 полная версия
полная версияThe Major Operations of the Navies in the War of American Independence
During these days de Guichen, whose fleet, according to Rodney, sailed the better, and certainly sufficiently well to preserve the advantage of the wind, bore down more than once, generally in the afternoon, when the breeze is steadiest, to within distant range of the British. Upon this movement, the French base the statement that the British Admiral was avoiding an encounter; it is equally open to the interpretation that he would not throw away ammunition until sure of effective distance. Both admirals showed much skill and mastery of their profession, great wariness also, and quickness of eye; but it is wholly untenable to claim that a fleet having the weather-gage for five days, in the trade-winds, was unable to bring its enemy to action, especially when it is admitted that the latter closed the instant the wind permitted him to do so.
On the afternoon of May 15th, about the usual hour, Rodney "made a great deal of sail upon the wind." The French, inferring that he was trying to get off, which he meant them to do, approached somewhat closer than on the previous days. Their van ship had come within long range, abreast the centre of the British, who were on the port tack standing to the south-south-east, with the wind at east (aa, aa). Here the breeze suddenly hauled to south-southeast (wind b). The heads of all the ships in both fleets were thus knocked off to south-west (s, s), on the port tack, but the shift left the British rear, which on that tack led the fleet, to windward of the French van. Rodney's signal flew at once, to tack in succession and keep the wind of the enemy; the latter, unwilling to yield the advantage, wore all together (w), hauling to the wind on the starboard tack, and to use Rodney's words, "fled with a crowd of sail" (a', a').
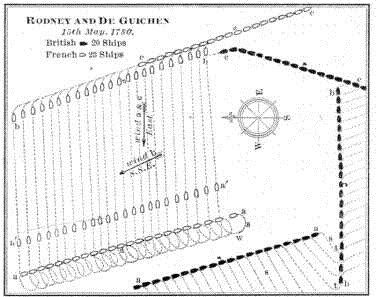
Rodney and De Guichen, May 15, 1780
The British fleet tacking in succession after their leaders, (t, t), the immediate result was that both were now standing on the starboard tack,—to the eastward,—the British having a slight advantage of the wind, but well abaft the beam of the French (bb, bb). The result, had the wind held, would have been a trial of speed and weatherliness. "His Majesty's fleet," wrote Rodney, "by this manœuvre had gained the wind, and would have forced the enemy to battle, had it not at once changed six points (back to east, its former direction,) when near the enemy, and enabled them to recover that advantage." When the wind thus shifted again, de Guichen tacked his ships together and stood across the bows of the advancing enemy (cc, cc). The British leader struck the French line behind the centre, and ran along to leeward, the British van exchanging a close cannonade with the enemy's rear. Such an engagement, two lines passing on opposite tacks, is usually indecisive, even when the entire fleets are engaged, as at Ushant; but where, as in this case, the engagement is but partial, the result is naturally less. The French van and centre, having passed the head of the enemy, diverged at that point farther and farther from the track of the on-coming British ships, which from the centre rearwards did not fire. "As the enemy were under a press of sail, none but the van of our fleet could come in for any part of the action without wasting his Majesty's powder and shot, the enemy wantonly expending theirs at such a distance as to have no effect." Here again the French were evidently taking the chance of disabling the distant enemy in his spars. The British loss in the action of May 15th was 21 killed and 100 wounded.

Comte de Guichen

George Brydges, Lord Rodney
The fleets continued their respective movements, each acting as before, until the 19th, when another encounter took place, of exactly the same character as the last, although without the same preliminary manœuvring. On that occasion the British, who in the interim had been reinforced by one 74 and one 50-gun ship, lost 47 killed and 113 wounded. The result was equally indecisive, tactically considered; but both by this time had exhausted their staying powers. The French, having been absent from Martinique since the 13th of April, had now but six days' provisions.87 Rodney found the Conqueror, Cornwall, and Boyne so shattered that he sent them before the wind to Santa Lucia, while he himself with the rest of the fleet stood for Barbados, where he arrived on the 22d. The French anchored on the same day at Fort Royal. "The English," says Chevalier, "stood on upon the starboard tack, to the southward, after the action of the 19th, and the next day were not to be seen." "The enemy," reported Rodney, "stood to the northward with all the sail they could possibly press, and were out of sight the 21st inst. The condition of his Majesty's ships was such as not to allow a longer pursuit."
