 полная версия
полная версияPsychotherapy
CHAPTER IX
WEIGHT AND GOOD FEELING
Probably the most important single condition for the maintenance of good health and good feeling is the carrying of weight normal for the height and age of the individual, or slightly in excess of normal. Popular expressions contain many proofs of this. The proverb "laugh and grow fat" is undoubtedly due to the recognition by all the world that stout people are nearly always laughers, and as a consequence, perhaps placing the effect for the cause, laughing has been regarded as a factor in putting on flesh.26 There is no doubt that the exercise for the diaphragm afforded by hearty laughing, with the stimulation of the intra-abdominal circulation consequent upon vigorous diaphragmatic movements, is an important element in producing a healthy state of the important organs of the human economy contained within the abdominal cavity. Dr. Abrams in his book, "The Blues, Causes and Cure," attributes this disturbing condition of depression so familiar to those who have much to do with nervous patients, to a disordered blood and nerve circulation in the splanchnic area, and calls it scientifically, splanchnic neurasthenia. This undoubtedly sums up one important element in the causation of a great many depressive conditions. Most of them are banished by frequent hearty laughter which, with its exercise of the diaphragm, tends to stimulate splanchnic blood vessels and nerves.
Thinness and Discontent.—In general, it is well understood that thin people are likely to be more gloomy and discontented than those of stouter build. The pessimists of the world have usually been lank and lean. Shakespeare, in "Julius Caesar," has the great Roman declare that he likes not "the lean and hungry Cassius," and that "discontent is bred in such bodies." The issue shows his prophetic power. Discontent with life is much more likely in thin people than in stout. Most suicides are under-weight. Where nutrition is under the normal, digestion is sure to be poor because the digestive organs themselves suffer even more than others from lack of food, apparently giving up some of their own substance at the call of other tissues; sleep is nearly always disturbed, constipation is almost the rule, and muscular action becomes distasteful. While in our day we hear much of people overeating, the nervous specialist finds that many of his patients are undereating. These patients grow out of many discomforts, dreads, and symptoms that often seem, even to the physician, to be due to organic change, when they take on enough weight to relieve them from the incessant calls for more nutrition to which insufficient food has made them subject.
Physical Disadvantages of Thinness.—There are many dangers that go with thinness besides the tendency to that irritability of the nervous system which we have come to associate with neurotic symptoms. It has long been known that a person who is under weight is much more likely to contract tuberculosis than a normal individual. From carefully selected statistics, the large insurance companies have determined, that it is far more dangerous to insure a man who is twenty pounds under weight and who has no family heredity of tuberculosis than to insure a man with a family history of tuberculosis on both sides of the house, provided he is well up to or above the normal weight, and is not living in special conditions of danger from contagion. It is contagion and not heredity that plays the most important role in tuberculosis, and the element that is still more important is that of vital resistance. Every adult of thirty years or over has probably at some time had tuberculosis, for traces of its presence are found in the bodies of all adults who come to autopsy. Seven-eighths of the human race are, however, able to resist, and among these seven-eighths by far the greater proportion are those who are above normal weight.
Of course, this matter of the relation of normal weight to good health did not escape the acute observation of the old physicians. Hippocrates, to take the first and greatest of them, realized that while excessive eating and drinking was serious, there were many people who suffered from not eating enough. One of his aphorisms runs, "A slender and restricted diet is generally more dangerous [manifestly he means to both the well and the ill] than one a little more liberal." He appreciated, too, the fact that while the old may restrict their diet with more or less impunity, this practice may be, and indeed is likely to be, more serious in young people. He has marshaled the ages and stated the effects of a low diet on them very definitely:
Old persons endure fasting most easily, next adults; young persons not nearly so well, and infants least of all, especially those who are of a particularly lively disposition.
Discomfort Due to Lack of Fat .—Many of the vague discomforts of the internal organs seem to be due to a lack of fat cushions round them, and fat blankets to keep them from being too much subjected to the vicissitudes of external temperature. Anyone who has noted in a series of cases the difference between the condition of patients suffering from a slightly movable kidney when they are well up to weight, and when, on the other hand, they are considerably reduced in weight, will have the significance of the first of these conditions brought home very clearly. Most of the people who suffer much from cold in winter are greatly benefited, as might be expected, by a blanket of fat. It is rather easy to grow accustomed to carrying ten additional pounds of fat when ten additional pounds of clothes would be an insupportable burden. Some fat people are prone to complain of the cold. These are not the plethoric but the anemic. This latter class often have a sluggish circulation, besides a lack of hemoglobin. As a consequence of this their oxidation processes are slow and imperfect, and this is one of the reasons for the over-accumulation of fat. The healthy individual with normal heart and normal blood-making apparatus will always be ever so much more comfortable with a reasonable panniculus adiposus and fat cushions and coverings for the internal organs.
