 полная версия
полная версияThe Major Operations of the Navies in the War of American Independence
"Why he should bring the fleet to because the Ville de Paris was taken, I cannot reconcile. He did not pursue under easy sail, so as never to have lost sight of the enemy in the night, which would clearly and most undoubtedly have enabled him to have taken almost every ship the next day.... Had I had the honour of commanding his Majesty's noble fleet on the 12th, I may, without much imputation of vanity, say the flag of England should now have graced the sterns of upwards of twenty sail of the enemy's ships of the line."125
Such criticisms by those not responsible are to be received generally with caution; but Hood was, in thought and in deed, a man so much above the common that these cannot be dismissed lightly. His opinion is known to have been shared by Sir Charles Douglas, Rodney's Captain of the Fleet;126 and their conclusion is supported by the inferences to be drawn from Rodney's own assumptions as to the condition of the French, contrasted with the known facts. The enemy, he wrote, in assigning his reasons for not pursuing, "went off in a close connected body,127 and might have defeated, by rotation, the ships that had come up with them." "The enemy who went off in a body of twenty-six ships of the line,128 might, by ordering two or three of their best sailing ships or frigates to have shown lights at times, and by changing their course, have induced the British fleet to have followed them, while the main of their fleet, by hiding their lights, might have hauled their wind, and have been far to windward by daylight, and intercepted the captured ships, and the most crippled ships of the English;" and he adds that the Windward Islands even might have been endangered. That such action was in a remote degree possible to a well-conditioned fleet may be guardedly conceded; but it was wildly improbable to a fleet staggering under such a blow as the day had seen, which had changed its commander just as dark came on, and was widely scattered and disordered up to the moment when signals by flags became invisible.
The facts, however, were utterly at variance with these ingenious suppositions. Instead of being connected, as Rodney represents, de Vaudreuil had with him next morning but ten ships; and no others during the whole of the 13th. He made sail for Cap François, and was joined on the way by five more, so that at no time were there upwards of fifteen129 French ships of the line together, prior to his arrival at that port on April 25th. He there found four others of the fleet. The tale of twenty-five survivors, from the thirty engaged on April 12th, was completed by six which had gone to Curaçao, and which did not rejoin until May. So much for the close connected body of the French. It is clear, therefore, that Rodney's reasons illustrate the frame of mind against which Napoleon used to caution his generals as "making to themselves a picture" of possibilities; and that his conclusion at best was based upon the ruinous idea, which a vivid imagination or slothful temper is prone to present to itself, that war may be made decisive without running risks. That Jamaica even was saved was not due to this fine, but indecisive battle, but to the hesitation of the allies. When de Vaudreuil reached Cap François, he found there the French convoy safely arrived from Guadeloupe, and also a body of fifteen Spanish ships of the line. The troops available for the descent upon Jamaica were from fifteen to twenty thousand. Well might Hood write: "Had Sir George Rodney's judgment, after the enemy had been so totally put to flight, borne any proportion to the high courage, zeal and exertion, so very manifestly shown by every captain, all difficulty would now have been at an end. We might have done just as we pleased, instead of being at this hour upon the defensive."130
The allies, however, though superior in numbers, did not venture to assume the offensive. After the battle, Rodney remained near Guadeloupe until the 17th of April, refitting, and searching the neighbouring islands, in case the French fleet might have entered some one of them. For most of this time the British were becalmed, but Hood remarks that there had been wind enough to get twenty leagues to the westward; and there more wind probably would have been found. On the 17th Hood was detached in pursuit with ten sail of the line; and a day or two later Rodney himself started for Jamaica. Left to his own discretion, Hood pushed for the Mona Passage, between Puerto Rico and Santo Domingo, carrying studding-sails below and aloft in his haste. At daybreak of the 19th he sighted the west end of Puerto Rico; and soon afterwards a small French squadron was seen. A general chase resulted in the capture of the Jason and Caton, sixty-fours, which had parted from their fleet before the battle and were on