 полная версия
полная версияWoman under socialism
An Austrian nobleman also, Karl Freiherr v. M – of Goeding in Moravia, seized the opportunity to angle for a rich American bride, and to this end sent to the swindle-bureau the following letter:
"According to a notice in the papers of this place, you are acquainted with American ladies who wish to marry. In this connection I place myself at your service, but must inform you that I have no fortune whatever. I am of very old noble stock (Baron), 34 years old, single, was a cavalry officer and am at present engaged in building railroads. I should be pleased to inspect one or more pictures, which, upon my word of honor, I shall return. Should you require my picture, I shall forward same to you. I also request you to give me fuller information. Expecting a speedy answer in this matter, I remain, very respectfully, your Karl Freiherr v. M – , Goeding, Moravia, Austria, November 29, 1889."
A young German nobleman, Hans v. H – , wrote from London that he was 5 feet 10 tall, of an old noble family, and employed in the diplomatic service. He made the confession that his fortune had been greatly reduced through unsuccessful betting at the horse races, and hence found himself obliged to be on the lookout for a rich bride, so as to be able to cover his deficit. He was, furthermore, ready to undertake a trip to the United States forthwith.
The chevalier d'industry in question claimed that, besides several counts, barons, etc., three Princes and sixteen dukes had reported to him as candidates for marriage. But not noblemen only, bourgeois also longed for rich American women. An architect, Max W – of Leipsic, demanded a bride who should possess not only money, but beauty and culture also. From Kehl on the Rhine, a young mill-owner, Robert D – , wrote that he would be satisfied with a bride who had but 400,000 marks, and he promised in advance to make her happy.
But why look so far, when at hand the quarry is rich! A very patriotic-conservative Leipsic paper, which plumes itself very particularly upon its Christianity, contained in the spring of 1894 an advertisement, that ran thus: "A cavalry officer of the Guards, of large, handsome build, noble, 27 years of age, desires a financial marriage. Please address, Count v. W. I., Post Office General Delivery, Dresden." In comparison with the fellow who makes so cynical an offer, the street-walker, who, out of bitter necessity, plies her trade, is a paragon of decency and virtue. Similar advertisements are found almost every day in the papers of all political parties —except the Social Democratic. A Social Democratic editor or manager, who would accept such or similar advertisements for his paper, would be expelled from his party as dishonorable. The capitalist press is not troubled at such advertisements: they bring in money: and it is of the mind of the Emperor Vespasian, —non olet, it does not smell. Yet all that does not hinder that same press from going rabid mad at "the marriage-undermining tendencies of Socialism." Never yet was there an age more hypocritical than the one we are living in. With the view to demonstrate the fact once more, the above instances were cited.
Bureaus of information for marriage, – that's what the advertisement pages of most of the newspapers of our day are. Whosoever, be it male or female, finds near at hand nothing desirable, entrusts his or her heart's wants to the pious-conservative or moral-liberal press, that, in consideration of cash and without coaxing, sees to it that the kindred souls meet. With illustrations, taken on any one day from a number of large newspapers, whole pages, could be filled. Off and on the interesting fact also crops out that even clergymen are sought for husbands, and, vice versa, clergymen angle for wives, with the aid of advertisements. Occasionally, the suitors also offer to overlook a slip, provided the looked-for woman be rich. In short, the moral turpitude of certain social circles of our society can be pilloried no better than by this sort of courtship.
State and Church play in such "holy matrimony" a by no means handsome role. Whether the civil magistrate or clergyman, on whom may devolve the duty to celebrate the marriage, be convinced that the bridal couple before him has been brought together by the vilest of practices; whether it be manifest that, neither in point of age nor that of bodily or mental qualities, the two are compatible with each other; whether, for instance, the bride be twenty and the bridegroom seventy years old, or the reverse; whether the bride be young, handsome and joyful, and the bridegroom old, ridden with disease and crabbed; – whatever the case, it concerns not the representative of the State or the Church; it is not for them to look into that. The marriage bond is "blessed," – as a rule, blessed with all the greater solemnity in proportion to the size of the fee for the "holy office."
