 полная версия
полная версияThe Principles of Biology, Volume 1 (of 2)
For what, expressed in mechanical terms, is the effect wrought on a species by some previously-unknown enemy, that kills such of its members as fail in defending themselves? The disappearance of those individuals which meet the destroying forces by the smallest preserving forces, is tantamount to the yielding of the species as a whole at the places where the resistances are the least. Or if by some general influence, such as alteration of climate, the members of a species are subject to increase of external actions which are ever tending to overthrow their equilibria, and which they are ever counter-balancing by certain physiological actions, which are the first to die? Those least able to generate the internal energies which antagonize these external energies. If the change be an increase of the winter's cold, then such members of the species as have unusual powers of getting food or of digesting food, or such as are by their constitutional aptitude for making fat, furnished with reserve stores of force, available in times of scarcity, or such as have the thickest coats and so lose least heat by radiation, survive; and their survival implies that in each of them the moving equilibrium of functions presents such an adjustment of internal forces, as prevents overthrow by the modified aggregate of external forces. Conversely, the members which die are, other things equal, those deficient in the power of meeting the new action by an equivalent counter-action. Thus, in all cases, a species considered as an aggregate in a state of moving equilibrium, has its state changed by the yielding of its fluctuating mass wherever this mass is weakest in relation to the special forces acting on it. The conclusion is, indeed, a truism. But now what must follow from the destruction of the least-resisting individuals and survival of the most-resisting individuals? On the moving equilibrium of the species as a whole, existing from generation to generation, the effect of this deviation from the mean state is to produce a compensating deviation. For if all such as are deficient of power in a certain direction are destroyed, what must be the effect on posterity? Had they lived and left offspring, the next generation would have had the same average powers as preceding generations: there would have been a like proportion of individuals less endowed with the needful power, and individuals more endowed with it. But the more-endowed individuals being alone left to continue the race, there must result a new generation characterized by a larger average endowment of this power. That is to say, on the moving equilibrium of a species, an action producing change in a given direction is followed, in the next generation, by a reaction producing an opposite change. Observe, too, that these effects correspond in their degrees of violence. If the alteration of some external factor is so great that it leaves alive only the few individuals possessing extreme endowments of the power required to antagonize it; then, in succeeding generations, there is a rapid multiplication of individuals similarly possessing extreme endowments of this power – the force impressed calls out an equivalent conflicting force. Moreover, the change is temporary where the cause is temporary, and permanent where the cause is permanent. All that are deficient in the needful attribute having been killed off, and the survivors having the needful attribute in a comparatively high degree, there will descend from them, not only some possessing equal amounts of this attribute with themselves, but also some possessing less amounts of it. If the destructive agency has not continued in action, such less-endowed individuals will multiply; and the species, after sundry oscillations, will return to its previous mean state. But if this agency be a persistent one, such less endowed individuals will be continually killed off, and eventually none but highly-endowed individuals will be produced – a new moving equilibrium, adapted to the new environing conditions, will result.
It may be objected that this mode of expressing the facts does not include the cases in which a species becomes modified in relation to surrounding agencies of a passive kind – cases like that of a plant which acquires hooked seed-vessels, by which it lays hold of the skins of passing animals, and makes them the distributors of its seeds – cases in which the outer agency has no direct tendency at first to affect the species, but in which the species so alters itself as to take advantage of the outer agency. To cases of this kind, however, the same mode of interpretation applies on simply changing the terms. While, in the aggregate of influences amid which a species exists, there are some which tend to overthrow the moving equilibria of its members, there are others which facilitate the maintenance of their moving equilibria, and some which are capable of giving their moving equilibria increased stability: instance the spread into their habitat of some new kind of prey, which is abundant at seasons when other prey is scarce. Now what is the process by which the moving equilibrium in any species becomes adapted to some additional external factor furthering its maintenance? Instead of an increased resistance to be met and counterbalanced, there is here a diminished resistance; and the diminished resistance is equilibrated in the same way as the increased resistance. As, in the one case, there is a more frequent survival of individuals whose peculiarities enable them to resist the new adverse factor; so, in the other case, there is a more frequent survival of individuals whose peculiarities enable them to take advantage of the new favourable factor. In each member of the species, the balance of functions and correlated arrangement of structures, differ slightly from those existing in other members. To say that among all its members, one is better fitted than the rest to benefit by some before-unused agency in the environment, is to say that its moving equilibrium is, in so far, more stably adjusted to the sum of surrounding influences. And if, consequently, this individual maintains its moving equilibrium when others fail, and has offspring which do the like – that is, if individuals thus characterized multiply and supplant the rest; there is, as before, a process which effects equilibration between the organism and its environment, not immediately but mediately, through the continuous intercourse between the species as a whole and the environment.
