 полная версия
полная версияExpositor's Bible: The Book of Jeremiah, Chapters XXI.-LII.

Expositor's Bible: The Book of Jeremiah, Chapters XXI.-LII
PREFACE
The present work deals primarily with Jeremiah xxi. – lii., thus forming a supplement to the volume of the Expositor's Bible on Jeremiah by the Rev. C. J. Ball, M.A. References to the earlier chapters are only introduced where they are necessary to illustrate and explain the later sections.
I regret that two important works, Prof. Skinner's Ezekiel in this series, and Cornill's Jeremiah in Dr. Haupt's Sacred Books of the Old Testament, were published too late to be used in the preparation of this volume.
I have again to acknowledge my indebtedness to the Rev. T. H. Darlow, M.A., for a careful reading and much valuable criticism of my MS.
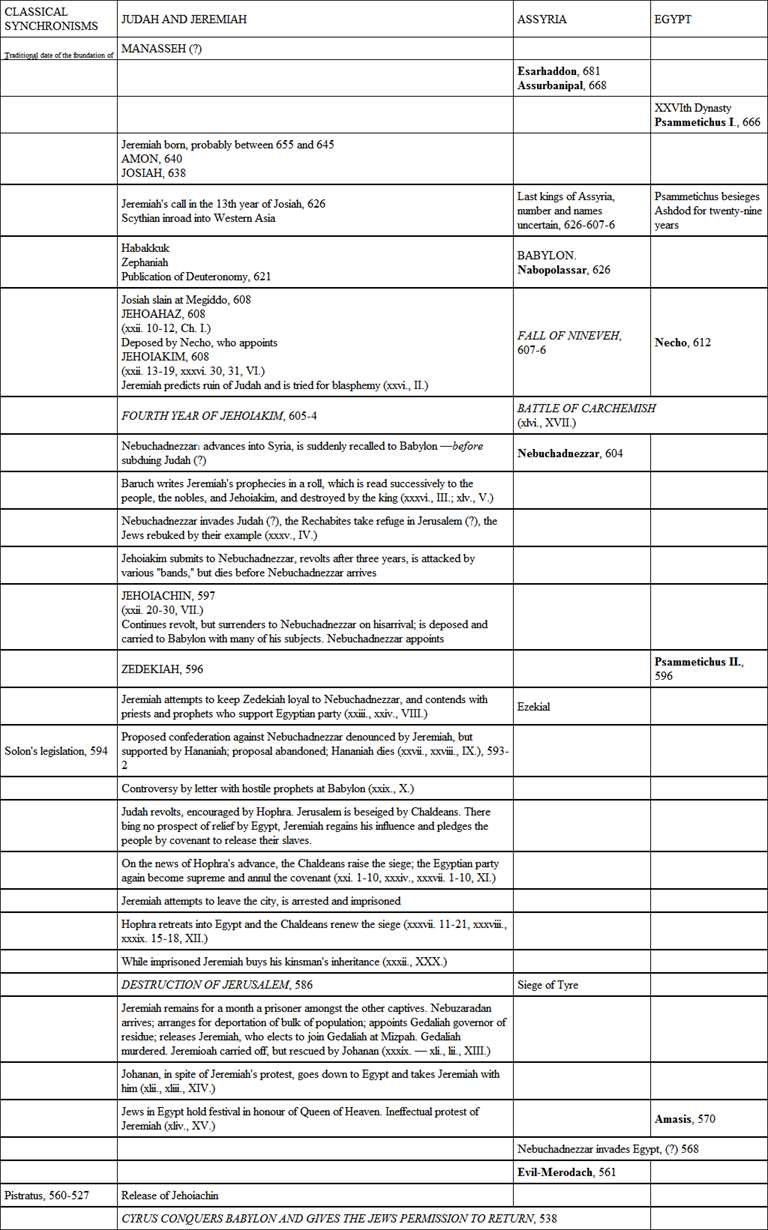
CHRONOLOGICAL TABLE
In the present stage of investigation of Old Testament Chronology, absolute accuracy cannot be claimed for such a table as the following. Hardly any, if any, of these dates are supported by a general consensus of opinion. On the other hand, the range of variation is, for the most part, not more than three or four years, and the table will furnish an approximately accurate idea of sequences and synchronisms. In other respects also the data admit of alternative interpretations, and the course of events is partly a matter of theory – hence the occasional insertion of (?).
