 полная версия
полная версияThe Seven Lamps of Architecture
XXVI. Of which the first is, that wherever Proportion exists at all, one member of the composition must be either larger than, or in some way supreme over, the rest. There is no proportion between equal things. They can have symmetry only, and symmetry without proportion is not composition. It is necessary to perfect beauty, but it is the least necessary of its elements, nor of course is there any difficulty in obtaining it. Any succession of equal things is agreeable; but to compose is to arrange unequal things, and the first thing to be done in beginning a composition is to determine which is to be the principal thing. I believe that all that has been written and taught about proportion, put together, is not to the architect worth the single rule, well enforced, "Have one large thing and several smaller things, or one principal thing and several inferior things, and bind them well together." Sometimes there may be a regular gradation, as between the heights of stories in good designs for houses; sometimes a monarch with a lowly train, as in the spire with its pinnacles: the varieties of arrangement are infinite, but the law is universal—have one thing above the rest, either by size, or office, or interest. Don't put the pinnacles without the spire. What a host of ugly church towers have we in England, with pinnacles at the corners, and none in the middle! How many buildings like King's College Chapel at Cambridge, looking like tables upside down, with their four legs in the air! What! it will be said, have not beasts four legs? Yes, but legs of different shapes, and with a head between them. So they have a pair of ears: and perhaps a pair of horns: but not at both ends. Knock down a couple of pinnacles at either end in King's College Chapel, and you will have a kind of proportion instantly. So in a cathedral you may have one tower in the centre, and two at the west end; or two at the west end only, though a worse arrangement: but you must not have two at the west and two at the east end, unless you have some central member to connect them; and even then, buildings are generally bad which have large balancing features at the extremities, and small connecting ones in the centre, because it is not easy then to make the centre dominant. The bird or moth may indeed have wide wings, because the size of the wing does not give supremacy to the wing. The head and life are the mighty things, and the plumes, however wide, are subordinate. In fine west fronts with a pediment and two towers, the centre is always the principal mass, both in bulk and interest (as having the main gateway), and the towers are subordinated to it, as an animal's horns are to its head. The moment the towers rise so high as to overpower the body and centre, and become themselves the principal masses, they will destroy the proportion, unless they are made unequal, and one of them the leading feature of the cathedral, as at Antwerp and Strasburg. But the purer method is to keep them down in due relation to the centre, and to throw up the pediment into a steep connecting mass, drawing the eye to it by rich tracery. This is nobly done in St. Wulfran of Abbeville, and attempted partly at Rouen, though that west front is made up of so many unfinished and supervening designs that it is impossible to guess the real intention of any one of its builders.
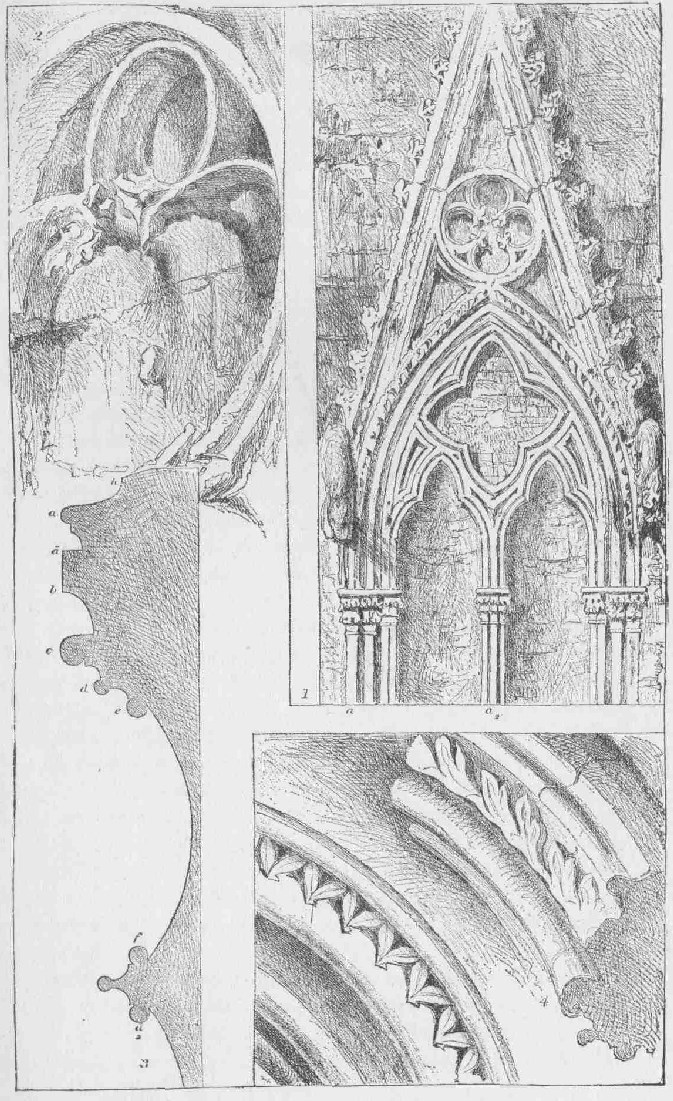
PLATE X.—(Page 122—Vol. V.)