§ 168. Thus we see that indirect equilibration does whatever direct equilibration cannot do. All these processes by which organisms are re-fitted to their ever-changing environments, must be equilibrations of one kind or other. As authority for this conclusion, we have not simply the universal truth that change of every order is towards equilibrium; but we have also the truth that life itself is a moving equilibrium between inner and outer actions – a continuous adjustment of internal relations to external relations; or the maintenance of a balance between the forces to which an organism is subject and the forces which it evolves. Hence all changes which enable a species to live under altered conditions, are changes towards equilibrium with the altered conditions; and therefore those which do not come within the class of direct equilibrations, must come within the class of indirect equilibrations.
And now we reach an interpretation of Natural Selection regarded as a part of Evolution at large. As understood in First Principles, Evolution is a continuous redistribution of matter and motion; and a process of evolution which is not expressible in terms of matter and motion has not been reduced to its ultimate form. The conception of Natural Selection is manifestly one not known to physical science: its terms are not of a kind physical science can take cognisance of. But here we have found in what manner it may be brought within the realm of physical science. Rejecting metaphor we see that the process called Natural Selection is literally a survival of the fittest; and the outcome of the above argument is that survival of the fittest is a maintenance of the moving equilibrium of the functions in presence of outer actions: implying the possession of an equilibrium which is relatively stable in contrast with the unstable equilibria of those which do not survive.
CHAPTER XIII.
THE CO-OPERATION OF THE FACTORS
§ 169. Thus the phenomena of Organic Evolution may be interpreted in the same way as the phenomena of all other Evolution. Fully to see this, it will be needful for us to contemplate in their ensemble, the several processes separately described in the four preceding chapters.
If the forces acting on any aggregate remain the same, the changes produced by them will presently reach a limit, at which the outer forces are balanced by the inner forces; and thereafter no further metamorphosis will take place. Hence, that there may be continuous changes of structure in organisms, there must be continuous changes in the incident forces. This condition to the evolution of animal and vegetal forms, we find to be fully satisfied. The astronomic, geologic, and meteorologic changes that have been slowly but incessantly going on, and have been increasing in the complexity of their combinations, have been perpetually altering the circumstances of organisms; and organisms, becoming more numerous in their kinds and higher in their kinds, have been perpetually altering one another's circumstances. Thus, for those progressive modifications upon modifications which organic evolution implies, we find a sufficient cause. The increasing inner changes for which we thus find a cause in the perpetual outer changes, conform, so far as we can trace them, to the universal law of the instability of the homogeneous. In organisms, as in all other things, the exposure of different parts to different kinds and amounts of incident forces, has necessitated their differentiation; and, for the like reason, aggregates of individuals have been lapsing into varieties, and species, and genera, and orders. Further, in each type of organism, as in the aggregate of types, the multiplication of effects has continually aided this transition from a more homogeneous to a more heterogeneous state. And yet again, that increasing segregation and concomitant increasing definiteness, associated with the growing heterogeneity of organisms, has been aided by the continual destruction of those which expose themselves to aggregates of external actions markedly incongruous with the aggregates of their internal actions, and the survival of those subject only to comparatively small incongruities. Finally, we have found that each change of structure, superposed on preceding changes, has been a re-equilibration necessitated by the disturbance of a preceding equilibrium. The maintenance of life being the maintenance of a balanced combination of functions, it follows that individuals and species that have continued to live, are individuals and species in which the balance of functions has not been overthrown. Hence survival through successive changes of conditions, implies successive adjustments of the balance to the new conditions.