Muscular Weakness and Discomfort .—There are a number of pains and aches occurring in lean persons that are due to nothing else than the weakness of muscle consequent upon the poor nutrition of their muscular tissues. Muscles which do not receive as much nourishment as they should, must necessarily be weak, and if asked to do much work they will resent it. Ordinarily it is not realized how much work is required even for such common muscular efforts as those that are needed to hold the body erect, or to keep it in a stooping position at a definite angle, or to move around on the feet.
I have seen patients lose their aches and pains, and become quite capable of standing weather changes and ordinary hard muscular labor without discomfort, simply as the result of a decided gain in weight. All that was needed was the persuasion to eat more, and especially to eat a full breakfast, the meal likely to be neglected. In some persons, appetite will only return after the correction of constipation and insistence on a certain amount of outdoor air every day, not necessarily exercise—for bus riding or the open cars are excellent appetizers.
Eating Enough.—It is very difficult to persuade some people to eat enough! They have all sorts of excuses. They rather pride themselves on the fact that they do not eat much. Persons who are twenty pounds under weight will calmly tell you that they do not need more than they eat. They are actually in debt to that extent to their tissues, yet they are persuaded that they are paying nature's claims in full. Sometimes the excuse is that they have heard, or read, of how much harm is done by overeating; they have taken to heart the phrase that people are digging their graves with their teeth, and so they are actually cultivating the habit of undereating instead of allowing their instinct for food to manifest itself. Many are found to be following the good old saw of getting up from the table hungry. The inventor of it is not known, but quite unlike the inventor of sleep, it would have been a great blessing if he had kept it to himself by patent right.
After a time habit for these people becomes second nature, and it is hard to get them to eat enough. When people undereat it is the digestive organs that, in my experience, always suffer the most. As a consequence, the appetite decreases because of gradually acquired lack of vitality in the digestive system, its nutrition having been lowered by drafts upon it from other portions of the body. Quite contrary to what is told in the old fable, the stomach apparently is not selfish and does not keep the lion's share for itself. The decrease in the amount of food brings on a decrease in digestive power.
Weight for Height.—The physician who wants to help patients by suggestion must keep before him weight tables for height, as they have been determined by statistics. When people are under weight, it matters not what they may be suffering from, improvement will come if they are made to gain in weight. To be able to show them that they are considerably below the normal and to point out what this probably means in lack of surplus energy, suffices of itself to make many people understand the necessity for effort in the matter and to give them a strong suggestion as to probable relief of their symptoms. The following tables are the best-known averages for men and women:
ADJUSTED TABLE OF WEIGHTS FOR INSURED WOMEN, BASED ON 58,855 ACCEPTED LIVES
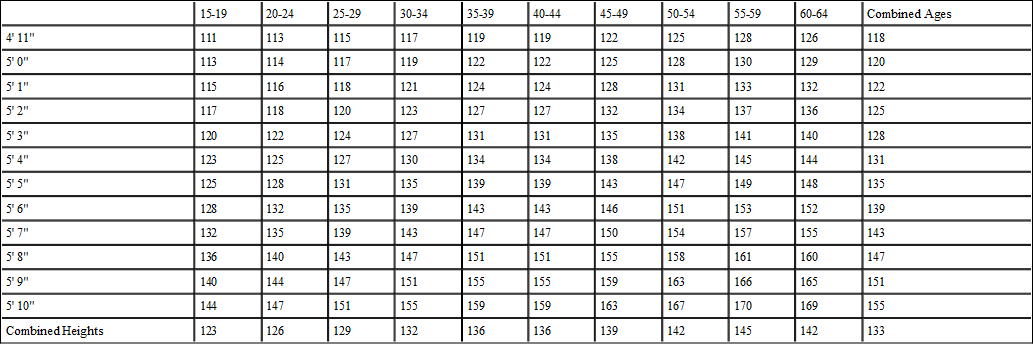
The average shoes of the average woman will raise her about 1-1/2 to 1-3/4 inches.
