
Полная версия
Construction for dummies in Russia: save money and mind
At the same time, we also tested conventional facade anchors with a longer length – 250 mm, which successfully passed the tests, because. they were fixed in ordinary masonry, which followed the facing hollow brick. Having received new test reports, we refuted the design solution, for the third time I repeat, which passed the state examination , and received permission from the customer to use extended length conventional anchors. Question substitutions one anchor to another was also affected by an increase in the cost of fasteners, but with respect to other aspects, nevertheless, this allowed us to get out of the situation at relatively low costs.
However, there were some consequences:
1. Due to carrying out all the tests and agreeing to replace the anchors, a week of time was spent, which led to a delay in the completion of work for this period.
2. For the delay in obligations for this week, the customer (and the contract was state-owned) first presented us with a penalty, although in fact he was to blame. In such situations, government customers never accepted the argument that the time it took to correct the documentation was not our fault, but their own. It is not customary for them, otherwise the performers (technical supervision, department heads, etc.) will then receive a cap for violating the deadlines for carrying out work and failing to take action against contractors. After refusing to pay the penalty, the customer sued us and sued her.
3. We used more expensive anchors, no one compensated us for the difference in price, again because there is an estimate approved in the budget – please be kind enough to fit into it. This is called “replacement without increasing the value of the contract”. Although the increase in the cost of fasteners was about 20%.
Prevention measures.
1. Extremely vigilantly compare not only the estimate with the project, but also the project with the real object.
2. Be sure to correspond and notify the customer in writing about the identified errors and inconsistencies in the design and estimate documentation, draw up acts for all, including commission inspection acts. In the future, this can help not only to make changes to the project documentation correctly, but also to justify the change in the cost of work.
3. Carefully read the contract, sometimes it provides for the possibility of an increase in the cost of work or materials upon bilateral agreement with the customer, but as a rule, such an increase is limited to an amount up to 10 or 15 % of the total contract value.
metal weight
Profit can be lost even where you do not expect it at all.
Example:
We had one object where, among other things, we had to make porches or canopies over the entrances to the building. We had an estimate, which included the amount of metal needed for the installation of the porches in tons, and the project did not contain a word about how these porches should look, no diagrams or sketches. If I'm not mistaken, the estimate was about 300 kg. metal without specifying its type, dimensions, profile and thickness. In the estimate, this metal was listed as processed metal, that is, as finished metal products, which immediately increases their cost, probably twice as much as the cost of pure metal. Complete lack of clarity on how to do the job…
The technical supervision explained how to be something like this: “Do it normally, so that it is reliable and beautiful enough, but without frills …”
We looked at how this is usually done at other objects, figured out what metal would be needed, its thickness, sketched out how it would all look like, figured out that snow could fall on the visors from the roof … It seems everything turned out fine on paper. We bought metal, welded spatial frames, racks, assembled everything, painted it. We are waiting for acceptance by the construction supervisor .
A representative of technical supervision came, measured each element of our porches, measured the thickness of each of their elements. In general, I calculated the real weight of the metal that we spent on the whole thing. In fact, it turned out to be 40 percent less … Accordingly, she said that since there is less metal, there will also be less money, and these 40% were cut out of the cost of work.
We went nuts from such a “flagrant injustice”, because the porches looked quite presentable, reliable. We did not expect this at all – we simply did not think that someone could have such an approach to the formation of technical specifications and to the acceptance of work. They conveyed their claims to the customer, explained that there was nowhere to sculpt excess metal, insisted on accepting 100% of the work … To which an absolutely logical answer followed, that we mounted exactly as much metal as we were paid for, and no matter what salary we paid workers for this work.
As a result, this money was withdrawn from us and it was useless to prove something, except that it was possible to weld this missing metal somewhere else, but it was just stupid, because. the structures were already absolutely finished, it was already unprofitable to pay for these works anew and spend time on this.
Recommendations:
If you are dealing with weight volumes and do not have a project for the execution of work, check everything in advance using a metal weight calculator or metal weight tables.
Even if you have both a project and an estimate in which the amount of material is the same, still compare, at least selectively, the weight of the metal that will be needed the most, again using the metal weight calculator or the metal weight table.
4. Why it is impossible to deviate from the design on the example of facade work. The right approach to preparing for facade work.
When a customer decides to update the facade of his building, he usually asks: “How much will it cost to mount the facade?”. Whatever the question is formulated …, such is the answer. In this review, we will figure out what questions, how and to whom to ask in order to get the right answer.
The solution of the facade issue is a series of stages that mutually influence each other, and at some point it may be necessary to revise the original plan completely.