their way to Cap François. A frigate, the Aimable, 32, and a sloop, the Cérès, 18, also were taken. In reporting this affair to Rodney, Hood got a thrust into his superior. "It is a very mortifying circumstance to relate to you, Sir, that the French fleet which you put to flight on the 12th went through the Mona Channel on the 18th, only the day before I was in it."131 A further proof of the utility of pursuit, here hinted at, is to be found in the fact that Rodney, starting six days later than de Vaudreuil, reached Jamaica, April 28th, only three days after the French got into Cap François. He had therefore gained three days in a fortnight's run. What might not have been done by an untiring chase! But a remark recorded by Hood summed up the frame of mind which dominated Rodney: "I lamented to Sir George on the 13th that the signal for a general chase was not made when that for the line was hauled down and that he did not continue to pursue so as to keep sight of the enemy all night, to which he only answered, 'Come, we have done very handsomely as it is.'"132
Rodney stayed at Jamaica until the 10th of July, when Admiral Hugh Pigot arrived from England to supersede him. This change was consequent upon the fall of Lord North's ministry, in March, 1782, and had been decided before the news of the victory could reach England. Admiral Keppel now became the head of the Admiralty. Rodney sailed for home from Port Royal on the 22d of July; and with his departure the war in the West Indies and North America may be said to have ended. Pigot started almost immediately for New York, and remained in North American waters until the end of October, when he returned to Barbados, first having detached Hood with thirteen ships of the line from the main fleet, to cruise off Cap François. It is of interest to note that at this time Hood took with him from New York the frigate Albemarle, 28, then commanded by Nelson, who had been serving on the North American station. These various movements were dictated by those of the enemy, either actually made or supposed to be in contemplation; for it was an inevitable part of the ill-effects of Rodney's most imperfect success, that the British fleet was thenceforth on the defensive purely, with all the perplexities of him who waits upon the initiative of an opponent. Nothing came of them all, however, for the war now was but lingering in its death stupor. The defeat of de Grasse, partial though it was; the abandonment of the enterprise upon Jamaica; the failure of the attack upon Gibraltar; and the success of Howe in re-victualling that fortress,—these had taken all heart out of the French and Spaniards; while the numerical superiority of the allies, inefficiently though it had been used heretofore, weighed heavily upon the imagination of the British Government, which now had abandoned all hope of subduing its American Colonies. Upon the conclusion of peace, in 1783, Pigot and Hood returned to England, leaving the Leeward Islands' Station under the command of Rear-Admiral Sir Richard Hughes, an officer remembered by history only through Nelson's refusing to obey his orders not to enforce the Navigation Acts, in 1785.
CHAPTER XIII
HOWE AGAIN GOES AFLOAT. THE FINAL RELIEF OF GIBRALTAR
1782
The fall of Lord North's Ministry, besides occasioning the recall of Rodney, drew Lord Howe out of his long retirement, to command the Channel Fleet. He hoisted his flag on the 20th of April, 1782, on board the Victory, 100. Owing to the various directions in which the efforts of Great Britain had to be made, either to defend her own interests or to crush the movements of the many enemies now combined against her, the operations of the Channel fleet were for some months carried on by detached squadrons,—in the North Sea, in the Bay of Biscay, and at the entrance of the Channel; Howe having under him several distinguished subordinates, at the head of whom, in professional reputation, were Vice-Admiral Barrington, the captor of Santa Lucia, and Rear-Admiral Kempenfelt. In the North Sea, the Dutch were kept in their ports; and a convoy of near 400 merchant ships from the Baltic reached England unmolested. In the Bay of Biscay, Barrington, having with him twelve of the line, discovered and chased a convoy laden with stores for the fleet in the East Indies. One of the ships of the line accompanying it, the Pégase, 74, surrendered, after a night action of three hours with the Foudroyant, 80, Captain John Jervis, afterwards Earl St. Vincent. Of nineteen transports, thirteen, one of which, the Actionnaire, was a 64-gun ship armed en flûte,133 were taken; a weighty blow to the great Suffren, whose chief difficulty in India was inadequate material of war, and especially of spars, of which the Actionnaire carried an outfit for four ships of the line. After Barrington's return, Kempenfelt made a similar but uneventful cruise of a month in the Bay.
