
Полная версия
The development of the culture of the ancient Indo-Europeans

Андрей Тихомиров
The development of the culture of the ancient Indo-Europeans
Hallstatt culture – further development of Sintashty-Arkaim culture
The Hallstatt culture is the culture of the Indo—European tribes of the southern part of Central Europe during the Early Iron Age (approximately 1000-500 BC). Got its name from the Hallstatt burial ground, located near the city of Hallstatt (south-western Austria) near large deposits of salt, developed already at the beginning of the Iron Age. Probably, the entire existence of the population that left this culture was based on the extraction of salt and its exchange. The burial ground was opened in 1846 and has been systematically excavated since then. Until the end of the 19th century . about 2000 burials were opened, in which 2 chronologically simultaneous burial rites are combined almost equally: corpse-burning and elongated corpse-laying. Usually, corpse immolations contain richer inventory, belonging mostly to men. Next to the burnt ashes in the graves are clay and bronze vessels, swords and things that survived the fire. Graves were often enclosed in a circle of stones and covered with stones from above. Corpse–burning spread in Vedism – Brahmanism – Hinduism. The inventory of Hallstatt graves is extremely rich and versatile. A lot of bronze and iron weapons, bronze dishes and ornaments typical of the entire archaeological culture, called Hallstatt, have been found.
The main territory of distribution of this culture (Austria, Slovenia, Croatia, Czech Republic and Slovakia) coincides with the area of settlement of tribes that belong to the ancient Illyrians. The Hallstatt culture was also widespread in southern Germany, in the Rhine departments of France, where it is associated with Celtic tribes, and in the eastern part of the Po River valley in Italy. In the basins of the Oder and Vistula, the culture of the Late Lusatian tribes belongs to this era, which was one of the components in the ethnogenesis of the Slavs. The transition from bronze to iron took place gradually, and the initial stage of the Hallstatt culture is characterized by the coexistence of bronze and iron tools with an increasing predominance of iron. In the economy of the population, agriculture became increasingly important, in the technique of which the transition from the hoe to the plough and plow was made. The social system of tribes is characterized by the disintegration of patriarchal-tribal relations and the transition to the relations of class society.
The dwellings of this culture are open in a number of those places. These were wooden pillar houses with an inner courtyard surrounded by buildings arranged in the form of the letter "P", having similarities with the Vars in the Southern Urals. There are also semi-dugouts. The forms of settlements are diverse and correspond to the economic foundations of various stages. There are pile settlements. The most common type is a village with a proper street layout, weakly fortified, but still surrounded by a palisade and a moat. Salt mines, copper mines, iron-smelting workshops and forges have been well explored. Due to the preservative properties of salt, tools are found in salt mines: axes, chisels, as well as remnants of clothing made of animal skin or woolen fabrics painted in different colors. In the copper mines, the sinking of the rock was carried out with the help of fire. A large amount of charred wood, copper and bronze picks, wooden buckets and gutters, pillars that served as props, etc. are found in the tunnels. The ore extracted from the mines was crushed on special stone slabs with the help of large stone hammers. Further processing was carried out in roasting and melting furnaces. The remains of a large Hallstatt forge were found in Moravia (Czech Republic), in the cave of the Bull Rock. Krits, hammers, tongs, anvils, stone foundries were found there (later the cave in which the forge was located was turned into the tomb of a noble leader). The specialization of crafts was limited to metallurgy.
The Hallstatt culture is divided into 2 periods: Early Hallstatt time (1000-700 BC) and Late Hallstatt time (700-500 BC). In this culture, the transition from bronze to iron was made first of all in weapons. In the early Hallstatt period, iron swords repeated the shape of bronze ones: they expanded in the middle part of the blade. The hilts of the swords had a knob in the form of a bell or in the form of an arc facing upwards (resembling modern antennas). This culture is characterized by an abundance of daggers, hatchets, knives, iron and copper arrowheads and spears. Helmets are usually bronze conical, with wide flat brims, with crests, sometimes woven from twigs, with a sharp bronze bump at the top. The shells consist of separate bronze plates sewn onto the skin. Decorations are diverse. Most of all bracelets: women wore bracelets not only on their hands, but also on their feet. Most of the jewelry is made of bronze, but occasionally there are things made of gold, glass, amber and ivory. In the late Hallstatt, beads made of opaque glass, yellow with blue eyes, circled with white, are very common. Many bronze vessels have been found. Especially the widespread use of bronze for the manufacture of tableware began due to the gradual displacement of this metal from the production of tools and weapons. Among the various forms of bronze vessels, it should be noted situlas – truncated conical buckets, sometimes decorated with images. Hallstatt ceramics are original and rather monotonous in different countries. Most vessels are rounded, with narrow necks and flat bottoms. The surface of the vessel is rubbed with graphite, which gives it a characteristic black luster, and is ornamented with linear patterns. The vessels were made by hand, there was no potter's wheel yet. The burials indicate a significant social stratification and separation of the tribal nobility. In the Bull Rock, in Moravia, the burial of a noble leader was accompanied by the murder of 40 servants and slaves, whose skeletons were found there. The Hallstatt culture is gradually being replaced in the western regions by the so-called Laten culture.