By their dexterity and vigilance each admiral had thwarted the other's aims. Rodney, by a pronounced, if cautious, offensive effort, had absolutely prevented the "ulterior object" of the French, which he clearly understood to be Santa Lucia. De Guichen had been successful in avoiding decisive action, and he had momentarily so crippled a few of the British ships that the fleet must await their repairs before again taking the sea. The tactical gain was his, the strategic victory rested with his opponent; but that his ships also had been much maltreated is shown by the fact that half a dozen could not put to sea three weeks later. The French admiral broke down under the strain, to which was added the grief of losing a son, killed in the recent engagements. He asked for his recall. "The command of so large a fleet," he wrote, "is infinitely beyond my capacity in all respects. My health cannot endure such continual fatigue and anxiety." Certainly this seems a tacit testimony to Rodney's skill, persistence, and offensive purpose. The latter wrote to his wife: "For fourteen days and nights the fleets were so near each other that neither officers nor men could be said to sleep. Nothing but the goodness of the weather and climate would have enabled us to endure so continual a fatigue. Had it been in Europe, half the people must have sunk under it. For my part, it did me good."
Rodney stated also in his home letters that the action of his subordinates in the last affairs had been efficient; but he gave them little credit for it. "As I had given public notice to all my captains, etc., that I expected implicit obedience to every signal made, under the certain penalty of being instantly superseded, it had an admirable effect; as they were all convinced, after their late gross behaviour, that they had nothing to expect at my hands but instant punishment to those who neglected their duty. My eye on them had more dread than the enemy's fire, and they knew it would be fatal. No regard was paid to rank: admirals as well as captains, if out of their station, were instantly reprimanded by signals, or messages sent by frigates; and, in spite of themselves, I taught them to be, what they had never been before,—officers." Rodney told his officers also that he would shift his flag into a frigate, if necessary, to watch them better. It is by no means obligatory to accept these gross aspersions as significant of anything worse than the suspiciousness prevalent throughout the Navy, traceable ultimately to a corrupt administration of the Admiralty. The latter, like the government of 1756, was open to censure through political maladministration; every one feared that blame would be shifted on to him, as it had been on to Byng,—who deserved it; and not only so, but that blame would be pushed on to ruin, as in his case. The Navy was honeycombed with distrust, falling little short of panic. In this state of apprehension and doubt, the tradition of the line of battle, resting upon men who did not stop to study facts or analyse impressions, and who had seen officers censured, cashiered, and shot, for errors of judgment or of action, naturally produced hesitations and misunderstandings. An order of battle is a good thing, necessary to insure mutual support and to develop a plan. The error of the century, not then exploded, was to observe it in the letter rather than in the spirit; to regard the order as an end rather than a means; and to seek in it not merely efficiency, which admits broad construction in positions, but preciseness, which is as narrowing as a brace of handcuffs. Rodney himself, Tory though he was, found fault with the administration. With all his severity and hauteur, he did not lose sight of justice, as is shown by a sentence in his letter to Carkett. "Could I have imagined your conduct and inattention to signals had proceeded from anything but error in judgment, I had certainly superseded you, but God forbid I should do so for error in judgment only,"—again an illusion, not obscure, to Byng's fate.
In Barbados, Rodney received certain information that a Spanish squadron of twelve ships of the line, with a large convoy of ten thousand troops, had sailed from Cadiz on April 28th for the West Indies. The vessel bringing the news had fallen in with them on the way. Rodney spread a line of frigates "to windward, from Barbados to Barbuda," to obtain timely warning, and with the fleet put to sea on the 7th of June, to cruise to the eastward of Martinique to intercept the enemy. The latter had been discovered on the 5th by a frigate, fifty leagues east of the island, steering for it; but the Spanish admiral, seeing that he would be reported, changed his course, and passed north of Guadeloupe. On the 9th he was joined in that neighbourhood by de Guichen, who was able to bring with him only fifteen sail,—a fact which shows that he had suffered in the late brushes quite as severely as Rodney, who had with him seventeen of his twenty.