Примечание 11
BOOK I
PERSONAL UTTERANCES AND NARRATIVES
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTORY: 2 JEHOAHAZ
xxii. 10-12"Weep ye not for the dead, neither bemoan him: but weep sore for him that goeth away: for he shall return no more." – Jer. xxii. 10As the prophecies of Jeremiah are not arranged in the order in which they were delivered, there is no absolute chronological division between the first twenty chapters and those which follow. For the most part, however, chapters xxi. – lii. fall in or after the fourth year of Jehoiakim (b. c. 605). We will therefore briefly consider the situation at Jerusalem in this crisis. The period immediately preceding b. c. 605 somewhat resembles the era of the dissolution of the Roman Empire or of the Wars of the French Revolution. An old-established international system was breaking in pieces, and men were quite uncertain what form the new order would take. For centuries the futile assaults of the Pharaohs had only served to illustrate the stability of the Assyrian supremacy in Western Asia. Then in the last two decades of the seventh century b. c. the Assyrian Empire collapsed, like the Roman Empire under Honorius and his successors. It was as if by some swift succession of disasters modern France or Germany were to become suddenly and permanently annihilated as a military power. For the moment, all the traditions and principles of European statesmanship would lose their meaning, and the shrewdest diplomatist would be entirely at fault. Men's reason would totter, their minds would lose their balance at the stupendous spectacle of so unparalleled a catastrophe. The wildest hopes would alternate with the extremity of fear; everything would seem possible to the conqueror.
Such was the situation in b. c. 605, to which our first great group of prophecies belongs. Two oppressors of Israel – Assyria and Egypt – had been struck down in rapid succession. When Nebuchadnezzar3 was suddenly recalled to Babylon by the death of his father, the Jews would readily imagine that the Divine judgment had fallen upon Chaldea and its king. Sanguine prophets announced that Jehovah was about to deliver His people from all foreign dominion, and establish the supremacy of the Kingdom of God. Court and people would be equally possessed with patriotic hope and enthusiasm. Jehoiakim, it is true, was a nominee of Pharaoh Necho; but his gratitude would be far too slight to override the hopes and aspirations natural to a Prince of the House of David.
In Hezekiah's time, there had been an Egyptian and an Assyrian party at the court of Judah; the recent supremacy of Egypt had probably increased the number of her partisans. Assyria had disappeared, but her former adherents would retain their antipathy to Egypt, and their personal feuds with Jews of the opposite faction; they were as tools lying ready to any hand that cared to use them. When Babylon succeeded Assyria in the overlordship of Asia, she doubtless inherited the allegiance of the anti-Egyptian party in the various Syrian states. Jeremiah, like Isaiah, steadily opposed any dependence upon Egypt; it was probably by his advice that Josiah undertook his ill-fated expedition against Pharaoh Necho. The partisans of Egypt would be the prophet's enemies; and though Jeremiah never became a mere dependent and agent of Nebuchadnezzar, yet the friends of Babylon would be his friends, if only because her enemies were his enemies.
We are told in 2 Kings xxiii. 37 that Jehoiakim did evil in the sight of Jehovah according to all that his father had done. Whatever other sins may be implied by this condemnation, we certainly learn that the king favoured a corrupt form of the religion of Jehovah in opposition to the purer teaching which Jeremiah inherited from Isaiah.
When we turn to Jeremiah himself, the date "the fourth year of Jehoiakim" reminds us that by this time the prophet could look back upon a long and sad experience; he had been called in the thirteenth year of Josiah, some twenty-four years before. With what sometimes seems to our limited intelligence the strange irony of Providence, this lover of peace and quietness was called to deliver a message of ruin and condemnation, a message that could not fail to be extremely offensive to most of his hearers, and to make him the object of bitter hostility.