Traceries and Mouldings from Rouen and Salisbury.
XXVII. This rule of supremacy applies to the smallest as well as to the leading features: it is interestingly seen in the arrangement of all good mouldings. I have given one, on the opposite page, from Rouen cathedral; that of the tracery before distinguished as a type of the noblest manner of Northern Gothic (Chap. II. § XXII.). It is a tracery of three orders, of which the first is divided into a leaf moulding, fig. 4, and b in the section, and a plain roll, also seen in fig. 4, c in the section; these two divisions surround the entire window or panelling, and are carried by two-face shafts of corresponding sections. The second and third orders are plain rolls following the line of the tracery; four divisions of moulding in all: of these four, the leaf moulding is, as seen in the sections, much the largest; next to it the outer roll; then, by an exquisite alternation, the innermost roll (e), in order that it may not be lost in the recess and the intermediate (d), the smallest. Each roll has its own shaft and capital; and the two smaller, which in effect upon the eye, owing to the retirement of the innermost, are nearly equal, have smaller capitals than the two larger, lifted a little to bring them to the same level. The wall in the trefoiled lights is curved, as from e to f in the section; but in the quatrefoil it is flat, only thrown back to the full depth of the recess below so as to get a sharp shadow instead of a soft one, the mouldings falling back to it in nearly a vertical curve behind the roll e. This could not, however, be managed with the simpler mouldings of the smaller quatrefoil above, whose half section is given from g to g2; but the architect was evidently fretted by the heavy look of its circular foils as opposed to the light spring of the arches below: so he threw its cusps obliquely clear from the wall, as seen in fig. 2, attached to it where they meet the circle, but with their finials pushed out from the natural level (h, in the section) to that of the first order (g2) and supported by stone props behind, as seen in the profile fig. 2, which I got from the correspondent panel on the buttress face (fig. 1 being on its side), and of which the lower cusps, being broken away, show the remnant of one of their props projecting from the wall. The oblique curve thus obtained in the profile is of singular grace. Take it all in all, I have never met with a more exquisite piece of varied, yet severe, proportioned and general arrangement (though all the windows of the period are fine, and especially delightful in the subordinate proportioning of the smaller capitals to the smaller shafts). The only fault it has is the inevitable misarrangement of the central shafts; for the enlargement of the inner roll, though beautiful in the group of four divisions at the side, causes, in the triple central shaft, the very awkwardness of heavy lateral members which has just been in most instances condemned. In the windows of the choir, and in most of the period, this difficulty is avoided by making the fourth order a fillet which only follows the foliation, while the three outermost are nearly in arithmetical progression of size, and the central triple shaft has of course the largest roll in front. The moulding of the Palazzo Foscari (Plate VIII., and Plate IV. fig. 8) is, for so simple a group, the grandest in effect I have even seen: it is composed of a large roll with two subordinates.