Howe himself went first to the North Sea in the month of May. Having there held the Dutch in check during a critical moment, he was directed next to go to the entrance of the Channel, leaving only a division in the Downs. Information had been received that an allied fleet of thirty-two ships of the line, five only of which were French, had sailed from Cadiz early in June, to cruise between Ushant and Scilly. It was expected that they would be joined there by a reinforcement from Brest, and by the Dutch squadron in the Texel, making a total of about fifty of the line, under the command of the Spanish Admiral, Don Luis de Cordova. The Dutch did not appear, owing probably to Howe's demonstration before their ports; but eight ships from Brest raised the allied fleet to forty. To oppose these Howe sailed on the 2d of July with twenty-two sail, of which eight were three-deckers. Before his return, in the 7th of August, he was joined by eight others; mostly, however, sixty-fours. With this inferiority of numbers the British Admiral could expect only to act on the defensive, unless some specially favourable opportunity should offer. The matter of most immediate concern was the arrival of the Jamaica convoy, then daily expected; with which, it may be mentioned, de Grasse also was returning to England, a prisoner of war on board the Sandwich.
On its voyage north, the allied fleet captured on June 25th eighteen ships of a British convoy bound for Canada. A few days later it was fixed in the chops of the Channel, covering the ground from Ushant to Scilly. On the evening of July 7th it was sighted off Scilly by Howe, who then had with him twenty-five sail. The allies prepared for action; but the British Admiral, possessing a thorough knowledge of the neighbouring coasts, either in his own person or in some of his officers, led the fleet by night to the westward through the passage between Scilly and Land's End. On the following morning he was no more to be seen, and the enemy, ignorant of the manner of his evasion, was thrown wholly off his track.134 Howe met the convoy; and a strong gale of wind afterwards forcing the allies to the southward, both it and the fleet slipped by successfully, and reached England.
Howe was ordered now to prepare to throw reinforcements and supplies into Gibraltar, which had not received relief since Darby's visit, in April, 1781. For this urgent and critical service it was determined to concentrate the whole Channel Fleet at Spithead, where also the transports and supply-ships were directed to rendezvous. It was while thus assembling for the relief of Gibraltar that there occurred the celebrated incident of the Royal George, a 100-gun ship, while being heeled for under-water repairs, oversetting and sinking at her anchors, carrying down with her Rear-Admiral Kempenfelt and about nine hundred souls, including many women and children. This was on the 29th of August, 1782. On the 11th of September the expedition started, one hundred and eighty-three sail in all; thirty-four being ships of the line, with a dozen smaller cruisers, the rest unarmed vessels. Of the latter, thirty-one were destined for Gibraltar, the remainder being trading ships for different parts of the world. With so extensive a charge, the danger to which had been emphasised by numerous captures from convoys during the war, Howe's progress was slow. It is told that shortly before reaching Cape Finisterre, but after a violent gale of wind, the full tally of one hundred eighty-three sail was counted. After passing Finisterre, the several "trades" probably parted from the grand fleet.
On the 8th of October, off Cape St. Vincent, a frigate was sent ahead for information. It was known that a great combined force of ships of war lay in Algeciras Bay,—opposite Gibraltar,—and that an attack upon the works was in contemplation; but much might have happened meantime. Much, in fact, had happened. A violent gale of wind on the 10th of September had driven some of the allied fleet from their moorings, one vessel, the San Miguel, 72, being forced under the batteries of Gibraltar, where she had to surrender; but there still remained the formidable number of forty-eight ships of the line, anchored only four miles from the point which the relief ships must reach. This was the problem which Howe had to solve. More important still, though of less bearing upon his mission, was the cheering news brought by the frigate, when she rejoined on October 10th, that the long-intended attack had been made on the 13th of September, and had been repelled gloriously and decisively. The heavily protected Spanish floating batteries, from which success had been expected confidently, one and all had been set on fire and destroyed. If Howe could introduce his succours, the fortress was saved.
The admiral at once summoned his subordinate officers, gave them full and particular instructions for the momentous undertaking, and issued at the same time, to the masters of the supply-ships, precise information as to local conditions of wind and currents at Gibraltar, to enable them more surely to reach their anchorage. On the 11th of October, being now close to its destination, the fleet bore up for the Straits, which it entered at noon with a fair westerly wind. The convoy went first,—sailing before the wind it was thus to leeward of the fleet, in a position to be defended,—and the ships of war followed at some distance in three divisions, one of which was led by Howe himself. At 6 P.M. the supply-ships were off the mouth of the Bay, with a wind fair for the mole; but, through neglect of the instructions given, all but four missed the entrance, and were swept to the eastward of the Rock, whither the fleet of course had to follow them.