Having evaded the British, the allies anchored at Fort Royal; but the Spanish admiral absolutely refused to join in any undertaking against the enemy's fleet or possessions. Not only so, but he insisted on being accompanied to leeward. The Spanish squadron was ravaged by an epidemic, due to unsanitary conditions of the ships and the uncleanliness of the crews, and the disease was communicated to their allies. De Guichen had already orders to leave the Windward Islands when winter approached. He decided now to anticipate that time, and on the 5th of July sailed from Fort Royal with the Spaniards. Having accompanied the latter to the east end of Cuba, he went to Cap François, in Haïti, then a principal French station. The Spaniards continued on to Havana.
At Cap François, de Guichen found urgent entreaties from the French Minister to the United States, and from Lafayette, to carry his fleet to the continent, where the clear-sighted genius of Washington had recognised already that the issue of the contest depended upon the navies. The French admiral declined to comply, as contrary to his instructions, and on the 16th of August sailed for Europe, with nineteen sail of the line, leaving ten at Cap François. Sealed orders, opened at sea, directed him to proceed to Cadiz, where he anchored on the 24th of October. His arrival raised the allied force there assembled to fifty-one sail of the line, besides the ninety-five sugar and coffee ships which he had convoyed from Haïti. It is significant of the weakness of Great Britain in the Mediterranean at that time, that these extremely valuable merchant ships were sent on to Toulon, instead of to the more convenient Atlantic ports, only five ships of the line accompanying them past Gibraltar. The French government had feared to trust them to Brest, even with de Guichen's nineteen sail.
The allied operations in the Windward Islands for the season of 1780 had thus ended in nothing, notwithstanding an incontestable inferiority of the British to the French alone, of which Rodney strongly complained. It was, however, contrary to the intentions of the Admiralty that things so happened. Orders had been sent to Vice-Admiral Marriot Arbuthnot, at New York, to detach ships to Rodney; but the vessel carrying them was driven by weather to the Bahamas, and her captain neglected to notify Arbuthnot of his whereabouts, or of his dispatches. A detachment of five ships of the line under Commodore the Hon. Robert Boyle Walsingham was detained three months in England, wind-bound. They consequently did not join till July 12th. The dispositions at once made by Rodney afford a very good illustration of the kind of duties that a British Admiral had then to discharge. He detailed five ships of the line to remain with Hotham at Santa Lucia, for the protection of the Windward Islands. On the 17th, taking with him a large merchant convoy, he put to sea with the fleet for St. Kitts, where the Leeward Islands "trade" was collecting for England. On the way he received precise information as to the route and force of the Franco-Spanish fleet under de Guichen, of the sickness on board it, and of the dissension between the allies. From St. Kitts the July "trade" was sent home with two ships of the line. Three others, he wrote to the Admiralty, would accompany the September fleet, "and the remainder of the ships on this station, which are in want of great repair and are not copper-bottomed, shall proceed with them or with the convoy which their Lordships have been pleased to order shall sail from hence in October next." If these arrived before winter, he argued, they would be available by spring as a reinforcement for the Channel fleet, and would enable the Admiralty to send him an equivalent number for the winter work on his station.
As de Guichen had taken the whole French homeward merchant fleet from Martinique to Cap François and as the height of the hurricane season was near, Rodney reasoned that but a small French force would remain in Haïti, and consequently that Jamaica would not require all the British fleet to save it from any possible attack. He therefore sent thither ten sail of the line, notifying Vice-Admiral Sir Peter Parker that they were not merely to defend the island, but to enable him to send home its great trade in reasonable security.