The actions that are here specified in succession, are in reality simultaneous; and they must be so conceived before organic evolution can be rightly understood. Some aid towards so conceiving them will be given by the annexed table, representing the co-operation of the factors.
§ 170. Respecting this co-operation, it remains only to point out the respective shares of the factors in producing the total result; and the way in which the proportions of their respective shares vary as evolution progresses.
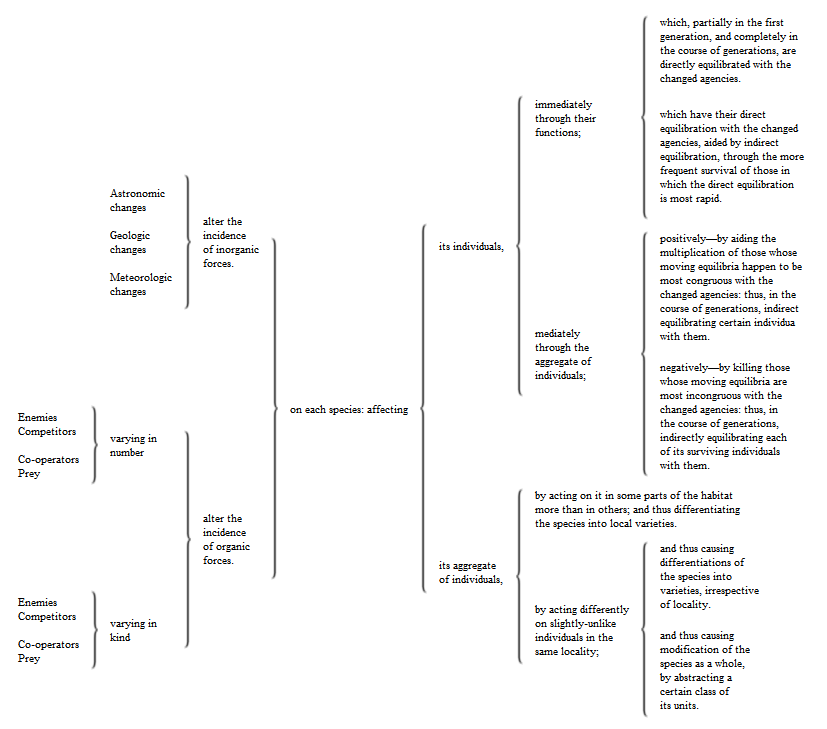
At first, changes in the amounts and combinations of inorganic forces, astronomic, geologic, and meteorologic, were the only causes of the successive modifications; and these changes have continued to be causes. But as, through the diffusion of organisms and consequent differential actions of inorganic forces, there arose unlikenesses among them, producing varieties, species, genera, orders, classes, the actions of organisms on one another became new sources of organic modifications. And as fast as types have multiplied and become more complex, so fast have the mutual actions of organisms come to be more influential factors in their respective evolutions: eventually becoming the chief factors.
Passing from the external causes of change to the internal processes of change entailed by them, we see that these, too, have varied in their proportions: that which was originally the most important and almost the sole process, becoming gradually less important, if not at last the least important. Always there must have been, and always there must continue to be, a survival of the fittest; natural selection must have been in operation at the outset, and can never cease to operate. While yet organisms had small abilities to coordinate their actions, and adjust them to environing actions, natural selection worked almost alone in moulding and remoulding organisms into fitness for their changing environments; and natural selection has remained almost the sole agency by which plants and inferior orders of animals have been modified and developed. The equilibration of organisms that are almost passive, is necessarily effected indirectly, by the action of incident forces on the species as a whole. But along with the evolution of organisms having some activity, there grows up a kind of equilibration which is in part direct. In proportion as the activity increases direct equilibration plays a more important part. Until, when the nervo-muscular apparatus becomes greatly developed, and the power of varying the actions to fit the varying requirements becomes considerable, the share taken by direct equilibration rises into co-ordinate importance or greater importance. As fast as essential faculties multiply, and as fast as the number of organs which co-operate in any given function increases, indirect equilibration through natural selection becomes less and less capable of producing specific adaptations; and remains capable only of maintaining the general fitness of constitution to conditions. The production of adaptations by direct equilibration then takes the first place: indirect equilibration serving to facilitate it. Until at length, among the civilized human races, the equilibration becomes mainly direct: the action of natural selection being limited to the destruction of those who are constitutionally too feeble to live, even with external aid. As the preservation of incapables is secured by our social arrangements; and as very few save incarcerated criminals are prevented by their inferiorities from leaving the average number of offspring; it results that survival of the fittest can scarcely at all act in such way as to produce specialities of nature, either bodily or mental. Here the specialities of nature, chiefly mental, which we see produced, and which are so rapidly produced that a few centuries show a considerable change, must be ascribed almost wholly to direct equilibration.54
CHAPTER XIV.