1. Preliminary concept
First, the desired appearance and, accordingly, the materials used are determined. It is important to understand that in addition to the main cladding of the building, you will have to plan the cost of installing window slopes and ebbs. Also, the cost of installing a new parapet will come out if the roof is flat, and if you have small cornice overhangs, then they may have to be increased.
Of course, you can hire a designer to draw everything approximately or exactly for you. At this stage, no one can tell you the exact cost of the work, but only the order of numbers. Alas, this is just the beginning.
2. Coordination of the facade and its changes by the state executive authorities
For example, in Krasnoyarsk there is a procedure approved by the city administration for approving the passport of the facades of buildings and structures, with the exception of individual housing construction. Therefore, your lawyer should check the existence of such requirements for your object.
In Krasnoyarsk, as part of the documents, it is necessary to provide information on the color scheme, on the materials used, lists and layouts of additional equipment, elements and devices, architectural lighting scheme, etc.
This means that it is easier to make a project than not to do it. But in fact, the project needs to be done. Now check it out.
3. Design
3.1. Design surveys, encumbrances
When constructing the facade, we increase the overall dimensions of the building. This value can be different, from 100 mm to 700 in my memory. In addition, often in the process of facade reconstruction, the owners decide to additionally arrange canopies over the entrances to the building or even porches – accordingly, this is an indent from the building up to 2 meters. Behind the facade, the blind area can also shift.
Therefore, at the design stage, it is necessary to check whether, after the reconstruction of the facade, the violation of the red lines, the boundaries of easements and the security zones of engineering networks will not occur – otherwise, you will have to dismantle everything that you mount in such areas.
3.2. Purpose, fire safety class of the building, height of the building
The parameters indicated in the title of the paragraph affect the requirements for the materials used, the arrangement of individual components of the facade structure, and further on the cost of work and materials. As a rule, most facing materials (granite, plaster, metal and composite panels) meet such requirements, but all kinds of PVC do not. The same with insulation, mineral wool – does not burn, polystyrene foam – is limited in use. In addition, heaters have restrictions on the height of the lined structures. In general, there are enough subtleties.
3.3. Inspection of the condition of walls and suspended structures
There is no point in explaining this. It is clear that all worn-out sections of the structures will need to be restored, which is not firmly fixed – it is necessary to remount. A project for such work is necessary by definition.
3.4. Fastener testing
During the examination of the walls, the type of facade anchors and insulation fasteners used is determined. It is not always possible to use conventional anchors, and chemical ones may be required. But the choice of fasteners is made not only by calculation methods, but is confirmed by acts of laboratory tests for pull-out directly at the object. Typically, pull-out tests cost about 5 – 10 thousand rubles. plus a round-trip if the facility is a long distance away, but manufacturers can do these tests at their own expense if you express interest in continuing to purchase and use the tested fasteners from them.
3.5. Thermal calculations and choice of insulation
This is generally a very important question, because. the cost of heaters ranges from 2000 to 9000 rubles / m3 , and possibly even higher. Expanded polystyrene heaters – provide better thermal insulation, but have limitations on use, because. are not non-combustible, unlike mineral wool . A combination of less dense (“cheap”) and denser (“expensive”) insulation materials is allowed to achieve optimal thermal insulation of the walls.
Often, customers have no idea about such subtleties and make a decision “by eye” and at a price – which is fundamentally wrong.
3.6. blind area
Depending on the chosen type of facade, its installation begins either directly from the blind area, or with an indent from it by 20 mm – if a ventilated gap is needed. Therefore, before performing facade work, it must already be completed.
But there is a certain problem with the blind area – this is the state of the soil and its seasonal swelling. The condition of the soil can spoil both a single flooding of the site, and a change in the state of groundwater, showers, etc. In this case, improper performance of work on the blind area may lead to its rise.
From practice, the lifting height can be both 50 and 100 mm. Accordingly, the pressure from the blind area passes to the facade elements, crushing them like an "accordion", shifting the facade subsystem along with the cladding. As a rule, a gap is made between the profiles for thermal expansion of the metal, but it is only about 10 mm. Considering everything, in the best case, only the facade of the first floor, or its lowest part, may suffer, in the worst case, the deformation of the facade will go higher.
Therefore, the development of a project and a survey of the state of the soil in terms of the blind area during the construction of the facade are mandatory.
3.7. seismicity
The choice of facade materials, fasteners, etc. the seismicity of the area in which the object is located. Therefore, in areas with high seismic hazard, the materials used must be certified for use in such conditions, and in the event of earthquakes, they must minimize the risk of injury during failure. This also makes adjustments to the final appearance of the facade, its technology and cost.
3.8. Gaps between metal elements of the facade
Often, customers want the joints between the individual panels of the facades not to be visible and ask to make the installation without gaps. Alas, due to the thermal expansion of metals, facing materials can become unusable, deformed. Even designers forget about it, but you must remember and demand compliance with these standards.