XXVIII. It is of course impossible to enter into details of instances belonging to so intricate division of our subject, in the compass of a general essay. I can but rapidly name the chief conditions of right. Another of these is the connection of Symmetry with horizontal, and of Proportion with vertical, division. Evidently there is in symmetry a sense not merely of equality, but of balance: now a thing cannot be balanced by another on the top of it, though it may by one at the side of it. Hence, while it is not only allowable, but often necessary, to divide buildings, or parts of them, horizontally into halves, thirds, or other equal parts, all vertical divisions of this kind are utterly wrong; worst into half, next worst in the regular numbers which more betray the equality. I should have thought this almost the first principle of proportion which a young architect was taught: and yet I remember an important building, recently erected in England, in which the columns are cut in half by the projecting architraves of the central windows; and it is quite usual to see the spires of modern Gothic churches divided by a band of ornament half way up. In all fine spires there are two bands and three parts, as at Salisbury. The ornamented portion of the tower is there cut in half, and allowably, because the spire forms the third mass to which the other two are subordinate: two stories are also equal in Giotto's campanile, but dominant over smaller divisions below, and subordinated to the noble third above. Even this arrangement is difficult to treat; and it is usually safer to increase or diminish the height of the divisions regularly as they rise, as in the Doge's Palace, whose three divisions are in a bold geometrical progression: or, in towers, to get an alternate proportion between the body, the belfry, and the crown, as in the campanile of St. Mark's. But, at all events, get rid of equality; leave that to children and their card houses: the laws of nature and the reason of man are alike against it, in arts, as in politics. There is but one thoroughly ugly tower in Italy that I know of, and that is so because it is divided into vertical equal parts: the tower of Pisa.12
XXIX. One more principle of Proportion I have to name, equally simple, equally neglected. Proportion is between three terms at least. Hence, as the pinnacles are not enough without the spire, so neither the spire without the pinnacles. All men feel this and usually express their feeling by saying that the pinnacles conceal the junction of the spire and tower. This is one reason; but a more influential one is, that the pinnacles furnish the third term to the spire and tower. So that it is not enough, in order to secure proportion, to divide a building unequally; it must be divided into at least three parts; it may be into more (and in details with advantage), but on a large scale I find three is about the best number of parts in elevation, and five in horizontal extent, with freedom of increase to five in the one case and seven in the other; but not to more without confusion (in architecture, that is to say; for in organic structure the numbers cannot be limited). I purpose, in the course of works which are in preparation, to give copious illustrations of this subject, but I will take at present only one instance of vertical proportion, from the flower stem of the common water plantain, Alisma Plantago. Fig. 5, Plate XII. is a reduced profile of one side of a plant gathered at random; it is seen to have five masts, of which, however, the uppermost is a mere shoot, and we can consider only their relations up to the fourth. Their lengths are measured on the line A B, which is the actual length of the lowest mass a b, A C=b c, A D=c d, and A E=d e. If the reader will take the trouble to measure these lengths and compare them, he will find that, within half a line, the uppermost A E=5/7 of A D, A D=6/8 of A C, and A C=7/9 of A B; a most subtle diminishing proportion. From each of the joints spring three major and three minor branches, each between each; but the major branches, at any joint, are placed over the minor branches at the joint below, by the curious arrangement of the joint itself—the stem is bluntly triangular; fig. 6 shows the section of any joint. The outer darkened triangle is the section of the lower stem; the inner, left light, of the upper stem; and the three main branches spring from the ledges left by the recession. Thus the stems diminish in diameter just as they diminish in height. The main branches (falsely placed in the profile over each other to show their relations) have respectively seven, six, five, four, and three arm-bones, like the masts of the stem; these divisions being proportioned in the same subtle manner. From the joints of these, it seems to be the plan of the plant that three major and three minor branches should again spring, bearing the flowers: but, in these infinitely complicated members, vegetative nature admits much variety; in the plant from which these measures were taken the full complement appeared only at one of the secondary joints.
