 полная версия
полная версияFictitious & Symbolic Creatures in Art
Should any reasons be needed to enforce the necessity of adhering strictly to the heraldic law in which attitude plays such an important part, it may be needful only to refer to one or two examples, and cite as an instance in point the noblest of all created beings, and ask whether, of the many acts in which imperious man himself may be heraldically portrayed, the action or position in which he is to be depicted should not indicate distinctly the idea that is to be associated with the representation? whether vauntingly, like the old kings,—
“with high exacting lookSceptred and globed”—attributes of his power,—or as a bishop or saint in the act of benediction,—kneeling in prayer as on mediæval seals,—the three savage men ambulant on the shield of Viscount Halifax,—or the dead men strewn over the field on the seal of the city of Lichfield—in each the primary idea is man, but how different the signification! It will therefore be understood that the particular action or posture, or any of the various forms in which real or imaginary creatures may be blazoned in heraldry, gives the keynote to its interpretation, which, in this respect, is nothing if not symbolic.
It will be seen that to interpret the meaning implied in any particular charge, the tinctures, as well as the attitude, must be considered. These, taken in combination with the qualities or attributes we associate with the creature represented, indicate in a threefold manner the complete idea or phase of meaning intended to be conveyed by the composition, and may be thus formulated:
(1) The Creature.—The primary idea in the symbol is in the particular being represented, whether real or fictitious, as a man, a lion, an eagle, a dragon, &c., of the form and accepted character for some particular quality or attribute of mind or body, as fierceness, valour, fleetness, &c.
(2) Attitude.—The various attitudes or positions in which it may be depicted in heraldry, each denoting some special meaning, as rampant, sejant, dormant, &c.
(3) Tincture.—Whether blazoned proper (that is, according to nature) or of some of the heraldic tinctures, as or (gold), gules (red), azure, vert, &c., each tincture, according to the old heralds, bearing a particular and special signification.
Tinctures in armorial devices were, however, not always introduced on these scientific principles or adopted from any symbolic meaning, but as arbitrary variations of colour for distinction merely, and as being in themselves equally honourable; colour alone in many instances serving to distinguish the arms of many families that would otherwise be the same. Hence the necessity for accuracy in blazoning.
Guillam lays down some general rules regarding the symbolic meaning by which all sorts of creatures borne in arms or ensigns are to be interpreted, and by which alone a consistent system can be regulated. “They must,” he says, “be interpreted in the best sense, that is, according to their most generous and noble qualities, and so to the greatest honour of their bearers.... The fox is full of wit, and withal given wholly to filching for his prey. If, then, this be the charge of an escutcheon, we must conceive the quality represented to be his wit and cunning, but not his pilfering and stealing;” and so of other beasts. Even in wild and ruthless animals and fictitious creatures, symbolic heraldry delights in setting forth their most commendable qualities, as fierceness and courage in overcoming enemies, though they may also possess most detestable qualities.
In like manner all sorts of peaceable or gentle-natured creatures must be set forth in their most noble and kindly action, each in its disposition and that which is most agreeable to nature, rather than of an opposite character. Heraldic art thus stamps a peculiar note of dignity for some particular respect in the emblematic figures it accepts, as for some special use, quality or action in the thing depicted; and this dignity or nobility may have a twofold relation, one betwixt creatures of divers kinds, as a lion or a stag, a wolf and a lamb; the other between beings of one and the same kind, according to their various attitudes or positions in which they may be represented, as a stag courant or at speed, and a stag lodged or at bay; a lion rampant and a lion coward—one will keep the field, the other seek safety in flight, just as one attitude conveys a different signification from another.