When, later, such a marriage proves a most unfortunate one – as foreseen by everybody, by the ill-starred victim, in most instances the woman, herself, – and either party decides to separate, then, State and Church, – who never first inquire whether real love and natural, moral impulses, or only naked, obscene egotism tie the knot – now raise the greatest difficulties. At present, moral repulsion is but rarely recognized a sufficient ground for separation; at present, only palpable proofs, proofs that always dishonor or lower one of the parties in public esteem, are, as a rule, demanded; separation is not otherwise granted. That the Roman Catholic Church does not allow divorces, – except by special dispensation of the Pope, which is hard to obtain, and, at best, only from board and bed – only renders all the worse the conditions, under which all Catholic countries are suffering. Germany has the prospect of receiving, in the not too far distant future, a civil code that shall embrace the whole Empire. It is, therefore, a side-light upon our times that, although even the superficial observer must reach the conclusion that at no previous period have unhappy marriages been so numerous as now – a natural consequence of our whole social development – the new draft for a civil code still renders divorce materially difficult. It is but a fresh instance of the old experience, – a social system, in the throes of dissolution, seeks to keep itself up by artificial means and compulsion, and to deceive itself upon its actual state. In declining Rome, marriage and births were sought to be promoted by premiums: in the German Empire, whose social order stands under a constellation similar with that of the decaying Empire of the Caesars, it is now sought to prevent the ever more frequent desire for the dissolution of marriage by means of forcible constraints.
Thus people remain against their will chained to each other through life. One party becomes the slave of the other, compelled to submit out of "conjugal duty" to that other's most intimate embraces, which, perhaps, it abhors worse than insult or ill-treatment. Fully justified is Montegazza's dictum:71 "There is probably no worse torture than that which compels a human being to put up with the caresses of a person it does not love."
We ask, Is such a marriage – and their number is infinite – not worse than prostitution? The prostitute has, to a certain degree, the freedom to withdraw from her disgraceful pursuit; moreover, she enjoys the privilege, if she does not live in a public house, to reject the purchase of the embraces of him who, for whatever reason, may be distasteful to her. But a sold married woman must submit to the embraces of her husband, even though she have a hundred reasons to hate and despise him.
When in advance, and with the knowledge of both parties, marriage is contracted as a marriage for money or rank, then, as a rule, matters lie more favorably. The two accommodate themselves mutually, and a modus vivendi is established. They want no scandal, and regard for their children compels them to avoid any, although it is the children who suffer most under a cold, loveless life on the part of their parents, even if such a life does not develop into enmity, quarrel and dissension. Often accommodation is reached in order to avoid material loss. As a rule it is the husband, whose conduct is the rock against which marriage is dashed. This appears from the actions for divorce. In virtue of his dominant position, he can indemnify himself elsewhere when the marriage is not pleasing to him, and he can not find satisfaction in it. The wife is not so free to step on side-roads, partly because, as the receiving sex, such action is, for physiologic reasons, a much more risky one on her part; then, also, because every infraction of conjugal fidelity is imputed a crime to her, which neither the husband nor society pardons. Woman alone makes a "slip" – be she wife, widow or maid; man, at worst, has acted "incorrectly." One and the same act is judged by society with wholly different standards, according as it be committed by a man or a woman. And, as a rule, women themselves judge a "fallen" sister most severely and pitilessly.72
As a rule, only in cases of crassest infidelity or maltreatment, does the wife decide upon divorce. She is generally in a materially dependent position, and compelled to look upon marriage as a means of support: moreover, as a divorced wife, she finds herself socially in no enviable situation: unless special reasons render intercourse with her desirable, she is considered and treated by society as a neuter, so to speak. When, despite all this, most actions for divorce proceed from wives, the circumstance is an evidence of the heavy moral torture that they lie under. In France, even before the new divorce law came into effect (1884), by far the more numerous actions for separation from bed and board came from women. For an absolute divorce they could apply only if the husband took his concubine into the married home, against the will of his wife. Actions for separations from bed and board occurred:73:
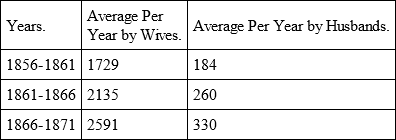
But not only did women institute by far the larger number of actions; the figures show that these increased from period to period. Furthermore, so far as reliable information before us goes, it appears that actions for absolute divorce also proceed preponderatingly from wives. In the Kingdom of Saxony, during the period of 1860-1868, there were instituted, all told, 8,402 actions for divorce; of these, 3,537 (42 per cent.) were by men, 4,865 (58 per cent.) by wives.