Much of this Jeremiah must have anticipated, but there were some from whose position and character the prophet expected acceptance, even of the most unpalatable teaching of the Spirit of Jehovah. The personal vindictiveness with which priests and prophets repaid his loyalty to the Divine mission and his zeal for truth came to him with a shock of surprise and bewilderment, which was all the greater because his most determined persecutors were his sacerdotal kinsmen and neighbours at Anathoth. "Let us destroy the tree," they said, "with the fruit thereof, and let us cut him off from the land of the living, that his name may be no more remembered."4
He was not only repudiated by his clan, but also forbidden by Jehovah to seek consolation and sympathy in the closer ties of family life: "Thou shalt not take a wife, thou shalt have no sons or daughters."5 Like Paul, it was good for Jeremiah "by reason of the present distress" to deny himself these blessings. He found some compensation in the fellowship of kindred souls at Jerusalem. We can well believe that, in those early days, he was acquainted with Zephaniah, and that they were associated with Hilkiah and Shaphan and King Josiah in the publication of Deuteronomy and its recognition as the law of Israel. Later on Shaphan's son Ahikam protected Jeremiah when his life was in imminent danger.
The twelve years that intervened between Josiah's Reformation and his defeat at Megiddo were the happiest part of Jeremiah's ministry. It is not certain that any of the extant prophecies belong to this period. With Josiah on the throne and Deuteronomy accepted as the standard of the national life, the prophet felt absolved for a season from his mission to pluck up and break down, and perhaps began to indulge in hopes that the time had come to build and to plant. Yet it is difficult to believe that he had implicit confidence in the permanence of the Reformation or the influence of Deuteronomy. The silence of Isaiah and Jeremiah as to the ecclesiastical reforms of Hezekiah and Josiah stands in glaring contrast to the great importance attached to them by the Books of Kings and Chronicles. But, in any case, Jeremiah must have found life brighter and easier than in the reigns that followed. Probably, in these happier days, he was encouraged by the sympathy and devotion of disciples like Baruch and Ezekiel.
But Josiah's attempt to realise a Kingdom of God was short-lived; and, in a few months, Jeremiah saw the whole fabric swept away. The king was defeated and slain; and his religious policy was at once reversed either by a popular revolution or a court intrigue. The people of the land made Josiah's son Shallum king, under the name of Jehoahaz. This young prince of twenty-three only reigned three months, and was then deposed and carried into captivity by Pharaoh Necho; yet it is recorded of him, that he did evil in the sight of Jehovah, according to all that his fathers had done.6 He – or, more probably, his ministers, especially the queen-mother7– must have been in a hurry to undo Josiah's work. Jeremiah utters no condemnation of Jehoahaz; he merely declares that the young king will never return from his exile, and bids the people lament over his captivity as a more grievous fate than the death of Josiah: —
"Weep not for the dead,Neither lament over him:But weep sore for him that goeth into captivity;For he shall return no more,Neither shall he behold his native land."8Ezekiel adds admiration to sympathy: Jehoahaz was a young lion skilled to catch the prey, he devoured men, the nations heard of him, he was taken in their pit, and they brought him with hooks into the land of Egypt.9 Jeremiah and Ezekiel could not but feel some tenderness towards the son of Josiah; and probably they had faith in his personal character, and believed that in time he would shake off the yoke of evil counsellors and follow in his father's footsteps. But any such hopes were promptly disappointed by Pharaoh Necho, and Jeremiah's spirit bowed beneath a new burden as he saw his country completely subservient to the dreaded influence of Egypt.