The Heraldic Spirit—Effective decorative Quality essential in Heraldry
It will be observable that in the hands of a capable designer imbued with the true heraldic spirit, all objects, animate and inanimate, conform after their kind to decorative necessities, and assume shapes more or less conventional, and, as far as is consistent with effective display of the charge, are made to accommodate themselves to the space they must occupy. Fierce and savage beasts are made to look full of energy and angry power, while gentle-natured creatures are made to retain their harmless traits. In a monster of the dragon tribe, strong leathern wings add to his terrors; his jaws are wide, his claws are strong and sharp; he is clothed in impenetrable armour of plates and scales, his breath is fire and flame, lightning darts from his eyes, he lashes his tail in fury; and all the while the artist is most careful so to spread the creature out on shield or banner that all his powers shall be displayed at once.
Whatever liberty the artist may take in his interpretation of the form of bird, beast, or monster, there is, however, a limit to his licence beyond which he may not go. He may not alter the recognised symbolic attitude, nor change the tincture; he is scarcely at liberty to add a feature. He may curl the mane of his lion, fancifully develop its tongue and tail, and display its claws in a manner for which there is little or no authority in nature; but if he add wings, or endow it with a plurality of heads or tails, it instantly becomes another creature and a totally different symbol.2 A wise reticence in treatment is more to be commended than such fanciful extravagance.
The early artists and heralds, in their strivings to exaggerate in a conventional manner the characteristics of animals for their most effective display, appear to have reached the limits of which their art was capable, and important lessons may be gained from their works. With the extended knowledge of natural history, and the advanced state of art at the present day, decorative and symbolic heraldry should take a leading place in the twentieth century, as in the words of Ruskin, it has been “hitherto the most brilliant” and “most effective of the Arts.”
Celestial Beings

Angels and Archangels the mind loves to contemplate as the ministers of God’s omnipotence and beneficence, and delights in believing these celestial beings to be endowed with a higher and purer intelligence, and as being nearer to the divine nature. In all ages civilised man has thought of them and represented them in art as of form like to his own, and with attributes of volition and power suggested by wings. Scripture itself justifies the similitude; the Almighty is sublimely represented as “walking upon the wings of the wind.” Wings have always been the symbol or attribute of volition, of mind, or of the spirit or air. No apter emblem could be found for a rapid and resistless element than birds or the wings of birds; and however incongruous such appendages may be, and anatomically impossible, it is figuratively as the messengers of God’s will to man that we have come to view these celestial habitants.
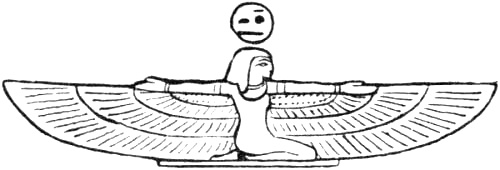
Egyptian Winged Deity.
The idea of adding wings to the human form has existed from remote antiquity, and for the earliest suggestion of celestial beings of the winged human type we must look to the art works of Egypt and Assyria. In Egyptian art, Neith, the goddess of the heavens, was sometimes represented with wings, and in the marbles of Nineveh we find human figures displaying four wings.3 In classic art wings are given to certain divinities and genii. The Jews probably borrowed the idea from the Egyptians, and the early Christians adopted—in this as in many other instances—existing ideas in their symbolical art to express the attribute of swiftness and power, and the sanction of the practice doubtless fixed it for acceptance through all future epochs of Christian Art.
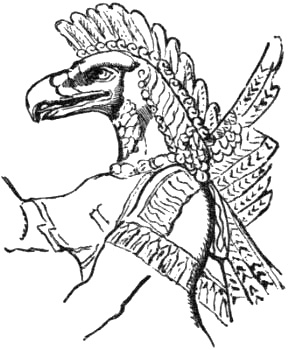
Hawk-headed and winged figure, emblem of Osiris, which, having of all birds the most piercing eye and the most rapid flight, serves to express the divine intelligence and activity.
(Palace of Nimrod in the Louvre.)
In holy writ and Jewish tradition angels are usually spoken of as men, and their wings appear to be implied rather than expressed, as when Abraham in the plains of Mamré addresses his celestial visitors as “my lord,” when Jacob wrestles with the angel, and more particularly when the Angel at the Sepulchre is described by St. Matthew, “His countenance was like the lightning and his raiment white as snow,” and by St. Mark as “A young man clothed in a long white garment.”
