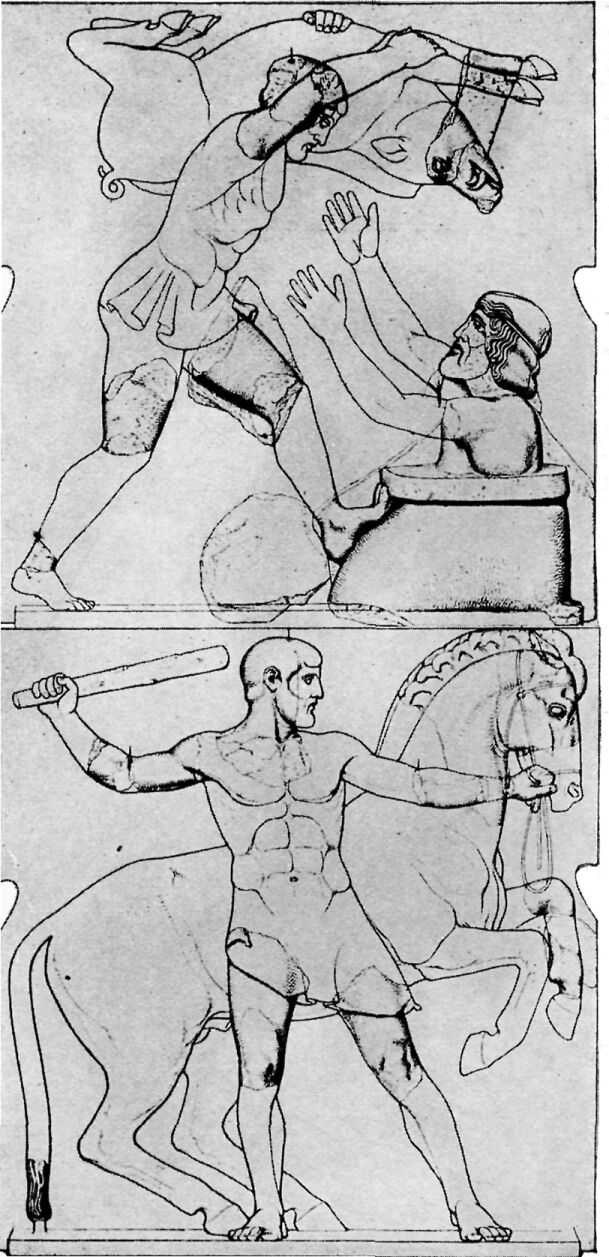
THE LABORS OF HERAKLES
Under the porches of the Temple of Zeus were twelve pictures in marble, six at each end, showing the Labors of Herakles. Herakles was highly honored at Olympia and, according to one tale, he, instead of Pelops, was the founder of the Olympic Games.
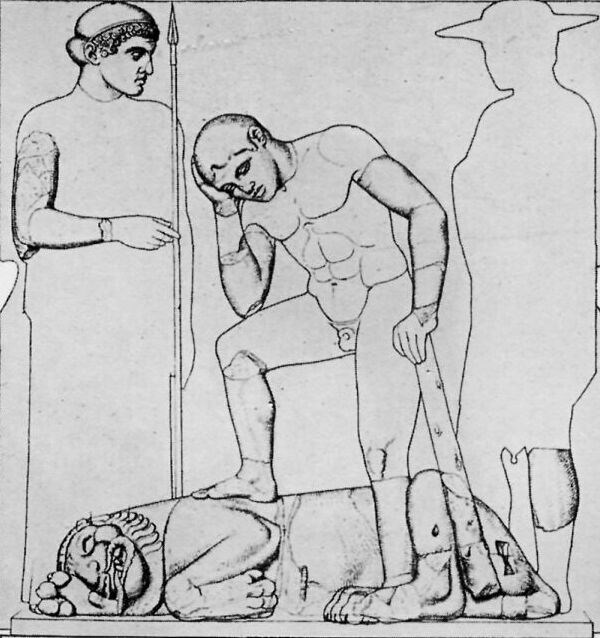
[Herakles and the Nemean lion.—Metropolitan Museum]