Thus, at the time when we take up the narrative, the government was in the hands of the party hostile to Jeremiah, and the king, Jehoiakim, seems to have been his personal enemy. Jeremiah himself was somewhere between forty and fifty years old, a solitary man without wife or child. His awful mission as the herald of ruin clouded his spirit with inevitable gloom. Men resented the stern sadness of his words and looks, and turned from him with aversion and dislike. His unpopularity had made him somewhat harsh; for intolerance is twice curst, in that it inoculates its victims with the virus of its own bitterness. His hopes and illusions lay behind him; he could only watch with melancholy pity the eager excitement of these stirring times. If he came across some group busily discussing the rout of the Egyptians at Carchemish, or the report that Nebuchadnezzar was posting in hot haste to Babylon, and wondering as to all that this might mean for Judah, his countrymen would turn to look with contemptuous curiosity at the bitter, disappointed man who had had his chance and failed, and now grudged them their prospect of renewed happiness and prosperity. Nevertheless Jeremiah's greatest work still lay before him. Jerusalem was past saving; but more was at stake than the existence of Judah and its capital. But for Jeremiah the religion of Jehovah might have perished with His Chosen People. It was his mission to save Revelation from the wreck of Israel. Humanly speaking, the religious future of the world depended upon this stern solitary prophet.
CHAPTER II
A TRIAL FOR HERESY
xxvi.: cf. vii. – x"When Jeremiah had made an end of speaking all that Jehovah had commanded him to speak unto all the people, the priests and the prophets and all the people laid hold on him, saying, Thou shalt surely die." – Jer. xxvi. 8The date of this incident is given, somewhat vaguely, as the beginning of the reign of Jehoiakim. It was, therefore, earlier than b. c. 605, the point reached in the previous chapter. Jeremiah could offer no political resistance to Jehoiakim and his Egyptian suzerain; yet it was impossible for him to allow Josiah's policy to be reversed without a protest. Moreover, something, perhaps much, might yet be saved for Jehovah. The king, with his court and prophets and priests, was not everything. Jeremiah was only concerned with sanctuaries, ritual, and priesthoods as means to an end. For him the most important result of the work he had shared with Josiah was a pure and holy life for the nation and individuals. Renan – in some passages, for he is not always consistent – is inclined to minimise the significance of the change from Josiah to Jehoiakim; in fact, he writes very much as a cavalier might have done of the change from Cromwell to Charles II. Both the Jewish kings worshipped Jehovah, each in his own fashion: Josiah was inclined to a narrow puritan severity of a life; Jehoiakim was a liberal, practical man of the world. Probably this is a fair modern equivalent of the current estimate of the kings and their policy, especially on the part of Jehoiakim's friends; but then, as unhappily still in some quarters, "narrow puritan severity" was a convenient designation for a decent and honourable life, for a scrupulous and self-denying care for the welfare of others. Jeremiah dreaded a relapse into the old half-heathen ideas that Jehovah would be pleased with homage and service that satisfied Baal, Moloch, and Chemosh. Such a relapse would lower the ethical standard, and corrupt or even destroy any beginnings of spiritual life. Our English Restoration is an object-lesson as to the immoral effects of political and ecclesiastical reaction; if such things were done in sober England, what must have been possible to hot Eastern blood! In protesting against the attitude of Jehoiakim, Jeremiah would also seek to save the people from the evil effects of the king's policy. He knew from his own experience that a subject might trust and serve God with his whole heart, even when the king was false to Jehovah. What was possible for him was possible for others. He understood his countrymen too well to expect that the nation would continue to advance in paths of righteousness which its leaders and teachers had forsaken; but, scattered here and there through the mass of the people, was Isaiah's remnant, the seed of the New Israel, men and women to whom the Revelation of Jehovah had been the beginning of a higher life. He would not leave them without a word of counsel and encouragement.
At the command of Jehovah, Jeremiah appeared before the concourse of Jews, assembled at the Temple for some great fast or festival. No feast is expressly mentioned, but he is charged to address "all the cities of Judah"10; all the outlying population would only meet at the Temple on some specially holy day. Such an occasion would naturally be chosen by Jeremiah for his deliverance, just as Christ availed Himself of the opportunities offered by the Passover and the Feast of Tabernacles, just as modern philanthropists seek to find a place for their favourite topics on the platform of May Meetings.
The prophet was to stand in the court of the Temple and repeat once more to the Jews his message of warning and judgment, "all that I have charged thee to speak unto them, thou shalt not keep back a single word." The substance of this address is found in the various prophecies which expose the sin and predict the ruin of Judah. They have been dealt with in the former volume11 on Jeremiah in this series, and are also referred to in Book III.