The Hallstatt art that emerged from the art of the Bronze Age reflected the social differentiation of the society of the early Iron Age; many of the created works of that era were intended for the distinguished tribal nobility. Monumental Hallstatt art is known from several tombstone steles (in northern Italy, Bosnia). Most of the monuments belong to the products found during the excavation of tombs. These are pottery decorated with decorative geometric ornaments (carvings and paintings, often multicolored), and metal products, mainly jewelry (the ornament is engraved).
The ornament consisted of meanders, triangles, rhombuses, rectangles, circles, spirals, etc. The Hallstatt sculpture is represented by small figurines made of clay or bronze depicting horsemen, people on foot, horses, bulls, birds, etc. Sometimes these sculptures were linked into a composition, as, for example, on a bronze cart from Stretweg in Styria, where a religious procession is depicted: female and male figures, armed horsemen, etc. Clay vessels were sometimes decorated with figures of people and animals stuck to their walls; the handles of bronze vessels were often made in the form of animal figures. Planar images have been preserved on clay vessels and on bronze tables (buckets), belt plaques and other objects. The subject matter of the images, which basically reflected events in the life of society, and partly had a symbolic meaning, was reduced to the same repeated scenes and images: feasting representatives of the nobility, farmers, mounted and foot soldiers, men and women, scenes of fist fighting and hunting, combat fights, processions, sacrifices. Images of animals occupy a prominent place (usually depicted in rows – a "procession of animals"), and herbivores are sometimes characterized by a branch in their mouth, and predators carry an animal or human leg in their mouths. The images of man and animals in the early days are strongly schematized, sometimes turning into an element of a geometrized ornament. The later situlas found in northern Italy and Austria are decorated with more developed multi-figure compositions, often arranged in several belts separated by horizontal lines. People and animals are depicted in profile. Many details of clothing, weapons, and everyday life are presented. The later stage of Hallstatt art dates back to the 6th-5th centuries BC and testifies to the cultural influences on it from the Etruscans and Greeks. However, in general, the developed Hallstatt art, the main focus of which was in northeastern Italy, is distinguished by a striking originality. In the 5th century BC, Hallstatt art began to be replaced by Gallic art from the west and Etruscan art from the south. The style and traditions of Hallstatt art were preserved in northern Italy, Austria and Bosnia until about 400 BC. The basics of the Hallstatt culture are the Vars of the Southern Urals.