THE CONVERGENCE OF THE EVIDENCES
§ 171. Of the three classes of evidences that have been assigned in proof of Evolution, the à priori, which we took first, were partly negative, partly positive.
On considering the "General Aspects of the Special-creation hypothesis," we discovered it to be worthless. Discredited by its origin, and wholly without any basis of observed fact, we found that it was not even a thinkable hypothesis; and, while thus intellectually illusive, it turned out to have moral implications irreconcilable with the professed beliefs of those who hold it.
Contrariwise, the "General Aspects of the Evolution-hypothesis" begot the stronger faith in it the more nearly they were considered. By its lineage and its kindred, it was found to be as closely allied with the proved truths of modern science, as is the antagonist hypothesis with the proved errors of ancient ignorance. We saw that instead of being a mere pseud-idea, it admits of elaboration into a definite conception: so showing its legitimacy as an hypothesis. Instead of positing a purely fictitious process, the process which it alleges proves to be one actually going on around us. To which add that, morally considered, this hypothesis presents no radical incongruities.
Thus, even were we without further means of judging, there could be no rational hesitation which of the two views should be entertained.
§ 172. Further means of judging, however, we found to be afforded by bringing the two hypotheses face to face with the general truths established by naturalists. These inductive evidences were dealt with in four chapters.
"The Arguments from Classification" were these. Organisms fall into groups within groups; and this is the arrangement which we see results from evolution, where it is known to take place. Of these groups within groups, the great or primary ones are the most unlike, the sub-groups are less unlike, the sub-sub-groups still less unlike, and so on; and this, too, is a characteristic of groups demonstrably produced by evolution. Moreover, indefiniteness of equivalence among the groups is common to those which we know have been evolved, and those here supposed to have been evolved. And then there is the further significant fact, that divergent groups are allied through their lowest rather than their highest members.
Of "the Arguments from Embryology," the first is that when developing embryos are traced from their common starting point, and their divergences and re-divergences symbolized by a genealogical tree, there is manifest a general parallelism between the arrangement of its primary, secondary, and tertiary branches, and the arrangement of the divisions and sub-divisions of our classifications. Nor do the minor deviations from this general parallelism, which look like difficulties, fail, on closer observation, to furnish additional evidence; since those traits of a common ancestry which embryology reveals, are, if modifications have resulted from changed conditions, liable to be disguised in different ways and degrees in different lines of descendants.
We next considered "the Arguments from Morphology." Apart from those kinships among organisms disclosed by their developmental changes, the kinships which their adult forms show are profoundly significant. The unities of type found under such different externals, are inexplicable except as results of community of descent with non-community of modification. Again, each organism analyzed apart, shows, in the likenesses obscured by unlikenesses of its component parts, a peculiarity which can be ascribed only to the formation of a more heterogeneous organism out of a more homogeneous one. And once more, the existence of rudimentary organs, homologous with organs that are developed in allied animals or plants, while it admits of no other rational interpretation, is satisfactorily interpreted by the hypothesis of evolution.
Last of the inductive evidences, came "the Arguments from Distribution." While the facts of distribution in Space are unaccountable as results of designed adaptation of organisms to their habitats, they are accountable as results of the competition of species, and the spread of the more fit into the habitats of the less fit, followed by the changes which new conditions induce. Though the facts of distribution in Time are so fragmentary that no positive conclusion can be drawn, yet all of them are reconcilable with the hypothesis of evolution, and some of them yield it strong support: especially the near relationship existing between the living and extinct types in each great geographical area.