According to the universal principle of Hebrew prophecy, the predictions of ruin were conditional; they were still coupled with the offer of pardon to repentance, and Jehovah did not forbid his prophet to cherish a lingering hope that "perchance they may hearken and turn every one from his evil way, so that I may repent Me of the evil I purpose to inflict upon them because of the evil of their doings." Probably the phrase "every one from his evil way" is primarily collective rather than individual, and is intended to describe a national reformation, which would embrace all the individual citizens; but the actual words suggest another truth, which must also have been in Jeremiah's mind. The nation is, after all, an aggregate of men and women; there can be no national reformation, except through the repentance and amendment of individuals.
Jeremiah's audience, it must be observed, consisted of worshippers on the way to the Temple, and would correspond to an ordinary congregation of church-goers, rather than to the casual crowd gathered round a street preacher, or to the throngs of miners and labourers who listened to Whitfield and Wesley. As an acknowledged prophet, he was well within his rights in expecting a hearing from the attendants at the feast, and men would be curious to see and hear one who had been the dominant influence in Judah during the reign of Josiah. Moreover, in the absence of evening newspapers and shop-windows, a prophet was too exciting a distraction to be lightly neglected. From Jehovah's charge to speak all that He had commanded him to speak and not to keep back a word, we may assume that Jeremiah's discourse was long: it was also avowedly an old sermon12; most of his audience had heard it before, all of them were quite familiar with its main topics. They listened in the various moods of a modern congregation "sitting under" a distinguished preacher. Jeremiah's friends and disciples welcomed the ideas and phrases that had become part of their spiritual life. Many enjoyed the speaker's earnestness and eloquence, without troubling themselves about the ideas at all. There was nothing specially startling about the well-known threats and warnings; they had become
"A tale of little meaning tho' the words were strong."
Men hardened their hearts against inspired prophets as easily as they do against the most pathetic appeals of modern evangelists. Mingled with the crowd were Jeremiah's professional rivals, who detested both him and his teaching – priests who regarded him as a traitor to his own caste, prophets who envied his superior gifts and his force of passionate feeling. To these almost every word he uttered was offensive, but for a while there was nothing that roused them to very vehement anger. He was allowed to finish what he had to say, "to make an end of speaking all that Jehovah had commanded him." But in this peroration he had insisted on a subject that stung the indifferent into resentment and roused the priests and prophets to fury.
"Go ye now unto My place which was in Shiloh, where I caused My name to dwell at the first, and see what I did to it for the wickedness of My people Israel. And now, because ye have done all these works, saith Jehovah, and I spake unto you, rising up early and speaking, but ye heard not; and I called you, but ye answered not: therefore will I do unto the house, that is called by My name, wherein ye trust, and unto the place which I gave to you and to your fathers, as I have done to Shiloh."13
The Ephraimite sanctuary of Shiloh, long the home of the Ark and its priesthood, had been overthrown in some national catastrophe. Apparently when it was destroyed it was no mere tent, but a substantial building of stone, and its ruins remained as a permanent monument of the fugitive glory of even the most sacred shrine.
The very presence of his audience in the place where they were met showed their reverence for the Temple: the priests were naturally devotees of their own shrine; of the prophets Jeremiah himself had said, "The prophets prophesy falsely, and the priests rule in accordance with their teaching."14 Can we wonder that "the priests and the prophets and all the people laid hold on him, saying, Thou shalt surely die"? For the moment there was an appearance of religious unity in Jerusalem; the priests, the prophets, and the pious laity on one side, and only the solitary heretic on the other. It was, though on a small scale, as if the obnoxious teaching of some nineteenth-century prophet of God had given an unexpected stimulus to the movement for Christian reunion; as if cardinals and bishops, chairmen of unions, presidents of conferences, moderators of assemblies, with great preachers and distinguished laymen, united to hold monster meetings and denounce the Divine message as heresy and blasphemy. In like manner Pharisees, Sadducees, and Herodians found a basis of common action in their hatred of Christ, and Pilate and Herod were reconciled by His cross.