These things being done by July 31st, Rodney, reasoning that the allies had practically abandoned all enterprises in the West Indies for that year, and that a hurricane might at any moment overtake the fleet at its anchors, possibly making for it a lee shore, went to sea, to cruise with the fleet off Barbuda. His mind, however, was inclined already to go to the continent, whither he inferred, correctly but mistakenly, that the greater part of de Guichen's fleet would go, because it should. His purpose was confirmed by information from an American vessel that a French squadron of seven ships of the line, convoying six thousand troops, had anchored in Narragansett Bay on the 12th of July. He started at once for the coast of South Carolina, where he communicated with the army in Charleston, and thence, "sweeping the southern coast of America," anchored with fourteen ships of the line at Sandy Hook, on the 14th of September, unexpected and unwelcome to friends and foes alike.
Vice-Admiral Arbuthnot, being junior to Rodney, showed plainly and with insubordination his wrath at this intrusion into his command, which superseded his authority and divided the prize-money of a lucrative station. This, however, was a detail. To Washington, Rodney's coming was a deathblow to the hopes raised by the arrival of the French division at Newport, which he had expected to see reinforced by de Guichen. Actually, the departure of the latter made immaterial Rodney's appearance on the scene; but this Washington did not know then. As it was, Rodney's force joined to Arbuthnot's constituted a fleet of over twenty sail of the line, before which, vigorously used, there can be little doubt that the French squadron in Newport must have fallen. But Rodney, though he had shown great energy in the West Indies, and unusual resolution in quitting his own station for a more remote service, was sixty-two, and suffered from gout. "The sudden change of climate makes it necessary for me to go on shore for some short time," he wrote; and although he added that his illness was "not of such a nature as shall cause one moment's delay in his Majesty's service," he probably lost a chance at Rhode Island. He did not overlook the matter, it is true; but he decided upon the information of Arbuthnot and Sir Henry Clinton, and did not inspect the ground himself. Nothing of consequence came of his visit; and on the 16th of November he sailed again for the West Indies, taking with him only nine sail of the line.
The arrival of de Ternay's seven ships at Newport was more than offset by a British reinforcement of six ships of the line under Rear-Admiral Thomas Graves which entered New York on July 13th,—only one day later. Arbuthnot's force was thus raised to ten of the line, one of which was of 98 guns. After Rodney had come and gone, the French division was watched by cruisers, resting upon Gardiner's Bay,—a commodious anchorage at the east end of Long Island, between thirty and forty miles from Rhode Island. When a movement of the enemy was apprehended, the squadron assembled there, but nothing of consequence occurred during the remainder of the year.
The year 1780 had been one of great discouragement to the Americans, but the injury, except as the lapse of time taxed their staying power, was more superficial than real. The successes of the British in the southern States, though undeniable, and seemingly substantial, were involving them ever more deeply in a ruinously ex-centric movement. They need here only to be summarised, as steps in the process leading to the catastrophe of Yorktown,—a disaster which, as Washington said, exemplified naval rather than military power.
The failure of d'Estaing's attack upon Savannah in the autumn of 177988 had left that place in the possession of the British as a base for further advances in South Carolina and Georgia; lasting success in which was expected from the numbers of royalists in those States. When the departure of the French fleet was ascertained, Sir Henry Clinton put to sea from New York in December, 1779, for the Savannah River, escorted by Vice-Admiral Arbuthnot. The details of the operations, which were leisurely and methodical, will not be given here; for, although the Navy took an active part in them, they scarcely can be considered of major importance. On the 12th of May, 1780, the city of Charleston capitulated, between six and seven thousand prisoners being taken. Clinton then returned to New York, leaving Lord Cornwallis in command in the south. The latter proposed to remain quiet during the hot months; but the activity of the American partisan troops prevented this, and in July the approach of a small, but relatively formidable force, under General Gates, compelled him to take the field. On the 16th of August the two little armies met at Camden, and the Americans, who were much the more numerous, but largely irregulars, were routed decisively. This news reached General Washington in the north nearly at the same moment that the treason of Benedict Arnold became known. Although the objects of his treachery were frustrated, the sorrowful words, "Whom now can we trust?" show the deep gloom which for the moment shadowed the constant mind of the American Commander-in-Chief. It was just at this period, too, that Rodney arrived at New York.