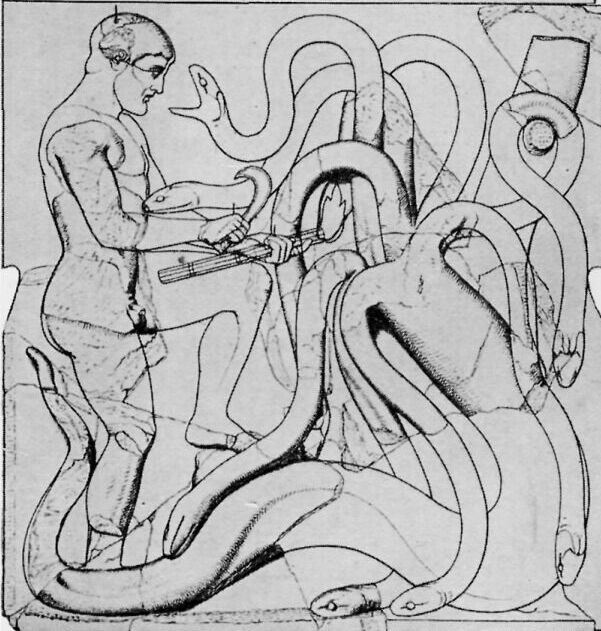
[Herakles and the hydra.—Metropolitan Museum]
THE STATUE OF VICTORY
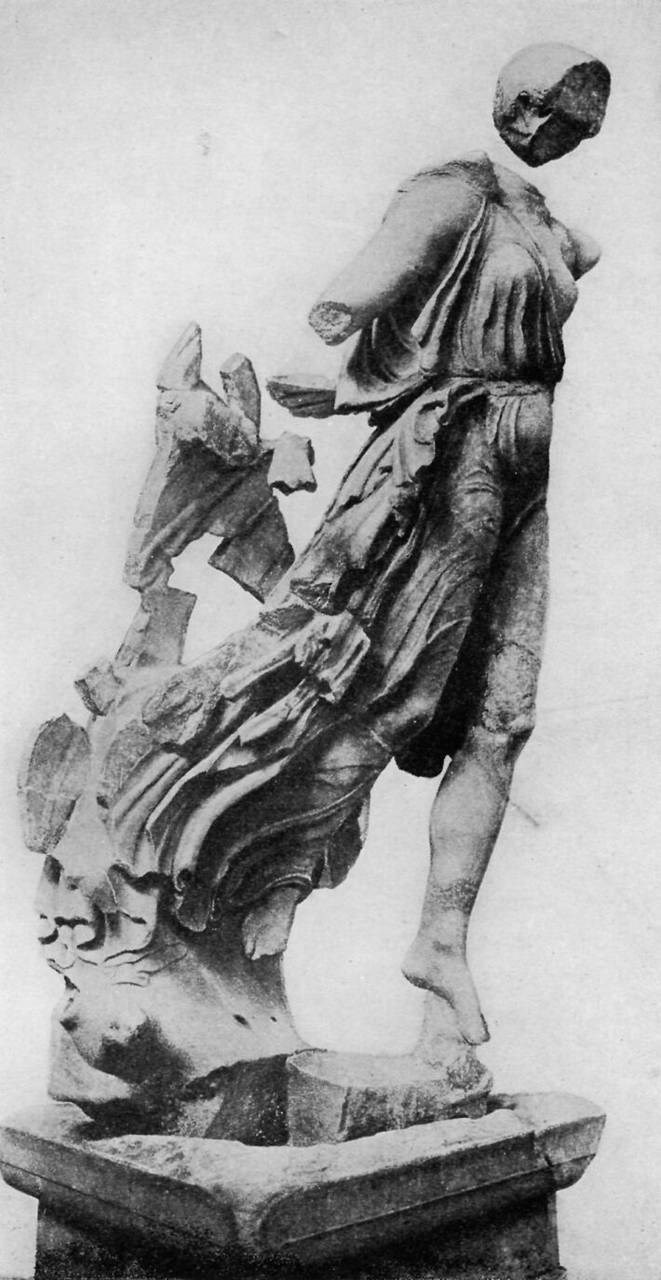
In the sand, not far from the Temple of Zeus, the explorers found the fragments of this statue. It shows the goddess flying down from heaven to bring victory to the men of Messene and Naupaktos. So the victors must have erected this statue at Olympia in gratitude.