The leaf of this plant has five ribs on each side, as its flower generally five masts, arranged with the most exquisite grace of curve; but of lateral proportion I shall rather take illustrations from architecture: the reader will find several in the accounts of the Duomo at Pisa and St. Mark's at Venice, in Chap. V. §§ XIV.-XVI. I give these arrangements merely as illustrations, not as precedents: all beautiful proportions are unique, they are not general formulæ.
XXX. The other condition of architectural treatment which we proposed to notice was the abstraction of imitated form. But there is a peculiar difficulty in touching within these narrow limits on such a subject as this, because the abstraction of which we find examples in existing art, is partly involuntary; and it is a matter of much nicety to determine where it begins to be purposed. In the progress of national as well as of individual mind, the first attempts at imitation are always abstract and incomplete. Greater completion marks the progress of art, absolute completion usually its decline; whence absolute completion of imitative form is often supposed to be in itself wrong. But it is not wrong always, only dangerous. Let us endeavor briefly to ascertain wherein its danger consists, and wherein its dignity.
XXXI. I have said that all art is abstract in its beginnings; that is to say, it expresses only a small number of the qualities of the thing represented. Curved and complex lines are represented by straight and simple ones; interior markings of forms are few, and much is symbolical and conventional. There is a resemblance between the work of a great nation, in this phase, and the work of childhood and ignorance, which, in the mind of a careless observer, might attach something like ridicule to it. The form of a tree on the Ninevite sculptures is much like that which, come twenty years ago, was familiar upon samplers; and the types of the face and figure in early Italian art are susceptible of easy caricature. On the signs which separate the infancy of magnificent manhood from every other, I do not pause to insist (they consist entirely in the choice of the symbol and of the features abstracted); but I pass to the next stage of art, a condition of strength in which the abstraction which was begun in incapability is continued in free will. This is the case, however, in pure sculpture and painting, as well as in architecture; and we have nothing to do but with that greater severity of manner which fits either to be associated with the more realist art. I believe it properly consists only in a due expression of their subordination, an expression varying according to their place and office. The question is first to be clearly determined whether the architecture is a frame for the sculpture, or the sculpture an ornament of the architecture. If the latter, then the first office of that sculpture is not to represent the things it imitates, but to gather out of them those arrangements of form which shall be pleasing to the eye in their intended places. So soon as agreeable lines and points of shade have been added to the mouldings which were meagre, or to the lights which were unrelieved, the architectural work of the imitation is accomplished; and how far it shall be wrought towards completeness or not, will depend upon its place, and upon other various circumstances. If, in its particular use or position, it is symmetrically arranged, there is, of course, an instant indication of architectural subjection. But symmetry is not abstraction. Leaves may be carved in the most regular order, and yet be meanly imitative; or, on the other hand, they may be thrown wild and loose, and yet be highly architectural in their separate treatment. Nothing can be less symmetrical than the group of leaves which join the two columns in Plate XIII.; yet, since nothing of the leaf character is given but what is necessary for the bare suggestion of its image and the attainment of the lines desired, their treatment is highly abstract. It shows that the workman only wanted so much of the leaf as he supposed good for his architecture, and would allow no more; and how much is to be supposed good, depends, as I have said, much more on place and circumstance than on general laws. I know that this is not usually thought, and that many good architects would insist on abstraction in all cases: the question is so wide and so difficult that I express my opinion upon it most diffidently; but my own feeling is, that a purely abstract manner, like that of our earliest English work, does not afford room for the perfection of beautiful form, and that its severity is wearisome after the eye has been long accustomed to it. I have not done justice to the Salisbury dog-tooth moulding, of which the effect is sketched in fig. 5, Plate X., but I have done more justice to it nevertheless than to the beautiful French one above it; and I do not think that any candid reader would deny that, piquant and spirited as is that from Salisbury, the Rouen moulding is, in every respect, nobler. It will be observed that its symmetry is more complicated, the leafage being divided into double groups of two lobes each, each lobe of different structure. With exquisite feeling, one of these double groups is alternately omitted on the other side of the moulding (not seen in the Plate, but occupying the cavetto of the section), thus giving a playful lightness to the whole; and if the reader will allow for a beauty in the flow of the curved outlines (especially on the angle), of which he cannot in the least judge from my rude drawing, he will not, I think, expect easily to find a nobler instance of decoration adapted to the severest mouldings.
