 полная версия
полная версияObservations on the Present State of the Affairs of the River Plate
Pastoral countries, such as the territory of Uruguay, New South Wales, Van Dieman's Land, and South Africa, have this great advantage over arable countries that their resources can be developed much more rapidly, with a much smaller amount of labour, and with much less capital. This is one of the causes of the sudden rise of the trade with Australia, and it is also a considerable cause of the rapid development of the prosperity of Monte Video. Its power of producing hides, wool, tallow, and provisions is unlimited, by any thing except the deficient numbers of its population; and whilst on this subject, I may mention that Monte Video is the only one of all the Republics formed out of the ancient possessions of Spain which has been sufficiently well governed to attract to its shores any considerable number of emigrants from Europe. It will be seen from the following table extracted from the books of the Custom House at Monte Video, that not less than 33,607 emigrants arrived in that port between November, 1835, and December, 1842: —
Table made from the books at the Sala de Comercio of the number of passengers who arrived at Monte Video from Nov. 1835 inclusive, to the end of 1842.
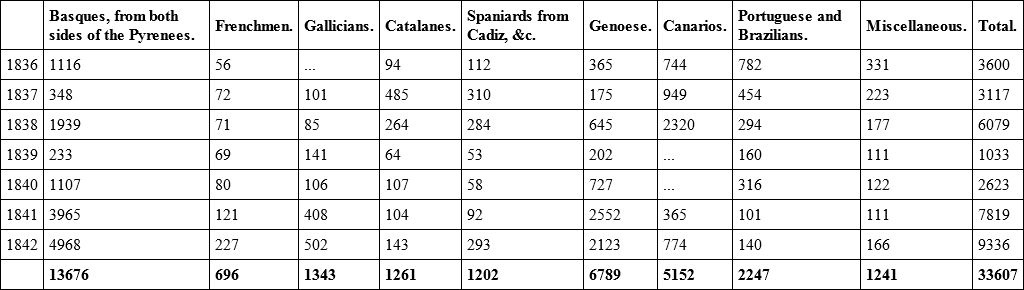
Of this large number of emigrants, 13,676, it will be seen, were from the Basque provinces; 696 from France; 3806 from Spain; 6789 from Genoa; 5152 from the Canary Islands; 2247 from Portugal and Brazil, and 1241 from other parts of the world. If, as has been said by one of our greatest writers, there is no worse sign of the condition of a country than the fact of large masses of its subjects leaving it, surely it must be considered an equally strong proof of the goodness of a Government and the resources of a country when great masses of foreign emigrants are pouring into it. In this respect, Monte Video stands pre-eminent above all the States of America, except those founded by the British race, and considering the limited extent of its territory, and the short period of its independent existence, it can scarcely be said to yield to them.
Having thus shown the grounds on which the Government and people of Monte Video are entitled to the sympathies and support of England, I shall now proceed to say a few words on the present disastrous position of the affairs of that Republic.
For the last two years, the city of Monte Video has been besieged by an army composed almost entirely of Buenos Ayrean troops, commanded by General Manuel Oribe, the expatriated President of Uruguay, who claims to be the legal President of the Republic, and whose avowed object is to overturn the present Government, and to seize on supreme power for himself, and blockaded by sea by a Buenos Ayrean squadron, commanded by William Brown, a British subject in the pay of General Rosas. If the army of General Oribe was composed of Monte Videans, England could have nothing to say in this matter, as his success would be merely the substitution of the chief of one native party for another; but this is not the case. Oribe has neither army, fleet, nor treasures of his own, and owes every thing to General Rosas as absolutely as if he was a Buenos Ayrean citizen. To allow him, therefore, to get and to retain possession of Monte Video, would be to establish the authority of Buenos Ayres on the east bank of the river as effectually as on the west, and this I have already shown would be most injurious to the interests of England, of Brazil, and the other adjoining States, as well as to Monte Video itself, and to the upper States of the Argentine confederation.