On the 13th the allied fleets came out, being induced to quit their commanding position at Algeciras by fears for two of their number, which shortly before had been driven to the eastward. During the forenoon of the same day the British were off the Spanish coast, fifty miles east of Gibraltar. At sunset the allies were seen approaching, and Howe formed his fleet, but sent the supply-ships to anchor at the Zaffarine Islands, on the coast of Barbary, to await events. Next morning the enemy was close to land northward, but visible only from the mastheads; the British apparently having headed south during the night. On the 15th the wind came east, fair for Gibraltar, towards which all the British began cautiously to move. By the evening of the 16th, eighteen of the convoy were safe at the mole; and on the 18th all had arrived, besides a fireship with 1,500 barrels of powder, sent in by the Admiral upon the governor's requisition. Throughout these critical hours, the combined fleets seem to have been out of sight. Either intentionally or carelessly, they had got to the eastward and there remained; having rallied their separated ships, but allowed Gibraltar to be replenished for a year. On the morning of the 19th they appeared in the north-east, but the relief was then accomplished and Howe put out to sea. He was not willing to fight in mid-Straits, embarrassed by currents and the land; but when outside he brought-to,—stopped, by backing some of the sails,—to allow the enemy to attack if they would, they having the weather-gage. On the following day, the 20th, towards sunset they bore down, and a partial engagement ensued; but it was wholly indecisive, and next day was not renewed. The British loss was 68 killed and 208 wounded; that of the allies 60 killed and 320 wounded. On the 14th of November the fleet regained Spithead.
The services rendered to his country by Howe on this occasion were eminently characteristic of the special qualities of that great officer, in whom was illustrated to the highest degree the solid strength attainable by a man not brilliant, but most able, who gives himself heart and soul to professional acquirement. In him, profound and extensive professional knowledge, which is not inborn but gained, was joined to great natural staying powers; and the combination eminently fitted him for the part we have seen him play in Delaware Bay, at New York, before Rhode Island, in the Channel, and now at Gibraltar. The utmost of skill, the utmost of patience, the utmost of persistence, such had Howe; and having these, he was particularly apt for the defensive operations, upon the conduct of which chiefly must rest his well-deserved renown.
A true and noble tribute has been paid by a French officer to this relief of Gibraltar:135—
"The qualities displayed by Lord Howe during this short campaign rose to the full height of the mission which he had to fulfil. This operation, one of the finest in the War of American Independence, merits a praise equal to that of a victory. If the English fleet was favoured by circumstances,—and it is rare that in such enterprises one can succeed without the aid of fortune—it was above all the Commander-in-Chief's quickness of perception, the accuracy of his judgment, and the rapidity of his decisions, that assured success."
To this well-weighed, yet lofty praise of the Admiral, the same writer has added words that the British Navy may remember long with pride, as sealing the record of this war, of which the relief of Gibraltar marked the close in European and American waters. After according credit to the Admiralty for the uniform high speed of the British vessels, and to Howe for his comprehension and use of this advantage, Captain Chevalier goes on:—
"Finally, if we may judge by the results, the Commander-in-Chief of the English fleet could not but think himself most happy in his captains. There were neither separations, nor collisions, nor casualties; and there occurred none of those events, so frequent in the experiences of a squadron, which often oblige admirals to take a course wholly contrary to the end they have in view. In contemplation of this unvexed navigation of Admiral Howe, it is impossible not to recall the unhappy incidents which from the 9th to the 12th of April befell the squadron of the Count de Grasse.... If it is just to admit that Lord Howe displayed the highest talent, it should be added that he had in his hands excellent instruments."
To quote another French writer: "Quantity disappeared before quality."
CHAPTER XIV
THE NAVAL OPERATIONS IN THE EAST INDIES, 1778-1783. THE CAREER OF THE BAILLI DE SUFFREN
The operations in India, both naval and military, stand by themselves, without direct influence upon transactions elsewhere, and unaffected also by these, except in so far as necessary succours were intercepted sometimes in European waters. The cause of this isolation was the distance of India from Europe; from four to six months being required by a fleet for the voyage.