3.9. The layout project of the profile system, cladding and individual components of the facade
Only at this design stage it is possible to see the future appearance of the facade as close to reality as possible, to see the visualization, to understand the cost of work and the need for materials.
But, now we have to wait for the decision of the supervisory authorities … And only then either correct the project, or finally start the work in accordance with the current regulations.
5. Learn how to properly plan money for project management: principles of cash flow ( cash flow ) in practice
It often happens that with the growth of a company or the number of projects or contracts it is carrying out, difficulties arise with planning further activities. The difficulty lies in understanding the question of whether you have enough resources, primarily financial, to complete the work in the future – from the next quarter to a year. Incorrect accounting of finances in this sense caused problems for many enterprises, especially when they took on additional, and in fact “unmanageable” projects at the expense of their own or borrowed funds, because they did not have enough resources at the right time, and to return what had already been invested in them was not possible. This includes, for example, all unfinished .
The second moment, when there is more than one project and they are extended in time, it means that the receipt of funds (revenue) from them will also be extended in time, and at some point, expenses in one project have to be made at the expense of proceeds from another, to the detriment of of course the second. Well, if there are 5 or 10 projects … Plus, such moments as unforeseen circumstances that shift both the execution of work on the project and the receipt of revenue.
Therefore, it is extremely important to distribute the efforts (expenses) and income in such a way that the incoming funds are enough for everything and do not lead to insolvency in certain periods. Getting into such situations, enterprises are forced to look for opportunities to attract additional financial resources (loans), which increases costs even more, and besides, the very receipt of these funds is not always possible for various reasons. Therefore, cash flow planning is a very important part of management, maybe even the most important.
Let's see how to organize and simplify all this.
In fact, there is nothing more visual than a graph or a simple table. In our case, we need a schedule for the receipt and expenditure of funds. But in order to build it, you need to set up accounting for two things.
1. Accounting for current and future costs and liabilities
The usual 1C type accounting system is not enough for this, either more advanced versions or more manual labor are needed. Programs usually show you the current situation – to whom you owe and how much, but your long-term plans will not get here and the data will not show you anything. Therefore, it is necessary to draw up a single schedule.
There are two types of expenses:
“ Prepaid ” – you spent money at a certain moment and received goods or services;
“With deferred payment” – you received goods and services, and you pay for them in a week or two, a month, and, if you're lucky, even after two.
The more detailed you set up planning, the better the result. But in general, the most convenient option is to conduct monthly planning. This should be reflected in the cost plan by date. In the “payment calendar” or “payment plan”, future expenses must be entered taking into account exactly when the need for payment arises, even if you have not yet received goods and services – we are planning for the future.
All expenses need to be planned. With permanent ones (rent, salary, taxes, loans, advertising, fuel, etc.) it is somewhat easier, half of them may not change from month to month, and each new project will require taking into account its specifics. There is no point in explaining how to build a cost plan by date or by project.
2. Accounting for income
In the same way as with expenses, we build a similar plan for cash receipts. For ordinary or core activities, it is relatively easy to plan these indicators. At the same time, each new project has its own specifics associated with the return on investment.
For example, if you take on the construction of an object for a year worth 120 million rubles, according to which the receipt of funds from the customer mainly occurs monthly upon completion of the work, which is stated in your contract, then on a monthly basis you can plan the receipt of revenue in the amount of 1/ 12 parts of the contract amount, i.e. 10 million rubles But some stages of work are more expensive, and some are cheaper – this must be planned and taken into account. In addition, there are projects that you finance for several months, and only then begin to receive a return on investment from them.
And we do the same for all existing projects on a monthly basis.
Do not duplicate or confuse individual indicators
Keep in mind that if you keep records of receipts without VAT, accordingly, its amount paid to the budget should not be included in the payment plan, since it is already “as if paid”. But to complete the picture, it is better to keep records of both revenue and cost including VAT, and take into account its amount in taxes planned for payment.
The same applies to depreciation charges. If you keep a record of them as part of the costs, do not forget to reflect the increase in the size of the depreciation fund in the cash balance, because. these funds are essentially real money, and when buying or repairing equipment (when spending), they are deducted from it.
It is also necessary to separate loan payments and payments to suppliers. What you pay suppliers is an expense. Interest on a loan is also an expense, and repayment of the principal amount of debts is reflected in the balance sheet as a reduction in debt to creditors.
We build a graph (table)
The principle of constructing cash flow ( cash flow ) is very simple, but very informative. We need to compare monthly revenue with expenses. You can accept other periods – at least a week, at least a quarter – but usually all payments occur within one month, and the consolidation of periods is acceptable for long-term planning of future and long-term projects, and not current and those that are already on the way.
