
Полная версия
Black History: History in an Hour

BLACK HISTORY
History in an Hour
Rupert Colley

About History in an Hour
History in an Hour is a series of ebooks to help the reader learn the basic facts of a given subject area. Everything you need to know is presented in a straightforward narrative and in chronological order. No embedded links to divert your attention, nor a daunting book of 600 pages with a 35-page introduction. Just straight in, to the point, sixty minutes, done. Then, having absorbed the basics, you may feel inspired to explore further.
Give yourself sixty minutes and see what you can learn . . .
To find out more visit: http://historyinanhour.com or follow us on twitter: http://twitter.com/historyinanhour
Contents
Cover
Title Page
About History in an Hour
Introduction
Slavery: The ‘Peculiar Institution’
The Black Slave: Three-Fifths the Man
North and South: ‘If slavery is not wrong, nothing is wrong’
War and Emancipation: ‘Previous condition of servitude’
The Jim Crow Era: ‘Separate but equal’
War, Migration and Depression: ‘Black is beautiful’
War and Windrush: ‘To secure these rights’
The Civil Rights Movement 1: ‘Injustice anywhere is a threat to justice everywhere’
The Civil Rights Movement 2: ‘Burn, burn, burn’
Black Power: ‘We gonna stop them white men from whuppin’ us’
Britain and South Africa: ‘Rivers of blood’
Forty Years later: ‘Because of the color of her skin’
Appendix 1: Key Players
Appendix 2: Timeline of Black History
Copyright
Got Another Hour?
About the Publisher
Introduction
This ebook cannot, by definition, be comprehensive. Even as a summary there is much that has to be excluded and such exclusions are naturally subjective. However, this book aims to provide the reader with an introduction to the powerful and dramatic history that is loosely termed ‘Black History’. The study of Black History in the West has to be seen primarily in the context of American history. It was in the USA, where all men are created equal, that slavery and the fight for civil rights had its most profound effect.
Freedom and the rights of the individual formed the basis of the Declaration of Independence. But Thomas Jefferson, the composer of the Declaration, was himself an owner of slaves, 200 of them at any one time, and 600 over the course of his life. George Washington, the first president of the United States, likewise owned slaves, as did most of his immediate successors. The thirteen British colonies of North America that had fought for and won their freedom in 1776 had felt enslaved by the British but saw no contradiction that at the point of independence no less than 18 per cent of their number were slaves.
The anti-slavery voice of the Northern states grew stronger and in 1780 Pennsylvania became the first state to abolish slavery within its borders. More Northern states were to follow, but the Southerners, dependent as they were on slavery, held their position. So polarized were the North and South, so divided on this one central, fundamental issue, that the country went to war with itself. The result, the American Civil War (1861–1865), brought about the end of slavery and the emancipation of America’s vast African-American population.
But the end of the American Civil War in 1865 and the liberation of the slaves, although a triumph, was merely the end of the first chapter in American Black History.
Ahead lay a struggle of epic proportions as African-Americans fought deep-seated discrimination, violence and intimidation to assert their political, cultural and economic identity – a story that, for many, concluded with the election, in 2008, of America’s first black president.
This, in an hour, is the story of Black History.
Slavery:
The ‘Peculiar Institution’
Seventeenth-century British North America needed labour. Tobacco, rice and indigo were potentially profitable industries but the manufacturers lacked the manpower to work the vast fields efficiently. The transatlantic slave trade, already delivering slaves from West Africa to the European colonies in the West Indies, began providing slaves to the ‘New World’, the first arriving in Jamestown, Virginia in 1619. From Senegal in the northern reaches of West Africa to Angola in the south, African rulers, such as the Yoruba kingdom of Oyo on the Guinea coast and the leaders of Dahomey (modern-day Benin), built successful kingdoms by delivering hoards of their fellow Africans to the European and North American traders.
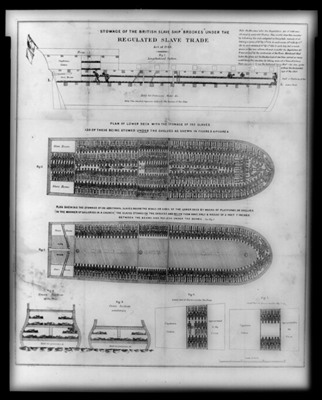
Contemporary poster illustrating the layout of a slave ship