The Seraphim and Cherubim as winged beings are more perfectly described in the Scriptures.
The Wings Variously Coloured.—Not content with a simple departure in form from all natural wings, the early and Middle Age artists resorted to many expedients to invest their angels’ wings with unearthly characteristics. Colour was a fertile field for their ingenuity, and they lavished all their brilliant hues in accentuating or separating the several orders of feathers comprising the wings; now rivalling the rainbow, now applying the startling contrasts of the most gorgeous tropical butterfly; at other times sprinkling or tipping the richly painted feathers with burnished gold, or making them appear alive with brilliant eyes.
Vesture.—In Early Christian Art the white vesture spoken of by St. Matthew and St. John, almost invariably adopted, consisted of garments resembling the classic tunica and pallium, sometimes bound with the “golden girdle” of Revelation. During the mediæval period they were clad in every brilliant colour. Angels do not often appear in the works of art executed during the first six centuries of the Church; and previous to the fifth century they were invariably represented without the nimbus—that attribute of divinity with which they were almost always invested throughout the whole range of Middle Age art.
Nimbus.—The nimbi given to all the orders of the angelic hierarchy are circular in form, with their fields either plain or covered with numerous radiating lines or rays, sometimes with broad borders of ornament, but never with the tri-radiate form, which was specially reserved for the persons of the trinity.
Lord Bacon (“Advancement of Learning,” Book i.) says we find, as far as credit is to be given to the ecclesiastical hierarchy of the supposed Dionysius, the Senator of Athens, that the first place or degree is given to the angels of love, which are termed Seraphim; the second to the angels of light, which are termed Cherubim; and the third, and so following places, to thrones, principalities, and the rest, which are all angels of power and ministry, so that the angels of knowledge and illumination are placed before the angels of office and domination.
Fallen Angels.—We learn from Tradition that many angels, originally holy like the rest, fell from their pristine purity, becoming so transformed in character that all their powers are now used for the purpose of doing evil instead of doing good. These are to be identified with the devils so frequently mentioned in holy writ. By the artists of the Middle Ages they are depicted in as hideous a manner as could be conceived, more generally of the Satyr form with horns and hoofs and tail, which last connects them with the Dragon of the Apocalypse, the impersonation of the Supreme Spirit of evil (see Dragon). In Milton’s conception Satan—the fallen Angel—assumes noble and magnificent proportions.
Mistaken Modern Conception of Angels
Many poets and artists of modern times appear to have lost sight of the traditions of sacred art, and in their endeavours to spiritualise the character of angelic beings have in this respect been led to portray them as altogether feminine in form and appearance. This error should be carefully avoided, because in a spiritual as well as in a human sense the vigorous active principle they represent, besides having the warrant of Scripture, is more fitly represented by man than by woman.
Mahomet, who borrowed his ideas mostly from the Christians, in this instance, possibly to guard his followers from some latent form of idolatry, said of angels with some show of reason, that “they were too pure in nature to admit of sex,” but to meet the ideas of his followers he invented another race of celestial beings for the delight and solace of the faithful in the paradise to which he lured them.