The data taken as an example assumes the presence of profitability in the range from 10 to 20% and a certain lag in the return on invested funds from the start of project expenditures. The first project can be the main activity. And all the rest are either the same, meaning just an additional amount of work, or fundamentally different, but generating income.
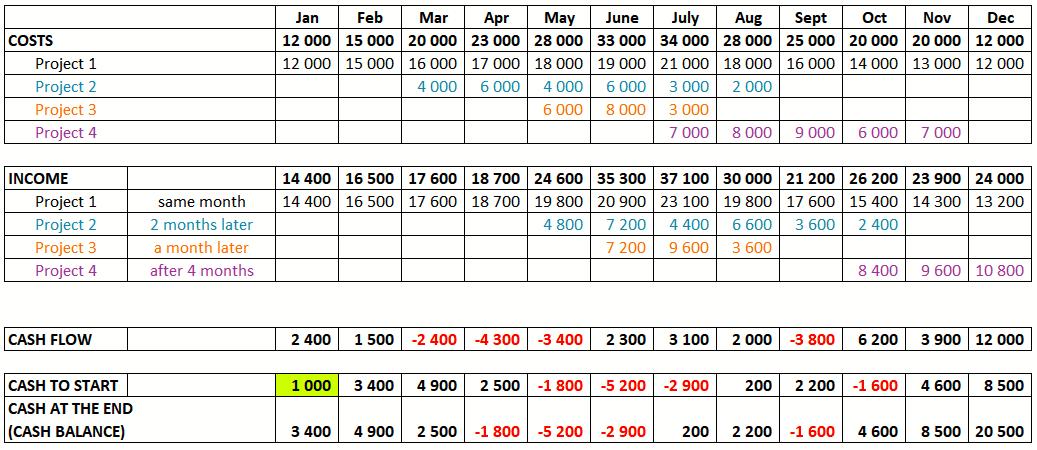
Table 1
Cash Flow Calculation Example
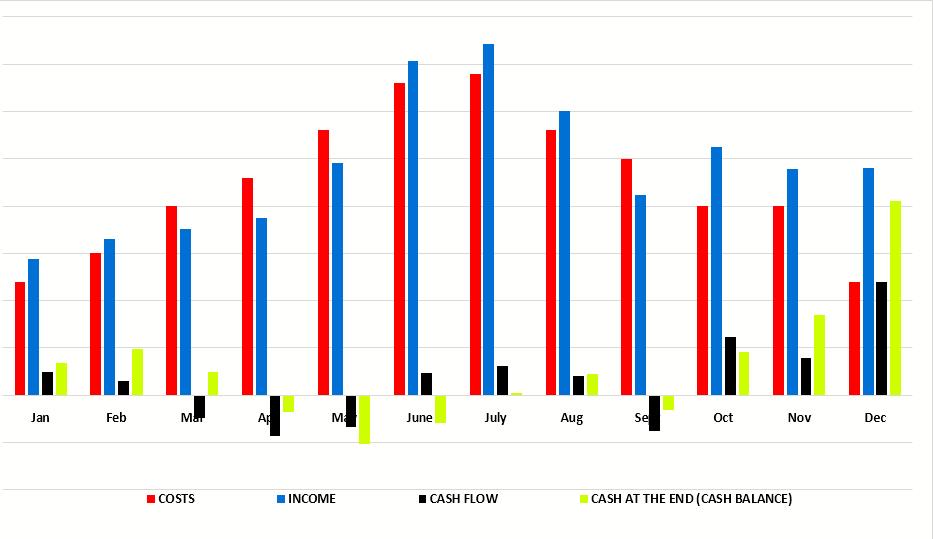
Rice. 1. Graphical display of cash flow to Table 1
Explanations
Cash flow is defined as the difference between receipts and expenditures over a period—in our case, a month.
Cash at the beginning – in our example, this is a conditional 1000 rubles. free cash that you have at the very beginning of the period under review. It can be equal to zero or negative – but it should reflect the real state of affairs at the moment.
Accordingly, the amount at the end of the period is the amount of money at its beginning plus cash flow.
The amount at the beginning of each period is the amount at the end of the previous period, so in the table the amount at the end changes on an accrual basis throughout the year, incorporating the cash flow values in each of the periods.
Конец ознакомительного фрагмента.
Текст предоставлен ООО «ЛитРес».
Прочитайте эту книгу целиком, купив полную легальную версию на ЛитРес.
Безопасно оплатить книгу можно банковской картой Visa, MasterCard, Maestro, со счета мобильного телефона, с платежного терминала, в салоне МТС или Связной, через PayPal, WebMoney, Яндекс.Деньги, QIWI Кошелек, бонусными картами или другим удобным Вам способом.