Whatever might be the wishes of General Oribe, it is evident that he would have no chance of retaining power any longer than he made himself agreeable to General Rosas. In the city he has a considerable number of supporters amongst the shopkeepers and a few amongst the merchants, but in the country, the landed proprietors and gauchos or peasantry are all opposed to him, and are enrolled in the armies of General Rivera, or his lieutenants. When President, he was besieged and deposed by this class, against which the mere townsmen can effect nothing. If he got possession of the city, he would not be able to raise such a native force as would sustain him. He must, therefore, retain the Buenos Ayrean army in his pay, or he could not stir a mile from the walls without being attacked by the army of Rivera. Hence he would continue in a state of dependence on General Rosas for many years, if indeed he ever became entirely independent of him. Thus, it will be seen, that this is not a struggle to decide whether Oribe or Rivera shall be chief of the Republic, but whether the Republic shall remain independent or become subservient to the will of its bitterest enemy.
If the will of General Rosas should thus be allowed to become the law of Monte Video, the prosperity of that country is at an end. A very large revenue would be required for the support of the Buenos Ayrean mercenaries, and it is not at all unlikely that Rosas, who confiscated the property of the whole of the Unitarian or Centralist Party to pay the expense of a former civil war, would insist on the repayment of the whole, or at least of a part of the expenses of the present war, in carrying on which the finances of Buenos Ayres have been brought to the verge of ruin. To raise the money required for these purposes, there are only two ways; the first, the confiscation of the property of Oribe's opponents; the second, a great increase of the taxes on foreign imports. The first of these measures would destroy all the best connections of the English merchants, and ruin all the most respectable men in the Republic, whilst the second would quite as effectually destroy its foreign commerce.
It is by no means certain, however, that even the name of independence would long be left to Monte Video, if General Oribe should succeed. General Rosas would, in all probability, soon grow tired of supplying troops and money to support another man's authority, whilst General Oribe's necessities would compel him to submit to anything which his patron might propose, even if he went the length of proposing the annexation of Monte Video to Buenos Ayres, in humble imitation of the annexation of Texas to the United States. The last letters from Monte Video state, that Oribe has been getting together, at the Buceo, all the members of his former Legislative Assembly, who had followed him to Buenos Ayres or joined him there, and with their aid he will soon form an assembly quite capable of performing any act which it may suit his convenience to have performed. With such materials we shall scarcely fail to have a repetition of the annexation of Texas on the banks of the River Plate, whenever it may suit the plans of General Rosas and the necessities of General Oribe to effect it.
It is not, however, merely on grounds of policy and humanity that England is called upon to interfere in this contest, but it is bound to do so by the distinct pledges of assistance given by Mr. Mandeville, the English Minister at Buenos Ayres, to the Government of Monte Video, in the name of his own Government. In December, 1842, at the most critical period of the war, that gentleman formally announced, both to the Governments of Monte Video and Buenos Ayres, that England and France had determined to put an end to the war, and demanded that they should both cease from hostilities.3 Not content with this, he addressed an official letter to Senor Vidal, the Secretary of State to the Republic of Uruguay, urging him and his Government not to relax, but rather to redouble their efforts to resist the Buenos Ayreans, until the arrival of the assistance which, he stated, might be expected daily from Europe.4 The letters of Mr. Mandeville will be found in the appendix to this pamphlet, and it will be for the public to decide whether promises so distinct and emphatic, accompanied by exhortations so strong, do not justify the Government of Monte Video, and the merchants trading with that country, in calling on the British Government to fulfil the engagements of its representative. Indeed it is impossible that the Government of England can allow Monte Video to be taken and plundered, the leading men of the Republic to be murdered or driven into exile, and the Republic itself to be annihilated, without destroying the high reputation which England has so long possessed in all those countries for honour and uprightness.