In the period from 1871 to 1878, there were actions for divorce in Saxony74:
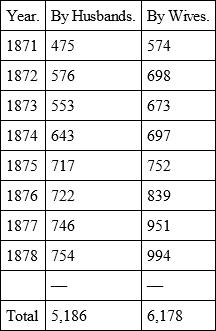
The fact that divorce, as a rule, hurts women more, did not restrain them in Saxony either from instituting most of the actions. The total actions for divorce increased, however, in Saxony, as in France, much faster than population. In Switzerland, during the year 1892, there were granted 1,036 applications for divorce. Of these, wives had instituted 493, husbands 229, and both parties 314.
Statistics teach us, however, not alone that wives institute the larger number of actions for divorce; they also teach us that the number of divorces is in rapid increase. In France, divorce has been regulated anew by law since 1884. Since then, divorces have greatly increased from year to year. The number of divorces, and years they fell in, were as follows:
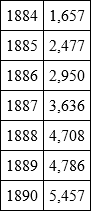
In Vienna there were, from 1870 to 1871, 148 divorces; they increased from year to year; from 1878 to 1879 they ran up to 319 cases.75 But in Vienna, being a preponderatingly Catholic city, divorce is hard to obtain. That notwithstanding, about the year 1885 a Vienna Judge made the remark: "Complaints on the ground of broken marriage vows are as frequent as complaints for broken window-panes." In England and Wales there was, in 1867, 1 divorce to every 1,378 marriages, but in 1877 there was 1 to every 652 marriages; and in 1886, 1 to as few as 527. In the United States the number of divorces for 1867 was 9,937, and for 1886 as many as 25,535. The total number of divorces in the United States between 1867 and 1886 was 328,716, and the fault fell in 216,176 cases upon the husband, in 112,540 upon the wife.
Relatively speaking, the largest number of divorces occurs in the United States. The proportion between marriages and divorces during the period of 1867 to 1886 stood for those States in which an accurate record is kept:
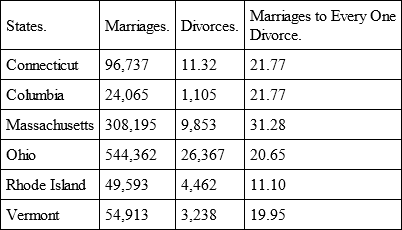
In the other States of the Union, from which less accurate returns are at hand, the proportion seems to be the same. The reasons why in the United States divorces are more frequent than in any other country, may be sought in the circumstance, first, that divorce is there more easily obtained than elsewhere; secondly, that women occupy in the United States a far freer position than in any other country, hence are less inclined to allow themselves to be tyrannised by their marital lords.76
In Germany there was, by judicial decision, 1 dissolution of marriage —
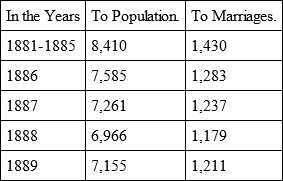
According to Dr. S. Wernicke, there were to every 1,000 marriages, divorces in:
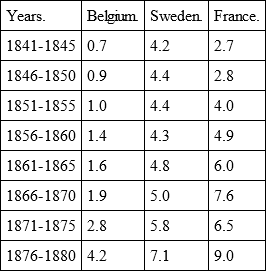
It would be an error to attempt to arrive at any conclusion touching the different conditions of morality, by deductions from the large discrepancy between the figures for the different countries cited above. No one will dare assert that the population of Sweden has more inclination or cause for divorce than that of Belgium. First of all must the legislation on the subject be kept in mind, which in one country makes divorce difficult, in another easier, more so in some, less in others. Only in the second instance does the condition of morality come into consideration, i. e., the average reasons that, now the husbands, then the wives, consider determining factors in applying for separation. But all these figures combine in establishing that divorces increase much faster than population; and that they increase while marriages decline. About this, more later.