Thus of these four groups, each furnished several arguments which point to the same conclusion; and the conclusion pointed to by the arguments of any one group, is that pointed to by the arguments of every other group. This coincidence of coincidences would give to the induction a very high degree of probability, even were it not enforced by deduction. But the conclusion deductively reached, is in harmony with the inductive conclusion.
§ 173. Passing from the evidence that evolution has taken place, to the question – How has it taken place? we find in known agencies and known processes, adequate causes of its phenomena.
In astronomic, geologic, and meteorologic changes, ever in progress, ever combining in new and more involved ways, we have a set of inorganic factors to which all organisms are exposed; and in the varying and complicating actions of organisms on one another, we have a set of organic factors that alter with increasing rapidity. Thus, speaking generally, all members of the Earth's Flora and Fauna experience perpetual re-arrangements of external forces.
Each organic aggregate, whether considered individually or as a continuously-existing species, is modified afresh by each fresh distribution of external forces. To its pre-existing differentiations new differentiations are added; and thus that lapse to a more heterogeneous state, which would have a fixed limit were the circumstances fixed, has its limit perpetually removed by the perpetual change of the circumstances.
These modifications upon modifications which result in evolution structurally considered, are the accompaniments of those functional alterations continually required to re-equilibrate inner with outer actions. That moving equilibrium of inner actions corresponding with outer actions, which constitutes the life of an organism, must either be overthrown by a change in the outer actions, or must undergo perturbations that cannot end until there is a re-adjusted balance of functions and correlative adaptation of structures.
But where the external changes are either such as are fatal when experienced by the individuals, or such as act on the individuals in ways that do not affect the equilibrium of their functions; then the re-adjustment results through the effects produced on the species as a whole – there is indirect equilibration. By the preservation in successive generations of those whose moving equilibria are least at variance with the requirements, there is produced a changed equilibrium completely in harmony with the requirements.
§ 174. Even were this the whole of the evidence assignable for the belief that organisms have been gradually evolved, it would have a warrant higher than that of many beliefs which are regarded as established. But the evidence is far from exhausted.
At the outset it was remarked that the phenomena presented by the organic world as a whole, cannot be properly dealt with apart from the phenomena presented by each organism, in the course of its growth, development, and decay. The interpretation of either implies interpretation of the other; since the two are in reality parts of one process. Hence, the validity of any hypothesis respecting the one class of phenomena, may be tested by its congruity with phenomena of the other class. We are now about to pass to the more special phenomena of development, as displayed in the structures and functions of individual organisms. If the hypothesis that plants and animals have been progressively evolved be true, it must furnish us with keys to these phenomena. We shall find that it does this; and by doing it gives numberless additional vouchers for its truth.
CHAPTER XIVA.
RECENT CRITICISMS AND HYPOTHESES
§ 174a. Since the first edition of this work was published, and more especially since the death of Mr. Darwin, an active discussion of the Evolution hypothesis has led to some significant results.
That organic evolution has been going on from the dawn of life down to the present time, is now a belief almost universally accepted by zoologists and botanists – "almost universally," I say, because the surviving influence of Cuvier prevents acceptance of it by some of them in France. Omitting the ideas of these, all biological interpretations, speculations, and investigations, tacitly assume that organisms of every kind in every era and in every region have come into existence by the process of descent with modification.
But while concerning the fact of evolution there is agreement, concerning its causes there is disagreement. The ideas of naturalists have, in this respect, undergone a differentiation increasingly pronounced; which has ended in the production of two diametrically opposed beliefs. The cause which Mr. Darwin first made conspicuous has come to be regarded by some as the sole cause; while, on the part of others there has been a growing recognition of the cause which he at first disregarded but afterwards admitted. Prof. Weismann and his supporters contend that natural selection suffices to explain everything. Contrariwise, among many who recognize the inheritance of functionally-produced changes, there are a few, like the Rev. Prof. Henslow, who regard it as the sole factor.