That these consequences will be justly chargeable either on the Representative or the Government of this country, if Monte Video should be taken, is evident from a consideration of the circumstances under which Mr. Mandeville gave his promises and his urgent recommendation quoted above. The letters containing them were written in the period which intervened between the total defeat of the Monte Videan army at Arroyo Grande, and the advance of General Oribe and the Buenos Ayrean forces on that city. When they were given, the Monte Videan Government was in a state of the utmost uncertainty as to whether further resistance would not be a useless waste of human life, and whether it could have any other effect than to render its own position more desperate. The infantry of Rivera, the only force up to that time available for the defence of the city was destroyed, and the cavalry was broken, and discouraged, besides being totally useless for the purpose of resisting a siege. Within the city were a considerable number of Oribe's supporters, and many neutrals, including nine-tenths of the foreign population. At this critical moment the letters of Mr. Mandeville, given above, were written, and it is the opinion of those who were at Monte Video at the time, that it was those letters which induced the Government to forego all attempts at negotiation, and to call upon the whole population to rise and resist to the last. With this view, besides calling on those classes of the people which had previously taken part in the struggle, to rally round the Government, it declared all the negro slaves in the Republic free, and formed them into regiments of infantry for the defence of the capital, and it also gave every encouragement to the foreign population which had emigrated for the purpose of following the pursuits of peaceful industry, to take up arms. By these means, an army of some thousand men was formed within the city, chiefly from classes not before compromised, whilst in the open country, the landed proprietors and peasantry, were encouraged to take arms again under the command of their favourite chief Rivera. Thus the war was renewed, and the whole population of the Republic was again engaged in a struggle which, from the great disproportion of the forces, nothing but the promised intervention of England and France can bring to a close which will not be fatal to them.
My object in referring to these facts is not to excite odium against Mr. Mandeville, who could have had no object in making the promises contained in his letters of the 28th December and 12th of January, except that of preserving the independence of Monte Video, until the forces which he expected from Europe had arrived. In a previous letter, quoted in the Appendix, he positively refused to give any such promises without the permission of his own Government; and in his letter of the 12th of January he bases his promises of aid to the Monte Videan Government on this assertion: – "The Interview between the British Ambassador (at Paris) and Guizot took place on the 9th September, when he agreed to all that Lord Cowley proposed of uniting their forces to put an end to the war." I will not suppose, even for the sake of argument, that an English Minister made such a statement as the above without believing it to be true, still less that he made it for the sake of exciting fallacious and unfounded hopes in the minds of men struggling for existence. He must have believed his own assertions, and he must have had some strong, if not conclusive reasons for believing them.
It is just as little my wish to cast odium on the English Government as on Mr. Mandeville. Its foreign policy in other parts of the world has been wise, dignified, and honest, and all that is asked is that it will act on the same principles in this transaction. No one can doubt that it is sincerely desirous of restoring peace in the River Plate. The reason which Sir Robert Peel gives for the non-fulfilment of Mr. Mandeville's promises is that he had exceeded his orders in giving them. That there was a mistake somewhere or other cannot be doubted, though whether it arose from want of explicitness in the directions given to Mr. Mandeville or from want of comprehension on his part no one is in a position to decide, except those who have seen them. What, however, is perfectly clear is this, that the promises given by him to the Monte Videan Government and the assurances given by him to his own countrymen have had a most important influence on their conduct, and have so far compromised the British Government as to add greatly to the other many and strong reasons for interposing. It is no longer a question of whether an independent Government, formed under the mediation of England shall be sacrificed, and along with it the peace which it has so long been the means of preserving between two of the most important states of South America, neither is it a mere question of whether the commercial intercourse with the finest regions of that great continent shall be carried on without impediment; it is not now even a question of whether a friendly Government shall be destroyed and all connected with it ruined; these considerations, great as they are, yield to the consideration that the honour of this country has been pledged by its authorized representative, and that promises have been given which cannot be violated without deep disgrace to the hitherto unsullied honour of the English name.
Postscript. – Since the above observations were written, explanations have been given by the Prime Minister in Parliament which encourage us to hope that her Majesty's Ministers have at last decided to fulfil the promises made by their late representative Mr. Mandeville, by taking effectual steps to terminate the war, and to secure the independence of the Republic of Uruguay. They have only to speak the word, and to make such a display of force as will show that they are in earnest, and Monte Video is saved. Admiral Brown, or as Commodore Purvis calls him, "Mr. Brown, the British subject, commanding the Buenos Ayrean squadron before Monte Video," will never run the double risk of being sunk by an English broadside, or of being hung as a traitor by resisting the orders of his own Government, if he is convinced that his Government means to be obeyed, and the moment that he strikes his flag, Oribe will have nothing left but to make the best terms for himself and his army. He draws all his provisions from the fleet, and must retire when his supplies are cut off.