Something like the picture used as the frontispiece, men believe the statue looked originally. It stood upon a base thirty feet high so that the goddess really looked as if she were descending from heaven.

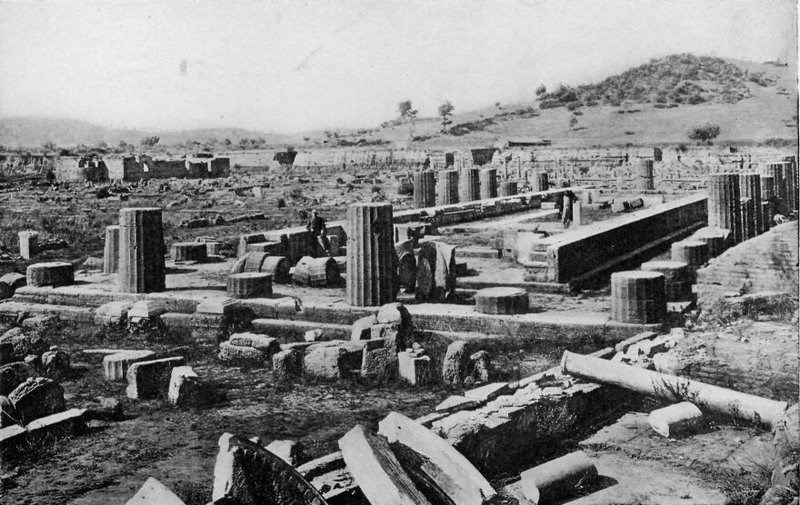
THE TEMPLE OF HERA
This shows the ruins of the temple where Charmides saw the statue of Hermes, perhaps the most beautiful statue in the world.


HEAD OF AN ATHLETE
The Greek artist who made this statue believed that a beautiful body is glorious, as well as a beautiful mind, and a fine spirit. Do you think his statue shows all these things? The original is now at the Metropolitan Museum.

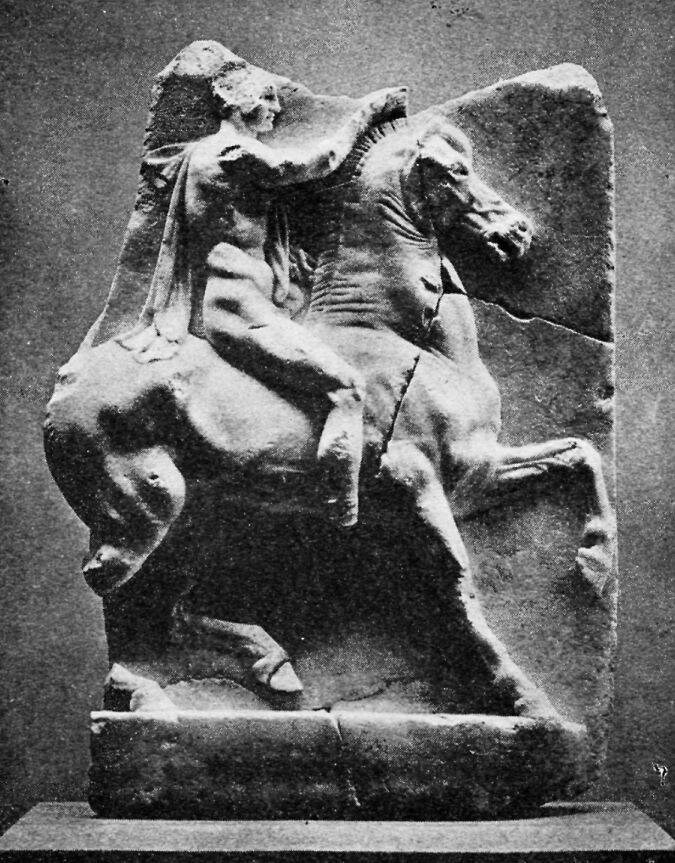
A GREEK HORSEMAN
The artist had great skill who could chisel out of marble such a strong, bold rider, and such a spirited horse.