On the question how the actions for divorce distribute themselves among the several strata of society, there is only one computation at our disposal, from Saxony, but which is from the year 1851.77 At that time, to each 100,000 marriages, there were actions for divorce from the stratum of
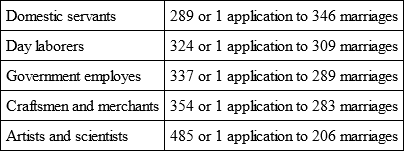
Accordingly, the actions for divorce were at that period in Saxony 50 per cent. more frequent in the higher than in the lower social strata.
The increasing number of divorces signifies that, in general, the marriage relations are becoming ever more unfavorable, and that the factors multiply which destroy marriage. On the other hand, they also furnish evidence that an ever larger number of spouses, women in particular, decide to shake off the unbearable oppressing yoke.
But the evils of matrimony increase, and the corruption of marriage gains ground in the same measure as the struggle for existence waxes sharper, and marriage becomes ever more a money-match, or be it, marriage by purchase. The increasing difficulty, moreover, of supporting a family determines many to renounce marriage altogether; and thus the saying that woman's activity should be limited to the house, and that she should fill her calling as housewife and mother, becomes ever more a senseless phrase. On the other hand, the conditions can not choose but favor the gratification of sexual intercourse outside of wedlock. Hence the number of prostitutes increases, while the number of marriages decreases. Besides that, the number increases of those who suffer from unnatural gratification of the sexual instinct.
Among the property classes, not infrequently the wife sinks, just as in old Greece, to the level of a mere apparatus for the procreation of legitimate offspring, of warder of the house, or of nurse to a husband, wrecked by debauchery. The husbands keep for their pleasure and physical desires hetairae – styled among us courtesans or mistresses – who live in elegant abodes, in the handsomest quarters of the city. Others, whose means do not allow them to keep mistresses, disport themselves, after marriage as before, with Phrynes, for whom their hearts beat stronger than for their own wives. With the Phrynes they amuse themselves; and quite a number of the husbands among the "property and cultured classes" is so corrupt that it considers these entertainments in order.78
In the upper and middle classes of society, the money matches and matches for social position are the mainspring of the evils of married life; but, over and above that, marriage is made rank by the lives these classes lead. This holds good particularly with regard to the women, who frequently give themselves over to idleness or to corrupting pursuits. Their intellectual food often consists in the reading of equivocal romances and obscene literature, in seeing and hearing frivolous theatrical performances, and the fruition of sensuous music; in exhilarating nervous stimulants; in conversations on the pettiest subjects, or scandals about the dear fellow mortals. Along therewith, they rush from one enjoyment into another, from one banquet to another, and hasten in summer to the baths and summer retreats to recover from the excesses of the winter, and to find fresh subjects for talk. The chronique scandaleuse recruits itself from this style of life: people seduce and are seduced.
In the lower classes money-matches are unknown, as a rule, although they occasionally do play a role. No one can wholly withdraw himself from the influence of the society he lives in, – and the existing social conditions exercise a particularly depressing influence upon the circumstances of the lower classes. As a rule, the workingman weds out of inclination, but there is no lack of causes to disturb his marriage. A rich blessing of children brings on cares and troubles; but too often want sets in. Sickness and death are frequent guests in the workingman's family. Lack of work drives misery to its height. Many a circumstance pares off the worker's earnings, or temporarily robs him wholly of it. Commercial and industrial crises throw him out of work; the introduction of new machinery, or methods of work, casts him as superfluous on the sidewalk; wars, unfavorable tariffs and commercial treaties, the introduction of the new indirect taxes, disciplinary acts on the part of the employer in punishment for the exercise of his convictions, etc., destroy his existence, or seriously injure it. Now one thing, then another happens, whereby, sometimes for a shorter, sometimes for a longer period, he becomes an unemployed, i. e., a starving being. Uncertainty is the badge of his existence. When such blows of fortune happen, they at first produce dissatisfaction and bitterness, and in the home life this mood finds its first expression when daily, every hour, demands are made by wife and children for the most pressing needs, needs that the husband can not satisfy. Out of despair, he visits the saloon, and seeks comfort in bad liquor. The last penny is spent. Quarrel and dissension break out. The ruin of both marriage and the family is accomplished.