Within the last few days information has been received from Buenos Ayres strongly confirmatory of some of the views stated above. According to letters from that city of the 7th February, the Governments of Brazil and Paraguay have formed a treaty offensive and defensive, in which they stipulate for the freedom of the rivers flowing through the territories of both. This is a movement of the greatest commercial as well as political importance, and if the independence of Monte Video is preserved, there can be no doubt that it will join this league, and that the line of communication with the interior of South America up the River Uruguay will be kept open, even if General Rosas should persist in his illegal anti-social policy of closing the Parana against foreign nations.
APPENDIX
CORRESPONDENCE OF H. J. MANDEVILLE, ESQ.,British Minister to the Argentine Confederation,WITHSENHOR VIDAL,Secretary of State of the Republic of UruguayBuenos Ayres, May 26th, 1842.My dear M. de Vidal, – I have received your official letter of the 20th May, with the enclosure which you have had the goodness and frankness to communicate to me, – and also the two private letters of the same date, which you have done me the honour to write to me.
I beg you to believe that I share with you all the disagreeableness of the suspense which the silence of the British Government to my despatches of the 4th December last causes to us both. To me it is only a matter of a little personal inconvenience that I ought not, nor do I, regard; to you it is very different – and all that I can say to you on the subject is, that the moment that I hear from England respecting it, I will not lose a moment in communicating it to you – of this be assured, as of the sincere esteem and consideration with which I remain,
My dear M. de Vidal, always truly yours,J. H. MANDEVILLE.(PRIVATE AND CONFIDENTIAL.)Buenos Ayres, June 8th,1842.My dear M. de Vidal, – Although I have not received any official answer to the proposals which I transmitted by your Excellency's desire to her Majesty's Government, on the 6th of December last, as a basis for the conclusion of a Treaty of Amity and Commerce with the Republic of the Uruguay, I am led to believe and know that they will not be accepted, for the reasons which I stated to your Excellency at the time these proposals were made to me – namely, that the acceptance of this offer would be at variance with the policy and practice of her Majesty's Government, whose wish, in matters of commerce, is to stand on the same footing as other nations, and to enjoy no advantages but such as would, upon similar terms, be conceded to any other friendly power, and that accordingly her Majesty's Government have no intention of availing themselves of this proposal.
I therefore again most pressingly renew, to your Excellency, the proposals I made when I first had the honour to see your Excellency, to negociate with me a Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation, upon the basis which was presented to the Monte Videan Government by Mr. Hamilton, in the year 1835, and brought forward by me at a later period.
I am enabled to assure your Excellency that Her Majesty's Government is not indifferent to the welfare and prosperity of the Republic of the Uruguay, as your Excellency will shortly see by the measures which will be taken for its preservation, and to which I am sure you will be a willing party, and I beg your Excellency to believe that nothing will strengthen these good intentions on the part of Her Majesty's Government so much as a frank and cordial acceptance of the terms of the above mentioned Treaty.
I have the honour to be with the highest consideration, Sir,
Your Excellency's obedient humble servant,J. H. MANDEVILLE.To his Excellency, Don Jose Antonino Vidal, &c. &c. &c.
(MOST CONFIDENTIAL.)Buenos Ayres, June 10th, 1842.My dear M. de Vidal, – My Government has seen with regret that the results of my visits to Monte Video, in December and January last, was not concession of a Treaty of Amity, Commerce and Navigation between Great Britain and the Republic of Uruguay upon the footing proposed by my predecessor Mr. Hamilton, and subsequently by me, and I have been represented as not having been sufficiently urgent with your Excellency to conclude this treaty with me, and I have been blamed in consequence.
I therefore appeal to your Excellency if I did not do my utmost to induce you to negociate it with me, observing, that once concluded, it would not prejudice the acceptance of any other additional proposal on your part which might be added to it afterwards and form additional articles – and that I only desisted from urging it upon you, when I saw that my solicitations were of no avail, and you were resolved to await the answer to the proposition which I transmitted to London by your Excellency's desire.