DR. SHEPHERD'S TABLE OF HEIGHT AND WEIGHT FOR MEN AT DIFFERENT AGES
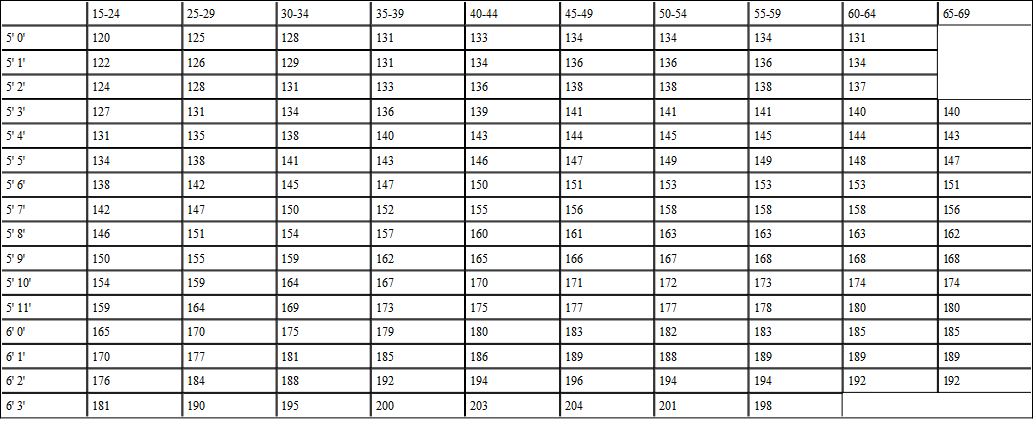
Correction of Underweight.—Underweight is undesirable for many reasons, and gain in weight is often the solution of many problems in ill feeling. It is well to bear in mind that most patients who are under weight can be made to gain in weight by an appeal to their reason and by proper directions and care in seeing that those directions are carried out. Patients have told me that they could not eat more and yet I have been able to persuade them that they must eat more, and they have done so. Anyone who has much to do with tuberculous patients knows that utter repugnance for food can be overcome by will-power, when it is once made clear to the patient that they must eat if they want to live. The most interesting event in the process is that with the increase in the amount of food taken, instead of the appetite becoming more and more satiated, as patients are likely to anticipate, and instead of the repugnance for food growing, the appetite grows stronger, and the repugnance gradually disappears. There is only one way to gain in weight; that is by eating more than one has been accustomed to eat. Persons who are twenty pounds under weight ought easily to gain three pounds a week, half a pound a day, if seriously intent on doing so, but in order to do this they will probably have to increase the amount they eat by double this quantity. That means that a solid additional pound of food, quite apart from the watery elements of the food, must be taken every day.
In the correction of under-weight details are all-important. Patients must be given specific directions as to what and how much of the various foods they should take. With regard to supposed idiosyncrasies against such nutritious substances as eggs, milk and butter, enough is said elsewhere to make it clear that, as a rule, these are merely pet notions, beginning in some unfortunate incident and cherished until they have become a mental persuasion strong enough to disturb the digestion of these substances. What is true for quality of food is true also for quantity. People must be made to understand that the amount of food is to be increased. The results attained by this method are well worth the efforts required for it. Of course, the bitter tonics, especially strychnin and cinchona, will do much to help. Just as soon as patients begin to gain in weight many of their neurotic symptoms leave them. Their tired feelings are no longer complained of and when they are up to normal weight they are quite other individuals, both in good humor and efficiency.
If for years patients have been eating less than they should, then they will have discomfort when they begin to eat more. They will have no more discomfort, however, than would be occasioned if they took more exercise than they had been accustomed to. The stomach and intestines must be gradually accustomed to the new task of disposing of more food. Unfortunately, the usual impression among these patients is that discomfort in the abdominal region, by which they mean any sense of fullness, proceeds from indigestion, and indigestion signifies developing dyspepsia with all the horrors that are supposed to go with it. In reality the slight discomfort which comes from increased eating is usually not manifest whenever the patients are occupied with something reasonably interesting. After a time the organs will become accustomed to it, and then the discomfort will cease.