Now it will be observed, that there is in its treatment a high degree of abstraction, though not so conventional as that of Salisbury: that is to say, the leaves have little more than their flow and outline represented; they are hardly undercut, but their edges are connected by a gentle and most studied curve with the stone behind; they have no serrations, no veinings, no rib or stalk on the angle, only an incision gracefully made towards their extremities, indicative of the central rib and depression. The whole style of the abstraction shows that the architect could, if he had chosen, have carried the imitation much farther, but stayed at this point of his own free will; and what he has done is also so perfect in its kind, that I feel disposed to accept his authority without question, so far as I can gather it from his works, on the whole subject of abstraction.
XXXII. Happily his opinion is frankly expressed. This moulding is on the lateral buttress, and on a level with the top of the north gate; it cannot therefore be closely seen except from the wooden stairs of the belfry; it is not intended to be so seen, but calculated for a distance of, at least, forty to fifty feet from the eye. In the vault of the gate itself, half as near again, there are three rows of mouldings, as I think, by the same designer, at all events part of the same plan. One of them is given in Plate I. fig. 2 a. It will be seen that the abstraction is here infinitely less; the ivy leaves have stalks and associated fruit, and a rib for each lobe, and are so far undercut as to detach their forms from the stone; while in the vine-leaf moulding above, of the same period, from the south gate, serration appears added to other purely imitative characters. Finally, in the animals which form the ornaments of the portion of the gate which is close to the eye, abstraction nearly vanishes into perfect sculpture.
XXXIII. Nearness to the eye, however, is not the only circumstance which influences architectural abstraction. These very animals are not merely better cut because close to the eye; they are put close to the eye that they may, without indiscretion, be better cut, on the noble principle, first I think, clearly enunciated by Mr. Eastlake, that the closest imitation shall be of the noblest object. Farther, since the wildness and manner of growth of vegetation render a bona fide imitation of it impossible in sculpture—since its members must be reduced in number, ordered in direction, and cut away from their roots, even under the most earnestly imitative treatment,—it becomes a point, as I think, of good judgment, to proportion the completeness of execution of parts to the formality of the whole; and since five or six leaves must stand for a tree, to let also five or six touches stand for a leaf. But since the animal generally admits of perfect outline—since its form is detached, and may be fully represented, its sculpture may be more complete and faithful in all its parts. And this principle will be actually found. I believe, to guide the old workmen. If the animal form be in a gargoyle, incomplete, and coining out of a block of stone, or if a head only, as for a boss or other such partial use, its sculpture will be highly abstract. But if it be an entire animal, as a lizard, or a bird, or a squirrel, peeping among leafage, its sculpture will be much farther carried, and I think, if small, near the eye, and worked in a fine material, may rightly be carried to the utmost possible completion. Surely we cannot wish a less finish bestowed on those which animate the mouldings of the south door of the cathedral of Florence; nor desire that the birds in the capitals of the Doge's palace should be stripped of a single plume.