I am anxious that this circumstance should be put in its true light, and that I may be exonerated from an undeserved censure – and still more that your Excellency should commence the negociations of the treaty with me, which would be the best answer to the reports of the lukewarmness of my wishes in this business.
Believe me to be, my dear M. de Vidal, with great truth and regard, most sincerely and faithfully yours,
J. H. MANDEVILLE.To his Excellency Don Antonino Vidal.
(SECRET AND CONFIDENTIAL)Buenos Ayres, June 18th, 1842.My dear M. de Vidal, – The measures which I alluded to in my private letter to your Excellency of the 10th instant – that her Majesty's Government will take for the effectual protection of the Republic of Uruguay are a joint mediation of Great Britain and France, which I am formally to tender to the Buenos Ayrean Government, upon the arrival of the French Minister here, Baron de Lurde, to adjust the difference between Monte Video and Buenos Ayres.
I did not acquaint you of this important intelligence in my last letters, on account of the possibility of their falling into other hands; and as I am not to make the formal offer of joint mediation of Great Britain and France, until the arrival of the French Minister at Buenos Ayres, I think, for many reasons, which I am sure you will share with me, that it should not be made known; but I have taken the first safe opportunity of communicating it to you, for your own satisfaction and for that of your colleagues.
Believe me always, my dear M. de Vidal, with great regard and esteem, most faithfully yours,
J. H. MANDEVILLE.To his Excellency M. de Vidal, &c. &c. &c.
Buenos Ayres, June 23d,1842.Sir, – I have had the honour to receive your Excellency's dispatch, marked confidential, of the 18th instant, in answer to mine of the 8th, which was delivered to me this morning, the contents of which will cause great satisfaction to her Majesty's Government, as to me they have procured the highest gratification. Her Majesty's Ministers will see, in the determination of the Monte Videan Government to conclude a Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation, with Great Britain, on the terms proposed by Mr. Hamilton and by me, the most unequivocal proof of the loyalty of its intentions towards the British Empire, and of its friendly sentiments towards her Majesty's Government.
I shall, in consequence, avail myself of the friendly dispositions of the Monte Videan Government for the adjustment and conclusion of the treaty which your Excellency has done me the honour to communicate to me, and I propose, in a few days, to embark for Monte Video, for the termination of so honourable and desirable an event.
I have the honour to be, with the highest consideration, Sir,
Your Excellency's obedient humble servant,J. H. MANDEVILLE.To his Excellency D. Jose Antonino Vidal, &c. &c. &c.
(PRIVATE.)Buenos Ayres, June 24th, 1842.My dear M. de Vidal, – I have received your two most amiable and friendly letters of the 18th and 20th instant; it is needless for me to tell you the delight and gratification which they have procured to me.
I have little more to add to my acknowledgement of the receipt of these letters, as I shall so very soon have, God willing, the satisfaction of seeing you, except to renew to my heartfelt thanks for their contents, which only serve to increase the sentiments of friendship and esteem which your conduct to me has inspired me with, since the first day of our personal acquaintance.
I reserve all communications upon any other subject until we meet, which will be about the middle of next week, but rely upon it, and it is with pride I tell you, you and your Government will be satisfied.
Believe me ever, my dear M. de Vidal, with the highest regard and consideration,
Most faithfully yours,J. H. MANDEVILLE.(CONFIDENTIAL.)Buenos Ayres, June 25th, 1842.My dear M. de Vidal, – Would you have any objections to have the treaty copied immediately?
I have motives so strong not for coming back to Buenos Ayres, but for being able to return at the moment when it becomes necessary, that I should impart them to you, which I cannot well by this conveyance.
I will answer for your concurrence with me in this desire to be ready, at a moment's notice, to come back here.
Another motive, which is a very secondary one, and that is, having no steward at this moment, the one who was with me for six years having left me to set up a coffee-house. I cannot bring my establishment with me, even if I had a house to go to at Monte Video, and therefore I am obliged to live at the Consul's, which is a great inconvenience to him, and consequently very disagreeable to me; but, as I have said, this is a trifling consideration, which may be got over very easily. Again, Mr. Hood may come by the next packet – where shall I go then?