This picture and the one before it are not pictures of things found at Olympia. They are two of the most beautiful statues of Greek athletes, and we give them to remind you of the sort of people who came to the games at Olympia.

MYCENÆ

HOW A LOST CITY WAS FOUND
Thirty years ago a little group of people stood on a hill in Greece. The hilltop was covered with soft soil. The summer sun had dried the grass and flowers, but little bushes grew thick over the ground. In this way the hill was like an ordinary hill, but all around the edge of it ran the broken ring of a great wall. In some places it stood thirty feet above the earth. Here and there it was twenty feet thick. It was built of huge stones. At one place a tower stood up. In another two stone lions stood on guard. It was these ruined walls that interested the people on the hill. One of the men was a Greek. A red fez was on his head. He wore an embroidered jacket and loose white sleeves. A stiff kilted skirt hung to his knees. He was pointing about at the wall and talking in Greek to a lady and gentleman. They were visitors, come to see these ruins of Mycenae.
“Once, long, long ago,” he was saying, “a great city was inside these walls. Giants built the walls. See the huge stones. Only giants could lift them. It was a city of giants. See their great ovens.”
He pointed down the hill at a doorway in the earth. “You cannot see well from here. I will take you down. We can look in. A great dome, built of stone, is buried in the earth. A passage leads into it, but it is filled with dirt. We can look down through the broken top. The room inside is bigger than my whole house. There giants used to bake their bread. Once a wicked Turk came here. He was afraid of nothing. He said, ‘The giants’ treasure lies in this oven. I will have it.’ So he sent men down. But they found only broken pieces of carved marble—no gold.”
While the guide talked, the gentleman was tramping about the walls. He peered into all the dark corners. He thrust a stick into every hole. He rubbed the stones with his hands. At last he turned to his guide.
“You are right,” he said. “There was once a great city inside these walls. Houses were crowded together on this hill where we stand. Men and women walked the streets of a city that is buried under our feet, but they were not giants. They were beautiful women and handsome men.
“It was a famous old city, this Mycenae. Poets sang songs about her. I have read those old songs. They tell of Agamemnon, its king, and his war against Troy. They call him the king of men. They tell of his gold-decked palace and his rich treasures and the thick walls of his city.
“But Agamemnon died, and weak kings sat in his palace. The warriors of Mycenae grew few, and after hundreds of years, when the city was old and weak, her enemies conquered her. They broke her walls, they threw down her houses, they drove out her people. Mycenae became a mass of empty ruins. For two thousand years the dry winds of summer blew dust over her palace floors. The rains of winter and spring washed down mud from her acropolis into her streets and houses. Winged seeds flew into the cracks of her walls and into the corners of her ruined buildings. There they sprouted and grew, and at last flowers and grass covered the ruins. Now only these broken walls remain. You feed your sheep in the city of Agamemnon. Down there on the hillside farmers have planted grain above ancient palaces. But I will uncover this wonderful city. You shall see! You shall see how your ancestors lived.
“Oh! for years I have longed to see this place. When I was a little boy in Germany my father told me the old stories of Troy, and he told me of how great cities were buried. My heart burned to see them. Then, one night, I heard a man recite some of the lines of Homer. I loved the beautiful Greek words. I made him say them over and over. I wept because I was not a Greek. I said to myself, ‘I will see Greece! I will study Greek. I will work hard. I will make a bankful of money. Then I will go to Greece. I will uncover Troy-city and see Priam’s palace. I will uncover Mycenae and see Agamemnon’s grave.’ I have come. I have uncovered Troy. Now I am here. I will come again and bring workmen with me. You shall see wonders.” He walked excitedly around and around the ruins. He told stories of the old city. He asked his wife to recite the old tales of Homer. She half sang the beautiful Greek words. Her husband’s eyes grew wet as he listened.
This man’s name was Dr. Henry Schliemann. He kept his word. He went away but he came again in a few years. He hired men and horse-carts. He rented houses in the little village. Myceae was a busy place again after three thousand years. More than a hundred men were digging on the top of this hill. They wore the fezes and kilts of the modern Greek. Little two-wheeled horse-carts creaked about, loading and dumping.
Some of the men were working about the wall near the stone lions.