Nervous Patients .—One of the strongest suggestions that we have in our power for thin nervous patients, suffering from many and various ills, is to have them gain in weight. Many of them will be found to be distinctly under weight for their height. They insist that they cannot eat more, that they are eating as much as they care to, and that they have no appetite, that when they eat more they have discomfort, etc. It must be made clear to them that their one easy road to health is to gain in weight. If they are under weight this makes a very definite purpose to put before their minds. The objection so often urged, that they come from a thin family, must not be listened to. The unalterable purpose to make them gain in weight must be insisted upon. If they can be made to eat more than they have been eating before, they will surely gain in weight. To see themselves gaining in weight is a daily renewal of the suggestion that they will be better when they get up to their normal weight. It is much better than electricity or the rest cure, or anything else that I know; it is perfectly natural and, above all, because it may be made an auto-suggestion, it does not leave the patient after a time dependent on anyone else.
CHAPTER X
VAGUE ABDOMINAL DISCOMFORTS—LOOSE KIDNEY
After the vague pains around joints so commonly called rheumatic, and which occur so frequently that probably there is no one over forty who is quite ready to confess that he has not had rheumatism, the most important source of vague discomfort is the abdominal region. This occurs particularly in people who are engaged in a sedentary occupation which prevents much exercise, keeps them indoors, and gives them abundant opportunity as a rule for introspection and dwelling upon their sensations. There are few people who live the intellectual life who have not suffered from some of this abdominal discomfort, which they presumed must mean some definite lesion, or portend some serious development, and yet, as a rule, they have lived for years afterward without any of their fears proving true.
Physicians are not spared from this source of worry and discomfort. They suffer from it even a little more than others. Their knowledge of the possibilities of serious pathological developments within the abdomen, especially after the age of forty, makes them a little more concerned as to the significance of these vague discomforts.
At least half a dozen times a year, for the last ten years, I have heard physicians say that they were sure that some organ or other within was not performing its function properly, and that there was probably some organic lesion. The thought has usually been in their minds for months, sometimes for years, and they have come to be thoroughly examined. Sometimes they rather expect to be told that they should go to a surgeon. They are usually half concealing a question as to how soon they should set about putting their affairs to rights and how serious the outlook is. As a rule, I am able to dismiss them without any further treatment than the injunction not to think so persistently about certain obscure feelings which they are allowing to occupy their consciousness. Sometimes I know they take the advice—even oftener, perhaps, I know they do not. Once it has got hold of us, it is hard to get away from morbid introspection, and I sometimes hear of them consulting others. All of these patients are improved for a time after their consultation by the reassurance that so long as they have a good appetite—which is the case with all of them—and their bowels are regular—which unfortunately is not the case with most of them—and so long as they sleep well and have no acute pain, there is little likelihood of any serious latent abdominal condition.
Such reassurance cannot be given until the abdominal region is carefully palpated, and especially the right side explored as thoroughly as possible. Here lies the appendix, the head of the colon, which is sometimes the seat of trouble not necessarily originating in the appendix. Just above them one may find a loose kidney, for the right kidney is more likely to be movable than the left, because of the overhanging liver, and finally the gall-bladder, and the bile passages, so likely to be the seat of serious trouble. If none of these organs are tender on deep palpation, if the kidney does not come down when the patient is examined in the standing position, if there are no serious derangements of digestion, except such as can be attributed to nervous indigestion, and if there is no dilatation of the stomach, and no enlargement of the spleen, there is no reason why one should do anything but try to get the patient's mind off himself.
There is always the danger of overlooking an abdominal cancer, in these eases, though with the care in diagnosis I have suggested this is minimal. The best therapeutic test that I know to determine this, if there should be any doubt, is to put the patient on an increased diet and watch the scales. If he is able to digest the added food well, and without trouble, and if he proceeds promptly to gain in weight, there is much less than one chance in a hundred that he is the subject of latent cancer in the abdominal region. The old farmer's maxim is: "A sick hog don't get fat." When human beings properly respond to increased feeding, it is probable, not only that there is nothing serious the matter with them, but that the symptoms of which they complained before may very likely have been due to lack of nutrition. The digestive organs not having enough to occupy them, were tempted to digest themselves, or at least to have their function disturbed by the short circuiting of nervous energy looking for something to do.