Meanwhile the crowd was increasing: new worshippers were arriving, and others as they left the Temple were attracted to the scene of the disturbance. Doubtless too the mob, always at the service of persecutors, hurried up in hope of finding opportunities for mischief and violence. Some six and a half centuries later, history repeated itself on the same spot, when the Asiatic Jews saw Paul in the Temple and "laid hands on him, crying out, Men of Israel, help: This is the man, that teacheth all men everywhere against the people and the law and this place, … and all the city was moved, and the people ran together and laid hold on Paul."15
Our narrative, as it stands, is apparently incomplete: we find Jeremiah before the tribunal of the princes, but we are not told how he came there; whether the civil authorities intervened to protect him, as Claudius Lysias came down with his soldiers and centurions and rescued Paul, or whether Jeremiah's enemies observed legal forms, as Annas and Caiaphas did when they arrested Christ. But, in any case, "the princes of Judah, when they heard these things, came up from the palace into the Temple, and took their seats as judges at the entry of the new gate of the Temple." The "princes of Judah" play a conspicuous part in the last period of the Jewish monarchy: we have little definite information about them, and are left to conjecture that they were an aristocratic oligarchy or an official clique, or both; but it is clear that they were a dominant force in the state, with recognised constitutional status, and that they often controlled the king himself. We are also ignorant as to the "new gate"; it may possibly be the upper gate built by Jotham16 about a hundred and fifty years earlier.
Before these judges, Jeremiah's ecclesiastical accusers brought a formal charge; they said, almost in the very words which the high priest and the Sanhedrin used of Christ, "This man is worthy of death, for he hath prophesied against this city, as ye have heard with your ears" —i. e. when he said, "This house shall be like Shiloh, and this city shall be desolate without inhabitant." Such accusations have been always on the lips of those who have denounced Christ and His disciples as heretics. One charge against Himself was that He said, "I will destroy this Temple that is made with hands, and in three days I will build another that is made without hands."17 Stephen was accused of speaking incessantly against the Temple and the Law, and teaching that Jesus of Nazareth would destroy the Temple and change the customs handed down from Moses. When he asserted that "the Most High dwelleth not in temples made with hands," the impatience of his audience compelled him to bring his defence to an abrupt conclusion.18 Of Paul we have already spoken.
How was it that these priests and prophets thought that their princes might be induced to condemn Jeremiah to death for predicting the destruction of the Temple? A prophet would not run much risk nowadays by announcing that St. Paul's should be made like Stonehenge, or St. Peter's like the Parthenon. Expositors of Daniel and the Apocalypse habitually fix the end of the world a few years in advance of the date at which they write, and yet they do not incur any appreciable unpopularity. It is true that Jeremiah's accusers were a little afraid that his predictions might be fulfilled, and the most bitter persecutors are those who have a lurking dread that their victims are right, while they themselves are wrong. But such fears could not very well be evidence or argument against Jeremiah before any court of law.
In order to realise the situation we must consider the place which the Temple held in the hopes and affections of the Jews. They had always been proud of their royal sanctuary at Jerusalem, but within the last hundred and fifty years it had acquired a unique importance for the religion of Israel. First Hezekiah, and then Josiah, had taken away the other high places and altars at which Jehovah was worshipped, and had said to Judah and Jerusalem, "Ye shall worship before this altar."19 Doubtless the kings were following the advice of Isaiah and Jeremiah. These prophets were anxious to abolish the abuses of the local sanctuaries, which were a continual incentive to an extravagant and corrupt ritual. Yet they did not intend to assign any supreme importance to a priestly caste or a consecrated building. Certainly for them the hope of Israel and the assurance of its salvation did not consist in cedar and hewn stones, in silver and gold. And yet the unique position given to the Temple inevitably became the starting-point for fresh superstition. Once Jehovah could be worshipped not only at Jerusalem, but at Beersheba and Bethel and many other places where He had chosen to set His name. Even then, it was felt that the Divine Presence must afford some protection for His dwelling-places. But now that Jehovah dwelt nowhere else but at Jerusalem, and only accepted the worship of His people at this single shrine, how could any one doubt that He would protect His Temple and His Holy City against all enemies, even the most formidable? Had He not done so already?