“This is the great gate of the city,” said Dr. Schliemann. “Here the king and his warriors used to march through, thousands of years ago. But it is filled up with dirt. We must clear it out. We must get down to the very stones they trod.”
But it was slow work. The men found the earth full of great stone blocks. They had to dig around them carefully, so that Dr. Schliemann might see what they were.
“How did so many great stones come here?” they said among themselves.
Then Dr. Schliemann told them. He pointed to the wall above the gate.
“Once, long, long ago,” he said, “the warriors of Mycenae stood up there. Down here stood an army—the men of Argos, their enemies. The men of Argos battered at the gate. They shot arrows at the men of Mycenae, and the men of Mycenae shot at the Argives, and they threw down great stones upon them. See, here is one of those broken stones, and here, and here. After a long time the people of Mycenae had no food left in their city. Their warriors fainted from hunger. Then the Argives beat down the gate. They rushed into the city and drove out the people. They did not want men ever again to live in Mycenae, so they took crowbars and tried to tear down the wall. A few stones they knocked off. See, here, and here, and here they are, where they fell off the wall. But these great stones are very heavy. This one must weigh a hundred twenty tons,—more than all the people of your village. So the Argives gave up the attempt, and there stand the walls yet. Then the rain washed down the dirt from the hill and covered these great stones, and now we are digging them out again.”
The men worked at the gateway for many weeks. At last all the dirt and the blocks had been cleared away. The tall gateway stood open. A hole was in the stone door-casing at top and bottom. Schliemann put his hand into it.
“See!” he cried. “Here turned the wooden hinge of the gate.”
He pointed to another large hole on the side of the casing. “Here the gatekeeper thrust in the beam to hold the gate shut.”
Just inside the gate he found the little room where the keeper had stayed. He found also two little sentry boxes high up on the wall. Here guards had stood and looked over the country, keeping watch against enemies. From the gate the wall bent around the edge of the hilltop, shutting it in. In two places had been towers for watchmen. Inside this great wall the king’s palace and a few houses had been safe. Outside, other houses had been built. But in time of war all the people had flocked into the fortress. The gate had been shut. The warriors had stood on the wall to defend their city.
But while some of Dr. Schliemann’s men were digging at the gateway and the wall, others were working outside the city. They were making a great hole, a hundred and thirteen feet square. They put the dirt into baskets and carried it to the little carts to be hauled away. And always Dr. Schliemann and his wife worked with them. From morning until dusk every day they were there. It was August, and the sun was hot. The wind blew dust into their faces and made their eyes sore, and yet they were happy. Every day they found some little thing that excited them,—a terra cotta goblet, a broken piece of a bone lyre, a bronze ax, the ashes of an ancient fire.
At first Dr. Schliemann and his wife had fingered over every spadeful of dirt. There might be something precious in it. “Dig carefully, carefully!” Dr. Schliemann had said to the workmen. “Nothing must be broken. Nothing must be lost. I must see everything. Perhaps a bit of a broken vase may tell a wonderful story.”
But during this work of many weeks he had taught his workmen how to dig. Now each man looked over every spadeful of earth himself, as he dug it up. He took out every scrap of stone or wood or pottery or metal and gave it to Schliemann or his wife. So the excavators had only to study these things and to tell the men where to work. When a man struck some new thing with his spade, he called out. Then the excavators ran to that place and dug with their own hands. When anything was found, Dr. Schliemann sent it to the village. There it was kept in a house under guard. At night Dr. Schliemann drew plans of Mycenae. He read again old Greek books about the city. As he read he studied his plans. He wrote and wrote.
“As soon as possible, I must tell the world about what we find,” he said to his wife. “People will love my book, because they love the stories of Homer.”
There had been four months of hard work. A few precious things had been uncovered,—a few of bronze and clay, a few of gold, some carved gravestones. But were these the wonders Schliemann had promised? Was this to be all? They had dug down more than twenty feet. A few more days, and they would probably reach the solid rock. There could be nothing below that. November was rainy and disagreeable. The men had to work in the mud and wet. There was much disappointment on the hilltop.
Then one day a spade grated on gravel. Once before that had happened, and they had found gold below. They called out to Dr. Schliemann. He and his wife came quickly. Fire leaped into Schliemann’s eyes.