Cornwallis, not content with his late success, decided to push on into North Carolina. Thus doing, he separated himself from his naval base in Charleston, communication with which by land he had not force to maintain, and could recover effective touch with the sea only in Chesapeake Bay. This conclusion was not apparent from the first. In North Carolina, the British general did not receive from the inhabitants the substantial support which he had expected, and found himself instead in a very difficult and wild country, confronted by General Greene, the second in ability of all the American leaders. Harassed and baffled, he was compelled to order supplies to be sent by sea to Wilmington, North Carolina, an out-of-the-way and inferior port, to which he turned aside, arriving exhausted on the 7th of April, 1781. The question as to his future course remained to be settled. To return to Charleston by sea was in his power, but to do so would be an open confession of failure,—that he could not return by land, through the country by which he had come—much the same dilemma as that of Howe and Clinton in Philadelphia. To support him in his distress by a diversion, Sir Henry Clinton had sent two successive detachments to ravage the valley of the James River in Virginia. These were still there, under the command of General Phillips; and Cornwallis, in the circumstances, could see many reasons that thither was the very scene to carry the British operations. On the 25th of April, 1781, he left Wilmington, and a month later joined the division at Petersburg, Virginia, then commanded by Benedict Arnold; Phillips having died. There, in touch now with his fate, we must leave him for the moment.
To complete the naval transactions of 1780, it is necessary to mention briefly two incidents, trivial in themselves, but significant, not only as associated with the greater movements of the campaign, but as indicative of the naval policy of the States which were at war. The two, though not otherwise connected, have a certain unity of interest, in that the same British officer commanded on both occasions.
It will be remembered that in Byron's action off Grenada, in July, 1779, the 64-gun ship Lion received such injuries that her commander, Captain Cornwallis, had been compelled to run down before the trade-winds to Jamaica, in order to save her from capture. Since that time she had remained there, as one of the squadron of Vice-Admiral Sir Peter Parker. In March, 1780, still commanded by Cornwallis, she was making an ordinary service cruise off the north side of Haïti, having in company the Bristol, 50, and the Janus, 44. On the 20th of March, off Monte Christi, a number of sail were sighted to the eastward, which proved to be a French convoy, on its way from Martinique to Cap François, protected by La Motte-Picquet's squadron of two 74's, one 64, one 50, and a frigate. The French merchant ships were ordered to crowd sail for their port, while the men-of-war chased to the north-west. La Motte-Picquet's flagship, the Annibal, 74, got within range at 5 P.M., when a distant cannonade began, which lasted till past midnight, and was resumed on the following morning. From it the Janus was the chief sufferer, losing her mizzen topmast and foretopgallant mast. It falling nearly calm, the Bristol and Lion got out their boats and were towed by them to her support. The two other French ships of the line got up during the forenoon of the 21st, so that the action that afternoon, though desultory, might be called general.
The two opposing commodores differ in their expressed opinions as to the power of the French to make the affair more decisive. Some of La Motte-Picquet's language seems to show that he felt the responsibility of his position. "The Janus, being smaller and more easily worked, lay upon our quarter and under our stern, where she did considerable damage. A little breeze springing up enabled us (the Annibal) to stand towards our own ships, which did everything possible to come up and cover us, without which we should have been surrounded." It is easy to see in such an expression the reflection of the commands of the French Cabinet, to economise the ships. This was still more evident in La Motte-Picquet's conduct next day. On the morning of the 22d, "at daylight we were within one and a half cannon-shot, breeze fresh at the east-north-east, and I expected to overtake the British squadron in an hour, when we perceived four ships in chase of us. At 6.30 A.M. three were seen to be men-of-war. This superiority of force compelled me to desist, and to make signal to haul our wind for Cap François." These three new-comers were the Ruby, 64, and two frigates, the Pomona, 28, and Niger, 32. The comparison of forces, therefore, would be: French, two 74's, one 64, one 50, and one frigate, opposed to, British, two 64's, one 50, and three frigates. La Motte-Picquet evidently did not wait to ascertain the size of the approaching ships. His courage was beyond all dispute, and, as Hyde Parker had said, he was among the most distinguished of French officers; but, like his comrades, he was dominated by the faulty theory of his government.