I have seen a number of these cases that had been operated on for vague discomfort—some whose appendices had been removed, some whose kidneys had been fastened up because they were slightly movable, some whose gall passages had been examined for adhesions that were supposed to exist, or perhaps for a stone that it was thought might be found there, and except where some actual organic lesion was found and relieved, none of them was materially improved when seen several years after operation. I have heard reports of cures of these cases by surgeons who felt that the removal of an appendix presumed to show a catarrhal process, or a hyperemia, or an adhesion at its tip, had meant the cure of vague abdominal discomfort which had continued for many years and made the patient profoundly miserable. But these reports were founded on the patient's condition at the end of convalescence after the operation, and not on the condition that established itself some months, or perhaps a year, later. Operations on the abdomen, except for very definite indications, have, in my experience, always done more harm than good, and I have seen serious conditions—hernia, displacement of organs and disturbance of the peristalsis of the intestines—develop subsequent to them.
I have in mind two typical cases. One was a physician whom I had seen on a number of occasions, and who complained of vague discomfort, mainly in the right side of the abdomen, though never acute, never accompanied by fever, nor even by any disturbance of pulse when he was not in an excitable mood. His bowels were not always regular, and he had had some disturbance of circulation as the result of thrombosis of veins on that side after an attack of typhoid fever. My opinion was that his discomfort was entirely due to the disturbance of circulation. There was probably some interference with the normal full circulation to the large intestine, in its ascending portion, that gave him a feeling of uneasiness, or of consciousness of its function. Eventually he became convinced that he was suffering from a chronic form of appendicitis. After considerable persuasion he convinced a surgeon friend that his appendix should be removed, and the operation was done. I saw his appendix afterwards. It was supposed to be thickened, but considering the normal limits of size of the appendix, I could not think that it was beyond them in any marked way. At most there was but a slight catarrhal inflammation.
For a time after operation he was much improved. He felt confident that all his trouble has disappeared, and he took some pains to impress me with the supposed fact that in these vague cases of discomfort there was always some underlying organic lesion that needed surgical treatment. During convalescence he had gained in weight, and was looking very well. When I met him a year and a half later he said that some of his discomfort had returned. He had grown thinner and was feeling discouraged. Six months later he was about to submit to another operation, this time for the breaking up of adhesions in the neighborhood of his gall-bladder. He had become convinced that this must be the seat of the difficulty. After this operation he was sure, beyond peradventure, that his trouble was gone never to return. Two years later I found him preparing to have his right kidney sewed up. I had known that his right kidney was slightly movable, but it did not move sufficiently to cause any disturbance of kidney function, and certainly not enough to justify serious surgical intervention.
After this operation I met him once casually and he assured me that now everything was surely all right. I have since heard that he submitted to an operation either for the breaking up of some adhesions around his stomach or in order to tuck up that organ for ptosis. It had not been quite decided whether an adhesion caused a slight hour-glass constriction of the stomach, with some dilatation of the splenic end of the fundus, or whether there had been some actual sagging. I am sure that after this operation, as after preceding ones, with the strong suggestion that he ought to be better and an increase of weight during convalescence, he lost his vague abdominal discomfort for a time, though I have no doubt that it either has or will return. When he gets something to so occupy his mind that he does not dwell too much on his discomfort, he will not increase it to the extent that makes it intolerable. Then he will remember that most people have some discomfort, and he will learn to distract his mind, rather than allow it to dwell on the thought of his particular ailment until it becomes intolerable.
It has taken twelve years or more to develop this case to the point where it is as instructive as it now is, and it is a typical example of what may happen even to a physician. There are other cases in my notes that are quite as instructive, two of them occurring in thoroughly educated men, clergymen who were of good intellectual capacity, but who became too much occupied with themselves. One of these had more operations done on him than my friend the physician. He first had his appendix removed, and was better for a time. Then his kidney was fastened up, and improvement once more took place. After this he lost in weight considerably and suffered so much from headaches that a friendly surgeon suggested that there must be adhesions between his dura and his brain. Accordingly a trephining was done, and these adhesions, real or supposed, were broken up. For a time he seemed to be better. Then he had some urinary trouble. A long prepuce, though one that was never tight or adherent, and only required a little attention to cleanliness to keep it from giving bother, was removed. Some disturbance of his appetite led him to limit his eating for a time, and then he suffered from constipation. This was diagnosed by a specialist in rectal troubles as due to abnormally developed valves in his rectum, and these were cut. He still complained very much of abdominal discomfort at times. This was diagnosed as ptosis of his organs, and an operation was done to tuck these up. After this he developed a large ventral hernia, which had to be relieved by a subsequent operation.