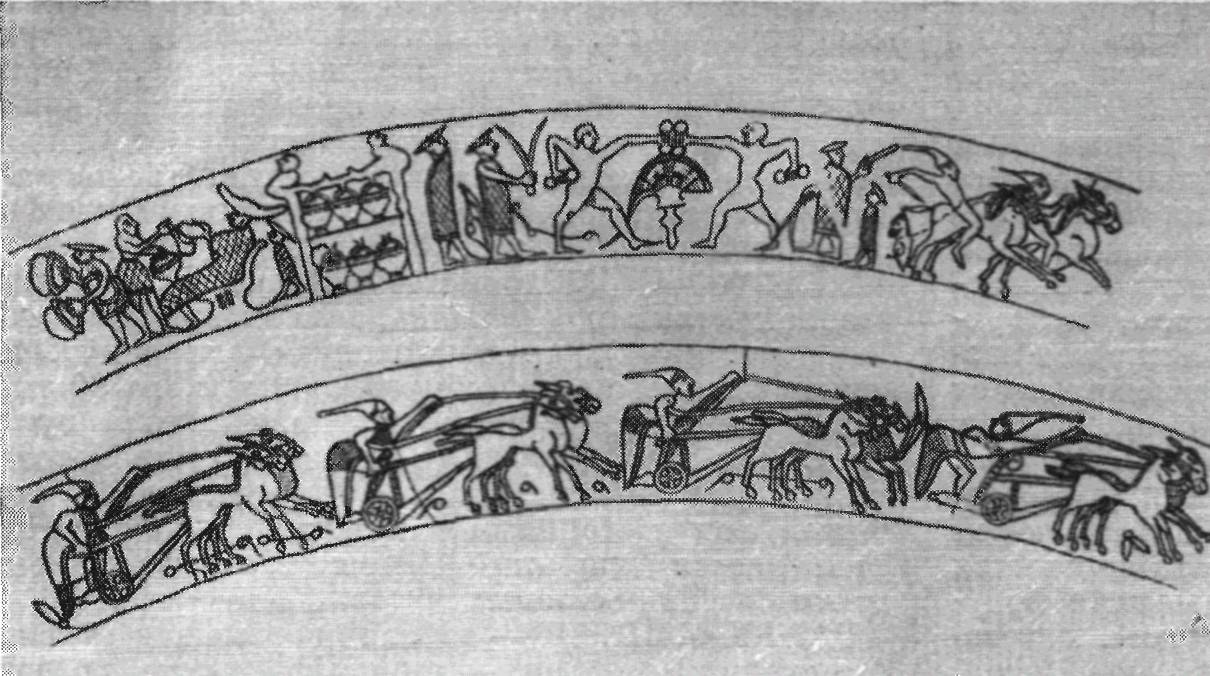


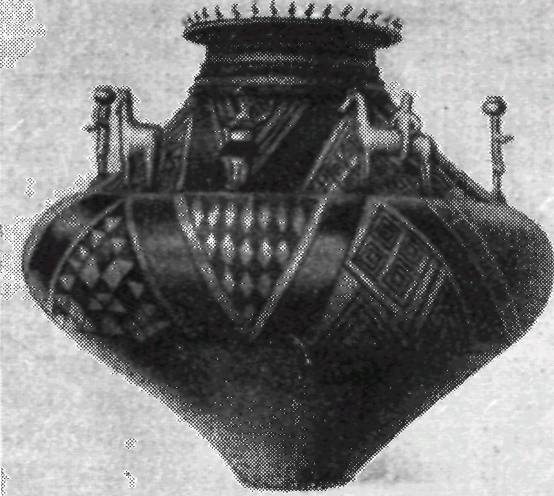
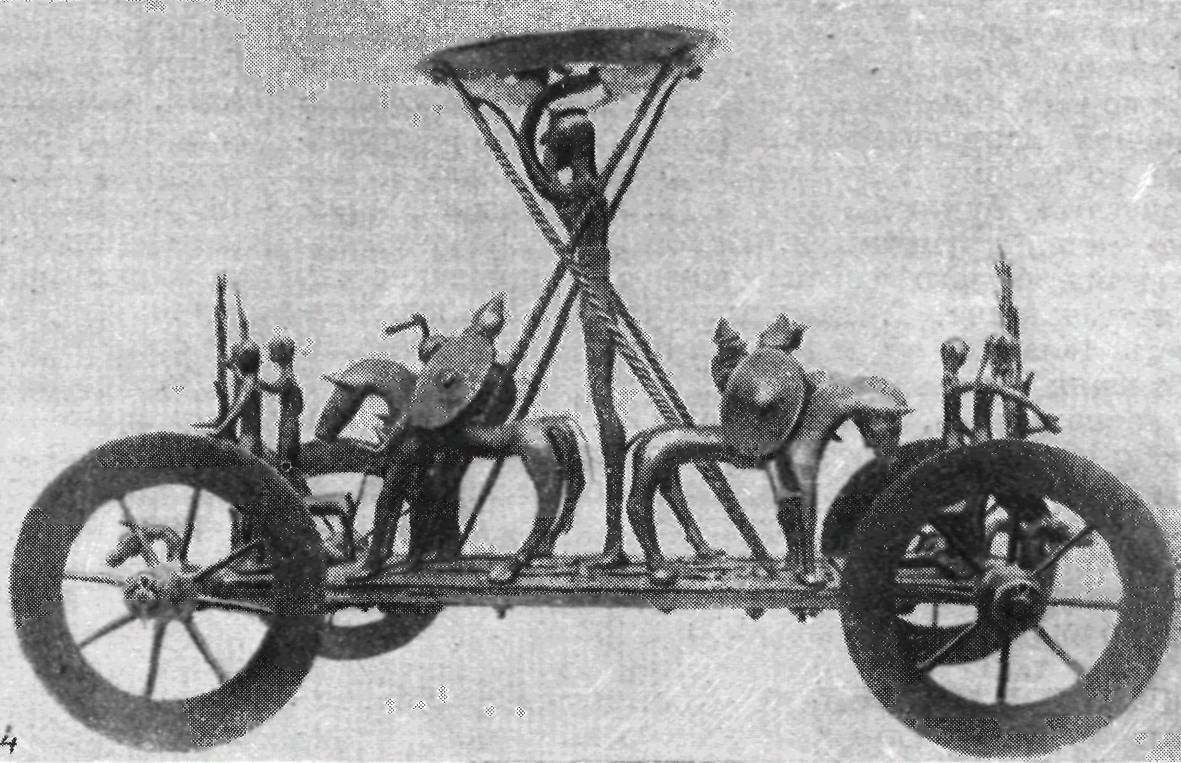
Hallstatt Art:
1 – images on a situla from Kuffarn in Styria. Figures of people in the form of a slightly modified Phrygian cap. Vienna Museum, Austria;
2 – the situation from Vacha to Extremely. Figures of people in the form of a slightly modified Phrygian cap. Museum in Ljubljana, Slovenia;
3 – a clay vessel with sculptural figures from Gemeinlebarn
in Lower Austria. Vienna Museum, Austria;
4 – a bronze carriage from Stretweg in Styria. Museum in Graz, Austria.
The Great Soviet Encyclopedia, Moscow, 1952, volume 10, p. 180
Meander is a common type of ornament of Indo -Europeans
A meander is a common type of Indo-European ornament in the form of a broken, curved line with curls or bends of a riverbed. Apparently, this kind of art developed among the bends of the tributaries of the Daitiya River (Ural) in the Southern Urals. It was widely developed later in the art of Ancient Greece; it got its name from the winding Meander River (now the Great Menderes) in Asia Minor. For example, the word "El Dorado" originated from the Spanish el Dorado – gilded, golden. A non-existent "golden" country that the Spanish conquistadors (invaders) were looking for in Latin America.

Types of meander