Let us take up another picture. Both – husband and wife – go to work. The little ones are left to themselves, or to the care of older brothers and sisters, themselves in need of care and education. At noon, the so-called lunch is swallowed down in hot haste, – supposing that the parents have at all time to rush home, which, in thousands of cases is impossible, owing to the shortness of the hour of recess, and the distance of the shop from the home. Tired out and unstrung, both return home in the evening. Instead of a friendly, cheerful home, they find a narrow, unhealthy habitation, often lacking in light and air, generally also in the most necessary comforts. The increasing tenement plague, together with the horrible improprieties that flow therefrom, is one of the darkest sides of our social order, and leads to numerous evils, vices and crimes. Yet the plague increases from year to year in all cities and industrial regions, and it draws within the vortex of its evils ever new strata of society: small producers, public employes, teachers, small traders, etc. The workingman's wife, who reaches home in the evening tired and harassed, has now again her hands full. She must bestir herself at breakneck speed in order but to get ready the most necessary things in the household. The crying and noisy children are hurried off to bed; the wife sits up, and sews, and patches deep into the night. The so-much-needed mental intercourse and encouragement are absent. The husband is often uneducated and knows little, the wife still less; the little they have to say to each other is soon got through with. The husband goes to the saloon, and seeks there the entertainment that he lacks at home; he drinks; however little that be that he spends, for his means it is too much. At times he falls a prey to gambling, which, in the upper circles of society also, claims many victims, and he loses more than he spends in drink. The wife, in the meantime, sits at home and grumbles; she must work like a dray-horse; for her there is no rest or recreation; the husband avails himself of the freedom that accident gives him, of having been born a man. Thus disharmony arises. If, however, the wife is less true to duty, she seeks in the evening, after she has returned home tired, the rest she is entitled to; but then the household goes back, and misery is twice as great. Indeed, we live "in the best world possible."
Through these and similar circumstances, marriage is shattered ever more among the working class also. Even favorable seasons of work exert their destructive influence: they compel him to work Sundays and overtime: they take from him the hours he still had left for his family. In many instances he has to travel hours to reach the shop; to utilize the noon recess for going home is an impossibility; he is up in the morning at the very earliest, when the children are still sound asleep, and returns home late, when they are again in the same condition. Thousands, especially those engaged in the building trades in the cities, remain away from home all week, owing to the vastness of the distance, and return only on Saturdays to their family. And yet it is expected of family life that it thrive under such circumstances. Moreover, female labor is ever on the increase, especially in the textile industry, whose thousands of steam weaving and spinning looms are served by cheap woman and children's hands. Here the relations of sex and age have been reversed. Wife and child go into the mill, the now breadless husband sits at home and attends to household duties. In the United States, that, due to its rapid large-capitalist development, produces all the evils of European industrial States in much larger dimensions, a characteristic name has been invented for the state of things brought on by such conditions. Industrial places that employ women mainly, while the husbands sit at home, are called "she-towns."
The admission of women to all the manual trades is to-day conceded on all hands. Capitalist society, ever on the hunt for profit and gain, has long since recognized what an excellent subject for exploitation is woman – more docile and submissive, and less exacting woman – in comparison with man. Hence the number of trades and occupations, in which women are finding employment increases yearly. The extension and improvement of machinery, the simplification of the process of production through the ever minuter subdivision of labor, the intenser competition of capitalists among themselves, together with the competitive battle in the world's market among rival industrial countries, – all these continue to favor the ever further application of female labor. It is a phenomenon noticeable in all industrial countries alike. But in the same measure that the number of working-women increases, competition among the workingmen is thereby intensified. One branch of industry after another, one branch of work after the other, is being taken by working-women, who are ever more displacing the men. Numerous passages in the reports of factory inspectors, as well as in the statistical figures on the occupation of working-women, go to confirm the fact.