XXXIV. Under these limitations, then, I think that perfect sculpture may be made a part of the severest architecture; but this perfection was said in the outset to be dangerous. It is so in the highest degree; for the moment the architect allows himself to dwell on the imitated portions, there is a chance of his losing sight of the duty of his ornament, of its business as a part of the composition, and sacrificing its points of shade and effect to the delight of delicate carving. And then he is lost. His architecture has become a mere framework for the setting of delicate sculpture, which had better be all taken down and put into cabinets. It is well, therefore, that the young architect should be taught to think of imitative ornament as of the extreme of grace in language; not to be regarded at first, not to be obtained at the cost of purpose, meaning, force, or conciseness, yet, indeed, a perfection—the least of all perfections, and yet the crowning one of all—one which by itself, and regarded in itself, is an architectural coxcombry, but is yet the sign of the most highly-trained mind and power when it is associated with others. It is a safe manner, as I think, to design all things at first in severe abstraction, and to be prepared, if need were, to carry them out in that form; then to mark the parts where high finish would be admissible, to complete these always with stern reference to their general effect, and then connect them by a graduated scale of abstraction with the rest. And there is one safeguard against danger in this process on which I would finally insist. Never imitate anything but natural forms, and those the noblest, in the completed parts. The degradation of the cinque cento manner of decoration was not owing to its naturalism, to its faithfulness of imitation, but to its imitation of ugly, i.e. unnatural things. So long as it restrained itself to sculpture of animals and flowers, it remained noble. The balcony, on the opposite page, from a house in the Campo St. Benedetto at Venice, shows one of the earliest occurrences of the cinque cento arabesque, and a fragment of the pattern is given in Plate XII. fig. 8. It is but the arresting upon the stone work of a stem or two of the living flowers, which are rarely wanting in the window above (and which, by the by, the French and Italian peasantry often trellis with exquisite taste about their casements). This arabesque, relieved as it is in darkness from the white stone by the stain of time, is surely both beautiful and pure; and as long as the renaissance ornament remained in such forms it may be beheld with undeserved admiration. But the moment that unnatural objects were associated with these, and armor, and musical instruments, and wild meaningless scrolls and curled shields, and other such fancies, became principal in its subjects, its doom was sealed, and with it that of the architecture of the world.
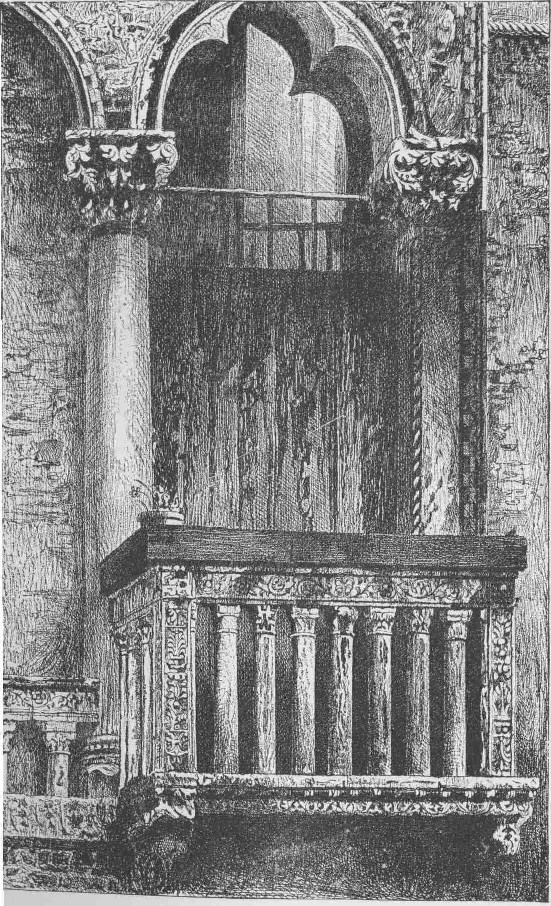
PLATE XI.—(Page 131—Vol. V.)
Balcony in the Campo, St. Benedetto, Venice.