Ministering Spirits or Guardian Angels.—These form a frequent theme of poets and artists. The idea was apparently evolved from the mention of “ministering spirits” before the throne of God in holy writ, and from the ecclesiastical legends and traditions of the Christian mythology of early date, derived from still earlier sources. Thus Milton speaks of—
“one of the SevenWho in God’s presence, nearest to the throneStand ready at command, and are his eyesThat run thro’ all the heavens, and down to earthBear his swift errands.” Paradise Lost, iii.According to ancient Jewish belief, each person had his or her guardian angel, and a spirit could assume the aspect of some visible being:
“But she constantly affirmed that it was even so.Then said they, ‘It is his angel.’” Acts xii. 15.“Brutus as you know was Cæsar’s Angel:Judge, O ye God, how dearly Cæsar loved him.”Shakespeare, Julius Cæsar, Act iii. sc. 2.Spenser finely expresses the idea of the good and evil influences continually warring unseen about us, and his gratitude for the effective protection of the guardian spirits:
“How oft do they their silver bowers leave,To come to succour us that succour want!How oft do they with golden pinions cleaveThe flitting skies, like flying pursuivant,Against fowle fiends to ayde us militant!They for us fight, they watch, and dewly ward,And their bright squadrons round about us plant;And all for love, and nothing for reward:O why should heavenly God to men have such regard?”Milton beautifully assumes the pure nature of saintly chastity attended by ministering spirits:
“A thousand liveried angels lackey her,Driving far off each thing of sin and guilt,And in clear dream and solemn vision,Tell her of things that no gross ear can hear;Till oft converse with heavenly habitantsBegins to cast a beam on the outward shape.”“Comus.”And Scott, in figurative language, apostrophising woman in her higher and more spiritual sphere, says in “Marmion”:
“When pain and anguish wring the brow,A ministering angel thou!”Shakespeare expresses a prevailing idea that the pure in heart will become ministering angels in heaven; Laertes, at the grave of Ophelia, fiercely thunders forth:
“I tell thee, churlish priest,A ministering angel shall my sister beWhen thou liest howling.”Mediæval Art Treatment of Angels
According to ecclesiastical legend and tradition there are nine degrees of angelic beings. St. Dionysius relates that there are three hierarchies of angels and three orders in each; and by wise allegories each had his special mission, and they were each depicted with certain insignia by which they were recognised in art representations, which vary somewhat in examples of different periods.
The nine choirs of angels are classed as follow, with the name of the chief of each, according to ancient legend:

According to A. Welby Pugin’s “Glossary of Architectural Ornament and Costume,” and other authorities, we learn the mediæval conception of these beings.
The following emblems are borne by angels: Flaming Swords, denoting “the wrath of God”; Trumpets, “the voice of God”; Sceptres, “the power of God”; Thuribles, or censers, the incense being the prayers of saints; Instruments of Music, to denote their felicity.
The Apparels, or borders of their robes, are jewelled with Sapphire for “celestial contemplation”; Ruby, “divine love”; Crystal, “purity”; Emerald, “unfading youth.”
Archangels are the principal or chief angels, and are extraordinary ambassadors. Among these the name of Gabriel—the angel of the annunciation, the head of the entire celestial hierarchy—denotes “the power of God”; Michael, “who is like God”; Raphael, “the healing of God”; Uriel, “the fire of God.”
Angel is the name, not of an order of beings, but of an office, and means messenger: wherefore angels are represented young to show their continued strength, and winged to show their unweariedness; without sandals, for they do not belong to the earth; and girt, to show their readiness to go forth and execute the will of God. Their garments are either white, to denote their purity, or golden, to show their sanctity and glory, or they are of any of the symbolical colours used in Christian Art.
A writer in the Ecclesiastical Art Review, May 1878, I. Lewis André, architect, says that “we seldom find angels clad in any other ecclesiastical vestments than the Alb (or tunic of various colours), and the amice. The Amice is sometimes like a mere loose collar; at other times it has richly embroidered Apparels (or borders), and is exactly like the priestly vestment as worn in the Middle Ages. Instead of the amice we sometimes find a scarf or cloth tied in a knot around the neck, the ends falling down in front.
“In Anne of Brittany’s prayer-book is a beautiful figure of St. Michael. He has a rayed nimbus, a cross on a circlet round his head, a richly embroidered dalmatic (a long robe with sleeves partly open at the sides), and holds a sword in his left hand. The emblems of St. Michael are a crown, a sword, a shield charged with a cross of St. George, or a spear with the banner of the cross, or else with scales in his hand. Sometimes, as at South Leigh, Oxon., he is in complete armour.
“The archangels are often figured with a trumpet in the right hand, scarfs round neck and loins; six wings, sometimes four at the shoulders and two at the hips, the legs bare from the thighs. The four archangels are frequently represented in complete armour and with swords.