The traders sailed for Africa and bartered with the local African slave merchants, exchanging textiles, armoury, luxuries and alcohol for slaves. The slaves were local criminals, misfits, debtors, or increasingly, those randomly kidnapped from neighbouring tribes.
The journey across the Atlantic lasted several weeks and was a desperate passage. Frightened Africans, torn from home and family, were crammed into the bowels of a ship where overcrowding, lack of ventilation, insufficient nutrition, minimal toilet facilities and constant seasickness made for appalling conditions.
For the white merchants, very aware of how numerically outnumbered they were, mutiny remained a constant fear, necessitating brutal means to keep their cargo in check. Manacled and beaten, the slaves cowered. But it was disease, particularly dysentery, which posed the greatest threat. Once fully at sea, the slaves were allowed time on deck to help minimize the threat. Those showing even the smallest symptom of contamination were immediately thrown overboard. Commercially it was vital that as many slaves should arrive intact as possible.
Once at their destination, the slave faced an uncertain future. Those fortunate to be sold to a ‘good master’ found themselves in smallholdings in the Southern colonies of British North America, where lighter work combined with better food and provisions made this the least feared destination. The not so fortunate were dispatched to the Caribbean and on to the huge sugar plantations. Many failed to acclimatize to the conditions and the work, and up to 10 per cent died within their first year. Those who did survive this initial period were considered ‘seasoned’, in other words to have adapted to their new conditions and to have successfully made the transition from African to slave.
Sugar was the staple commodity of the Caribbean but the intensity of production impoverished the soil and the focus of British colonial production shifted to the American colonies.
In 1775, the thirteen North American colonies broke away from British rule and, following the American Revolution, became the United States of America. Blacks had served on the American side against the British, fighting alongside white soldiers at several battles. Crispus Attucks, a former slave, had died a martyr’s death in 1770, shot by the British whilst fighting in Boston for American independence.
But the recruitment of black slaves to the American cause was abruptly stopped when George Washington took command in 1775. The British, however, promised every slave their freedom if they came over to the British – or Loyalist – side. When America won the war and demanded the return of the ‘Black Loyalists’, the British refused and helped some 4,000 escape abroad, many to Nova Scotia or to London.
Thomas Jefferson, in the draft Declaration of Independence, wanted to speak out against slavery, the ‘peculiar institution’ as it was called, but it would have isolated the Southern states and weakened the Union from the outset. Unity was more important than the freedom of the slaves and the anti-slavery clause was quietly dropped.
Fourteen years after independence, the United States conducted its first national census and found that 757,363, or 19 per cent of the total population, were black. Of these, 697,897, or 92 per cent, were slaves, and 94 per cent of those slaves lived in the Southern states.

A whipped slave, 1863 Illustration from Harper’s Weekly
The slave was considered property. They had no civil rights, no rights in the judicial system, no access to education, no say in where or how they lived or worked; they were at the total mercy of their owner. The slave had no more rights than a mule. If an owner whipped or raped a slave, the slave had no recourse to complaint, nor any route to justice.
Slavery existed in all thirteen Southern states, but amongst the Northern states a strong anti-slavery voice arose, led, in the main, by the Quakers, whose opposition was based on moral and religious grounds. In 1780, Pennsylvania, with its strong Quaker influence, became the first state to abolish slavery within its borders, although Vermont, at the time a territory, had abolished slavery three years previously. Massachusetts, North Hampshire, Connecticut, Rhode Island, New York and New Jersey followed suit. By 1804, slavery had been banned in every Northern state. By 1810, there were over 185,000 free African-Americans in the US, virtually all in the North.
The country, barely a quarter of a century old, was firmly split between the North and the South.
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.