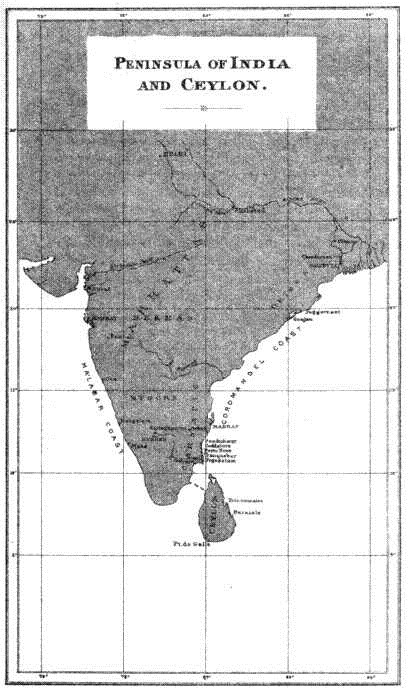
Peninsula of India, and Ceylon
Certain intelligence of the war between Great Britain and France reached Calcutta July 7th, 1778. On the same day the Governor-General ordered immediate preparations to attack Pondicherry, the principal seaport of the French. The army arrived before the place on the 8th of August, and on the same day Commodore Sir Edward Vernon anchored in the roads to blockade by sea. A French squadron, under Captain Tronjoly, soon after appearing in the offing, Vernon gave chase, and on the 10th an action ensued. The forces engaged were about equal, the French, if anything, slightly superior; a 60-gun ship and four smaller vessels being on each side. As the French then went into Pondicherry, the immediate advantage may be conceded to them; but, Vernon returning on the 20th, Tronjoly soon after quitted the roads, and returned to the Ile de France.136 From that day the British squadron blockaded closely, and on the 17th of October Pondicherry capitulated.
On the 7th of March, 1779, Rear-Admiral Sir Edward Hughes sailed for the East Indies with a small squadron. The French also sent out occasional ships; but in 1779 and 1780 these went no further than the Ile de France, their naval station in the Indian Ocean. Hughes's force remained unopposed during those years. The period was critical, for the British were at war with Hyder Ali, Sultan of Mysore, and with the Mahrattas; and all depended upon command of the sea. In January, 1781, when Hughes was wintering at Bombay, the French squadron under Comte d'Orves appeared off the Coromandel coast, but, despite Hyder Ali's entreaties, it refused to coöperate with him. The different spirit of the two commanders may be illustrated from contemporary documents.
"We have advices from Fort St. George of a French squadron which appeared off that place on January 25, 26, and 27, consisting of 1 seventy-four, 4 sixty-fours, and 2 fifties. They proceeded south without making any attempt on five Indiamen then in the roads, with a number of vessels laden with grain and provisions; the destroying of which might have been easily accomplished, and would have been severely felt."
"On December 8th, off Mangalore,"137 writes Hughes, "I saw two ships, a large snow, three ketches, and many smaller vessels at anchor in the road with Hyder's flag flying; and, standing close, found them vessels of force and all armed for war. I anchored as close as possible, sent in all armed boats, under cover of three smaller ships of war, which anchored in four fathoms water, close to the enemy's ships. In two hours took and burned the two ships, one of 28 and one of 26 guns, and took or destroyed all the others, save one which, by throwing everything overboard, escaped over the bar into the port. Lost 1 lieutenant and 10 men killed, 2 lieutenants and 51 wounded."
It is interesting to note these evidences of Hughes's conceptions of naval warfare and enterprise, common though they were to the British service; for their positive character brings into strong relief the qualities of his next antagonist, Suffren, and his great superiority in these respects over the average run of French officers of that day.
D'Orves returned to the Ile de France.
When war with Holland began, the British government decided to attempt the capture of the Cape of Good Hope. For that object a squadron of one 74, one 64, and three 50's, with numerous smaller vessels, under Commodore George Johnstone, convoying a considerable body of troops, sailed from England on the 13th of March, 1781, in company with the Channel fleet under Vice-Admiral George Darby, then on its way to relieve Gibraltar. The French government, having timely notice of the expedition, undertook to frustrate it; detailing for that purpose a division of two 74's, and three 64's, under the since celebrated Suffren.138 These ships left Brest on the 22d of March, with the fleet of de Grasse. They also carried some battalions of troops.