“The angels in the Benedictional of St. Ethelwold nearly resemble much later representations; they have wings and the nimbus or aureole, long hair and girded loins, whilst the feet are bare, as is generally the case at all periods of Gothic Art; but the characteristic drapery is loose and flowing as in the Saxon figures of saints; the wings are short and broad, the nimbus is generally rayed like the spokes of a wheel (a form seen in the work of Giotto, with whom it seems to have been a favourite). The alb or vesture has loose sleeves, and at times a mantle or cope envelops the figure; both sleeves and mantles have embroideries or apparels.”
“The modern taste,” says the same writer, “for giving angels pure white vesture does not appear to be derived from the Middle Ages, and certainly not from the best period when angels were clad in every brilliant colour, as a beautiful example at St. Michael’s, York, shows. Here an angel swinging a golden censer has a green tunic covered with a white cloak or mantle. The nimbus is bright blue, and the wings have the upper parts yellow, and are tipped with green. At Goodnestowe church, St. Michael has a deep crimson tunic, a white mantle edged with a rich gold border, green wings, and a light crimson nimbus,” and mention is here made of the white vesture of the angel at the Sepulchre, and that nowhere else does the Gospel mention any angel clad in white but in the narratives of Our Lord’s resurrection.

Angel with Cloud Symbol.
“Often the angels’ wings are feathered red and blue alternately, as on the pulpit at Cheddar, Somerset. Sometimes the wings have feathers like those of a peacock, on the Chapter House, Westminster; round the Wall Arcade, angels have their wings inscribed with a text on every feather. This corresponds with the French ‘hours’ of Anne of Brittany, where an angel (St. Gabriel) wears a mantle with a text running along the border.”
It was not uncommon to represent angels in carving and stained glass in the latter part of the fifteenth century as feathered all over like birds.
Cloud Symbol of the “Sky” or “Air.”—Artists of the Mediæval and Renaissance periods, following classical authority, employed the cloud symbol of the sky or air in their allegories and sacred pictures of divine persons, saints, and martyrs, to denote their divine or celestial condition, as distinguished from beings “of the earth—earthy.” The adoption of the little cloud underneath the feet, when the figure is not represented flying, naturally suggested itself as the most fitting emblem for a support, and avoided the apparent incongruity of beings in material human shape standing upon nothing. The suggestion of the aerial support here entirely obviates any thought of the outrage on the laws of gravity.
Another distinguishing attribute is the Nimbus—an emblem of divine power and glory—placed behind or over the head. The crown is an insignia of civil power borne by the laity; the nimbus is ecclesiastical and religious. The pagans were familiar with the use of the nimbus, which appears upon the coins of some of the Roman Emperors. It was widely adopted by the Early Christian artists, and up till the fifteenth century was represented as a circular disc or plate behind the head, of gold or of various colours, and, according to the shape and ornamentation of the nimbus, the elevation or the divine degree of the person was denoted. It was displayed behind the heads of the Persons of the Trinity and of angels. It is also worn as a mark of honour and distinction by saints and martyrs. At a later period, when the traditions of early art were to some extent laid aside, i.e., from the fifteenth century until towards the end of the seventeenth century, as M. Dideron informs us, a simple unadorned ring, termed a “circle of glory,” “takes the place of the nimbus and is represented as hovering over the head. It became thus idealised and transparent, showing an outer circle only; the field or disc is altogether omitted or suppressed, being drawn in perspective and formed by a simple thread of light as in the Disputer of Raphael. Sometimes it is only an uncertain wavering line resembling a circle of light. On the other hand, the circular line often disappears as if it were unworthy to enclose the divine light emanating from the head. It is a shadow of flame, circular in form but not permitting itself to be circumscribed.”

Angel Supporter.
Although the forms of angels are of such frequent occurrence in Mediæval Art they seem to abound more especially in the fifteenth century. Angels are seen in every possible combination, with ecclesiastical and domestic architecture, and form the subject of many allusions in heraldry. They are frequently used as supporters.