Alandskoye is an archaeological complex in the Orenburg region, belonging to the culture of the ancient Indo–Europeans of Sintashta-Arkaim.
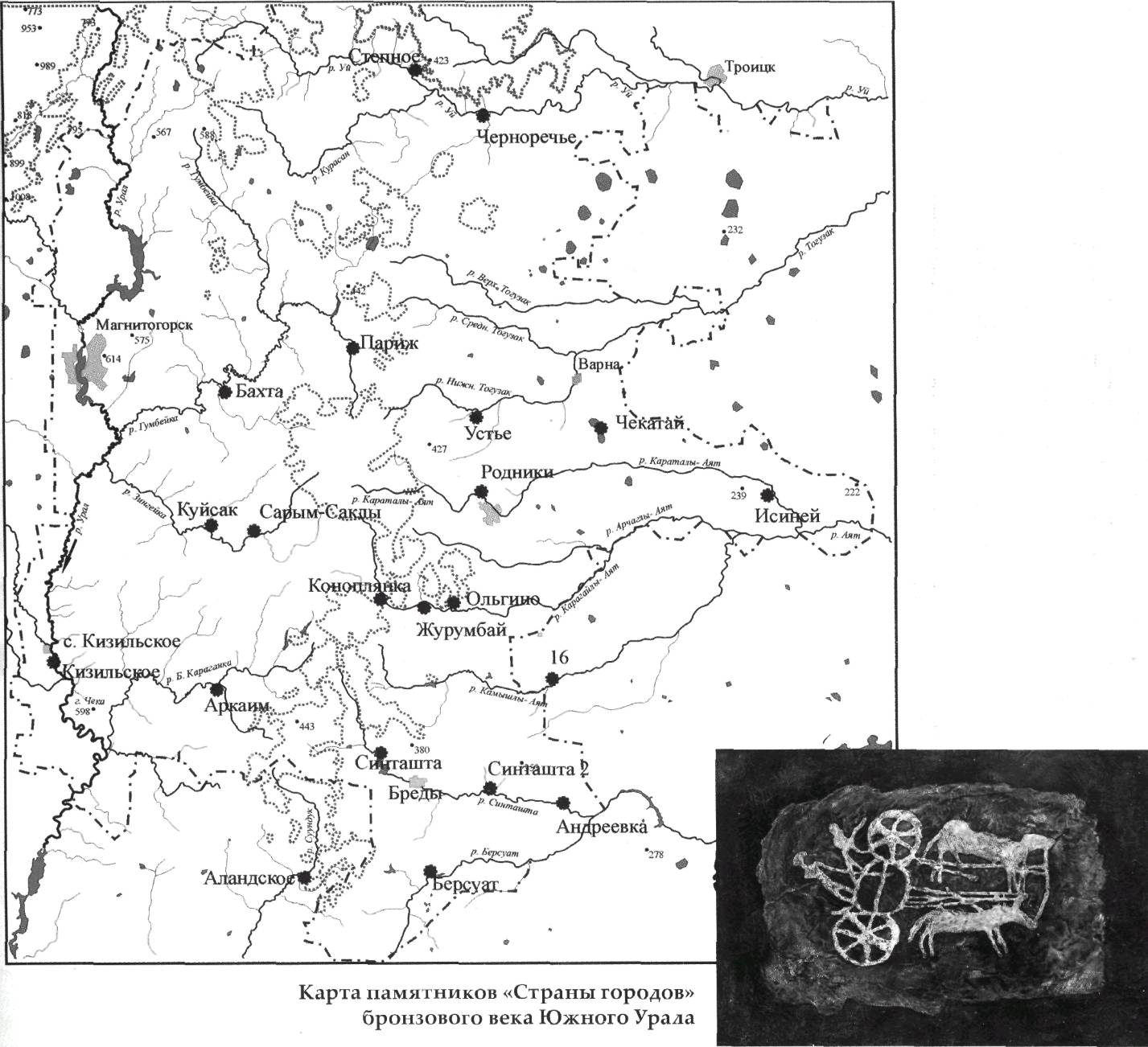
Map of the monuments of the "Country of Cities" of the Bronze Age of the Southern Urals. Chariots from the steppes of the Southern Urals. In the Southern Urals (Chelyabinsk and Orenburg regions, Bashkortostan, Northern Kazakhstan) there is a famous archaeological culture, including dozens of similar monuments of antiquity, named after the most famous settlement – the Arkaim culture (according to Arkaim in the Chelyabinsk region, 26 cities-settlements have been found at the present time in the Chelyabinsk, Orenburg regions, Bashkortostan and northern Kazakhstan). The "Country of Cities" is located in the territories of the Chelyabinsk Region, Orenburg Region, Bashkortostan of the Russian Federation and northern Kazakhstan. The settlements are scattered over an area with a diameter of 350 km . The term "Country" best characterizes this location of cities. In addition to the fact that all the cities found were built on a compact territory in the same period of time, in the same architectural style and using the same engineering solutions, similar materials, other unifying properties are also viewed. The cities of the Sintashta culture were inhabited by people of the same ethnic group (belonging to the Caucasians) and conducted similar economic activities. The age of the monuments is 3700 years old, the youngest of them. The presence of the so-called Magnetic Mountain, magnetism (modern Chelyabinsk region), apparently influenced the formation of ancient human settlements here, as well as on the territory of the modern Voronezh region in Kostenki, where the Kursk magnetic anomaly takes place. An ancient legend tells that a shepherd near the town of Magnesia in Asia Minor (now Turkey), in search of a sheep, went to the mountains where there were black stones and noticed with amazement that his stick with an iron tip stones attract to themselves, as if the stick attracts and holds an invisible hand, or maybe the hands, the shepherd took them to the city showed all residents that "magic" stones attract iron things, in addition, these same iron things attract other metals. And these stones were magnetic ironstone, which was named magnet on behalf of this city. Magnetism was known in Ancient Greece and Ancient Rome, the Chroniclers of Ancient China wrote about magnetic gates through which enemies with metal weapons could not pass. The multi-armed dancing Indian Shiva may be demonstrating a manifestation of magnetism.
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.









